1P - Biomechanics
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Braces setup
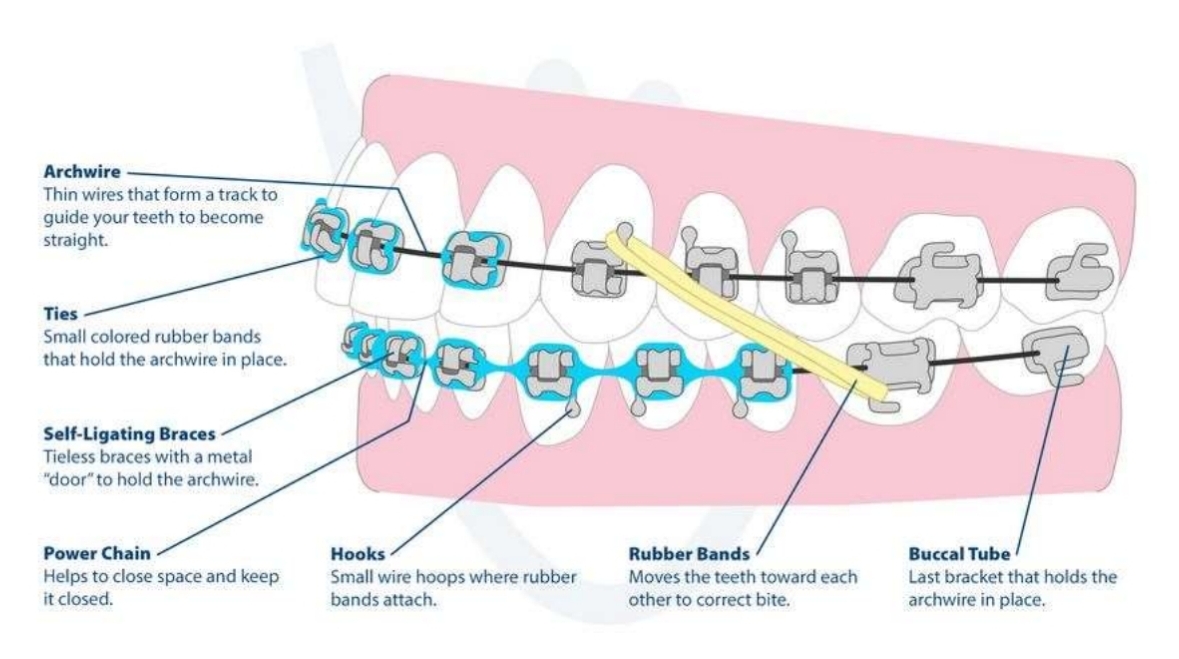
What is the first stage of braces?
Align and level crowns:
Crowns movement only
Round archwire
What archwires are used in the 1st stage (and diameters)
Round:
012 Niti
014 Niti
018 Niti/SS
What is the 2nd stage of braces?
Root control (and close/open space)
Rectangular archwire
What archwires are used in the 2nd stage (and dimensions)
Rectangular:
16×22 Niti/SS
17×25 Niti/SS
19×25 Niti/SS
What is biomechanics and why they are used in orthodontics?
Research and analysis of mechanical properties of living tissues and non-living objects that affect them.
Used to determine effect of orthodontic appliances on oral tissues
What are the living and non living components of biomechanics?
Non-living - Newtonian mechanical principles
Living - Biology of the tooth movement
What are the optimum forces for each type of tooth movement (forces in gm)
Tipping 35-60
Bodily movement (translation) 70-120
Root uprighting (torque) 50-100
Rotation 35-60
Extrusion 35-60
Intrusion 10-20
What can happen without proper biomechanical understanding?
Inefficient tooth movement, root resorption, bone loss, unwanted tooth movement
What force property determines whether tipping or translation?
Point of application
What are the 4 properties of a force required to move a tooth predictably?
Magnitude
Direction
Point of application
Line of action of force
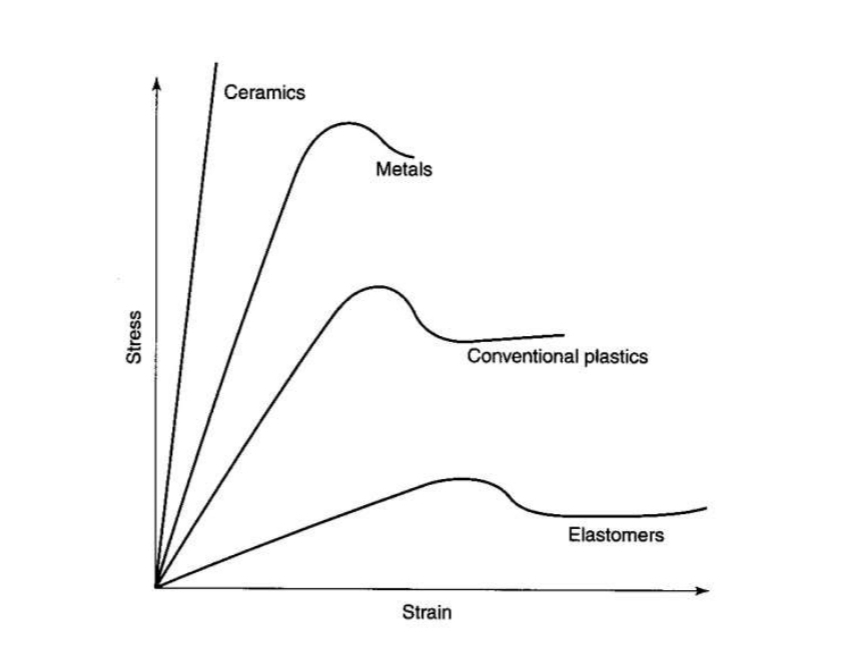
Basic properties of materials (elastic and plastic)
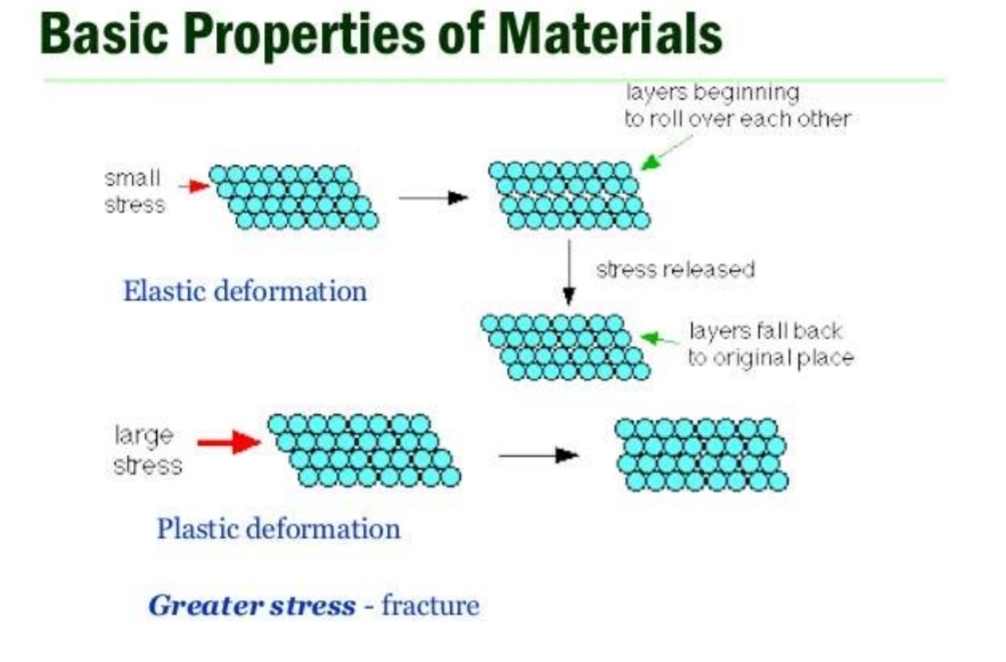
What is elastic behaviour defined by?
