Physics year 11 mocks
1/256
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
257 Terms
Radioactivity
The spontaneous emission of radiation by an unstable atomic nucleus
Radioactive decay
when an unstable nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation
ionisation
electrons are knocked out of atoms
ionising radiation
any form of radiation that has the ability to remove electrons from atoms and molecules
Alpha particles
2 protons and 2 neutrons (helium nucleus)
properties of alpha particles
-slow, and large
-highest ionising power
-travels a few centimetres in the air
-Low penetration power (stopped by paper)
Beta particles
fast-moving electrons emitted from the nucleus of radioactive atoms
properties of beta particles
-small and fast
-moderately ionising
-travels 1 m in the air
-medium penetration power (stopped by 5mm aluminium)
Gamma radiation
electromagnetic radiation emitted during radioactive decay and having an extremely short wavelength
Properties of gamma radiation
-wave of energy
-lowest ionising power
-can travel unlimited distances
-high penetrating power (stopped by several centimetres of lead or metres of concrete)
Becquerel
Unit that measures the rate at which a sample of radioactive material decays; 1 Bq = decay of 1 atom or nucleus per second.
half life
the time it takes for half of the radioactive atoms to decay
gold foil experiment
Conducted by Ernest Rutherford in which alpha particles that were shot at gold foil were deflected when they hit the positive center of gold atoms. The nucleus was discovered as a result of this experiment.
How is radiation used in medicine?
-To sterilise equipment: Gamma radiation can kill bacteria cells
-To help treat cancer, as gamma radiation can be used to kill cancer cells
contamination
when radioactive atoms get onto other materials
irridation
exposing an object or a person to nuclear radiation. we use gamma to kill insects, bacteria, fungi, and other organisms in food products
half life count rate formula
Count rate = initial count rate / 2^n
Nuclear fission
When a large, unstable nucleus absorbs an extra neutron, it splits into two smaller nuclei of roughly the same size. gamma radiation is released.
Spontaneous fission
Fission that occurs without the absorption of a neutron.
Nuclear fission in power stations
Uranium-235 nuclei splits, releasing energy that heats water to turn turbines and generate electricity. Neutrons released from Uranium-235 cause a chain reaction
Nuclear fission in power station safety features
-control rods ( absorb excess neutrons to control the chain reaction)
-moderators (slows down neutrons so they are more likely to cause fission)
-shielding (thick concrete or lead absorbs harmful radiation)
nuclear fusion
when two or more small nuclei fuse to make a bigger nucleus. ssome mass is converted to energy and is transferred as radiation.
conditions for nuclear fusion
high temperature for nuclei to move at high speeds, and high pressure to keep nuclei close enough to fuse. happens in places like stars' cores
hydrogen nuclear fusion
hydrogen + hydrogen → helium + energy
Still learning (2)
You've begun learning these terms. Keep up the good work!
How many electrons are in a coulomb?
6.25x10^18
What is conventional current?
The direction that a positive charge would take in a circuit
What produces DC current?
batteries
What produces AC current?
Generators
What does a high voltage mean
The electric charges are strongly pushed, which can result in a higher current if the circuit allows it
What is potential difference?
- a measure of how much energy each charge is carrying
- The driving force that pushes the charge around
What is ohms law
V = IR
What does a current/voltage graph look like for a filament lamp?
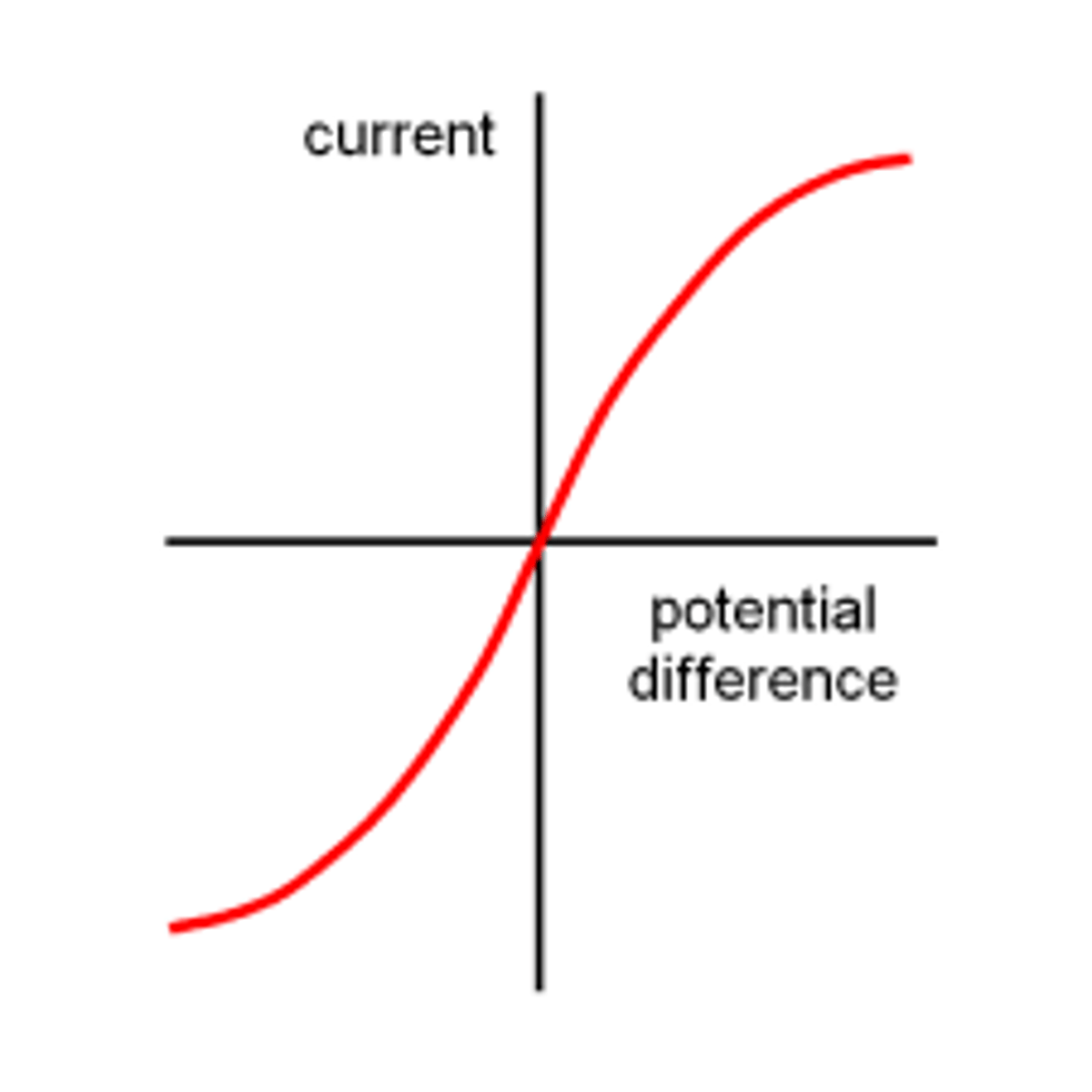
Why is a filament lamp graph S-shaped?
