Decolonization in Africa and Cold War Dynamics
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Decolonization
The process through which colonies gain independence from colonial powers, often resulting in the establishment of sovereign nations.
Imperialism
A policy or ideology where a country extends its power and influence over other nations or territories, often through military force or diplomacy.
Self-determination
The principle that nations have the right to freely choose their sovereignty and international political status without external interference.
Cold War
A period of geopolitical tension between the Soviet Union and the United States, characterized by ideological conflict, military competition, and proxy wars.
Nationalism
A political ideology that emphasizes the interests of a particular nation, often in opposition to foreign influence or control.
Strategic resources
Natural resources that are deemed essential for a nation's economy and security, often leading to geopolitical conflicts over their control.
Philippines
An archipelago in Southeast Asia that gained independence from the United States after World War II, reflecting the broader trend of decolonization.
Atlantic Charter
A joint declaration by the United States and Great Britain in 1941, outlining principles for post-war peace and the right of all peoples to self-determination.
Socialism
An economic and political system where the means of production are owned or regulated by the community as a whole, often associated with left-leaning governments.
Nationalist movements
Political movements aimed at achieving and maintaining the independence and sovereignty of a nation, often emerging in response to colonial rule.
Communism
A political and economic ideology advocating for a classless society where the means of production are owned communally, and goods are distributed according to need.
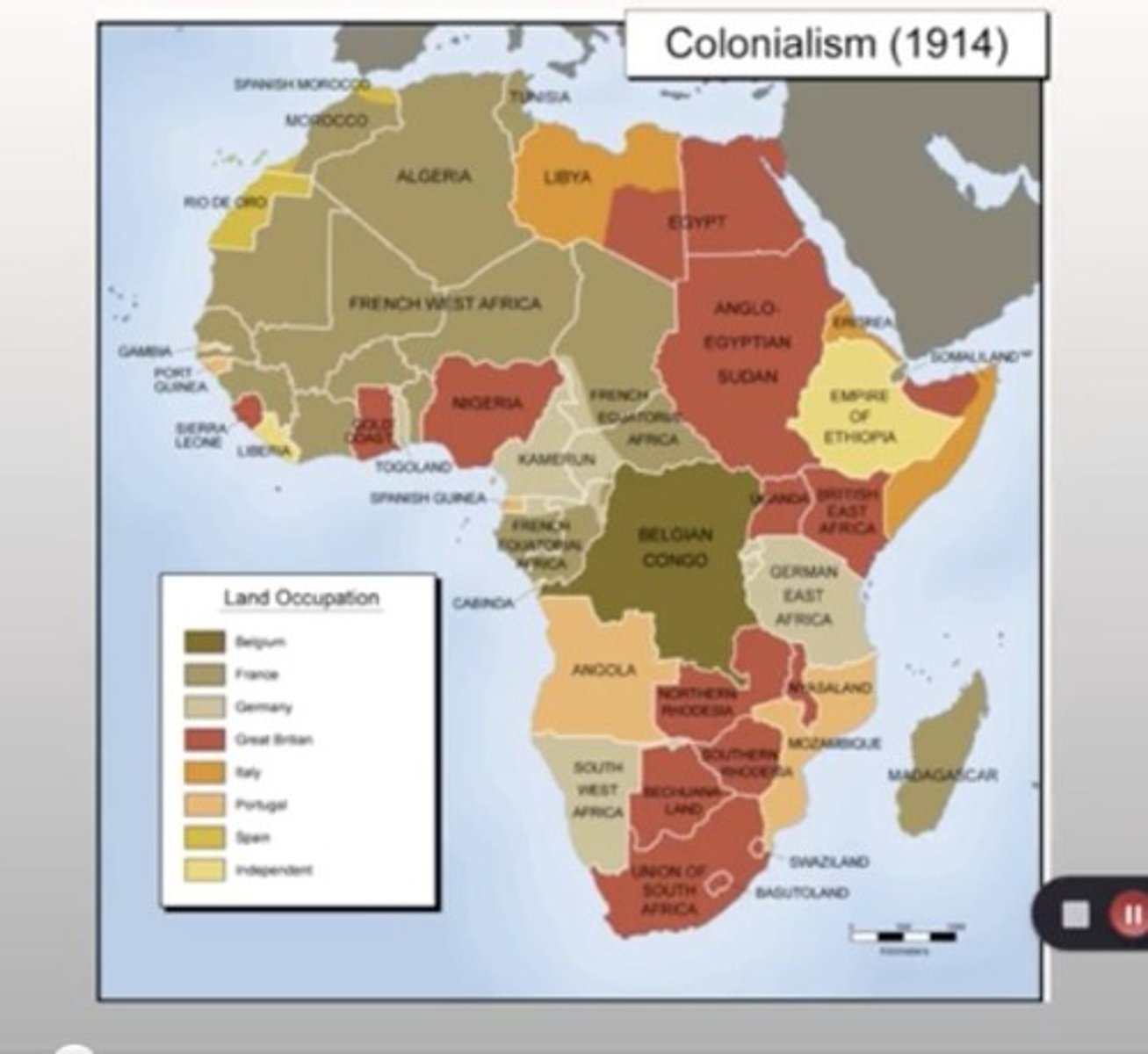
Scramble for Africa
The rapid invasion, colonization, and annexation of African territory by European powers during the late 19th century, particularly from the 1880s to the early 1900s.
Colonial Rule
A system of governance where a foreign power exerts control over a territory and its people, often exploiting resources and imposing its culture.
