carina macroeconomic objectives
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
What are the 5 macroeconomics objectives?
- Low unemployment
- Low and stable inflation
- Economic growth
- Sustainable level of government debt (HL)
- Equity in the distribution of income
Unemployment
refers to people who are working age who are actively looking for a job but unable to find one.
Underemployment
refers to people of working age who either have part-time jobs but would like to work full-time or those that are employed but not fully using their education or skills.
What do the terms of unemployment and underemployment mean?
that the economy is not using resources efficiently.
Labour force
is considered to be those that are employed plus those who are unemployed. The labour force is only a fraction of the total population as it does not consider those that are retired, children, working age students, those that do not want to work, or those with disabilities or who cannot work because of illness.
How can unemployment be measured? (2)
1- as a number: it is the total number of unemployed personas in the economy
2- as a percentage; unemployment rate
unemployment rate equation
(number of unemployed ÷ labour force) × 100
What are some underestimates due to hidden unemployment? (4)
1- Exclusion of discouraged workers.
2- Does not distinguish between full and part-time work.
3- Does not distinguish between the type of work done (underemployment).
4- Does not consider people on retraining programmes.
What are some overestimates due to the informal economy? (1)
1- Does not consider people working in the underground economy.
Why can there be discrepancies within a national population? (4)
1- regional differences; some regions may have declining industries and thus higher unemployment than others
2- Gender; women sometimes face higher unemployment rates than men
3- Ethnic groups; some are disadvantaged due to discrimination or lower levels of education and/or training
4- Age; youth unemployment (ppl under 25) usually face higher unemployment rates due to lower skill levels
What are the economic costs of unemployment? (8)
1- A loss in real output (rGDP).
2- A loss in income for unemployed workers.
3- A loss in tax revenue for the government.