As the voltage increases, the filament heats up, which increases its resistance
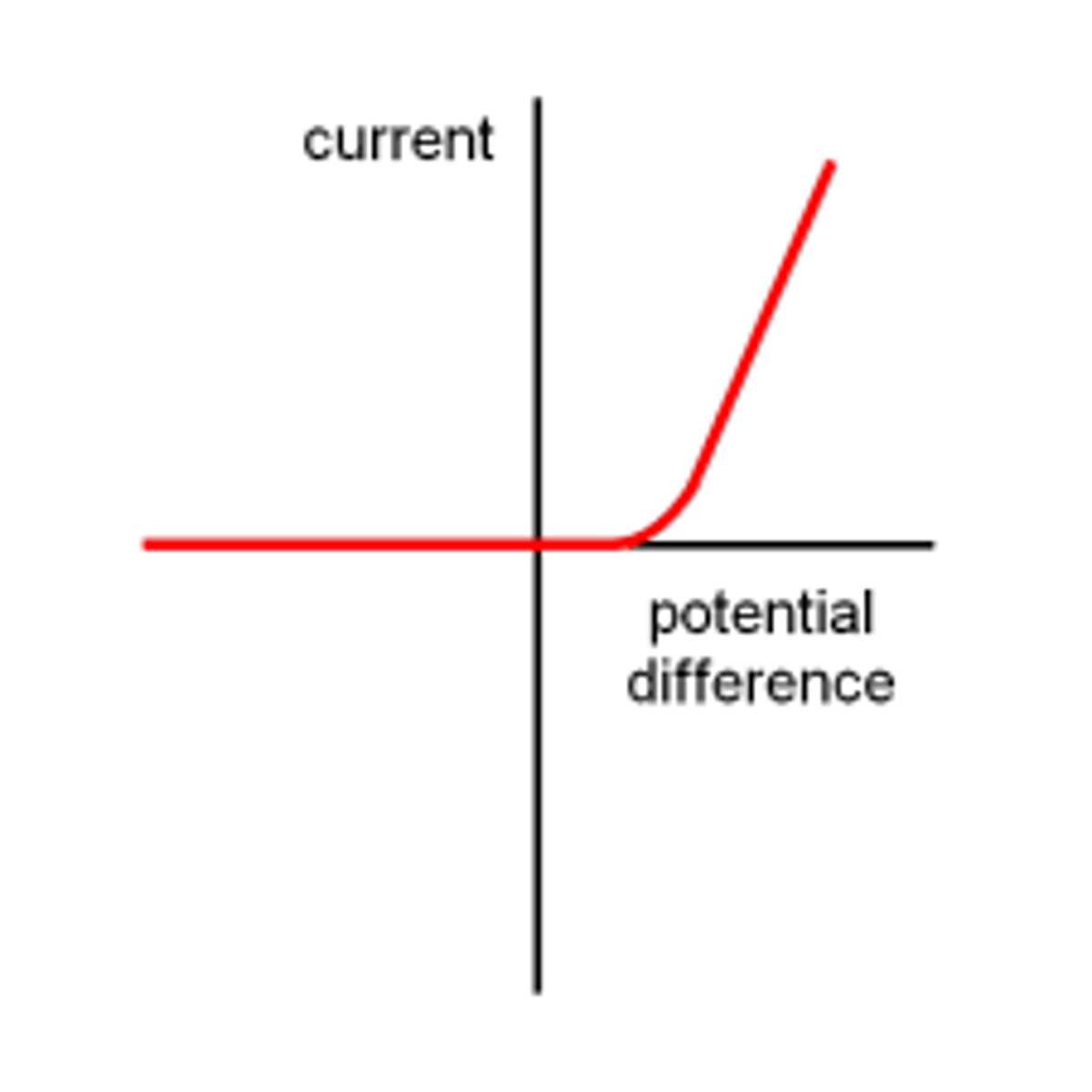
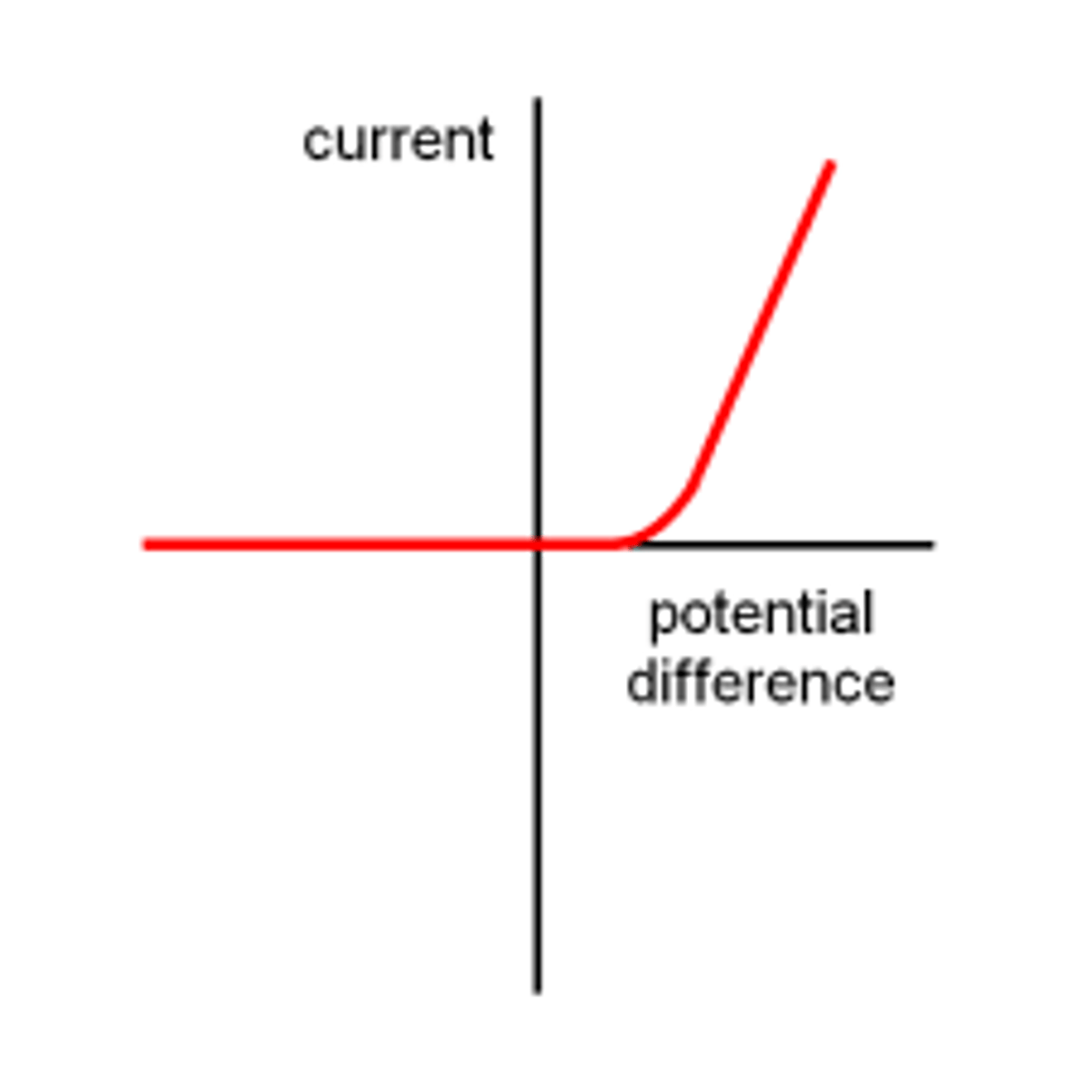
What does a current/voltage graph look like for a diode?
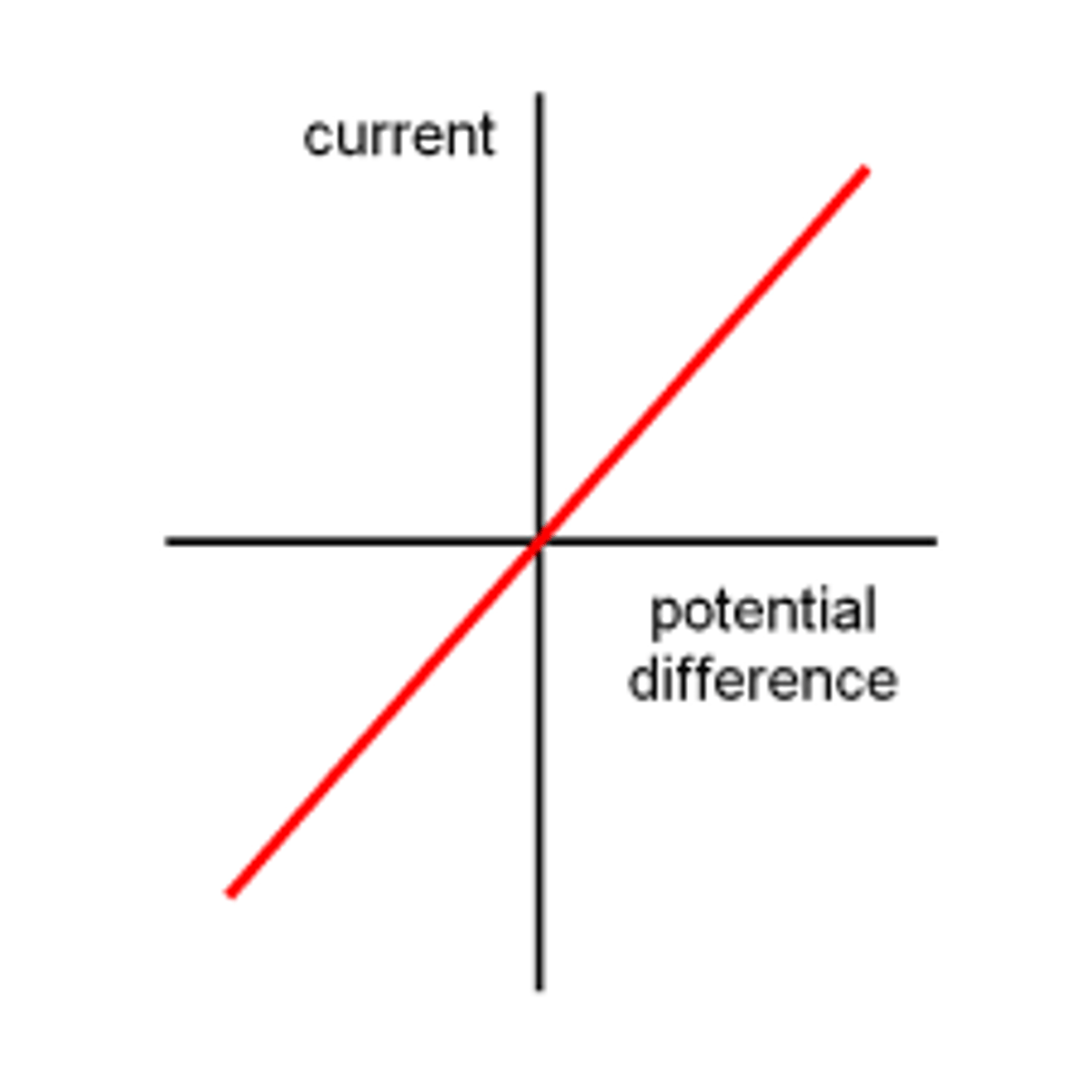
What does a current/voltage graph look like for a fixed resistor?