Strain and stress response to load:
Stress - Internal distribution of load
Strain - Internal distortion produced by load
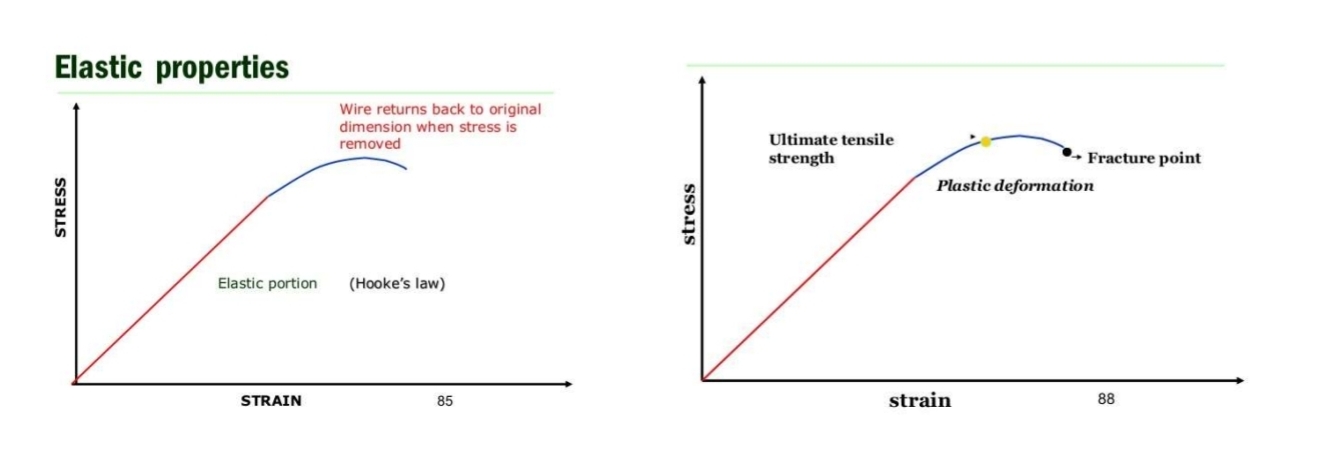
What is the proportional limit?
Point at which permanent deformation is first observed
Strain and stress directly proportional till that point
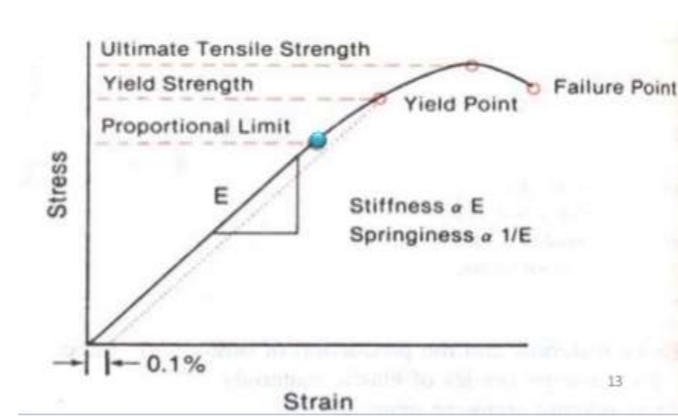
What is yield strength?
Point at which there is deformation of 0.1%
Wire wont return to original state after this
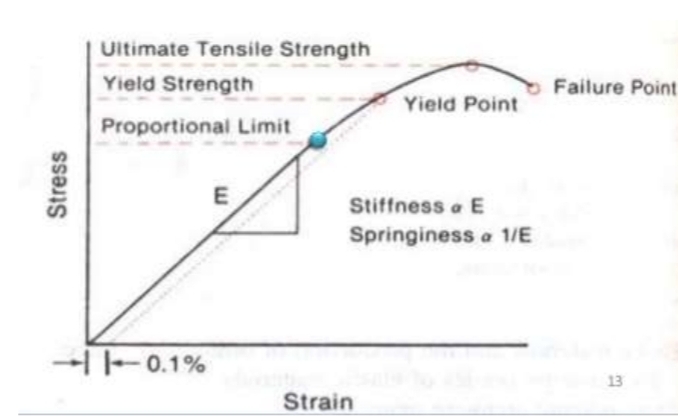
What is meant by ultimate tensile strength?
The maximum load a wire can sustain
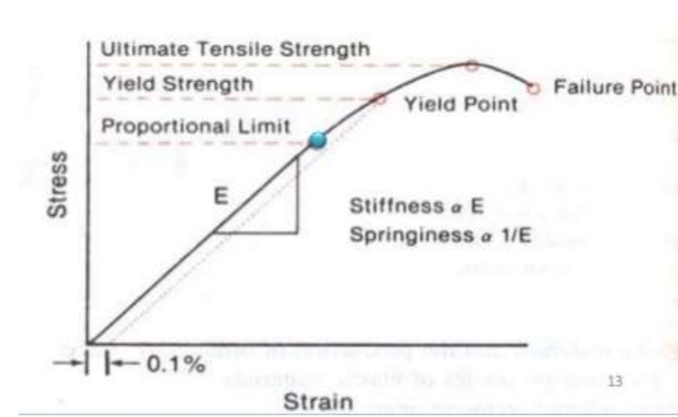
What is the failure point?