4- Costs to the government in terms of unemployment benefits.
5- Costs to the government dealing with social problems.
6- Larger budget deficit or smaller budget surplus.
7- More unequal distribution of income.
8- Unemployed have difficulties finding jobs in the future.
Budget deficits
refers to the governments budget in the situation where government tax revenues are less than government expenditures over a specific period of time (usually a year)
budget surplus
refers to the governments budget, it is the situation in which government tax revenues are greater than government expenditures over a specific period of time (usually a year)
What are the personal and societal costs of unemployment? (2)
1- Personal issues.
2- Greater social problems.
What are the 4 types of unemployment?
1- Structural unemployment
2- Frictional unemployment
3- Seasonal unemployment
4- cyclical unemployment
Which types of unemployment are included in the NRU?
all of them but cylical
Structural unemployment
occurs as a result of changes in demand for particular types of labour skills, changes in the geographical location of industries and therefore jobs, and labour market rigidities.
Causes of structural unemployment (2)
1- Changes in the demand for particular labour skills: This can happen due to technological changes or changes due to declining industries.
2- Changes in geographical location of jobs: If firms decide to relocate their factories to other locations workers can become structurally unemployed if they’re not able to find new work.
What are examples of labor market rigidities? (4)
1- Minimum wage
2- Labour union activities
3- Employment protection laws
4- Generous unemployment benefits
Labor market rigidities
Factors preventing demand and supply to meet
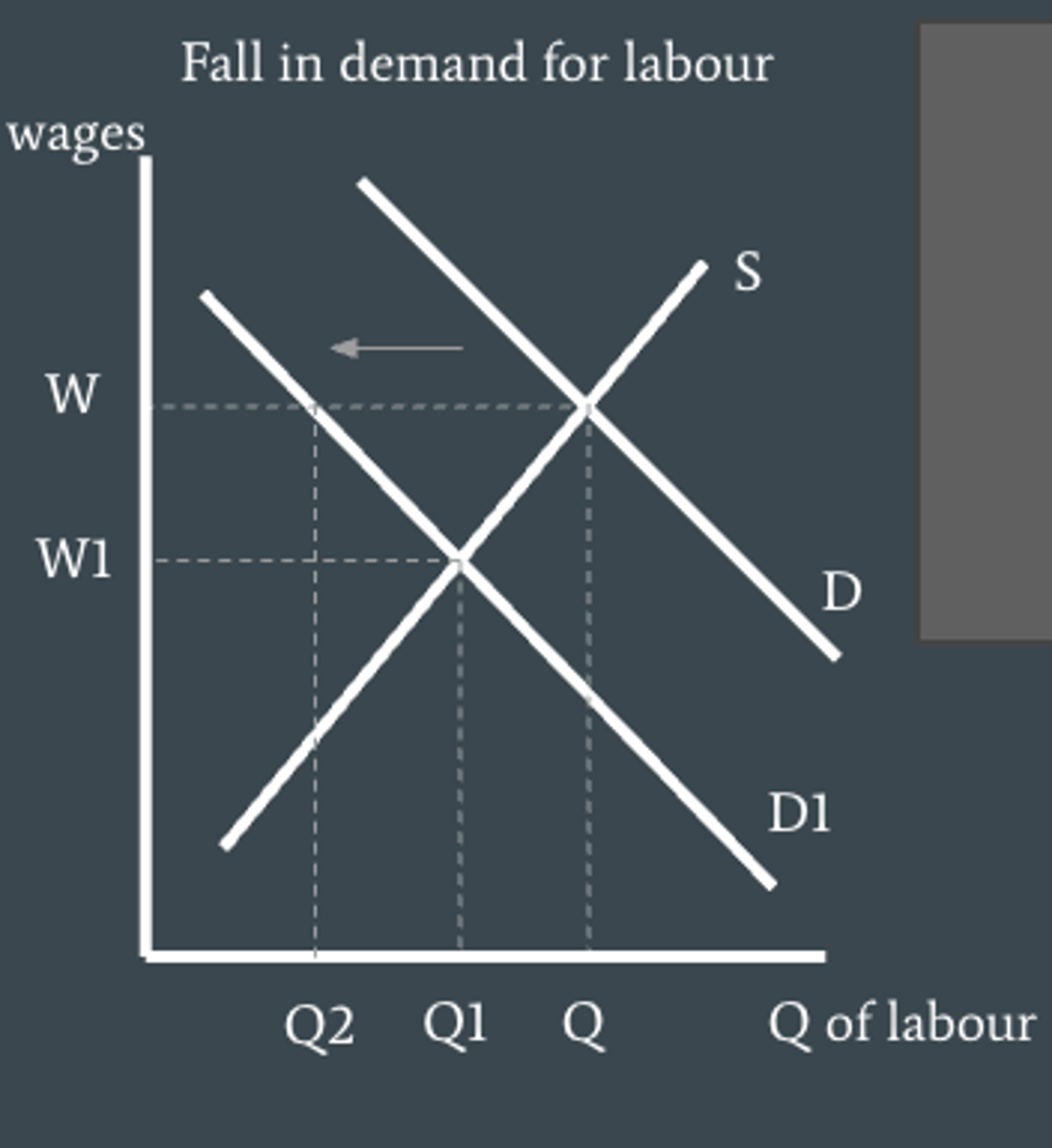
How can we illustrate structural unemployment (mismatches b/w labour demand and labour supply)?
The vertical axis measure the wage (price of labour), the horizontal measures the quantity of labour and the demand curve shows the quantity of labour firms are willing and able to hire at each wage, the supply curve shows the quantity of labor workers supply at each wage

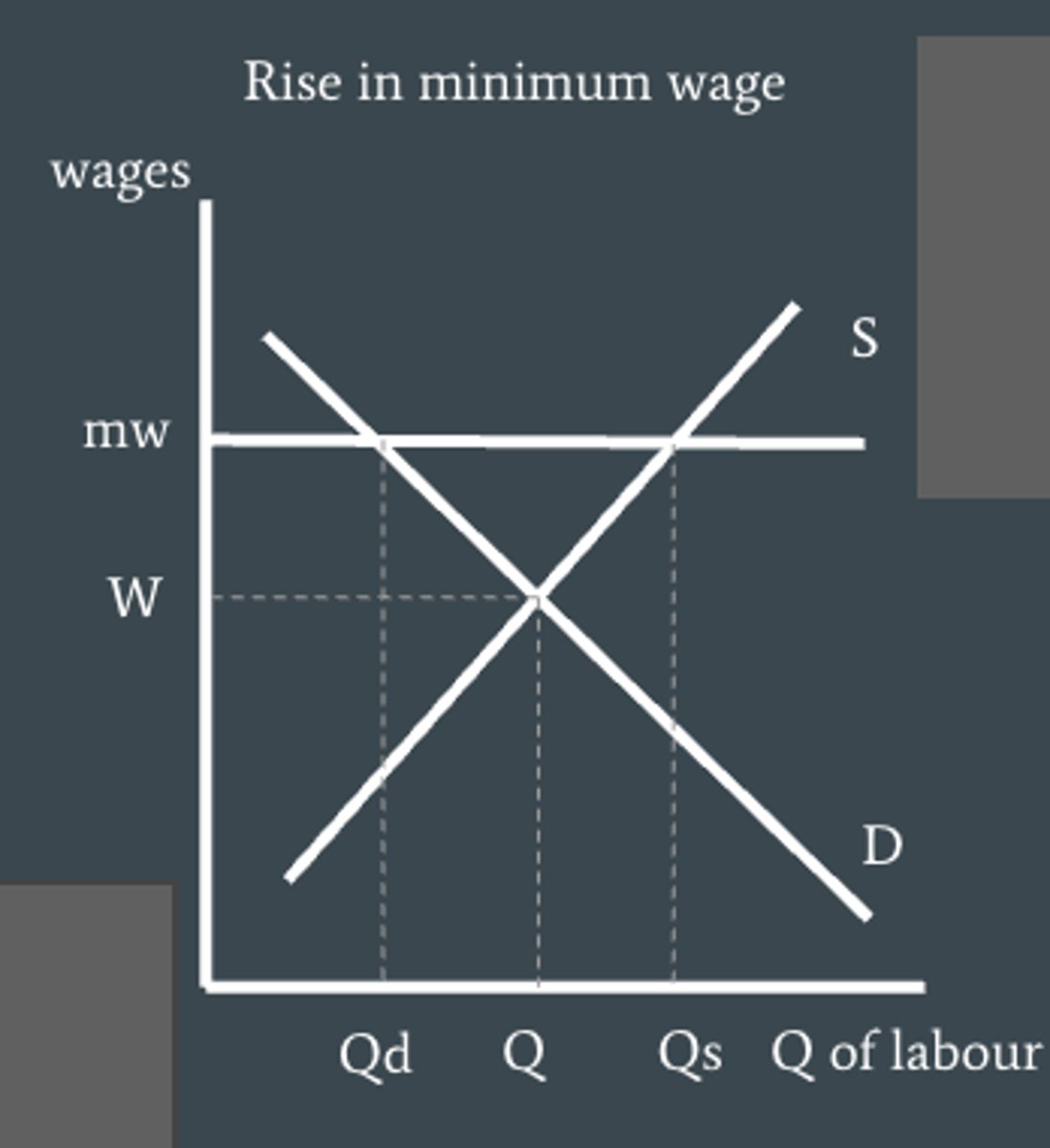
How can we illustrate structural unemployment (minimum wage legislations)?
