Science test #3 8A
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
What are cells visible through
microscopes
What are cells bigger than
atoms
How many cells are humans made of
100 trillion
What are cells made of
DNA
what are cells
the basic units of life
what did Robert Hooke discover??
cells in 1655 by examining cork under a microscope
What did Robert Hooke say the cells looked like
tiny boxes
what did Anton van Leeuwenhoek discover??
single-celled organisms, known as "animalcules," in 1673 using his microscopes.
What did Anton van Leeuwenhoe use in his homemade microscope?
animal and human blood
What did Anton van Leeuwenhoe observe cells in?
Fish, birds, frogs, dogs and humans
What are cells found in
all living things
what did Anton van Leeuwenhoek see protozoa in
pond water
between the hook/leuwenhoek discoveries and the mid 19th century were there any big changes
very little cells advancements were made
how come after Hooke’s and van Leeuwenhoek’s discoveries were made, there were very few cell advancements?
widely accepted traditional belief in spontaneous generation
what was an example of the traditional beliefs back then for mice?
came from dirty clothes or corn husks
what was an example of the traditional beliefs back then for maggots?
came from rotting meat
what was an example of the traditional beliefs back then for frogs
came from mud
what were the traditional beliefs of mice getting pregnant?
licking salt or grow from the moisture of the earth
Who descovered plants are made of cells
In 1838 German botanist Matthias Schleiden
Who discovered animals are made of cells
In 1839 German physiologist Theodor Schwann
Who discovered cells must arise from pre existing cells
In 1855 German pathologist Rudolf Virchow
What’s mitosis
single cell divides to make two identical cells
What are the 3 basic components of cell theory
All organisms are composed of 1 or more cells , the cell is the basic unit of life in living things, all cells are produced by the division of pre-existing cells.
Who discovered that the cell contains hereditary information in the form of DNA, which is passed from cell to cell?
In 1953 James Watson and Francis Crick
1 cell can be
30 cells through pre existing cells
What are the 4 additional statements in modern cell theory
Cells contain DNA passed to new cells.
All cells have similar chemical makeup.
All life’s energy flows in cells.
Cells have organelles with specific jobs.
What’s the total number of cell theory components
7
what do information do cells contain
hereditary information(dna) which is passed in from cell to cell during cell divison
what does dna stand for
deoxyribonucleic acid

what’s this called
dna ladder/ double helix
where cells are the same
chemical composition and metabolic activities
chemical and physical functions are
carried out inside the cells (movement, digestion, etc)
Cell activity depends on
sub cellular structures within the cells (organelles, nucleus, plasma, membrane).
How does cell theory help in medicine?
It helps us understand diseases and develop treatments.
How is cell theory used in medical research?
Scientists study cells to research cancer, AIDS, and vaccines.
How does cell theory relate to cloning?
It makes genetic cloning possible, like Dolly the sheep.
How is cell theory used in stem cell research?
Stem cells can replace damaged cells and help heal tissues.
How does cell theory contribute to biotechnology?
It allows advances in biotech, like genetic engineering and lab-grown tissues.

ocular lens
Eyepiece; magnifies and views specimen (10x)
Objective Lenses
magnifies the specimen, Low (4x), Medium (10x), High (40x)
Coarse Adjustment Knob
Moves stage for rough focus
Which objective lens should I only use for the coarse adjustment knob
low power objective lens
Why should I only use low power objective lens on a coarse adjustment knob?
high power can crash the lens into the slide, damaging both the lens and the slide
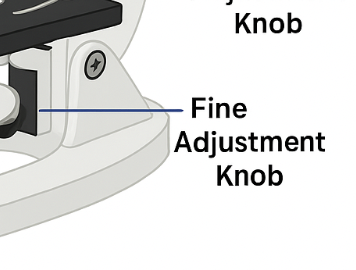
Fine Adjustment Knob
sharpens image

Stage
Platform for slide
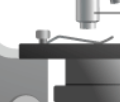
stage clips
holds slide in place

light source
shines light on specimen

Diaphragm
controls light intensity (settings 1–5)
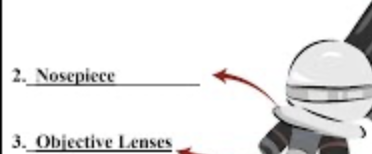
Revolving Nosepiece
Holds and rotates objective lenses
carrying microscope
one hand on the arm and one on the base.
storing microscope
Stage lowered, Objective lens at the lowest power, Stage clips facing back, Power cord wound neatly
do or don't : always clean slides and microscopes when done
do
do or dont ; touch microscopes lens or underneath
don't
do or dont use microscope in dry area
do
do or dont hands must be dry earn using a microscope
do
do or dont if using a microscope with a mirror direct sunlight at the light source(which won’t cause eye damage)
dont
If using microscope with a lighted microscope dont turn off light before pulling out the plug
dont
be cautious when handing glass slides and coverups
do
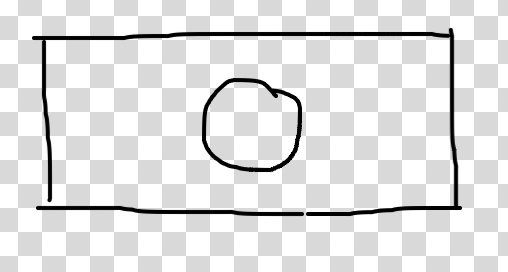
what’s this
weld- allows you to put water which suspends a specimen in place
whats this
double weld
base
the bottom part that provides stability and support for the entire instrument
dry mount
specimen is placed directly onto a slide without any liquid
cover slip
piece of glass or plastic placed over a specimen on a microscope slide to hold it in place and protect both the specimen and the microscope lens
wet mount
suspends specimen in water before placing cover slip
what do you only use fine adjust knobs for, explain
blue and yellow because it doesn’t raise the stage too quickly
what’s a dust cover for
a protective covering used to prevent dust, dirt, and moisture
whats objective lens red
4x
what level is red
low
what level is yellow
medium
what level is blue
high
what objective lens is yellow
10x
what objective lens is blue
40x
total red/low objective lense / ocular
40x
total yellow/medium objective lense / ocular
100x
total blue/high objective lense / ocular
400x
what’s magnification
how much a specimen is enlarged in appearance
how to prevent eye straining
keep both eyes opened
where store microscope With love power objective
in place with stage lowered
high power objective
fine adjustment knob
low power objective
course adjustment knob
how to unplug microscope
grasping and pulling plug
what does ocular lense show
field of view ; circular area which enlarges image of specimen
what’s the low power objective sometimes known as
scanning magnification
lease up close
low power/red/bigger view
lense far away
high power/ blue one/ more detail
what do you use to get a low power view of your specimen
coarse focus
what do you do after the specimen is clear
fine focus
how do you look around the specimen
moving the stage
Movement
Ability to move or change position
Response to Environment
React to stimuli or changes
Respiration
Chemical reaction in cells that releases energy from glucose
Growth
Increase in size, repair damage, and reproduce
Reproduction
Ability to produce offspring and pass on genetic material
Excretion
Removal of waste products from the body
Nutrition
Intake and use of nutrients (varies by organism)
how do you put away a microscope
first clean the lenses and stage, then turn it off and unplug it. Lower the stage, rotate the lowest power objective lens into position, and wrap the power cord. Finally, cover the microscope with its dust cover and carry it carefully with two hands to its storage location.
what's a condenser lens
collects a divergent light source and focuses it into the beam to illuminate a specimen