What does a steeper gradient mean in current/voltage graphs?
Lower resistance
Why is a diode graph L-shaped
At positive voltages, the curve rises, indicating that current is free to flow through the device
Why is a fixed resistor graph straight?
because of Ohm's Law, which states that current is directly proportional to voltage when resistance is constant
How do you find the resistance of a current/voltage graphs?
For ohmic components, the resistance is constant and is equal to 1/gradient
What factors affect resistance?
- materials
- length of wire
- thickness
- temperature
How does the material of the wire affect resistance?
conductors (like copper) have a low resistance, whilst insulators (like rubber) have a low resistance
Why do conductors have a low resistance?
they have a high density of free electrons, which are weakly bound to atoms and can move easily throughout the material
Why do insulators have a high resistance?
their electrons are tightly bound to their atoms, making it very difficult for them to move and create an electric current
How does the length of the wire affect resistance?
The longer the wire, the greater the resistance
Why do longer wires have more resistance?
because the electros have a longer distance to travel
How does the thickness of the wire affect resistance?
A thinner wire has more resistance because there is less space for electrons to flow
How does the temperature of the wire affect resistance?
Higher temperatures increase the resistance because the atoms in the wire vibrate more when warm, making it harder for electrons to pass through
What is static electricity?
The buildup of electric charge on an object, usually caused by friction