minimum wage legislations act as a price floor and minimum wage firms have to pay their laborers. This leads to higher than equilibrium wages and lower quantities of labour demanded
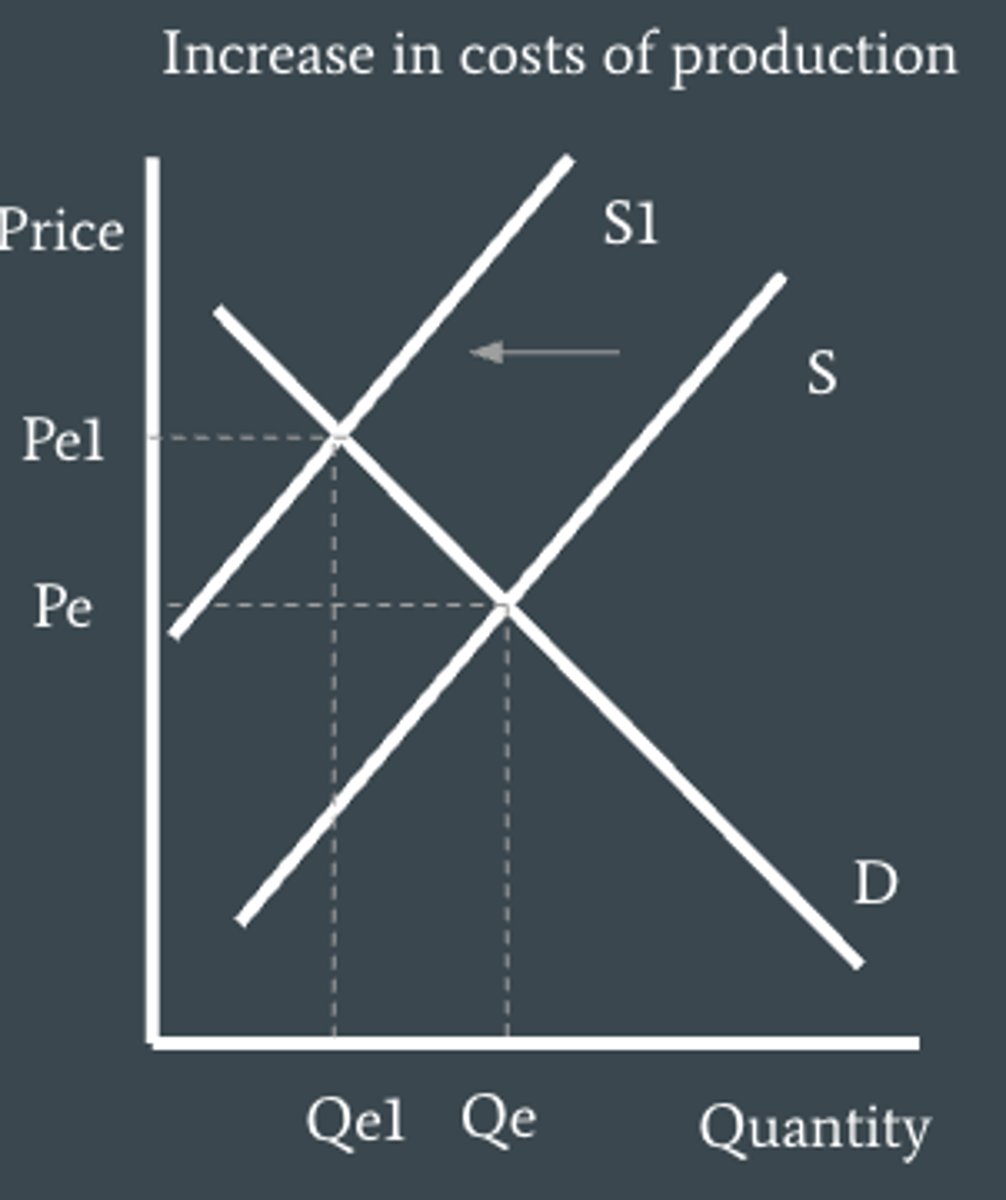
How can we illustrate structural unemployment (labor market rigidities) ?