The point at which the wire breaks
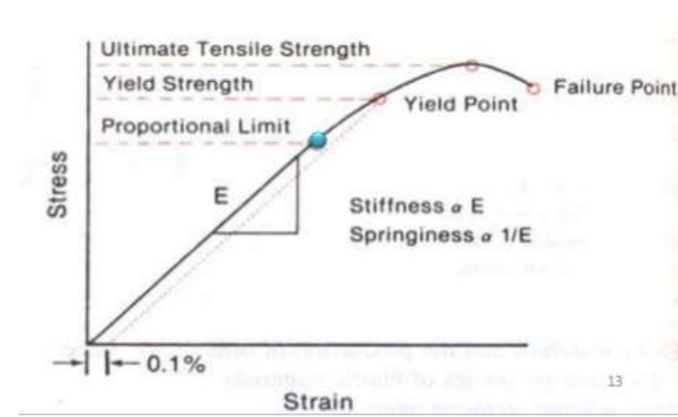
What is the modulus of elasticity?
Ratio between unit stress and strain
Measured by slope of elastic region
Describes relative stiffness/ridgitity of the material
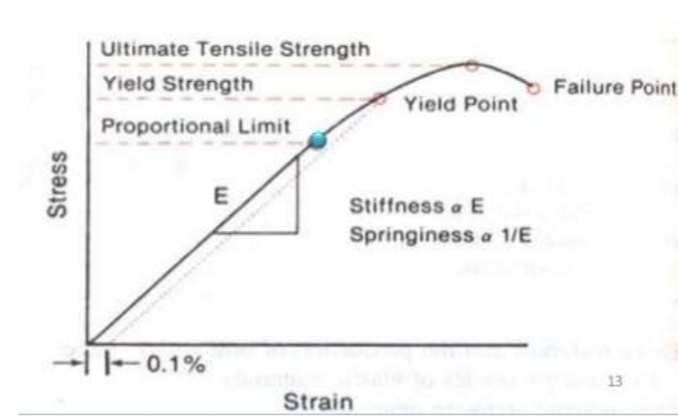
What is meant by stiffness
Proportional to the slope of linear (elastic) portion of the curve. The more vertical the slope, the stiffer the wire
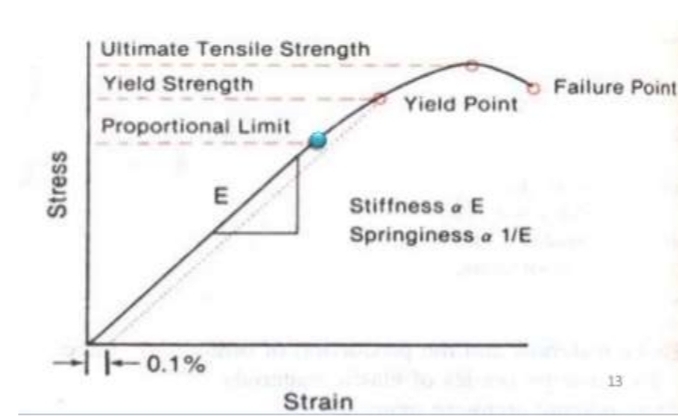
What is meant by range?
Distance the wire will bend elastically before permanent deformation occurs
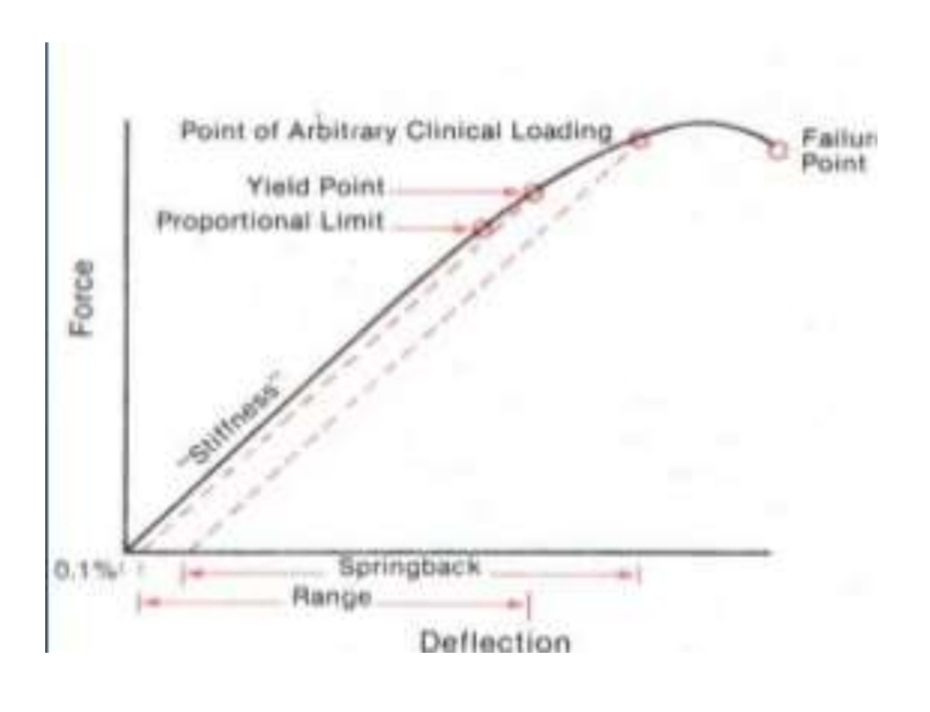
What is meant by springback?