Why does static electricity cause sparks?
the sudden, rapid movement of electrons to neutralize a large buildup of electric charge
How does static electricity work?
- When two insulating materials are rubbed together, electrons are transferred
- One material loses electrons and becomes positively charged, and the other gains electrons and becomes negatively charged.
- This static charge is a buildup of these imbalanced charges, which can then attract or repel other objects, or discharge in a spark.
How does lightning work?
occurs when oppositely charged particles within a storm cloud, between two clouds, or between a cloud and the ground become too strong for the air to insulate
What is static electricity used for?
photocopying, smoke precipitator, ink nozzle printer, spray paint
How can static build-up be prevented?
earthing. connecting objects to the ground with a wire allows excess charge to safely flow away
What are the dangers of static electricity?
- A build-up of charge can produce sparks, which may lead to explosions or fires if it happens near fuel which can be ignited.
- It's dangerous when you touch an object with a large electric charge, as it will discharge into you, causing an electric shock.
What are electric fields?
a region of space around a charged object where other charged particles will experience an electrostatic force
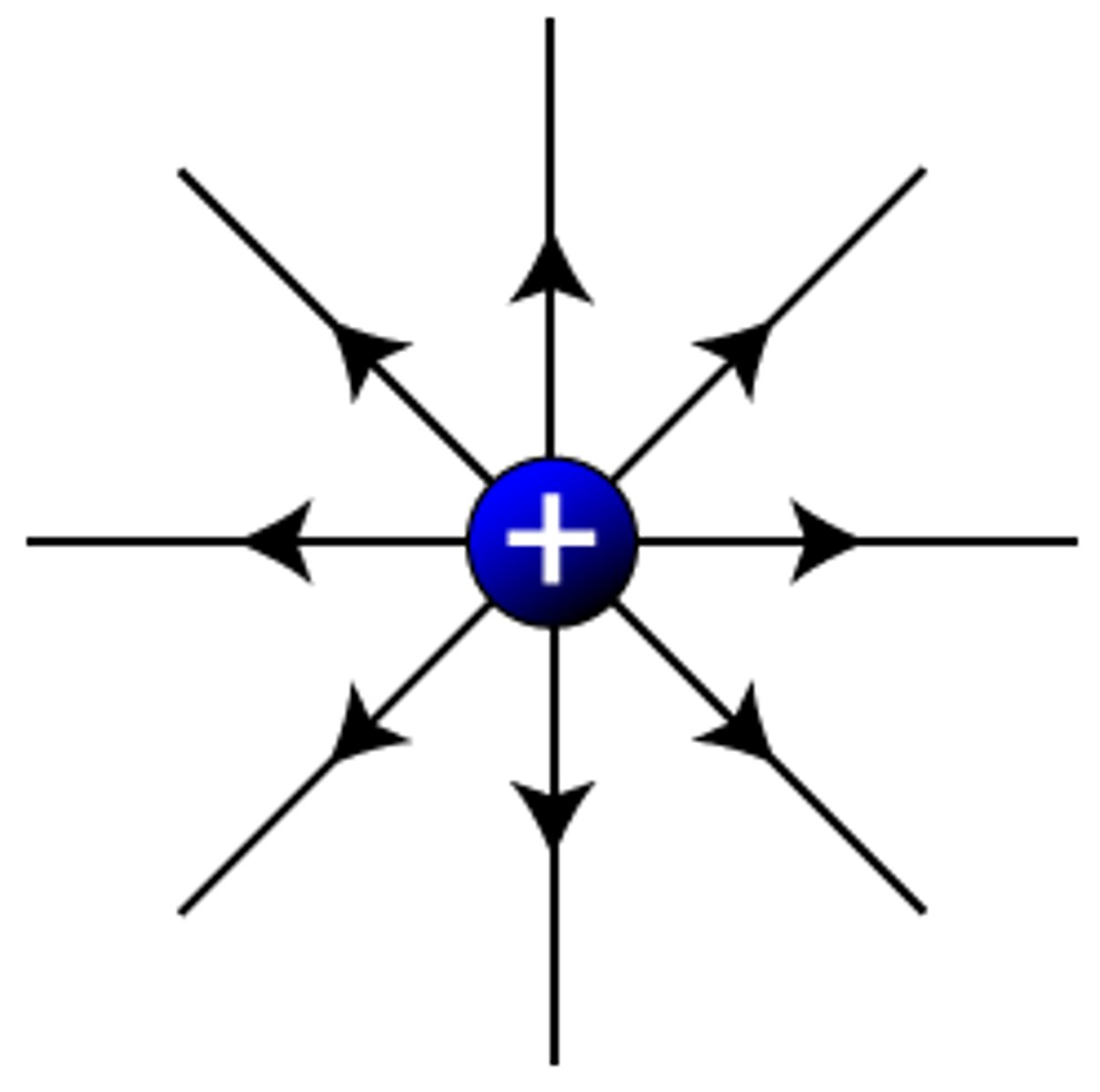
Positively charged electric field lines
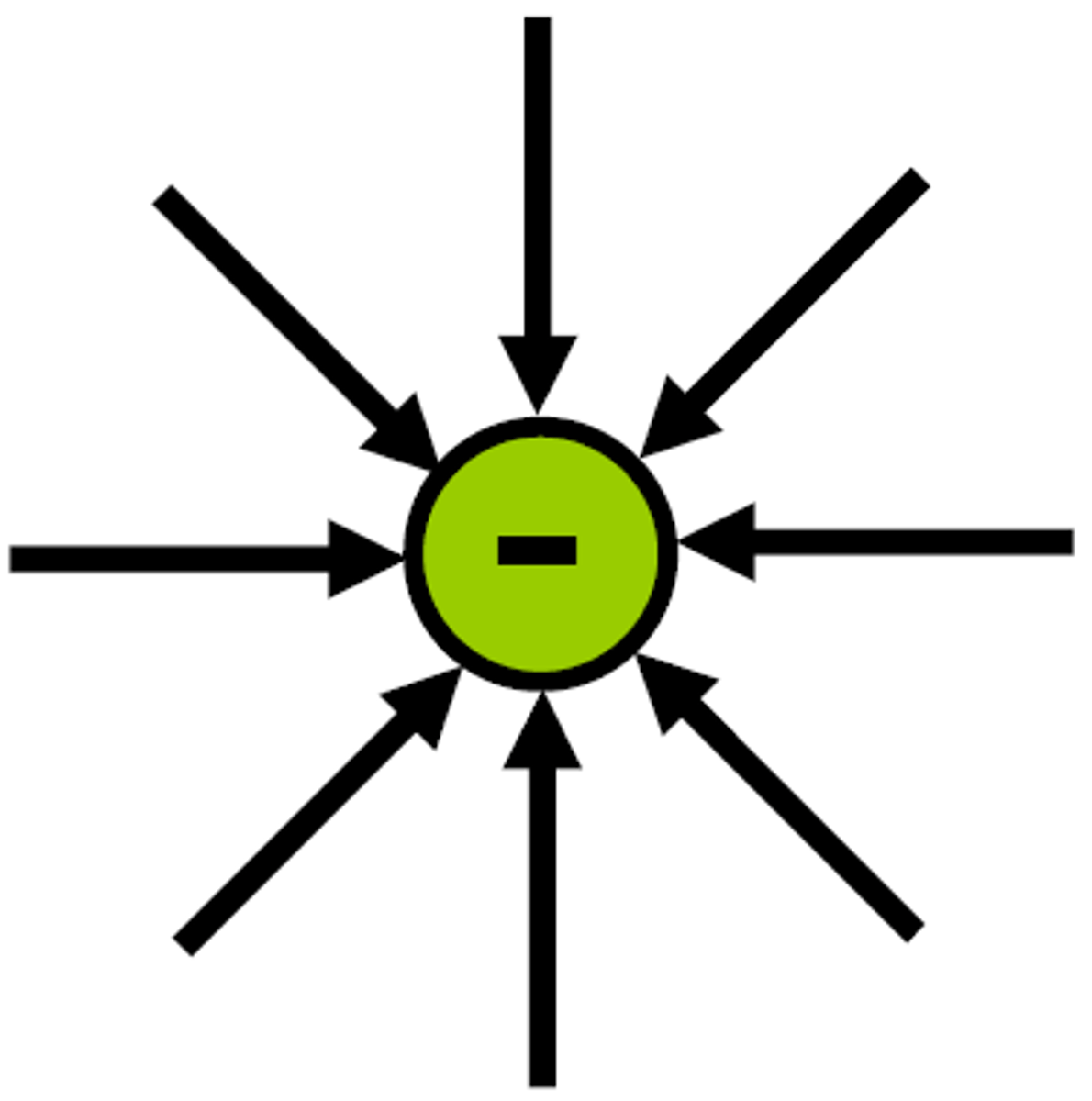
Negatively charged electric field lines
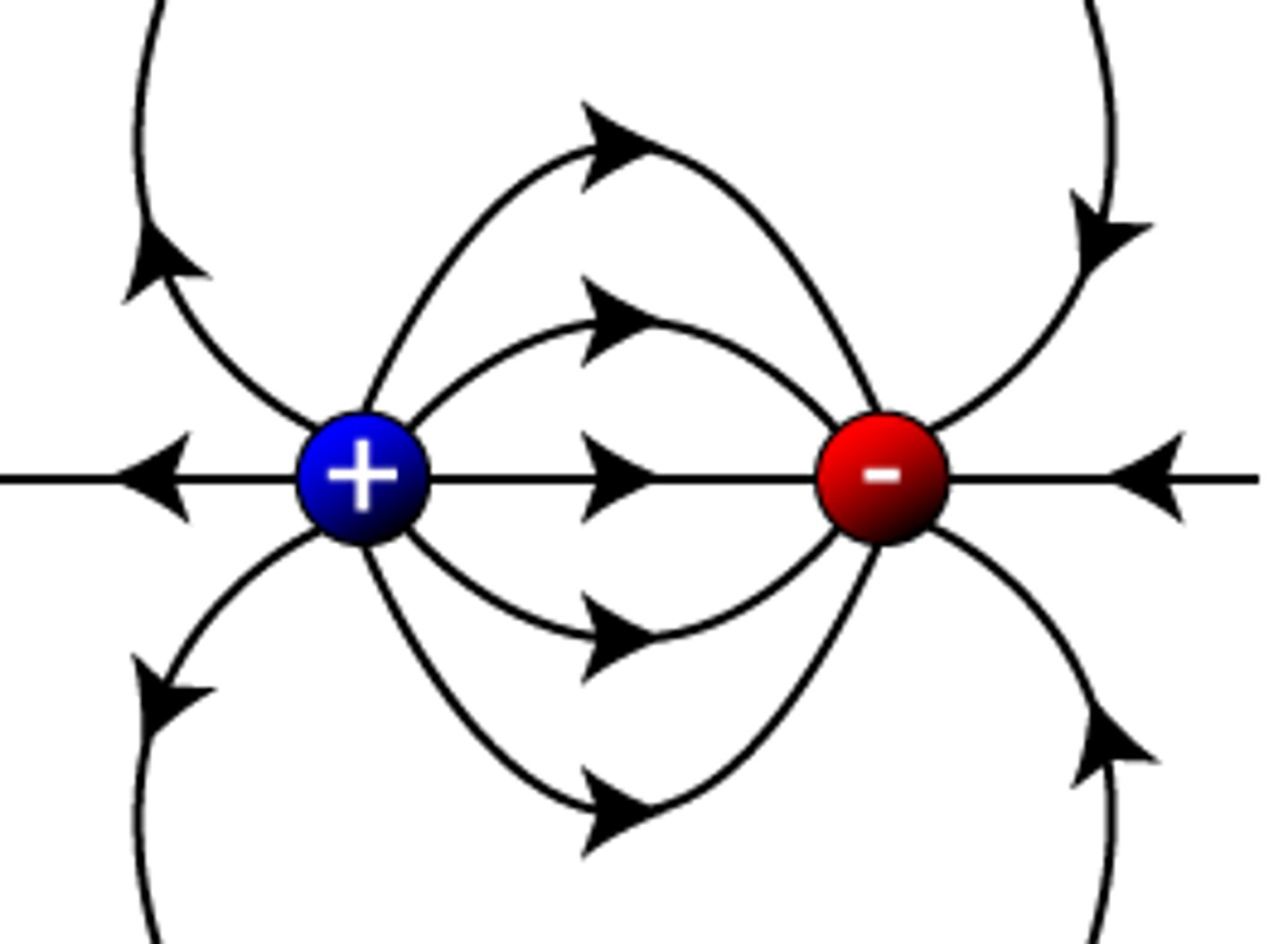
Oppositely charged electric field lines
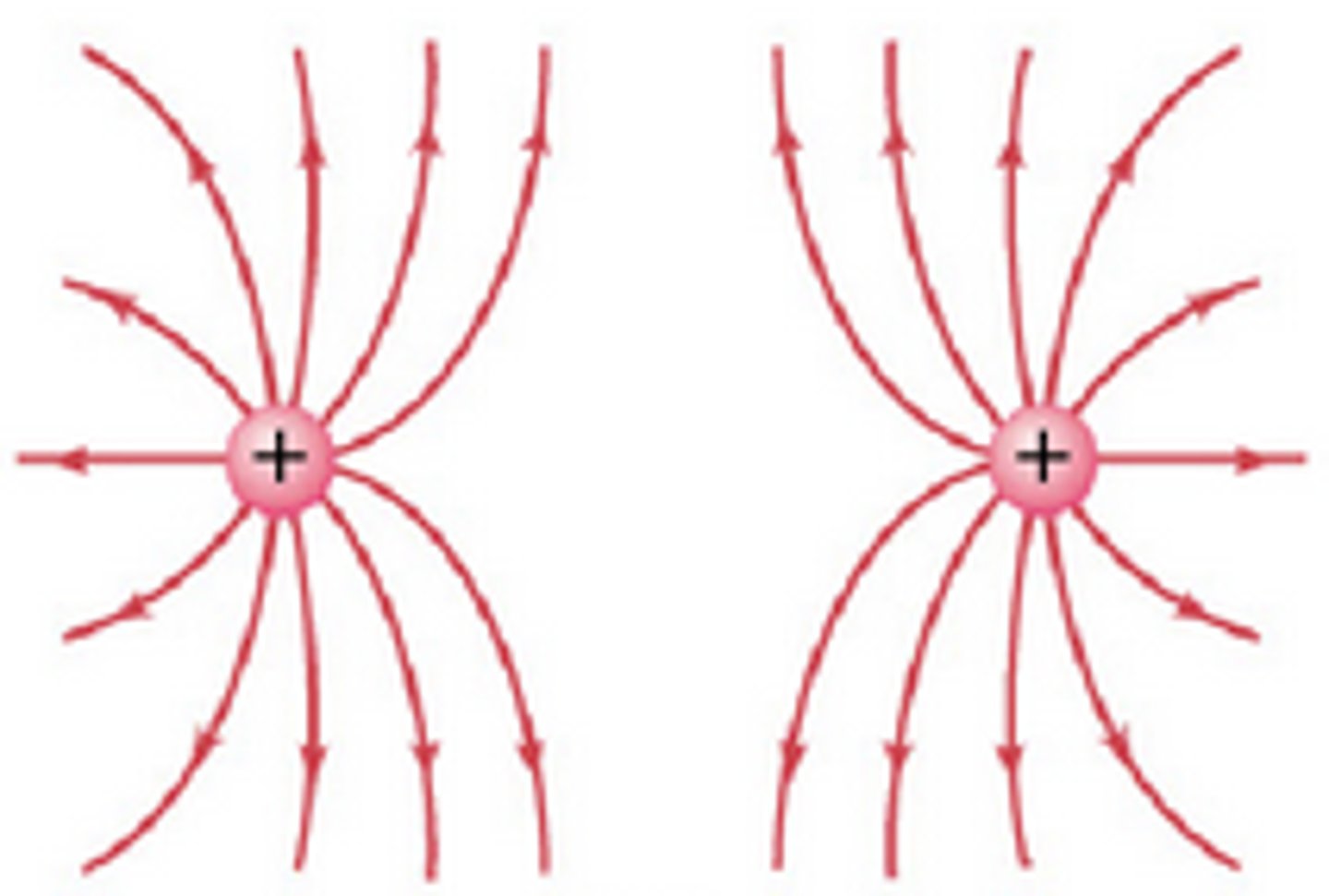
Similarly charged electric field lines
How do sparks in electric fields work?