These lead to an increase in costs of production so supply shifts to the left causing a fall in quantity produced and so firms hire less workers
Frictional unemployment
unemployment due to workers being in between jobs. This could be because the workers have quit or been fired. This type of unemployment is short-term and is generally considered to be less serious.
Seasonal unemployment
unemployment that occurs because of changes in demand for seasonal work. This type of unemployment often happens in the agricultural sector and tourism sector.
Cyclical (demand-deficient) unemployment
occurs during downturns or recessionary phases of the business cycle. When there are decreases in Aggregate Demand there is a fall in the demand for all goods and services in the economy and therefore firms need less workers to produce less output.
Which type of unemployment is seen as the most severe?
cyclical unemployment
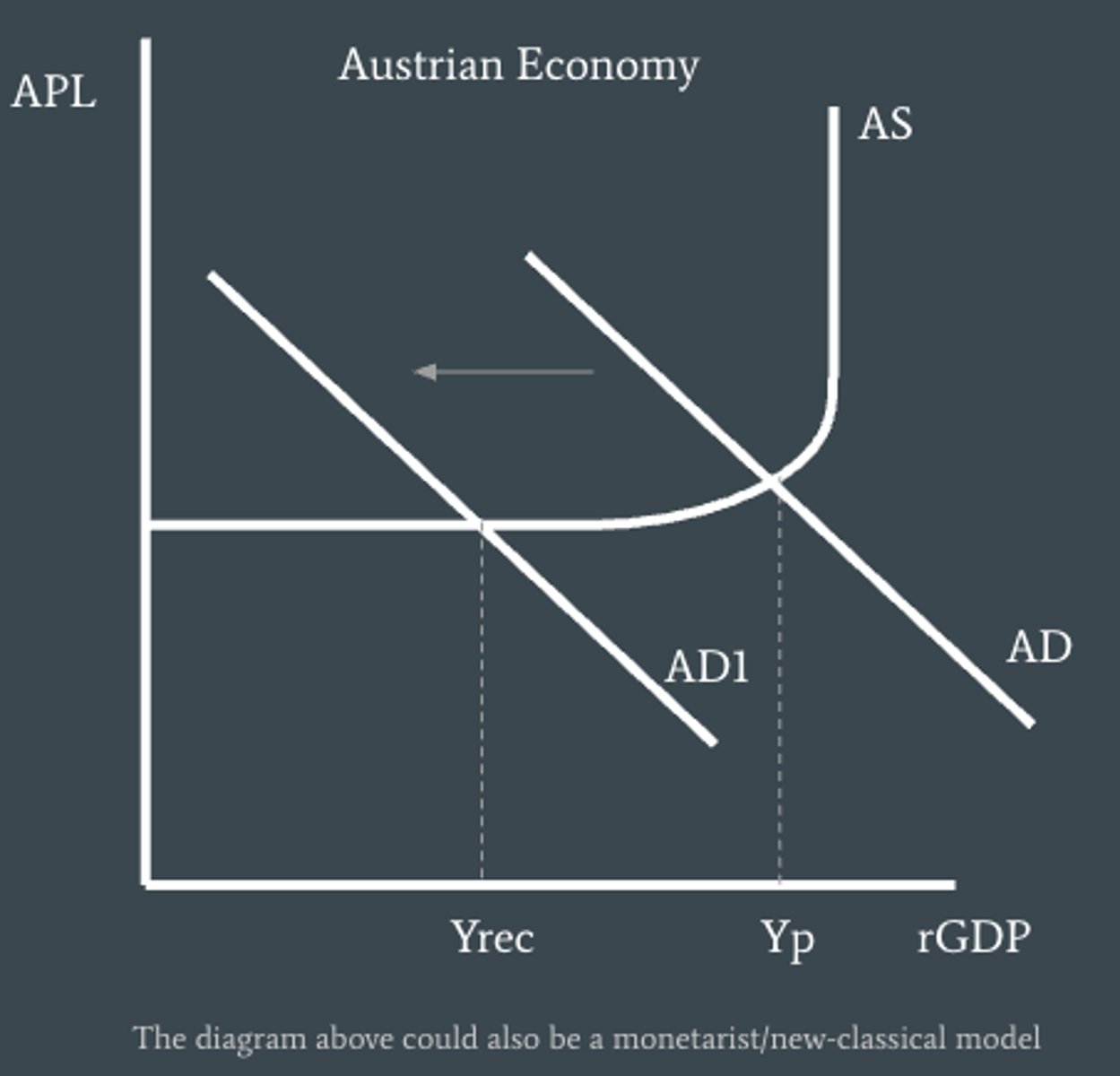
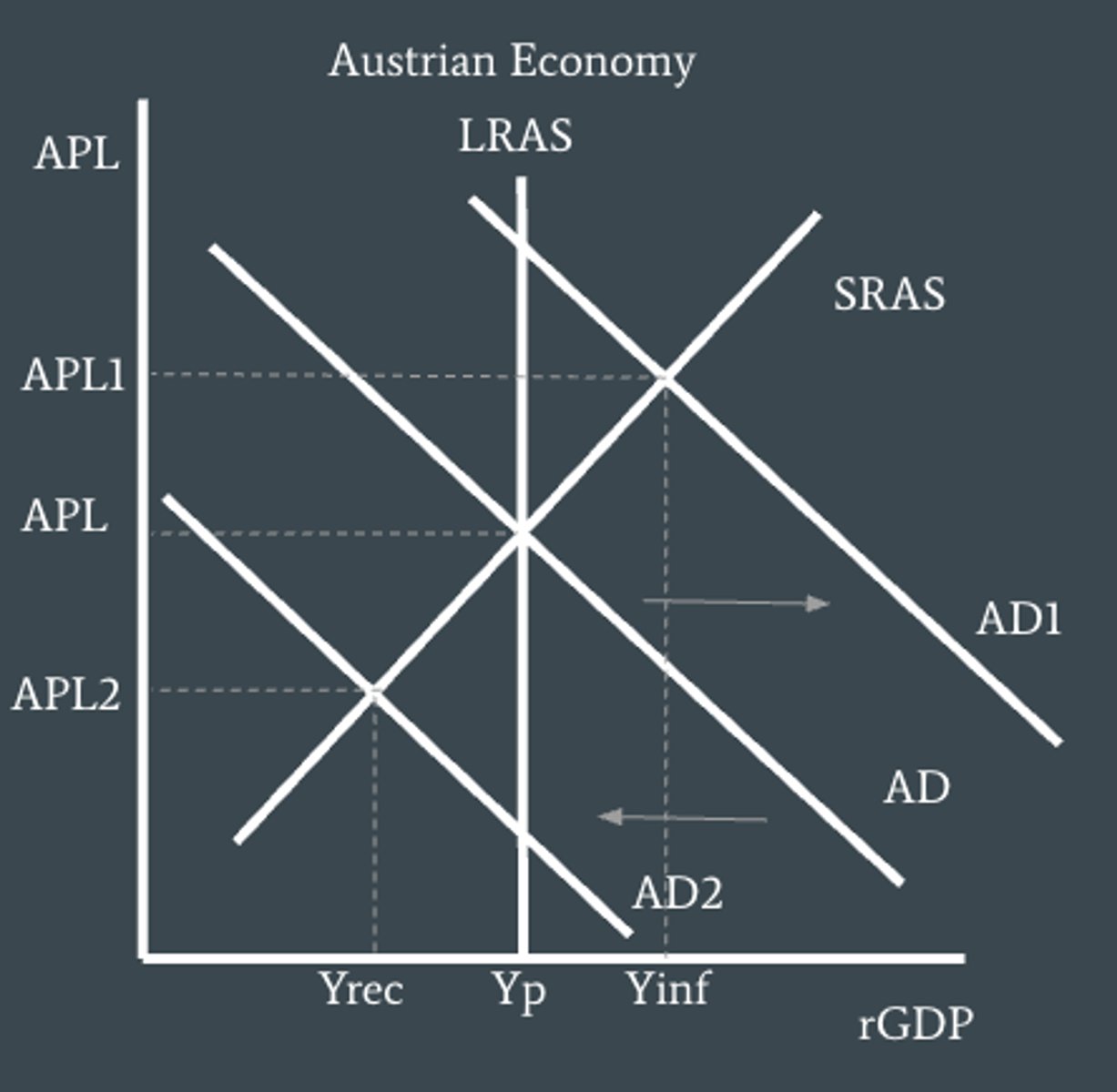
What is unemployment like on the monetarist model?
At Yp - unemployment is equal to the natural rate of unemployment which means there is structural, seasonal, and frictional but no cyclical.
At Yinf - unemployment is below the natural rate of unemployment and there are workers who are structurally, seasonally, and frictionally unemployed that find temporary work.
At Yrec - unemployment is above the natural rate of unemployment and there is cyclical unemployment.
Inflation
sustained increase in the average price level of goods and services.
Deflation
sustained decrease in the average price level of goods and services. (- inflation is deflation)
Disinflation
occurs when inflation happens at a slower rate.
How can we measure inflation?
using consumer price index (CPI)
The Consumer Price Index (CPI)
a measure of the cost of living for the typical household, and compares the value of a basket of goods and services in one year with the value of the same basket in a base year.
