Introduction to Evolution and Natural Selection
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Evolution
Change in species over time through adaptation.
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
Principle predicting genetic variation in a population.
Violations of Hardy-Weinberg
Factors disrupting genetic equilibrium in populations.
Species
Groups of organisms capable of interbreeding.
Speciation
Process by which new species arise.
Taxonomy
Science of classifying organisms into categories.
Classification
Grouping organisms based on shared characteristics.
Cladistic Method
Classification based on common ancestry and evolutionary relationships.
History of Life
Chronological record of biological evolution.
Human Evolution
Study of the origins and development of humans.
Natural Selection
Mechanism of evolution favoring advantageous traits.
Fossil Record
Historical evidence of past life forms.
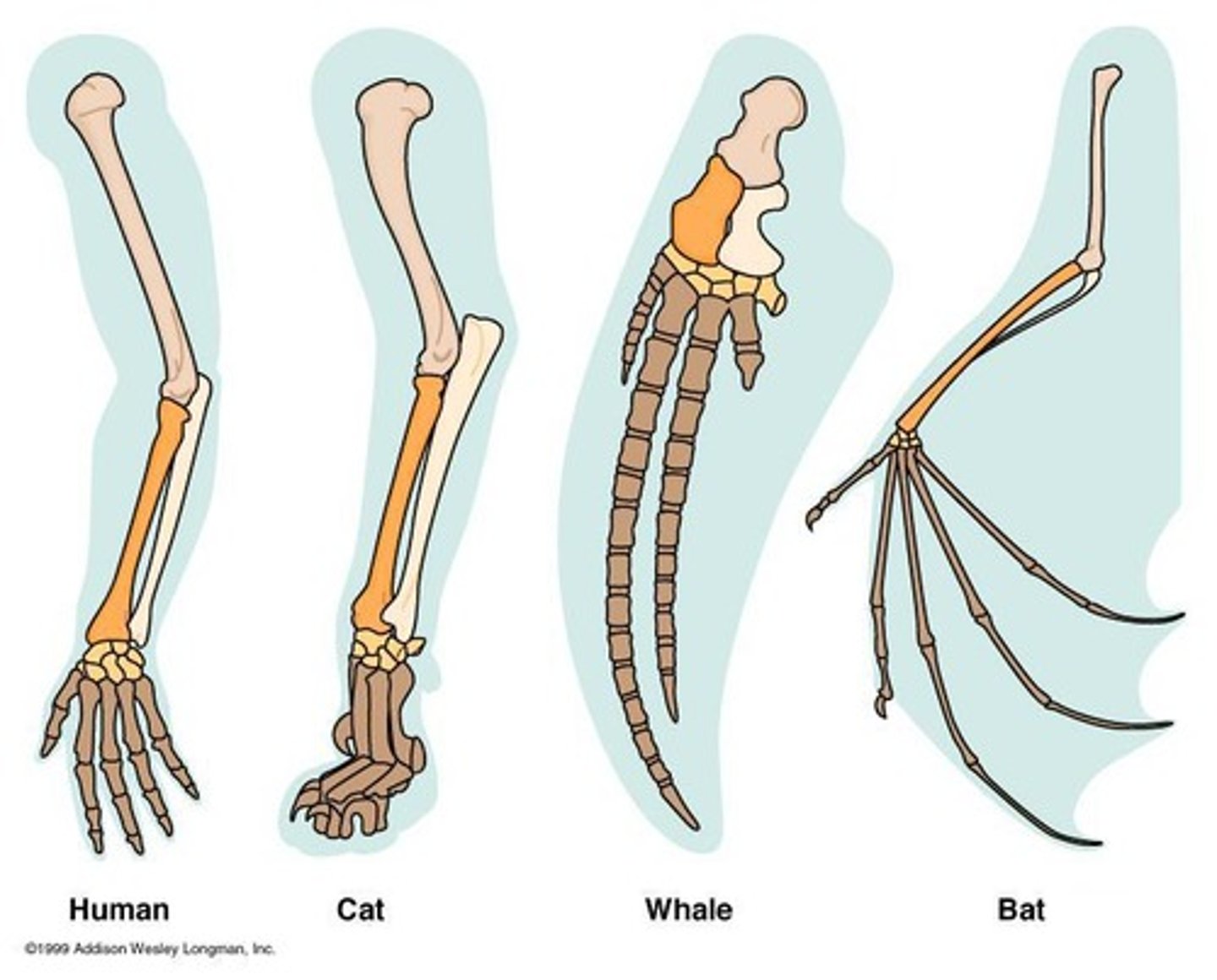
Homologous Similarity
Similar structures in different species indicating common ancestry.
Biogeographical Patterns
Distribution of species across geographical areas.
Embryology
Study of embryos revealing evolutionary relationships.