If an electric field is strong enough, it can pull electrons from the air, creating sparks
What is conduction?
transfer of energy through direct contact in solids
How does conduction work?
- particles in a solid are tightly packed together
- When heated, these particles gain more energy and vibrate more
- these vibrations pass energy to nearby particles, transferring heat
What is thermal conductivity?
Thermal conductivity is a measure of a material's ability to conduct heat.
or
how fast energy travels through a material
What is thermal conductivity measured in?
w/m°c
What is convection?
The movement of heat in fluids (gases and liquids)
How does convection work?
1. fluid near the heat source expands, becomes less dense and rises
2. cooler, denser fluid moves in to take its place
3. This cycle continues and creates a convection current
What is a convection current?
a cycle of heat transfer in fluids (liquids and gases) where warmer, less dense material rises and cooler, denser material sinks
What is radiation?
Radiation is energy that travels through space or matter as waves or particles.
What is thermal radiation?
The transfer of heat as infrared waves. it does not need particles, so it can travel through a vacuum
What is a black body?
a hypothetical perfect absorber and radiator of energy, with no reflecting power; we can approximate the sun as a black body; black bodies emit radiation of all wavelengths
What is the greenhouse effect?
The greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it. It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the sun. These heat-trapping gases are called greenhouse gases. The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane. Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to exist.
What is specific heat capacity?
The amount of energy required to heat 1 kg of a substance by 1 °C
Formula for specific heat capacity?
Energy = mass × specific heat capacity ×change in tempp
What happens to a material with a higher specific heat capacity?
it takes more energy to heat up 1kg by 1°C than a material with a lower specific heat capacity. It takes a long time to heat up and cool down, so it stored heat well
What happens to a material with a low specific heat capacity?
They heat up and cool down quickly
Why is specific heat capacity important?
Oceans absorb and store large amounts of heat, helping to regulate the Earth's temperature
Does water have a high or low specific heat capacity?
high
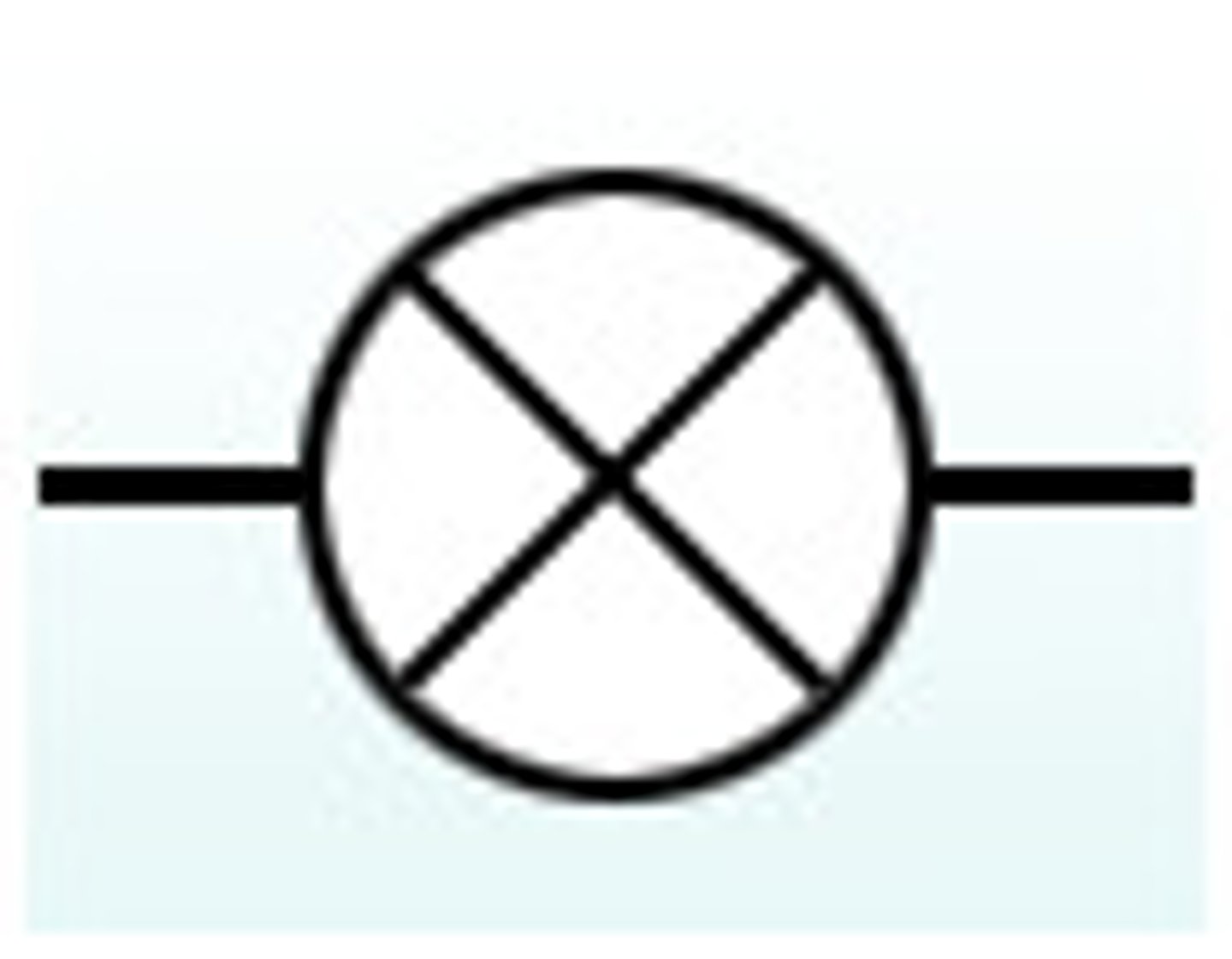
What is a bulb?