Calculating CPI (% change in price index)
% change in price index = (price index new - price index old / price index old) x 100
What are some problems with CPI? (7)
1- Different rates of inflation for different income earners.
2- Different rates of inflation depending on regional or cultural factors.
3- Changes in consumption patterns due to consumer substitutions when relative prices change.
4- Changes in consumption patterns due to introduction of new products.
5- Changes in product quality.
6- International comparisons.
7- Comparability over time.
What are causes of inflation? (2)
1. Demand-pull inflation
2. Cost-push inflation
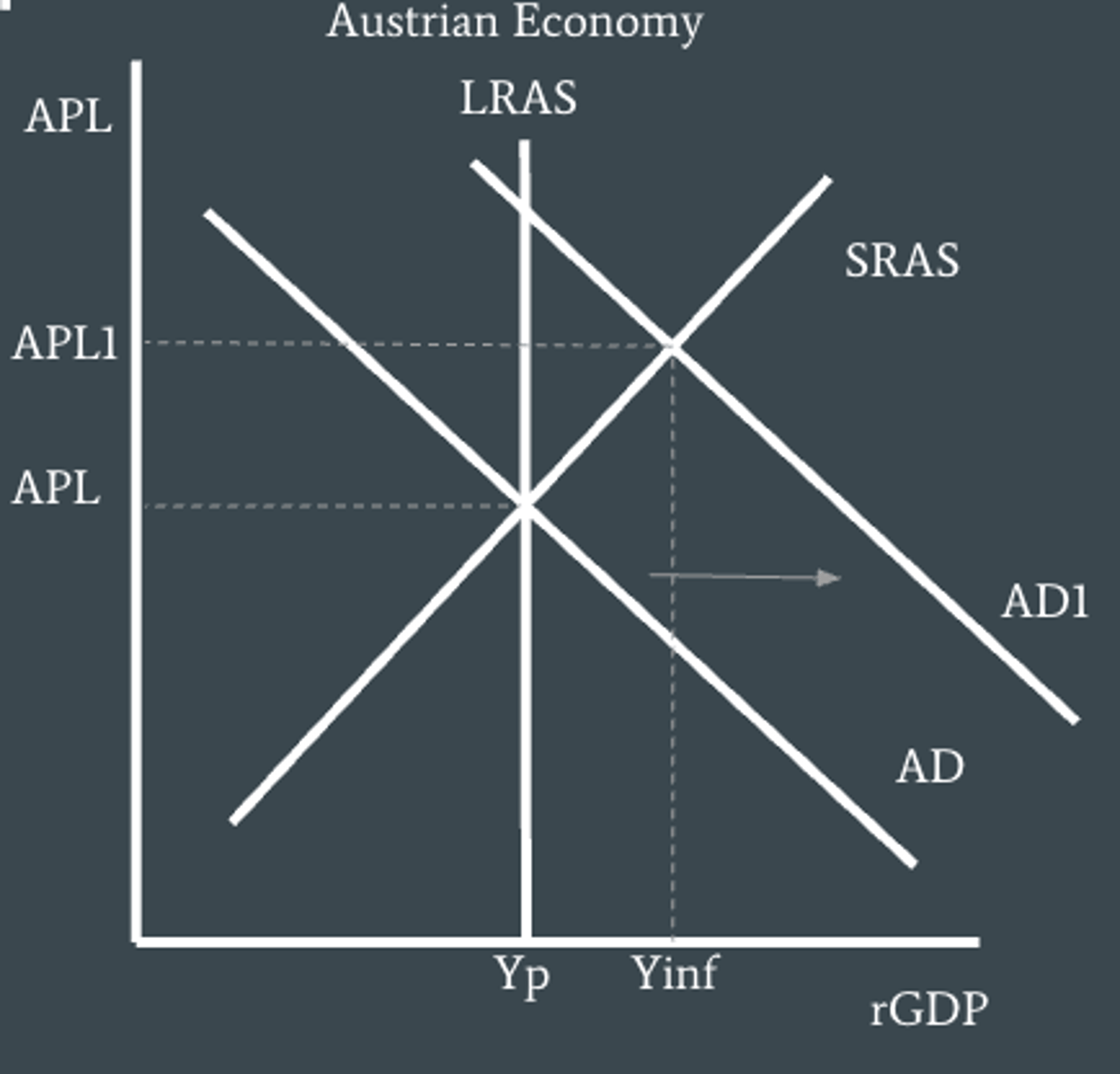
Demand-pull inflation
involves an excess of aggregate demand over aggregate supply at the full employment level of output, and is caused by an increase in aggregate demand. It is shown in the AD/AS model as a rightward shift in the AD curve.