Ability to undergo large deflections without permanent deformation
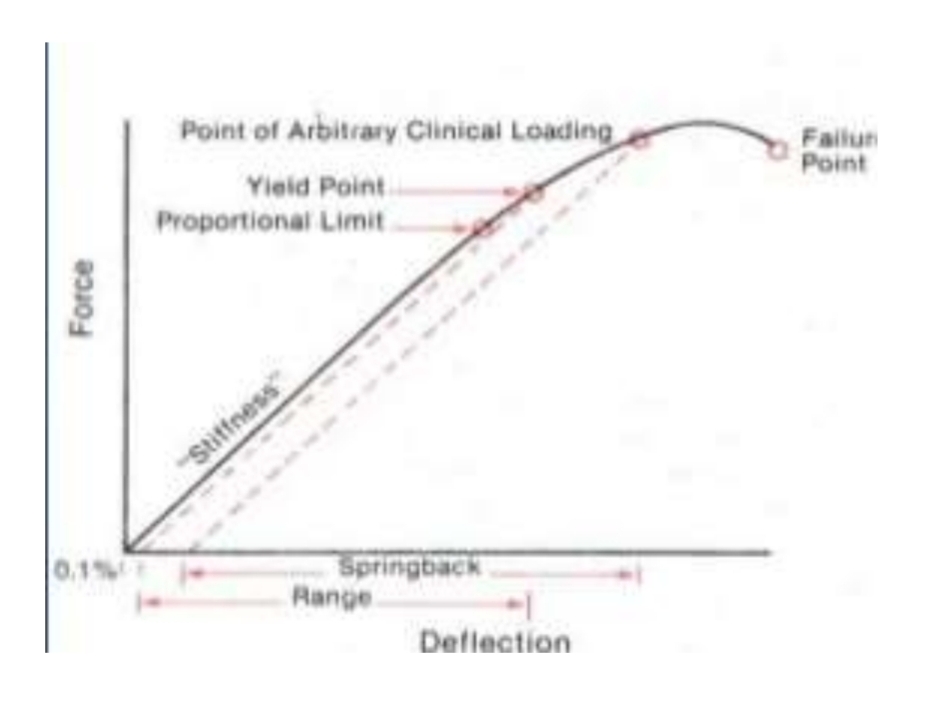
What is meant by resilience
Energy storage capacity of wire
Area under stress-strain curve, up to proportional limit
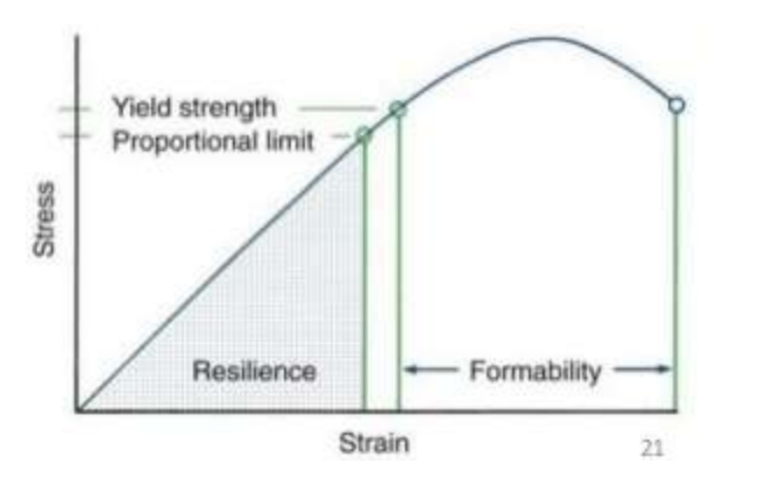
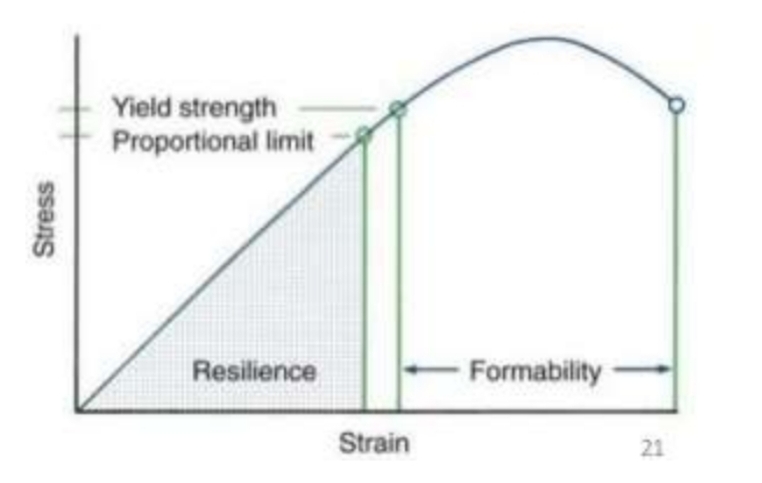
What is meant by formability?
Amount of permanent bending wire can take before it breaks or fails.
Area under curve from yeild point to failure point
What is meant by flexibility?
A flexible material can undergo a large deformation / strain with minimal force, withn its elastic limit
Maximum flexibility = Proportional limit/modulus of elasticity
Toughness
Force required to fracture a material
Total area under stress-strain graph
Brittleness
Opposite of toughness
Brittle material cant undergo plastic deformation
Fatigue
Repeated cyclic stress of a magnitude below fracture point of wire can result in fracture.
What are the Ideal requirements of orthodontic wires?
High strength, range, formability
Low stiffness
Solderable and weldable for hook or stop attachment
Reasonable cost
Stainless steel archwire properties
Low cost
Excellent formability
Good mechanical properties
Solderable and weldable
Is used for closing gaps
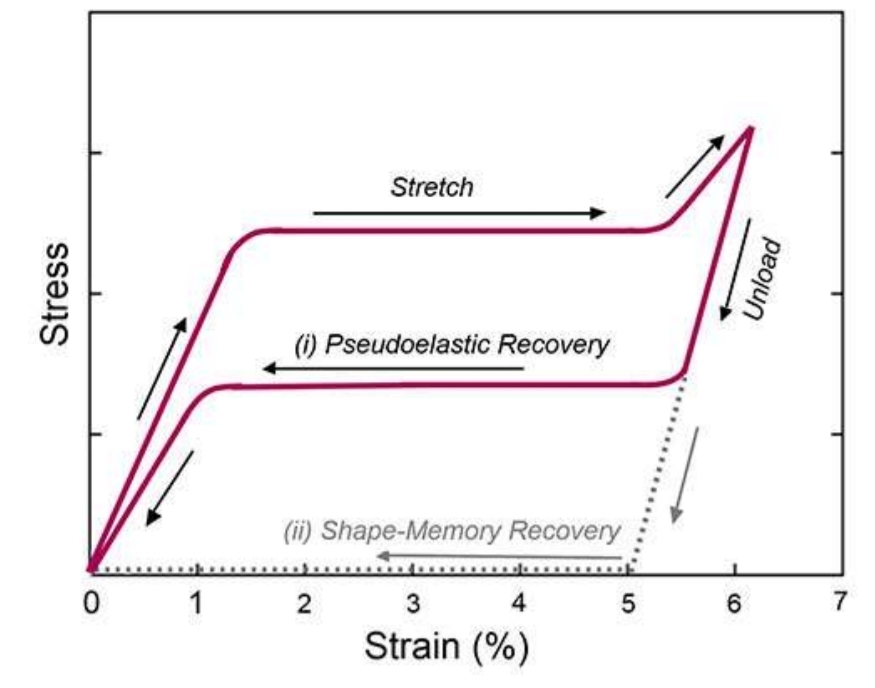
NiTi properties
Can apply light force over large range of activations
Ideal for inital orthodontic alignment
Shape memory
Superelasticity
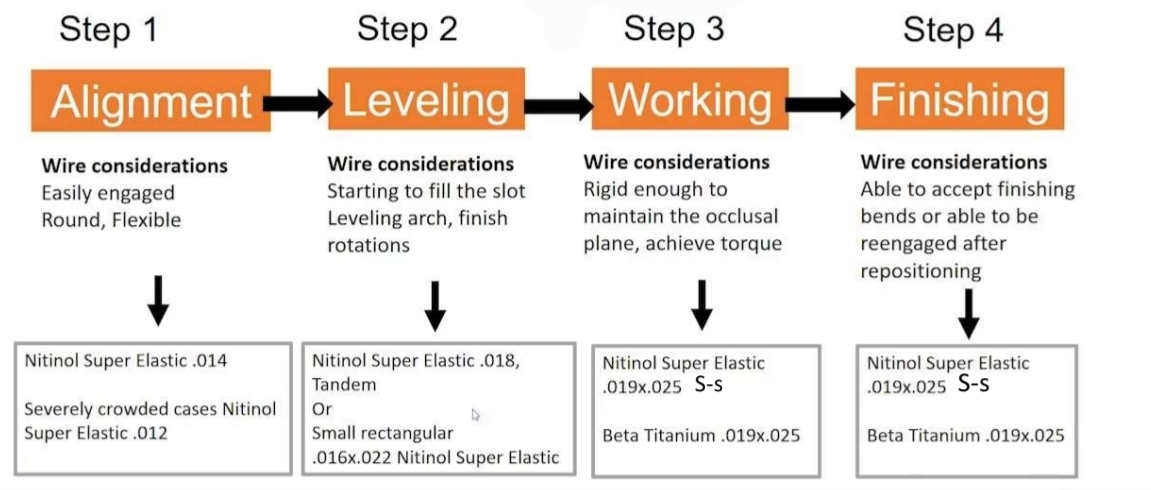
What are the 4 stages of wire progression, and the respective wire considerations?