Ethiopia
One of the few African nations that successfully resisted colonization during the Scramble for Africa, maintaining its sovereignty throughout the colonial period.
Liberia
A West African nation founded in the early 19th century as a settlement for freed African Americans, which maintained independence during the colonial era.
Independence Movements
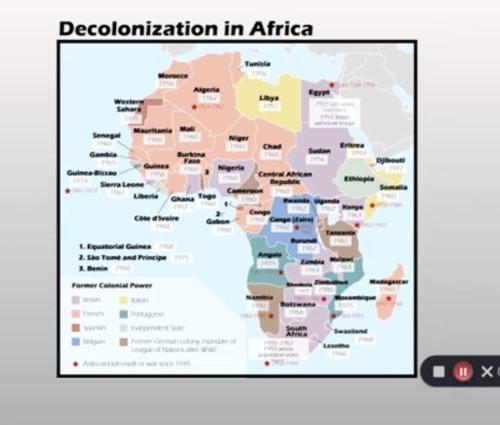
Political movements aimed at achieving self-governance and sovereignty from colonial powers, particularly prominent in Africa after World War II.
Western Imperialism
The policy of extending a country's power and influence through colonization, military force, or other means, particularly by European nations in the 19th and early 20th centuries.
Philosophical Foundations
The underlying principles and ideas that form the basis of a political ideology, such as the belief in equality and the elimination of social classes in communism and socialism.
Economic Control
The degree to which a government or entity regulates and manages the economy, including production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
Colonialism
The practice of acquiring full or partial political control over another country, occupying it with settlers, and exploiting it economically.
White Man's Burden
A paternalistic concept that justified European colonialism, suggesting that it was the duty of white Europeans to civilize and educate non-European peoples.
Pan-Africanism
A movement that seeks to unify African nations and peoples, advocating for solidarity and collective action towards independence and empowerment.
African Nationalists
Individuals who advocated for the independence and self-governance of African nations, often in opposition to colonial rule.
Ethnic Conflict
Tensions and disputes that arise between different ethnic groups, often exacerbated by colonial borders that ignored traditional divisions.
Ghana
The first African nation to gain independence from colonial rule in 1957, led by Kwame Nkrumah.
Kwame Nkrumah
A prominent Ghanaian leader and advocate for Pan-Africanism, who played a key role in the country's independence movement.