glows when the circuit is complete
Bulb
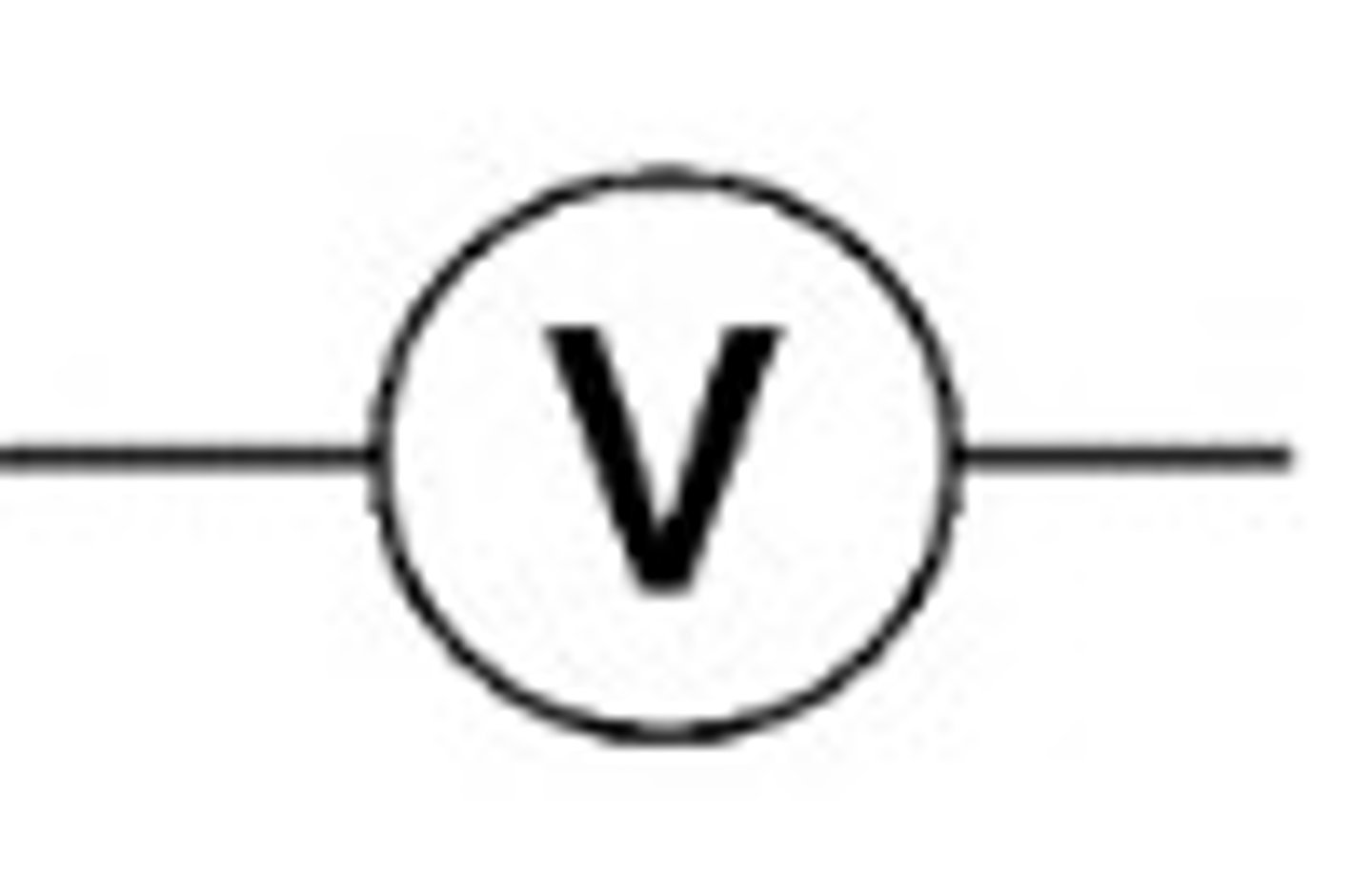
What is a voltmeter?
Measure the potential difference/voltage
How are voltmeters connected in a circuit?
in parallel
voltmeter
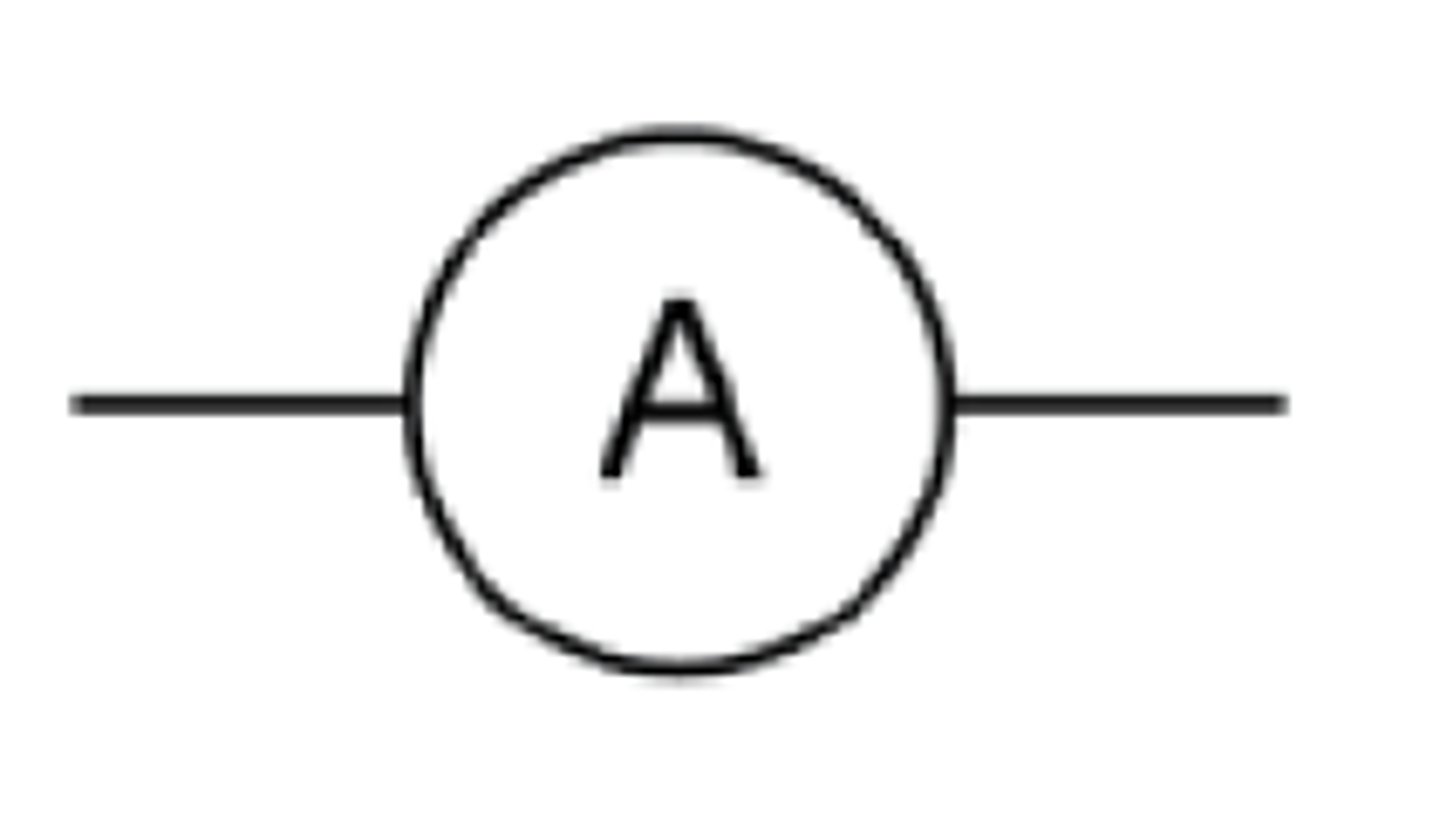
What is an ammeter?
measure of current
How are ammeters connected in a circuit?