Alignment - Easily engaged, round, flexible
Leveling - Starting to fill slot, leveling arch, filish rotations
Working - Rigid enough to maintain occlusal plane, achieve torque
Finishing - Able to accept finishing bends or be reengaged after repositioning
4 different shapes of archwire?
Round
Square
Rectangular - 19×25 fully fills slot, so is used for final wire
Multistranded
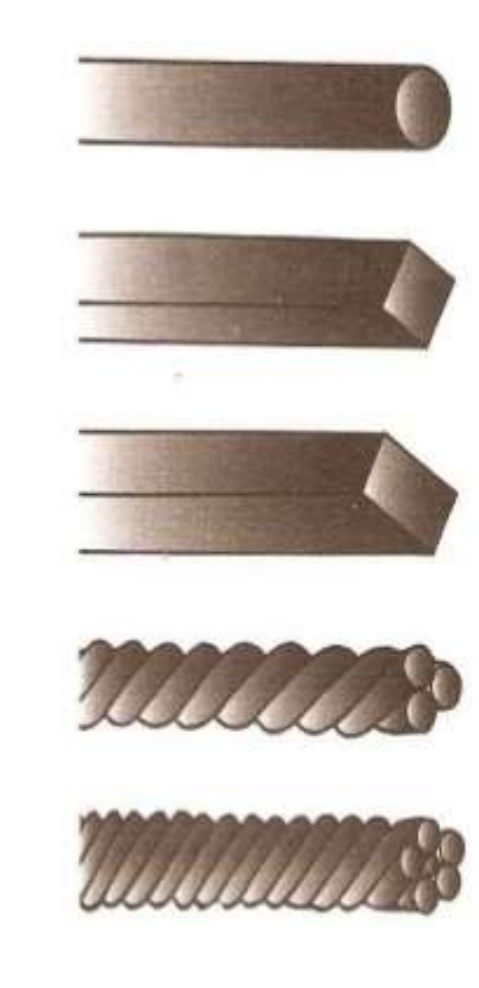

What unit is wire size specified in?
Thousandth of an inch. Example - .016 inch
Why is anchorage important?
Whenever tooth movement is attempted, there will be an equal and opposite reaction to force applied by components. (Forces also applied to anchoring teeth, may cause unwanted movement)
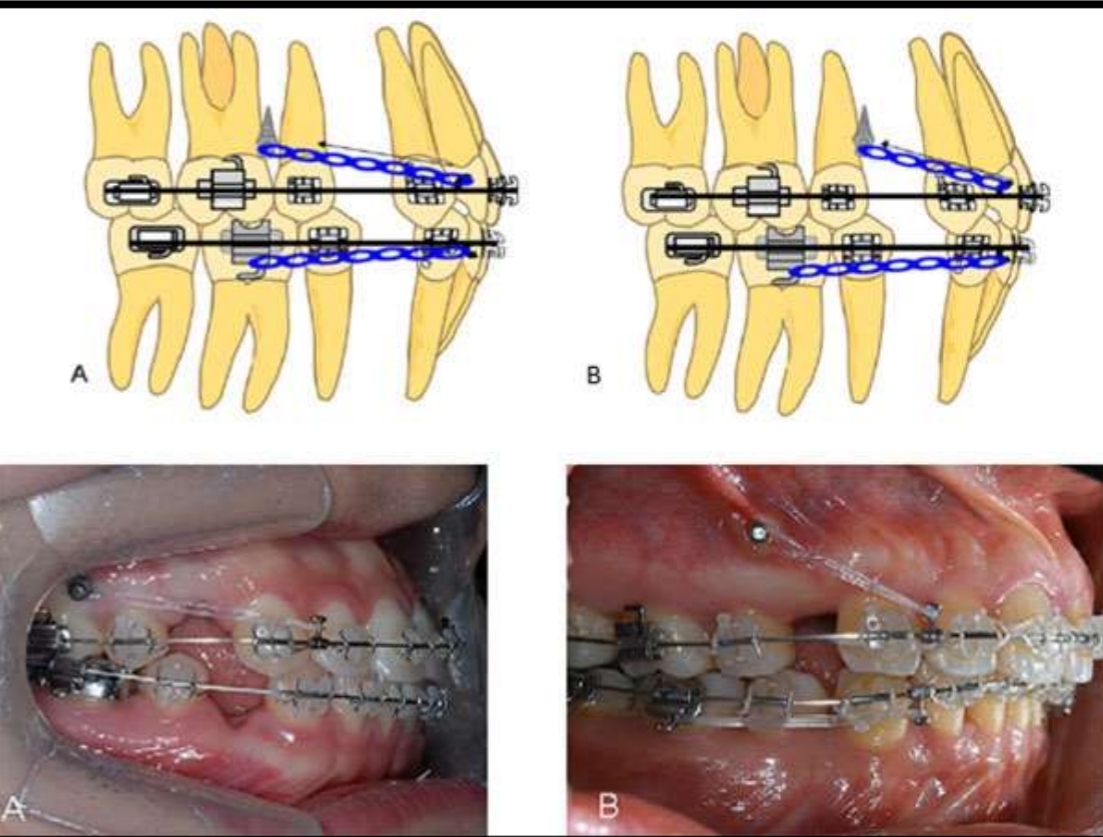
What are the 3 types of Intra-oral anchorage?
Simple - Active movement of one tooth versus several anchor teeth
Compound - Teeth of greater resistance as anchorage for the translation of teeth with less resistance
Reciprocal - Two groups of teeth pitted against each other, causing equal reiprocal movement of both
What are the two types of intermaxilar anchorage?
Extraoral anchorage (headgear)
Skeletic anchorage (microimplants)
What are the 4 fundamental concepts of tooth movement control?
Force
Center of resistance
Moment
Force systems
Force
Push/pull applied to tooth
Has magnitude, direction and point of application
What is the Centre of resistance (CR)?