Comparative Anatomy
Study of morphological similarities among organisms.
Analogous Similarity
Similarity based on function, not structure.
Homologous Similarity
Similarity based on shared ancestry, not function.
Morphological Series
Gradual changes in traits over evolutionary time.
Darwin's Hypothesis
Species change over time, reflecting common ancestry.
Special Creation
Species created separately with unique characteristics.
Descent with Modification
Darwin's model explaining evolutionary changes.
Embryology
Study of embryonic development across species.
Haeckel's Biogenetic Law
Embryos exhibit ancestral characteristics during development.
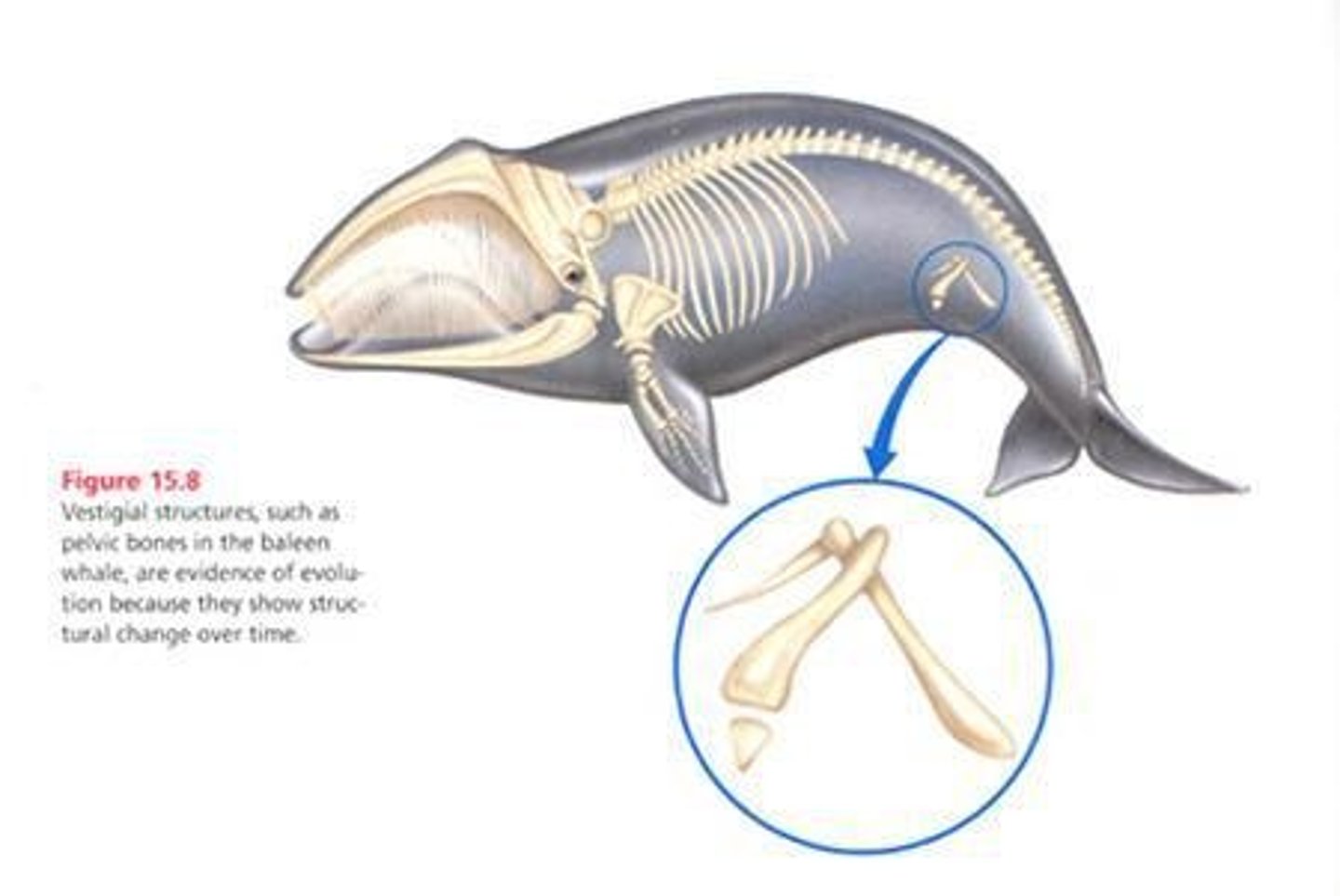
Vestigial Characters
Reduced or non-functional traits from ancestors.
Atavistic Characters
Traits reappearing from distant ancestors.
