Module 2 - Foundations in Chemistry
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
mass compared with 1/12th mass of carbon-12
what is the definition of relative isotopic mass?
weighted mean mass compared with 1/12th mass of carbon-12
what is the definition of relative atomic mass?
NO3^-
Nitrate ion formula
CO3^2-
Carbonate ion formula
SO4^2-
Sulfate ion formula
OH^-
Hydroxide ion formula
NH4^+
Ammonium ion formula
Zn^2+
Zinc ion formula
Ag^+
Silver ion formula
PO4^3-
Phosphate ion formula
HCO3^-
Hydrogencarbonate ion formula
H^-
Hydride ion formula
H3PO4
Phosphoric acid formula
HNO3
Nitric acid formula
H2SO4
Sulfuric acid formula
NH4^+
Ammonium ion formula
S8
Sulfur simple molecular formula
P4
Phosphorus simple molecular formula
10^6
How many cm³ in a m³?
10^-6
How many MPa in a Pa?
metal hydroxide + hydrogen
what do a metal + water produce?
salt + hydrogen
what do a metal + acid produce?
salt + water
what do an oxide + acid produce?
salt + water
what do a hydroxide + acid produce?
salt + water + carbon dioxide
what do a metal carbonate + acid produce?
salt + water + carbon dioxide
what do a metal hydrogencarbonate + acid produce?
ammonium salt
what do ammonia + acid produce?
metal oxide + carbon dioxide
what does a metal carbonate produce upon heating?
metal hydrides
When does hydrogen have an oxidation state of -1?
peroxide / -1
what is an example of a situation where oxygen doesn’t have an oxidation state of -2? what is its oxidation state here?
number of electrons needed to be gained or lost to make a neutral atom
what is the definition of oxidation state?
electrons, bonding & structure
2.2 - E__________, B___________ & S___________
sphere
What is the shape of an s orbital?
dumbell
What is the shape of a p orbital?
strong electrostatic attraction between a shared pair of electrons and nuclei of bonded atoms
What is the definition for a covalent bond?
both electrons come from one element
What is dative covalent bonding?
electrostatic attraction between two oppositely charged ions
What is the definition of ionic bonding?
soluble / polar / charged / dissolve
Ionic substances are __________ in water due to the attraction of the _________ water molecule to the __________ ions which pulls them away and they ___________.
dative covalent
Which type of bonding is where there is an arrow signifying electrons come from one element?
linear
What is the shape of this molecule?
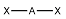
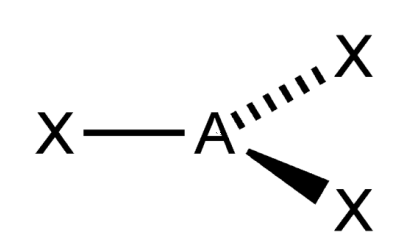
trigonal planar
What is the shape of this molecule?
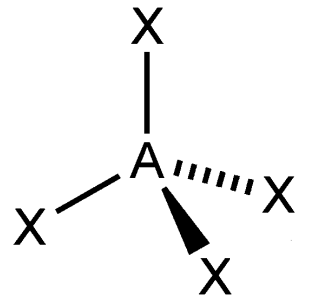
tetrahedral
What is the shape of this molecule?
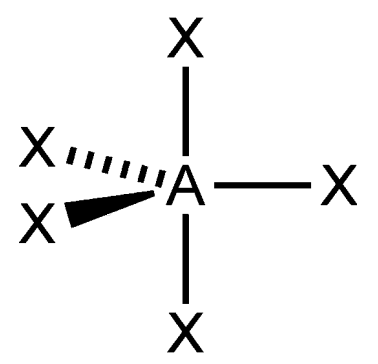
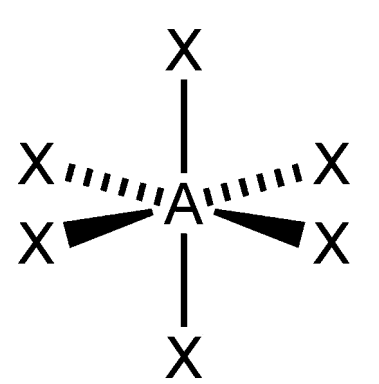
trigonal bipyramidal
What is the shape of this molecule?
Octohedral
What is the shape of this molecule?
decrease by 2.5
What is the effect of lone pairs on molecule shape?
Pauling scale
What is electronegativity measured with?
an atom’s ability to attract the electron pair in a covalent bond
What is the definition of electronegativity?
increases / decreases
Electronegativity….
______________ across periods
______________ across groups
covalent / polar covalent / ionic
Place the bond type in order of increasing electronegativity difference (polar covalent, ionic, covalent)
0 - _________
0 to 1.8 - ________
>1.8 - _________
difference in charge between two atoms caused by a shift in electron density of the bond
What is the definition of a dipole?
atoms of single element
Which are the only type of molecules that can be purely covalently bonded?
oxygen / fluorine / nitrogen
Which are the elements where hydrogen bonding can occur?
when half or completely full
When is the 3d subshell most stable?
1s^2 / 2s^2 / 2p^6 / 3s^2 / 3p^6 / 4s^2 / 3d^10 / 4p^6 / 4d^10 / 4f^14
What is the order of energy of subshells if they were all full (up to 4f)?
2 / 1s^2
How many electrons fit in shell 1? What is the electron configuration of these subshells?
8 / 2s^2 / 2p^6
How many electrons fit in shell 2? What is the electron configuration of these subshells?
18 / 3s^2 / 3p^6 / 3d^10
How many electrons fit in shell 3? What is the electron configuration of these subshells?
32 / 4s^2 / 4p^6 / 4d^10 / 4f^14
How many electrons fit in shell 4? What is the electron configuration of these subshells?