Point at which a force can cause bodily movement (translation) of the tooth, without tipping or rotation. A movement of pure translation (md/vb/intr/extr). Gravity centre of tooth
Single root - ½ to 1/3 of length of (clinical) root
Multiradicular - 1 to 2 mm apical of furcation
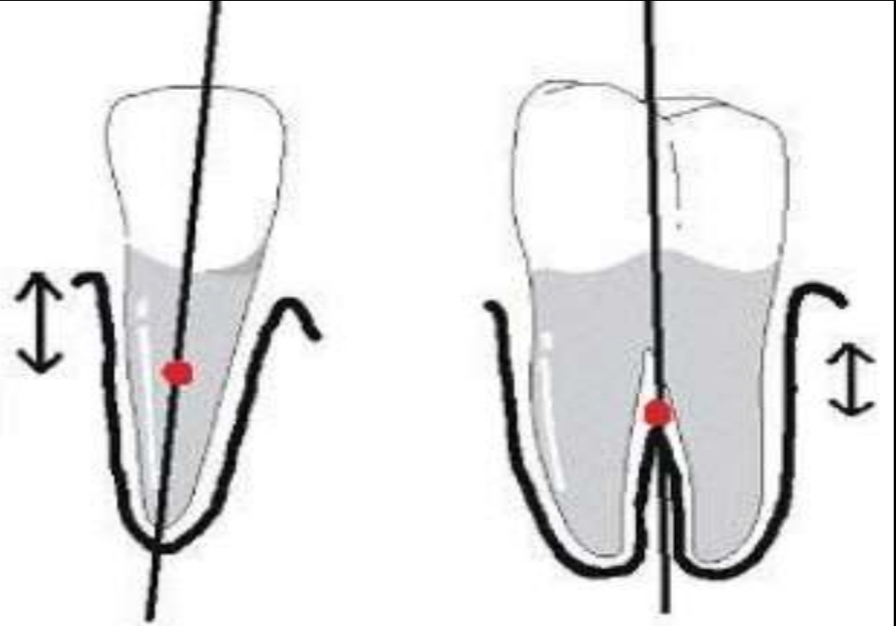
What does the location of the centre of resistance depend on?
Alveolar bone height and root length. Uses clinical root. Alveolar bone loss - shortened root.
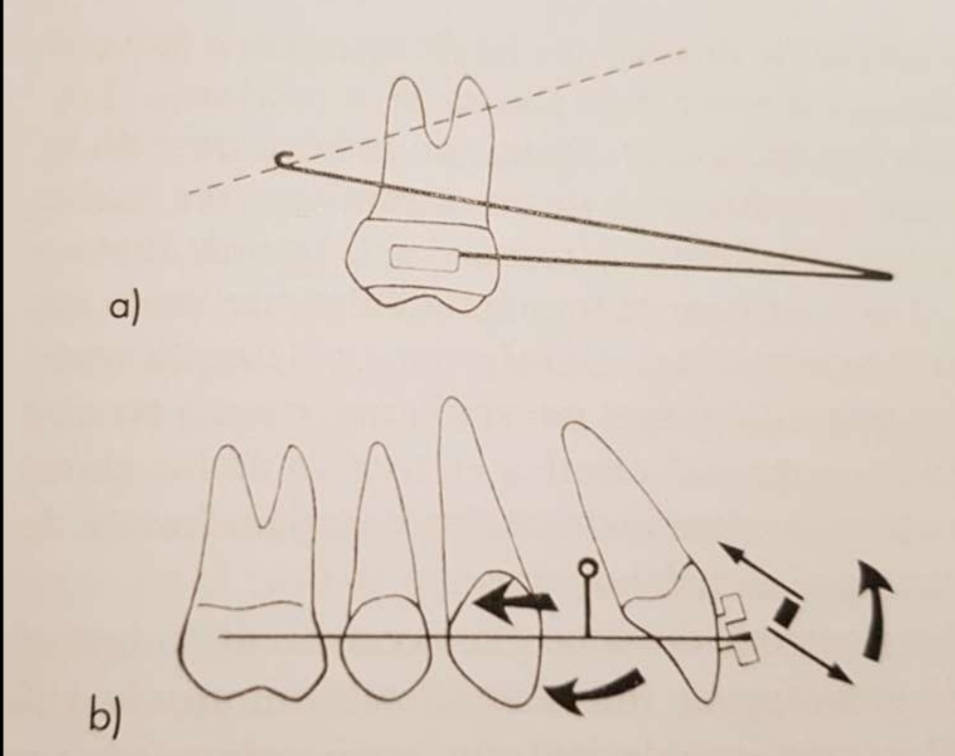
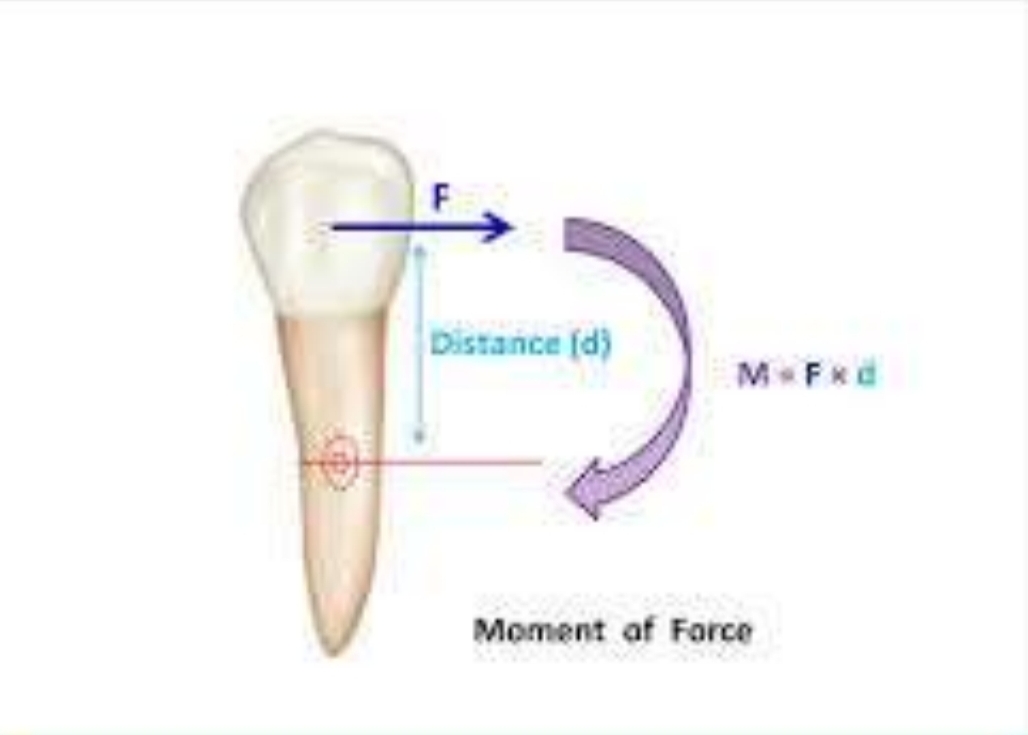
What is the Moment of a force?