in series
Ammeter
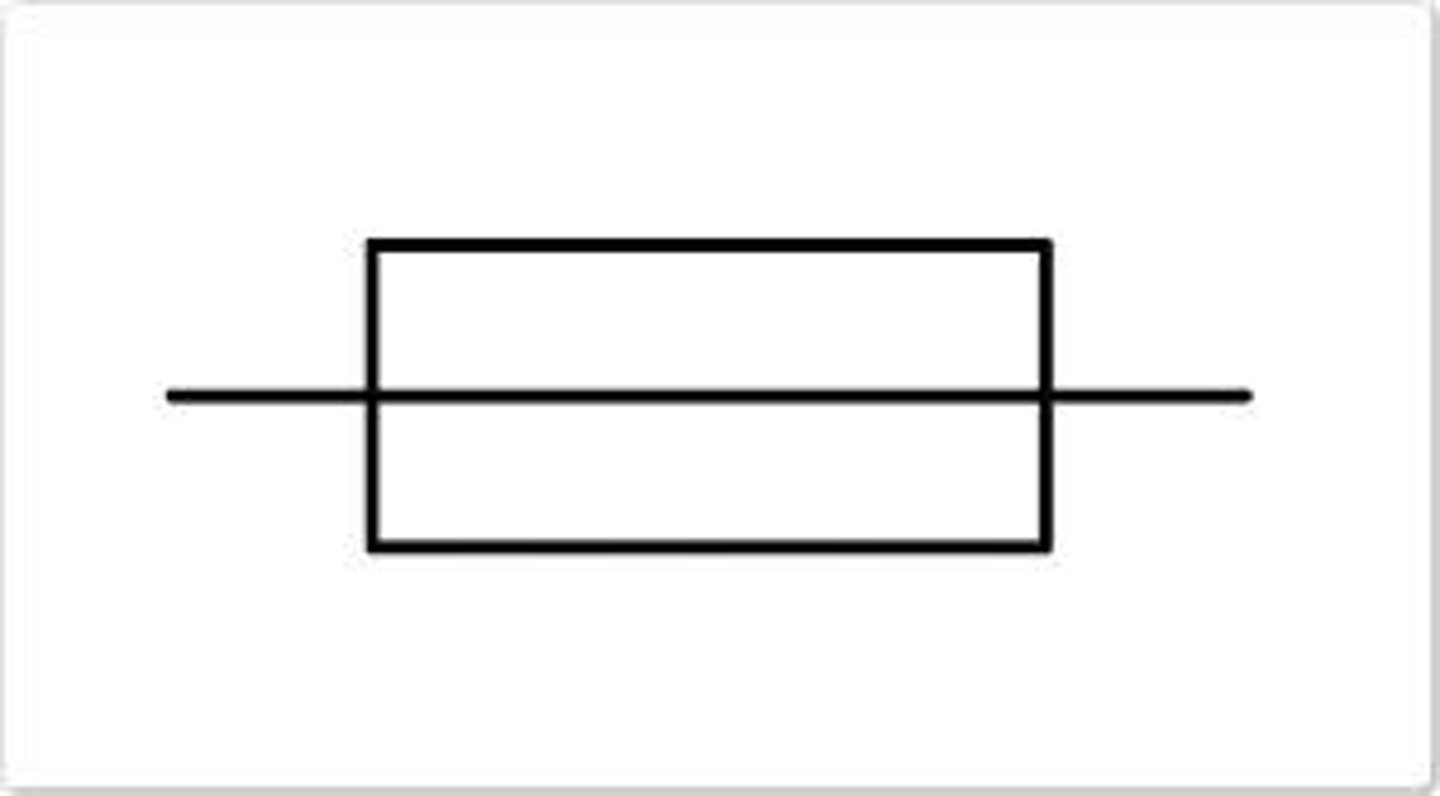
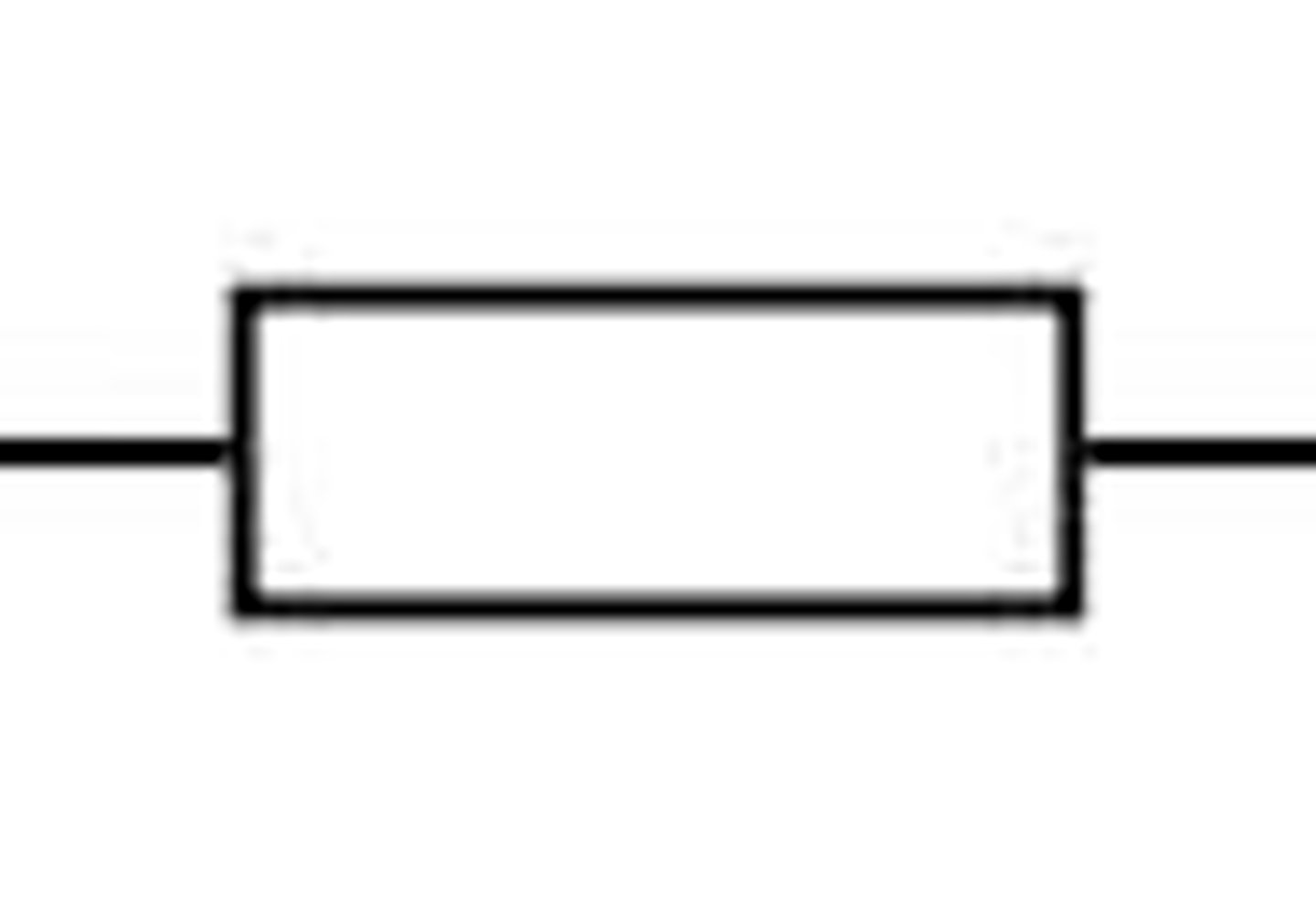
What is a resistor?
It reduces the flow of current through the circuit
Resistor
What is a variable resistor?
Changes its resistance with manual adjustment
Variable resistor
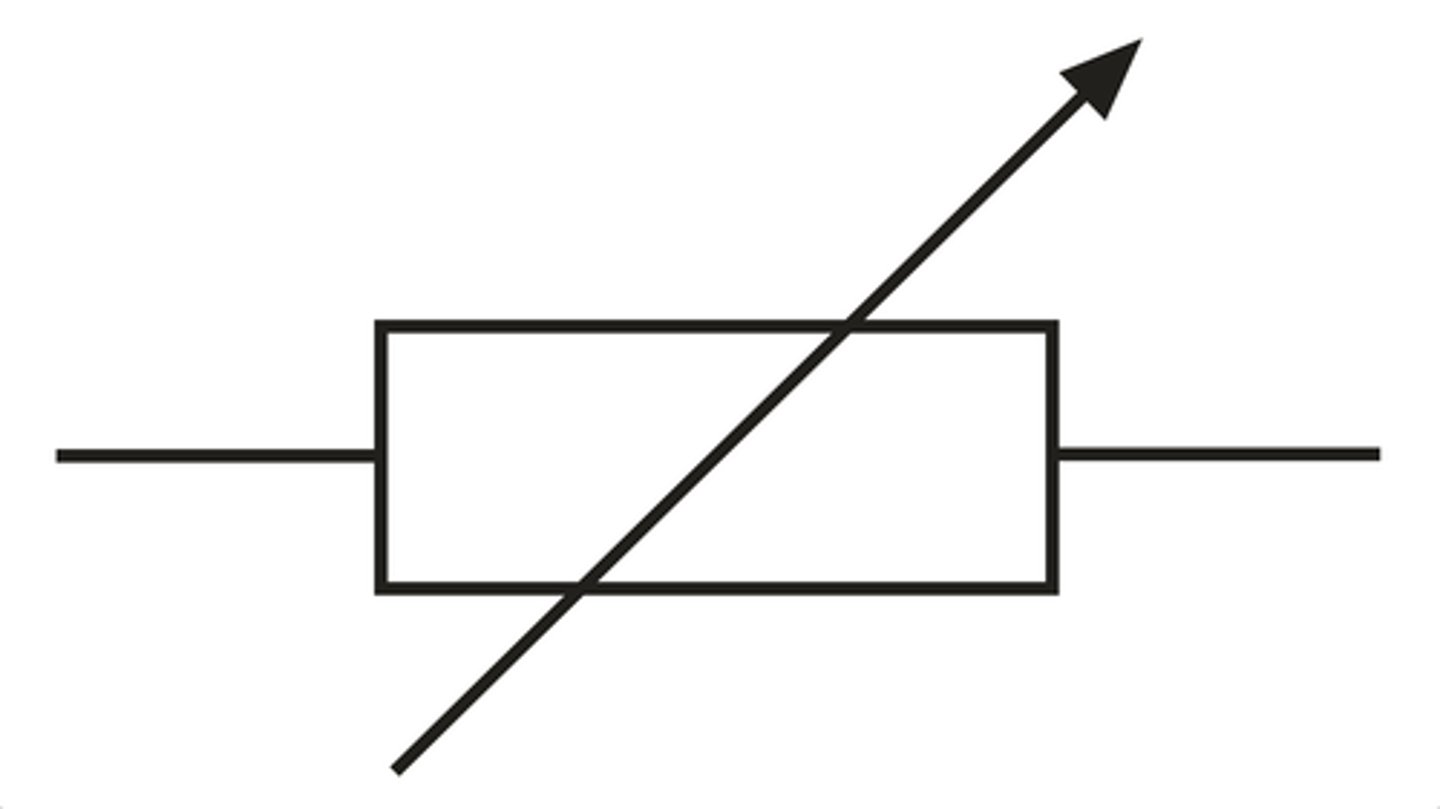
What is a battery?
