AP Human Geography Unit 3 Culture
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:30 AM on 11/10/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
1
New cards
creole
A language that results from the mixing of a colonizer's language with the indigenous language of the people being dominated.
2
New cards
dialect
A regional variety of a language distinguished by vocabulary, spelling, and pronunciation.
3
New cards
extinct language
A language that was once used by people in daily activities but is no longer used.
4
New cards
isogloss
A boundary that separates regions in which different languages usages predominate.
5
New cards
language
A system of communication through the use of speech, a collection of sounds understood by a group of people to have the same meaning.
6
New cards
language branch
A collection of languages related through a common ancestor that existed several thousand years ago. Differences are not as extensive or as old as with language families, and archaeological evidence can confirm that the branches derived from the same family.
7
New cards
language family
A collection of languages related to each other through a common ancestor long before recorded history.
8
New cards
lingua franca
A language that is mutually understood and commonly used in trade by people who have different native languages. Pilots and people in the control tower use English.
9
New cards
official language
The language adopted for use by the government for the conduct of business and publication of documents.
10
New cards
pidgin language
A form of speech that adopts a simplified grammar and limited vocabulary of a lingua franca; used for communications among speakers of two different languages.
11
New cards
Spanglish
A combination of Spanish and English spoken by Hispanic Americans.
12
New cards
accent
a distinctive way of pronouncing a language, especially one associated with a particular country, area, or social class.
13
New cards
toponym
Name of a place.
14
New cards
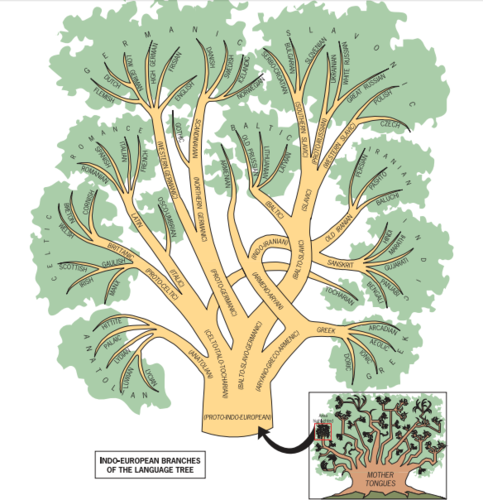
Indo-European
The language family that is the most widely-spoken and has the largest number of speakers; Includes the Germanic, Romance, and Slavic branches (among many others).
15
New cards
ethnicity
Cultural traits; Identity with people who share cultural traditions of a particular homeland or hearth.
16
New cards
Hispanic/Latino/Latina
a person of Cuban, Mexican, Puerto Rican, South or Central American, or other Spanish culture or origin regardless of race; One of the largest ethnic minorities in the U.S.

17
New cards
animism
The attribution of a soul to plants, inanimate objects, and natural phenomena; Associated with hunter-gatherer societies.
18
New cards
Buddhism
Belief system that started in India in the 500s BC. A religion founded in India by Siddhartha Gautama which teaches that the most important thing in life is to reach peace by ending suffering.
19
New cards
caste
A class or distinct hereditary order into which a person is assigned according to a religious law; Associated with Hinduism.
20
New cards
Christianity
A monotheistic universalizing religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus.

21
New cards
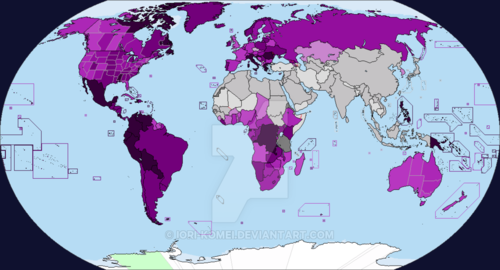
Christian population
A religion of 2.2 billion people; The largest religion by followers and the most widespread.
22
New cards
Confucianism
A philosophy that adheres to the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius. It shows the way to ensure a stable government and an orderly society in the present world and stresses a moral code of conduct.
23
New cards
denomination
A division of a branch that unites a number of local congregations in a single legal and administrative body
24
New cards
Jerusalem
Hearth of Christianity
25
New cards
ethnic religion
A religion that is particular to one, culturally distinct, group of people
26
New cards
missionary
An individual who helps to diffuse a universalizing religion
27
New cards
monotheism
The belief of the existence of only one god
28
New cards
pilgrimage
A journey to a place considered sacred for religious purposes
29
New cards
polytheism
Belief in or worship of more than one god
30
New cards
Hadj
Pilgrimage to Mecca; Fifth "Pillar of Islam".
31
New cards
Hinduism
An ethnic religion and philosophy developed in ancient India, characterized by a belief in reincarnation and a supreme being who takes many forms

32
New cards
Muslims
Followers of the religion of Islam.
33
New cards
Jainism
A religion founded in India in the sixth century BC as an offshoot of Hinduism; Believers practice an extreme form of nonviolence as a daily guiding principle.
34
New cards
Judaism
A monotheist ethnic religion that originated with Abraham and the Hebrew people in the 8th century BCE; Hearth at Canaan (modern day Israel and Palestine).

35
New cards
Muslim population
A religion of 1.5 billion people in the world; The predominant religion of the Middle East from North Africa to Central Asia.
36
New cards
reincarnation
In Hinduism and Buddhism, the process by which a soul is reborn continuously until it achieves perfect understanding.
37
New cards
religion
A system of beliefs shared by a group with objects for devotion, rituals for worship and a code of ethics.
38
New cards
sacred space
An area that has special religious significance or meaning that makes it worthy of reverence or devotion.
39
New cards
Sharia Law
The code of law derived from the Koran and from the teachings and example of Mohammed.
40
New cards
Shia
A Muslim group that accepts only the descendants of Muhammed's son-in-law Ali as the true rulers of Islam; A major branch of Islam.
41
New cards
Shintoism
The ancient indigenous religion of Japan lacking formal dogma.