Measure of a forces capacity to produce rotation. Vector with direction and magnitude.
Moment = force x perpendicular distance from CR
Important for controling rotation, torque, tipping
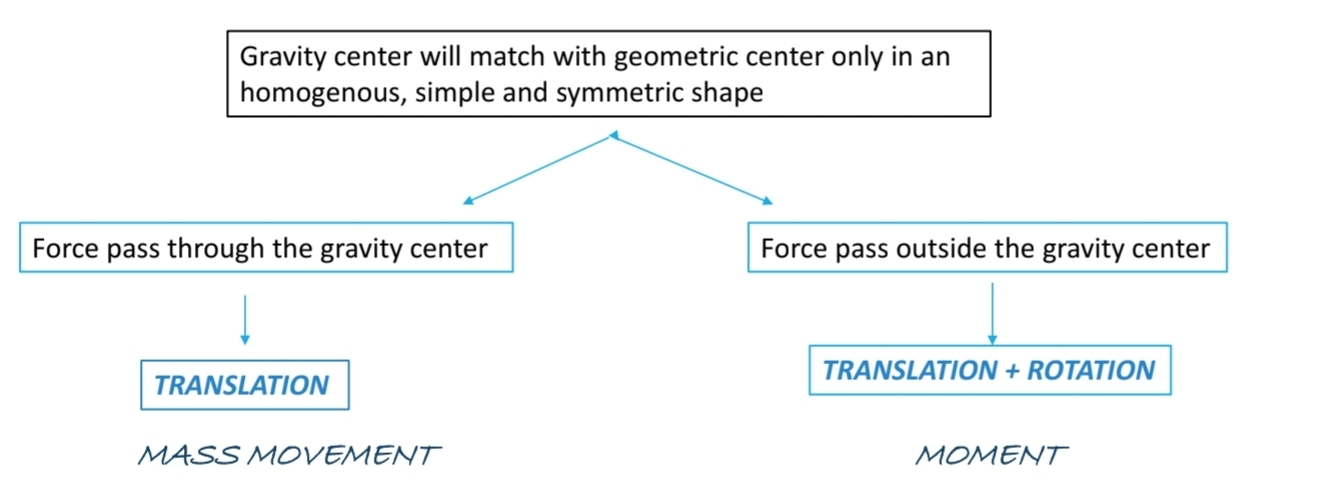
What happens when a force passes outside the gravity centre?
Translation + rotation
(Moment)
What are the 3 Force systems?
Single force - tipping
Force + couple - translation without tipping
Couple of forces - Two equal and opposite forces separated by a distance - pure rotation. Form of moment
What does the effect of a force applied on a body depend on?
Relation between the force’s Line of action and gravity centre of the body:
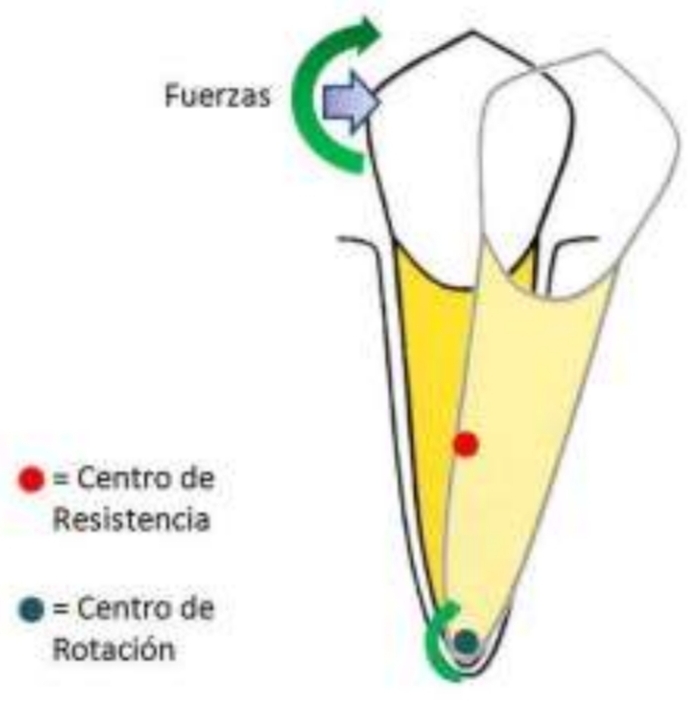
What is meant by centre of rotation?
Fixed point around which body appears to be rotated
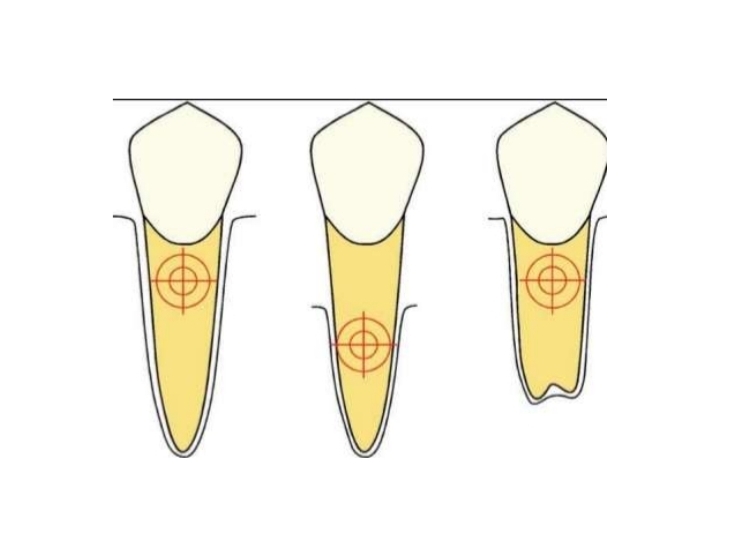
What are the 6 types of tooth movement and their force requirements?