Two or more cells connected together in series to provide greater voltage
Battery

What are electrical cells?
acts as a power source, converting chemical energy into electrical energy to drive the flow of current
Cell
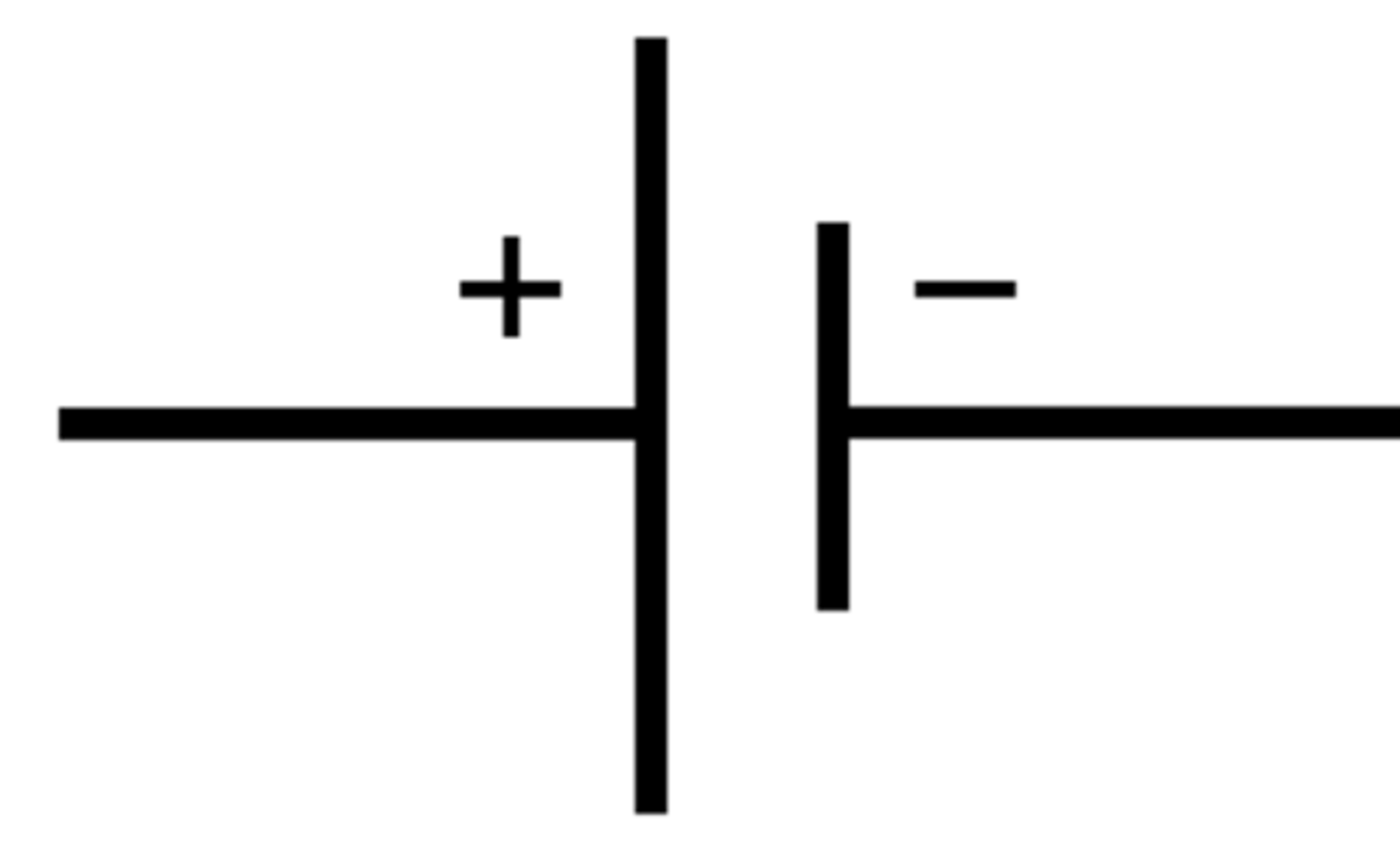
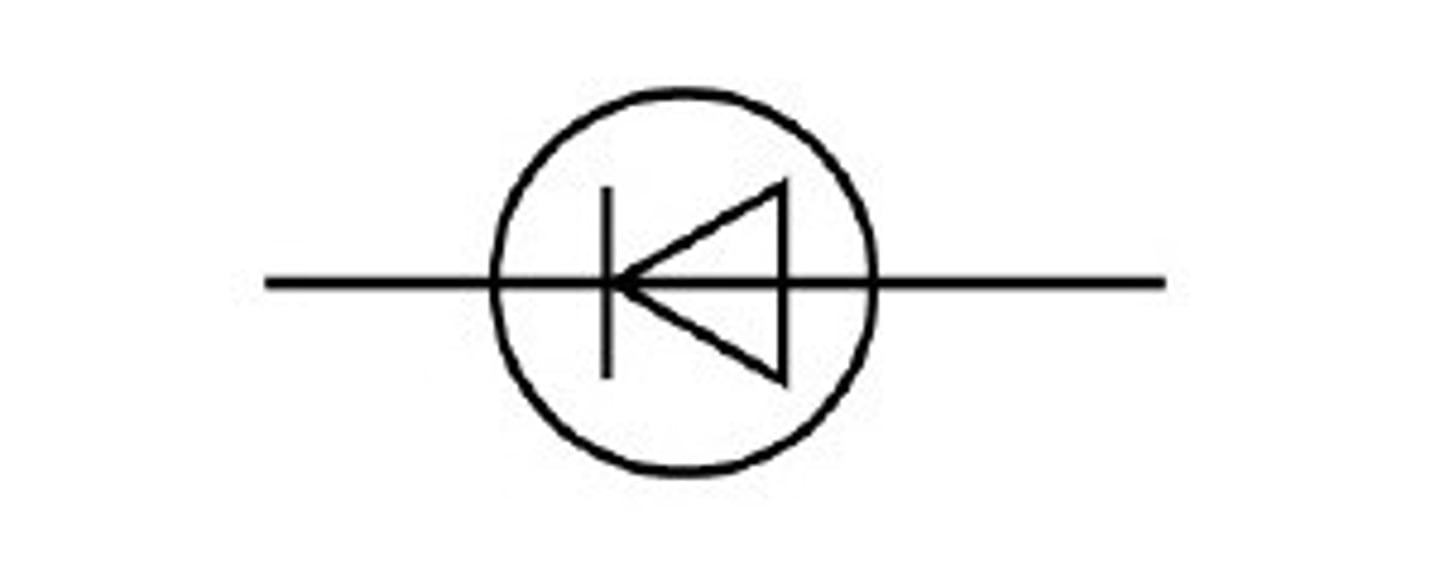
What is a diode?
A device that only allows current to flow in one direction
Diode
diode graph
What is a light-dependent diode (LED)?
A diode that glows when current flows
What is a fuse?
a safety device consisting of a strip of wire that melts and breaks an electric circuit if the current is too high
Fuse