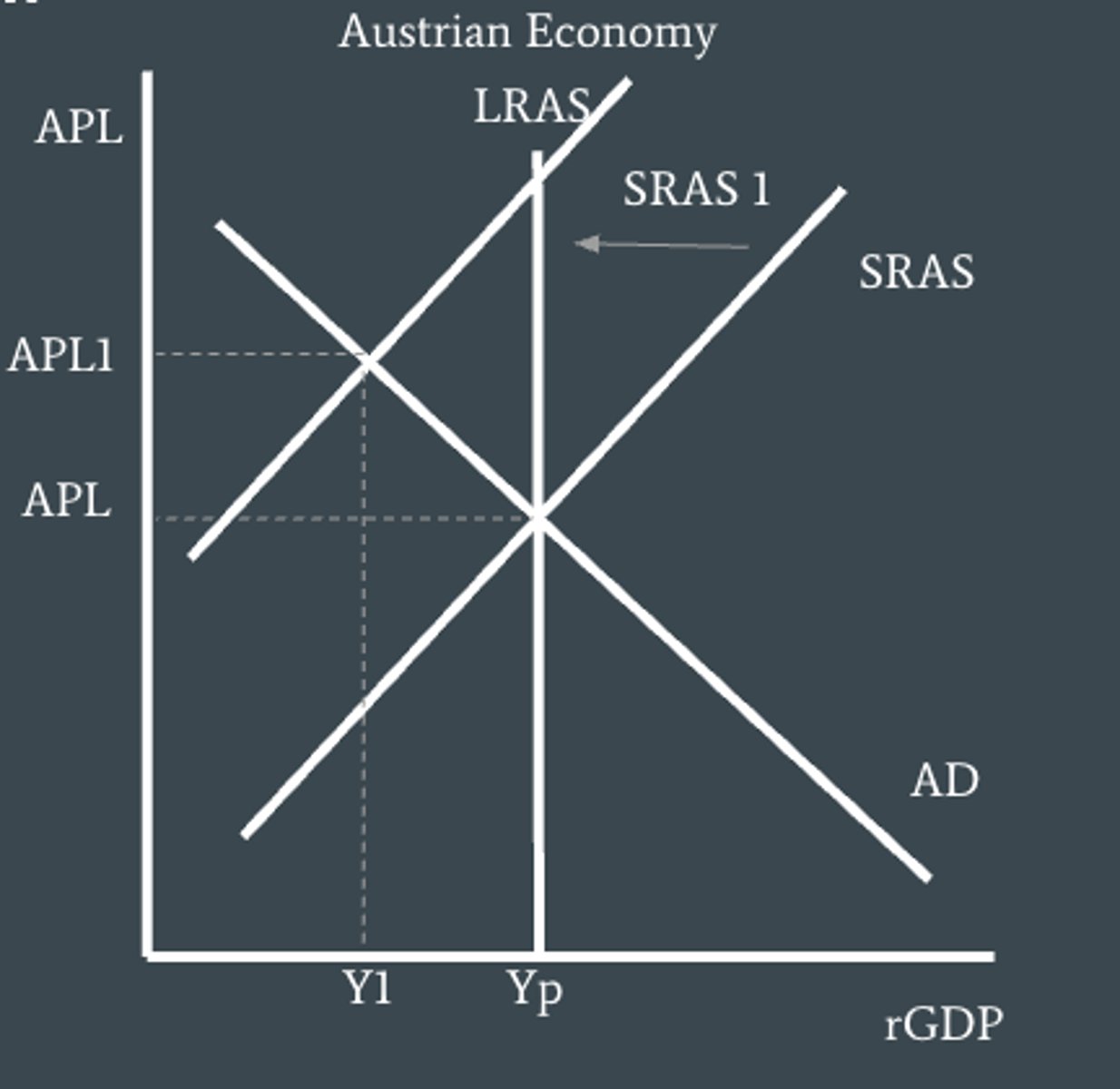
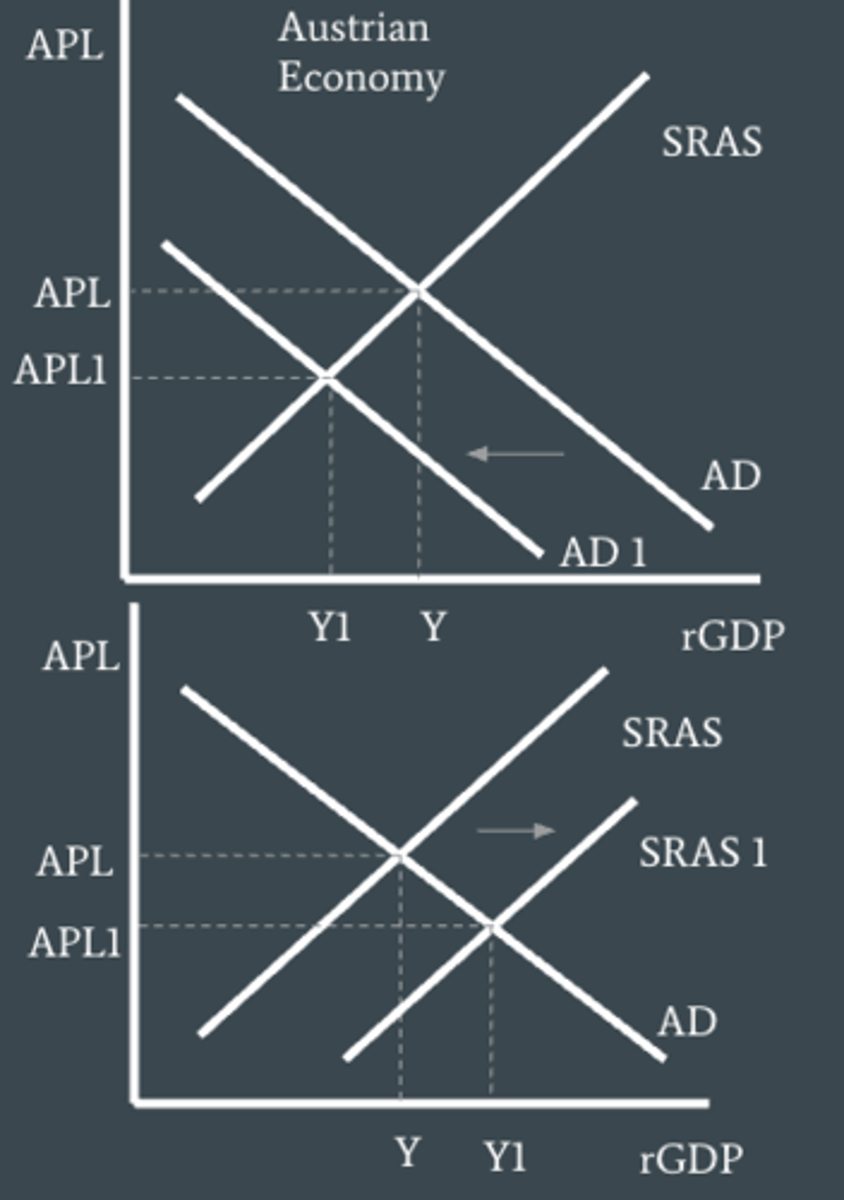
Cost-push inflation
is caused by a fall in aggregate supply, in turn resulting from an increase in wages or prices of other inputs like resource cost, shown in the AD/AS model as a leftward shift in the AS curve.
Als resulting in 'Stagflation'.
What are things that could drive increases in inflation?
- increases in minimum wage
- union organizations for increased wages
What are some consequences of high inflation? (3)
1- changes in buying power
2- retribution effects
3- Uncertainty
Changes in buyer power as a consequence of high inflation
High inflation can reduce household buying power. This can be a result of nominal incomes not rising with the price level. For example if your nominal income increases by 3% but the average price level increases by 5% your real income would fall by 2%
Redistribution effects
inflation redistributes income away from groups in the economy and towards others.
What are some groups that lose out form inflation? (5)
1- People who receive fixed income or wages
2- People who receive incomes or wages that increase less rapidly than the rate of inflation.
3- Holders of cash.
4- Savers
5- Lenders
What are some groups that gain from inflation? (3)
1- Borrowers
2- Payers of fixed incomes or wages
3- Payers of incomes or wages that increase less rapidly than the rate of inflation
Uncertainty as a consequence of high inflation
Uncertainty for stakeholders and allow them to change their behavior
In what ways could stakeholders change their behaviour due to uncertainty? (4)
1- Effect on saving - if savers are worried about the value of their savings falling they will be more inclined to spend it.
2- Export competitiveness - If an exporters prices look comparatively higher than its competitors exports could fall.