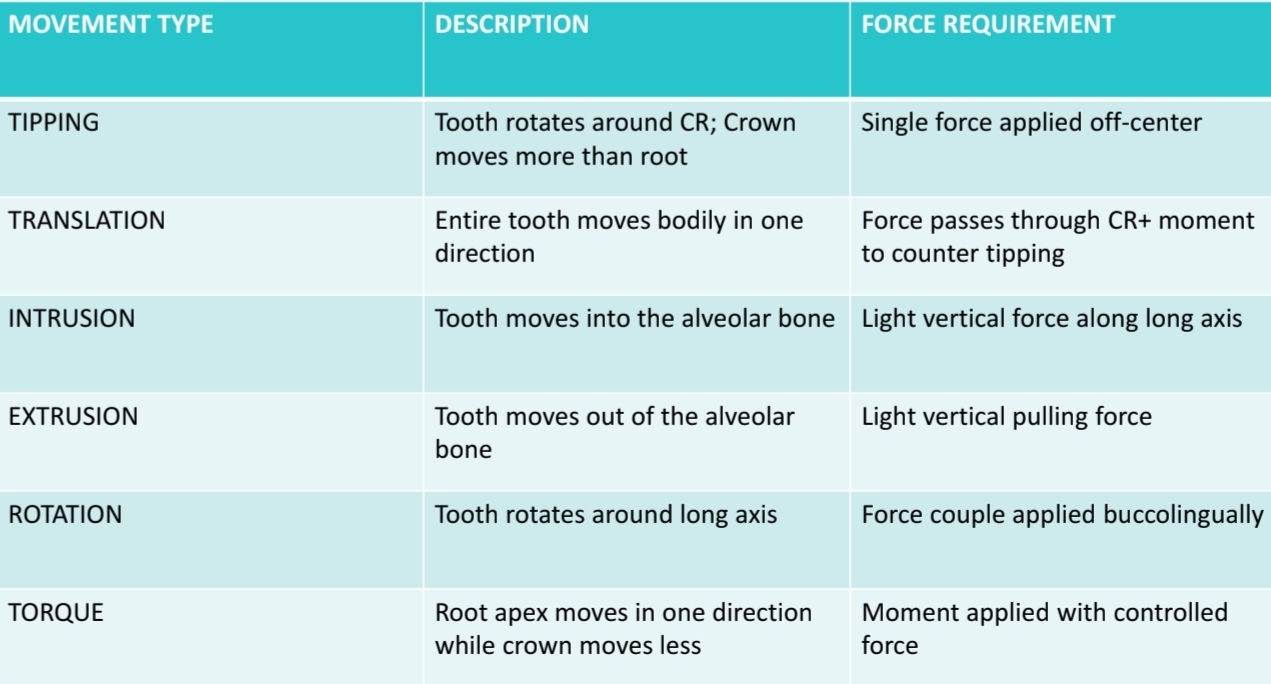
What is uncontrolled tipping?
Apex moves in opposite direction to crown

What is controlled tipping?
All parts of tooth move in same direction, but different distances.
Centre of rotation at apex.
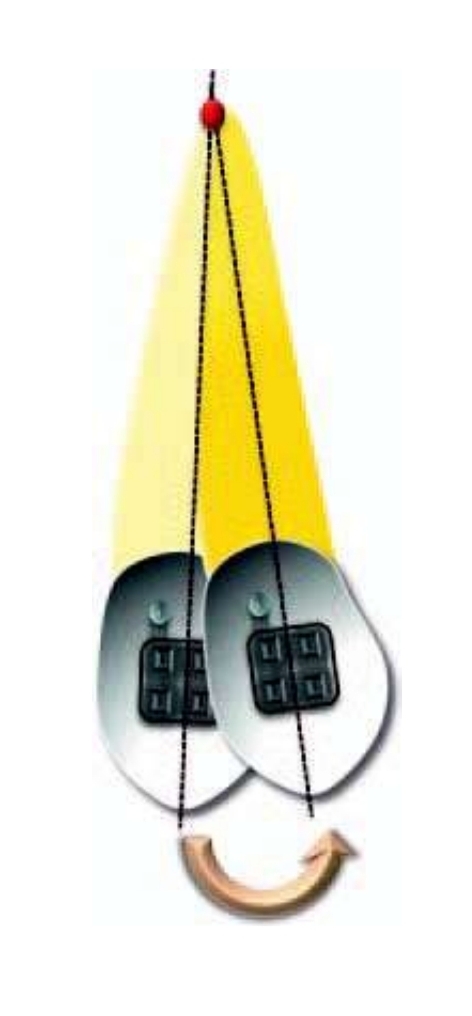

What is Torquing (root movement)?
All movement is in apex (and root)
Centre of rotation at crown tip
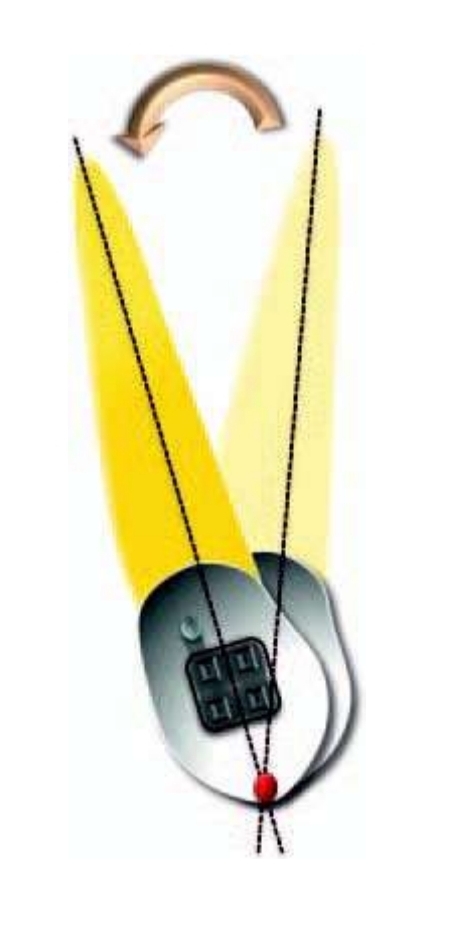

What is translation (bodily movement)?
Crown + root move same distance and direction with no rotation.
Centre of rotation is nonexistent/infinity
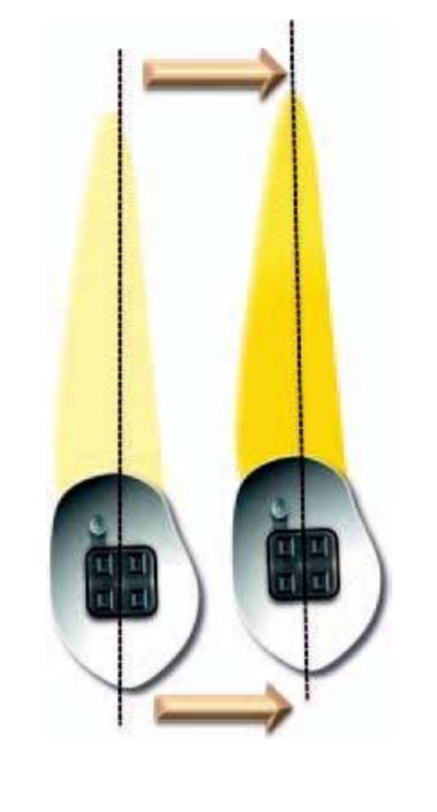

How can you acheive a mass movement of a tooth/teeth?
The force applied must pass through CR.
A) The only linear force, pass through CR
B) The sum of all forces applied pass through CR