42
New cards
Sikhism
A belief system which blends Hindu traditions with Islamic monotheistic traditions. Hearth in India and Pakistan; Holy city at Amritsar, India.

43
New cards
Sunni
A branch of Islam whose members acknowledge the first four caliphs as the rightful successors of Muhammad; The major branch of Islam.
44
New cards
Taoism (Daoism)
An indigenous Chinese philosophy in which people live a simple life in harmony with nature.
45
New cards
universalizing religion
A religion that attempts to appeal to all people
46
New cards
folk culture
Traditionally practiced by a small, homogeneous, rural group living in relative isolation.
47
New cards
popular culture
Found in a large, heterogeneous society that shares certain habits despite differences in personal characteristics.
48
New cards
custom
Frequent repetition of an act until it becomes characteristic of a group of people.
49
New cards
taboo
A restriction on behavior imposed by social custom.
50
New cards
homogenous
Of the same kind; alike; Used to describe social groups of cultural practices (especially popular culture).
51
New cards
assimilation
The process through which people lose originally differentiating traits, often used to describe immigrant adaptation to a new place of residence.
52
New cards
cultural hearth
Heartland, source area, innovation center; place of origin of a major culture.
53
New cards
Eastern Orthodox Church
An ancient Christian church concentrated in Eastern Europe, especially Russia and Greece.

54
New cards
Catholic Church
The largest Christian church; Headed by the Pope in the Vatican City, enclaved within Rome.

55
New cards
Protestant Church
The second largest form of Christianity with collectively more than 900 million adherents worldwide (40% of all Christians); Originated with the Reformation, a movement against what its followers considered to be errors in the Roman Catholic Church.

56
New cards
Kaaba
The most sacred temple of Islam, located at Mecca
57
New cards
Switzerland
multi-lingual state where French,German, Italian, and Romansch are spoken
58
New cards
Belgium
multilingual state where Flemish (Dutch) and Walloon (French) is spoken.
59
New cards
Hierarchical Diffusion
the spread of a feature or trend from one key person or node of authority, power, or influence to other persons or places
60
New cards
Relocation diffusion
the spread of an idea through physical movement of people from one place to another
61
New cards
Stimulus Diffusion
a form of diffusion in which a cultural adaptation is created as a result of the introduction of a cultural trait from another place (McDonald's spreads, but the menu items may differ from place to place)
62
New cards
Contagious Diffusion
The rapid, widespread diffusion of a feature or trend throughout a population.
63
New cards
cultural landscape
the visible imprint of human activity and culture on the landscape
64
New cards
Acculturation
Prolonged contact between two or more cultures may result in acculturation which is when people within one culture adopt some traits from the other culture.
65
New cards
Multiculturalism
The acceptance and tolerance of many different cultures which exist in close proximity to one another. Openness, acceptance, diversity.
66
New cards
syncretism
When two culture’s traits blend together and form a new cultural trait. This can happen through contact between peoples such as imperialism, military conquest, immigration or intermarriage
67
New cards
Buddhist god
Siddhartha
68
New cards
Christianity house of worship
Church
69
New cards
Judaism house of worship
Synagogue
70
New cards
Islam house of worship
Mosque
71
New cards
Hinduism house of worship
Temple
72
New cards
Jews, Christians, and Muslim Gods
same god
73
New cards
germanic
branch of indo-european family
74
New cards
indo-european
language family
75
New cards
Built environment
Produced by the physical material culture; the tangible human creation on the landscape.
76
New cards
Sequent occupancy
the current cultural landscape of a region as a combination of all the people which have 'sequentially' occupied that region from the past to the present.
77
New cards
Reverse hierarchical diffsuion
When ideas diffuse based on a low standard of a stereotype
78
New cards
sociofacts
ways of how a society behaves/organizes institutions
79
New cards
mentifacts
ideas, beliefs, values, and knowledge of a culture
80
New cards
cultural traits
visible/invisible traits combining to make up a groups culture
81
New cards
ancient cultural hearth
west africa, ganges river valley, mesoamerica, mesopotamia, mesopotamia
82
New cards
imperialism
dominance of one political community over another political community, weaker political is influenced to serve dominant powers interests
83
New cards
colonialism
process of using military force to conquer and settle another territory whether its occupied/unoccupied
84
New cards
neocolonialism
term has emerged in recent years because imperialism can be pursued through the assertion of political, economic, and cultural influence
85
New cards
terrior
contribution of a locations distinctive physical features to the way food tastes
86
New cards
cultural homogenization
process of reduction in cultural diversity through diffusion of popular culture
87
New cards
centripetal
a cultural value that tends to unify people
88
New cards
centrifu
a cultural value that tends to pull people apart
89
New cards
institutional language
used in education, work, mass media, and government
90
New cards
developing language
used in daily use with literary tradition that's not widely distributed
91
New cards
vigorous language
used in daily use but lacks literacy tradition
92
New cards
threatened language
used for face to face communication but loses users
93
New cards
literary tradition
language written as well as its spoken
94
New cards
dying language
used by older generations but not passed down onto younger ones
95
New cards
logogram
a single written symbol that represents an entire word or phrase without indicating its pronunciation
96
New cards
working language
working language used by international organization/ corporation as its primary means of communication