Sékou Touré
The first President of Guinea, who led the nation to independence from French colonial rule in 1958 and remained in power until his death in 1984.
Algerian War
A conflict between France and Algerian independence movements from 1954 to 1962, which significantly weakened France's ability to maintain its empire in Africa.
Independence
The state of being free from outside control or influence, particularly in relation to governance and political autonomy.
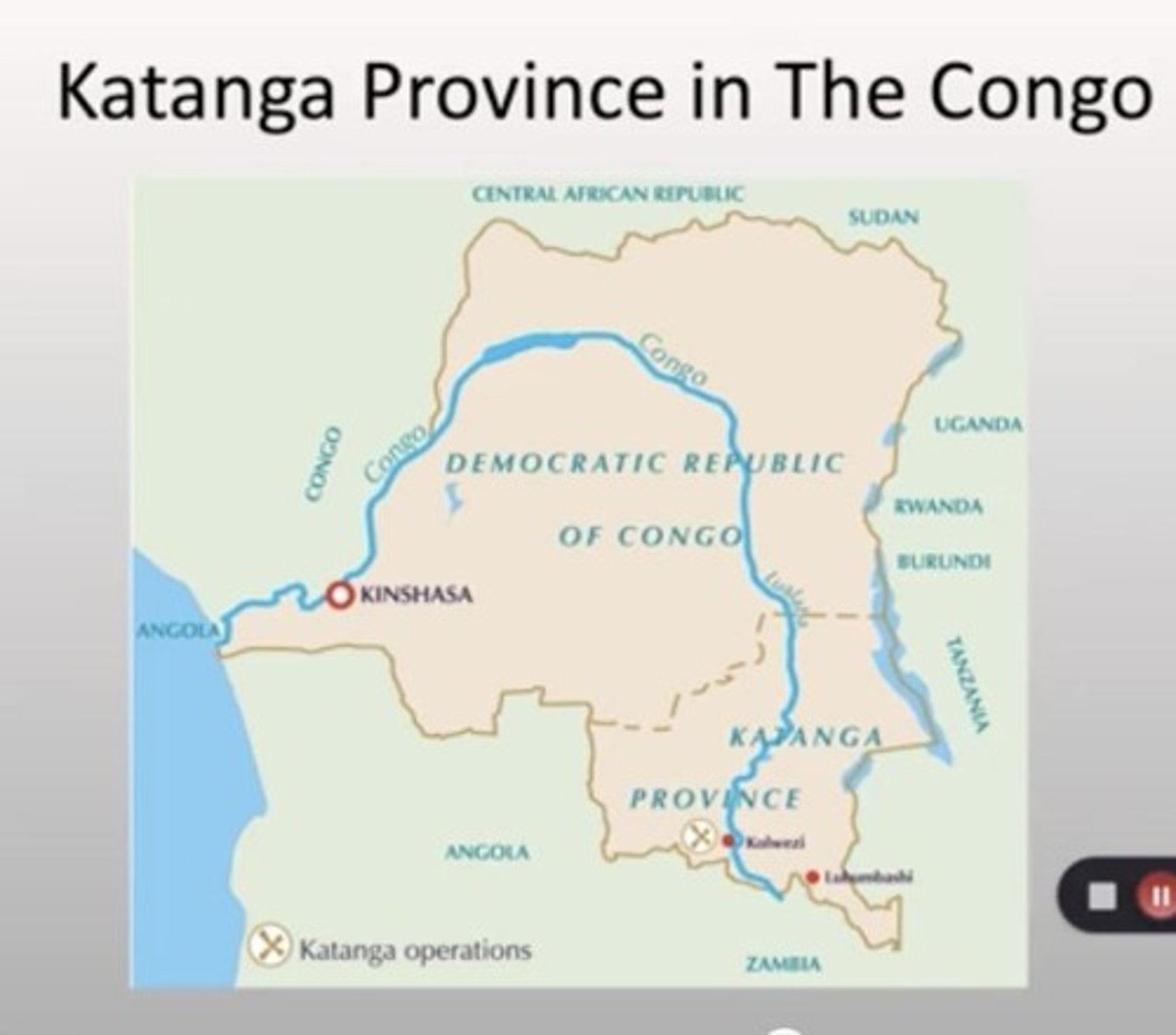
Patrice Lumumba
The first Prime Minister of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, known for his role in advocating for independence from Belgian colonial rule.