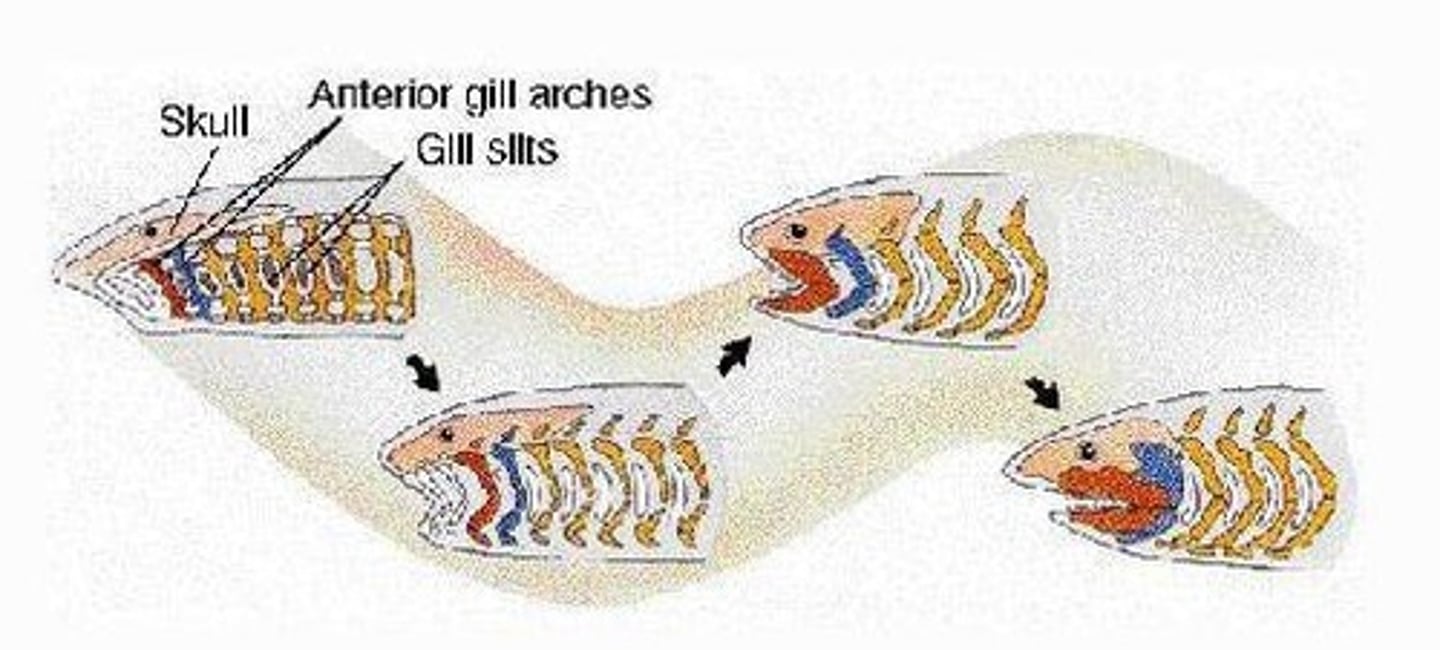
Gill Arches
Ancestral structures evolving into jaws in vertebrates.
Pelvic Bones in Whales
Example of vestigial characters in modern species.
Vermiform Appendix
Reduced structure in humans with no essential function.
Agnathan
Jawless fish, e.g., hagfish.
Teleost
Modern bony fish, e.g., clown fish.
Placoderm
Early jawed fish, type of gnathostome.
Spiny Thicket
Deciduous shrub, Alluaudia ascendans from Madagascar.
Ocotillo
Desert plant, Fouquieria splendans, related to cacti.
Forelimb Bones
Humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, phalanges.
Embryonic Teeth
Temporary teeth in embryos, later resorbed.
Milk Teeth
First set of teeth in mammals, replaced later.
Common Ancestry
The shared lineage of different species.
Functional Necessity
Requirement for a trait to serve a purpose.
Morphological Patterns
Structural features shared among different organisms.
Evolutionary Evidence
Data supporting the theory of species evolution.
Cecum
Large pouch in herbivores for cellulose breakdown.