3- Effects on economic growth - see the point above - and in addition to this less savings could mean less money to loan out for investment.
4- Social and personal costs that are unequally distributed - those of lower incomes (on fixed incomes) are likely to suffer more than higher income households.
What are some causes of deflation? (2)
Deflation is more rare in the real world than inflation some reason for it to occur:
1- Wages of workers do not normally fall.
2- Large oligopolistic firms may fear price wars.
Oligopolistic firms
a few big firms that dominate the industry
When does deflation typically occur?
Typically when deflation occurs it is for a short period of time and if it does occur for longer periods of time it is arguably more feared than inflation.
What are some consequences of deflation? (4)
1- Redistribution effects
2- Increase in the real value of debt
3- Uncertainty/deferred consumption
4- Policy ineffectiveness
Redistribution effects as a consequence of deflation
Those on fixed income, holders of cash, and savers gain as the real value of their incomes/holdings increases. However, borrowers and payers of fixed income lose out as the value of the money they pay out increases.
Increase in the real value of debt as a consequence of deflation
If you owe money the real value of money that you owe increases.
Uncertainty/deferred consumption as a consequence of deflation
Since firms cannot easily forecast their cost/revenues it makes it difficult for them to feel confident to invest. Consumers will also put off spending as they see prices falling. This will lead to falling AD and an increase in cyclical unemployment.
Policy ineffectiveness as a consequence of deflation
When households expectations of falling prices becomes established it can be difficult for them to change their mindset. This means that policies like expansionary monetary policy might be less effective than without this mindset.