Katanga
A mineral-rich province in the Democratic Republic of the Congo that became a focal point of conflict during the country's struggle for independence.
Coup
A sudden, violent, and illegal seizure of power from a government.
Soviet Union
A former federal socialist state in Eastern Europe and Northern Asia, known for its opposition to Western capitalism and its support for anti-colonial movements.
CIA
The Central Intelligence Agency, a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, tasked with gathering, processing, and analyzing national security information.
Uranium
A heavy metal used as fuel in nuclear reactors and in the manufacture of nuclear weapons, significant for its strategic value.
Civil War
A conflict between organized groups within the same state or country, often over control of the government or territory.
Token Independence
A situation where a country appears to be independent but is still heavily influenced or controlled by a foreign power.
Belgian Congo
The name of the Congo Free State and later the Belgian Congo, a large area in Central Africa that was a personal possession of King Leopold II of Belgium before becoming a Belgian colony.
Anti-imperialism
Opposition to colonial or imperial rule, advocating for the rights of nations to self-govern and resist foreign domination.
Mineral Resources
Natural substances found in the earth that are mined for economic use, often a source of conflict in regions rich in such resources.
Western Allies
Countries that were aligned with the United States and opposed to the Soviet Union during the Cold War, often involved in international politics and interventions.
Radical Leader
A political leader who advocates for significant or revolutionary changes in society, often challenging established norms and power structures.
Mobutu Sese Seko
The military leader who became the dictator of the Congo after Lumumba's removal, supported by the United States and Belgium.
Puppet Regime
A government that is controlled by an outside power, often used to describe Mobutu's rule in the Congo.
Human Rights Abuses
Violations of basic rights and freedoms, which were prevalent under Mobutu's regime.
Assassination
The deliberate killing of a prominent person, which was rumored to be a goal of the CIA regarding Lumumba.
Embezzlement
The act of wrongfully taking or misappropriating funds, a crime associated with Mobutu's leadership.
Proxy War
A conflict where two opposing countries or parties support combatants that serve their interests instead of waging war directly.
Coup d'état
The sudden overthrow of a government, often executed by a small group of individuals, typically involving the military.
Corruption
The abuse of entrusted power for private gain, often leading to the exploitation of resources and the undermining of public trust.
African Nationalism
A political movement advocating for the independence and self-determination of African nations, often in response to colonial rule.
Seko Touré
A prominent Guinean political leader who became the first President of Guinea after leading the country to independence from France in 1958.
Algerian War of Independence
A conflict between France and Algerian independence movements from 1954 to 1962, resulting in Algeria gaining independence.
Che Guevara
An Argentine Marxist revolutionary who played a key role in the Cuban Revolution and became an iconic figure in leftist movements worldwide.
Debt Dependency
A situation where a country relies heavily on loans and financial aid from foreign nations, often leading to economic instability and loss of sovereignty.
Ideological Battle
A conflict characterized by opposing beliefs and values, often manifesting in political, social, and military confrontations.
Colonial Powers
Nations that established colonies in other regions, exerting control over the local population and resources, often through force.
Brutal Regime
A government characterized by harsh and oppressive rule, often involving human rights violations and lack of political freedoms.
Strategic Ally
A country or entity that is supported for its importance in achieving specific political or military objectives, regardless of its internal policies.
Global Economy
The interconnected economies of nations around the world, influenced by trade, investment, and economic policies.