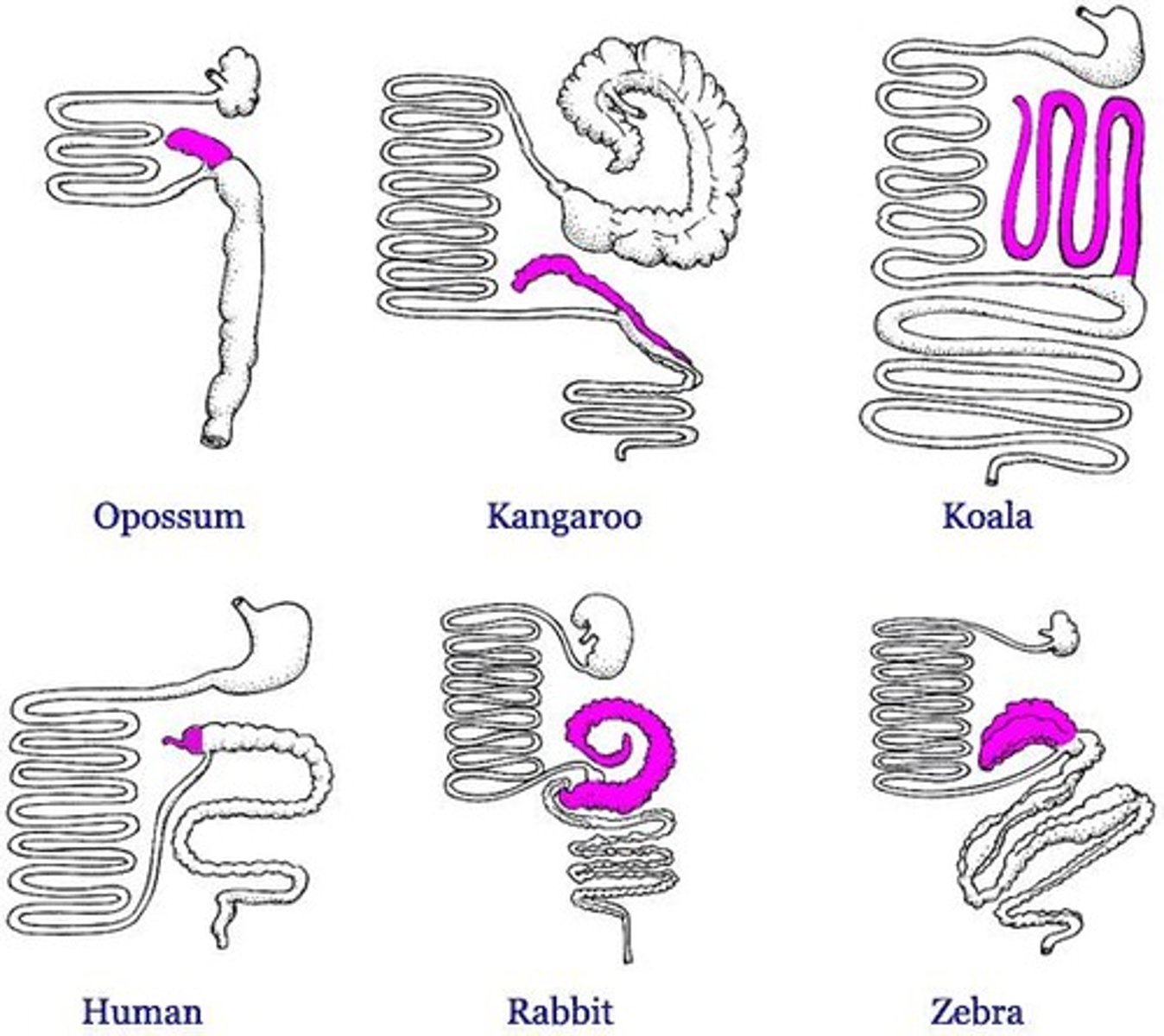
Appendix
Small, wormlike structure in humans, vestigial.
Atavistic Characters
Reappearance of ancestral traits in species.
Darwinian Evolution
Theory that species evolve over time.
Special Creation
Belief that species were created independently.
Vestigial Characters
Non-functional traits inherited from ancestors.
Biogeographic Realms
Distinct regions with unique species assemblages.
Neotropics
Region with diverse species, especially hummingbirds.
Hummingbirds
Over 300 species, sexually dimorphic, found in Americas.
Sunbirds
Old World equivalent to hummingbirds, distinct species.
Convergent Evolution
Different species evolve similar traits independently.
Toucans
Fruit-eating birds in Neotropics, important foraging role.
Hornbills
Old World equivalent to toucans, found in Africa.
Marsupials
Mammals with pouch, primarily in Australia.
Placental Mammals
Dominant mammal group outside of Australia.
Geographical Barriers
Natural obstacles preventing species dispersal.
Geographical Corridors
Routes allowing species movement between areas.
Fossil Record
Historical evidence of species evolution over time.
Comparative Anatomy
Study of similarities and differences in organisms' structures.
Embryology
Study of embryos, revealing evolutionary relationships.
Plate Tectonics
Movement of Earth's plates affecting species distribution.
Natural Selection
Mechanism driving adaptive changes in species.
Sexual Dimorphism
Differences in appearance between male and female.
Adaptive Change
Changes in species traits enhancing survival.
Evidence-based Conclusion
Findings supporting Darwin's evolution hypothesis.
Developmental Errors
Mistakes in development leading to trait reappearance.
Distinct Assemblages
Unique groups of species in specific regions.
Evolutionary Hypotheses
Theories explaining species changes over time.