Glycogen Phosphorylase (GP) Regulation + Hemoglobin and Myoglobin
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What reaction does glycogen phosphorylase catalyze?
Cleaves glucose units from nonreducing ends of glycogen via phosphorolysis → glucose-1-phosphate.
What cofactor does GP use?
Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (PLP), acts as an acid-base catalyst.
GP is ____ly and _____ly regulated
covalently; allosterically
What is the structure of glycogen phosphorylase?
Dimer (842 residues per subunit), each with active site, allosteric site, and phosphorylation site at Ser14.
What allosterically converts GP between R (active) and T(inactive) forms?
AMP is an activator T(Inact) → R (act), while ATP and glucose-6-p are inhibitors R(act) → T (inactive).

What happens when energy is low? GP
AMP binds → enzyme activated → glycogen breakdown increases.
How is GP covalently activated?
Phosphorylation by phosphorylase kinase converts GP-b (inactive) → GP-a (active).
What hormones trigger GO covalent modification?
glucagon and epinephrine (adrenaline)

What is the role of myoglobin? Oxygen ___ in muscles; ___mer with one heme group; __ O₂-binding curve.
storage ; mono; hyperbolic
What is the role of hemoglobin? oxygen ___ in blood; ___mer (α₂β₂); ___ O₂-binding curve (cooperative).
transport ; tetra; sigmoidal
How does Hb exhibit cooperativity?
Binding of one O₂ increases affinity of remaining subunits (T→R transition).
What causes the sigmoidal shape of the Hb binding curve?
Cooperative O₂ binding between Hb subunits.

What is the Bohr Effect?
At low pH (high [H⁺] and CO₂), Hb’s O₂ affinity decreases, enhancing O₂ release to tissues.
Does myoglobin show the Bohr effect?
No, Mb’s O₂ binding is unaffected by pH.
What is 2,3-BPG and what does it do?
A glycolysis byproduct that binds between Hb’s β-subunits, stabilizing T-state and decreasing O₂ affinity, releasing O2.
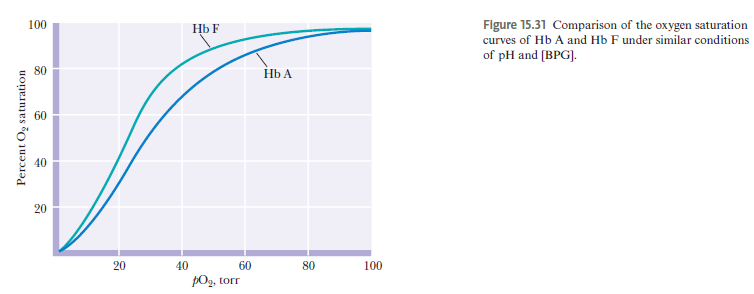
Why does fetal Hb bind O₂ tighter? What is the physiological importance?
A: Fetal Hb (α₂γ₂) has Ser instead of His at position 143 → weaker BPG binding → higher O₂ affinity. Allows fetus to extract oxygen from maternal blood.
What causes sickle-cell anemia?
Point mutation: Glu → Val at β-chain position 6 (HbS).
What effect does the sickle cell mutation have?
HbS polymerizes under low O₂ → RBCs deform/shrivel → block capillaries → cause anemia.
What metal is central to the heme group, and what is its oxidation state?
Fe²⁺ (ferrous iron) — coordinates 6 ligands (4 from porphyrin, 1 from His F8, 1 from O₂)
What local structure change happens to the iron atom when O₂ binds in Hb?
It moves into the plane of the porphyrin ring and drags His F8 along, triggering conformational change
What global structural change enables Hb cooperativity?
Movement of one αβ pair by ~15° relative to the other, breaking salt bridges, and improving O2 binding
What happens when CO₂ binds to Hb?
Forms carbamates on amino termini, stabilizing T-state and promoting O₂ release
Phosphofructokinase 1 (PFK 1) role and how is it controlled
commits glucose to glycolysis by forming fructose 1,6
bisphosphate. allosterically regulated.
PFK1 inhibitor
ATP and citrate
PFK1 activator
MP, ADP, fructose 2,6 bisphosphate
Aspartate Transcarbamoylase (ATCase) role and how is it controlled
first committed step of pyrimidine synthesis, Activity controlled by allosteric regulation and cooperativity
ATCase inhibitor
CTP (end-product)
ATCase activator
ATP
How many heme (containing Fe) groups are in Hb vs Mb
Hb: 4
Mb: 1
Hb function- what does it transport?
Transports oxygen from lungs to tissues and carries CO₂ back to the lungs for exhalation