(20): island biogeography
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
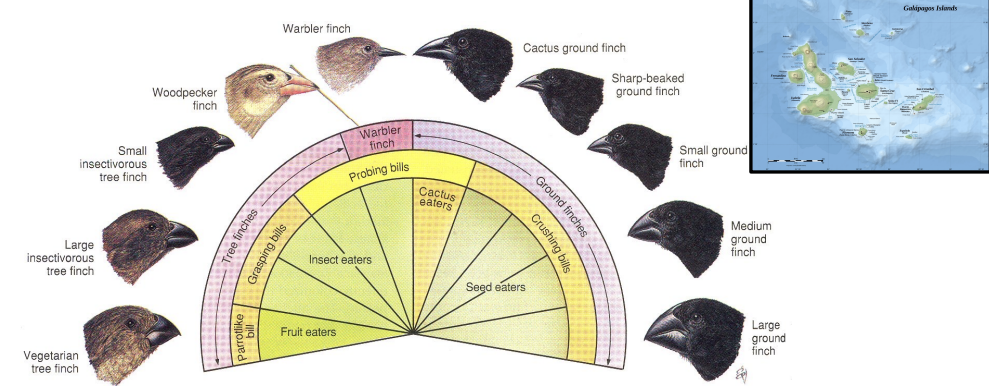
case study #1: darwin’s finches
18 species evolved from one single ancestor around 2-3 million years ago (galapagos)
example of adaptive radiation
beak size and shape evolved for different food sources
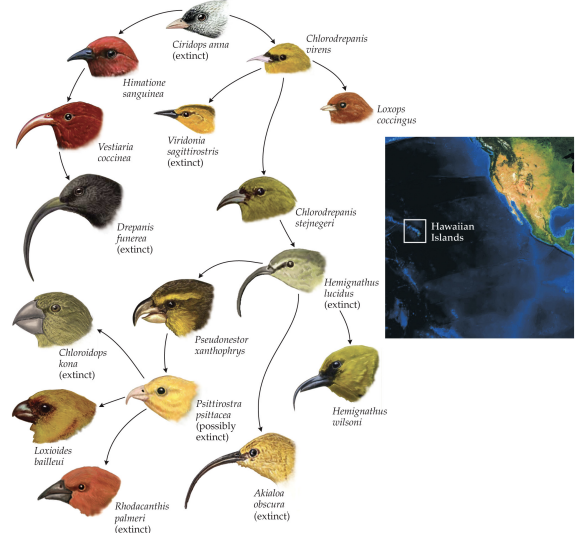
case study #2: honeycreepers and lobeliads
50 species evolved from a single finch ancestor around 5-7 million years ago
is autocatalytic (interactions alone) (coevolution)
parallel and hierarchical evolution across islands

honeycreepers:
50 species, 3,600 km from coast, larger islands in Hawaii, higher elevation, older island (5.1 million)
darwin’s finches
18 species, 950 km from coast, small islands in Isabella (Galapagos), lower elevation, younger island (3.2 million years old)
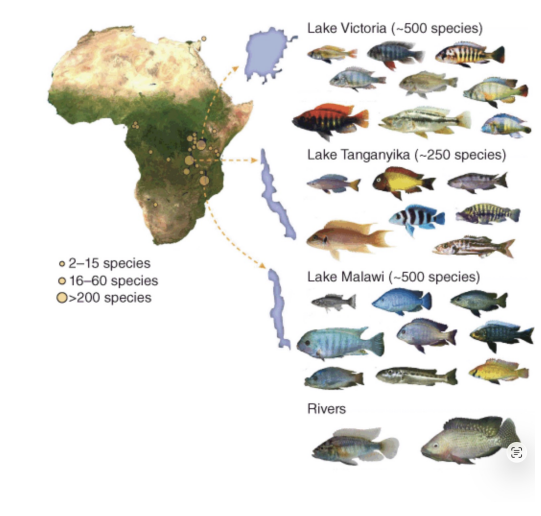
cast study #3: east African cichlids
fish! jaw and teeth adapted for different foods
sexual selection (like peacocks) females choose males based on color
reproductive isolation - speciation
200-300 went extinct with the introduction of the nile perch
case study #4: madagascar
isolation for 90 million years
diversification connected with residence time
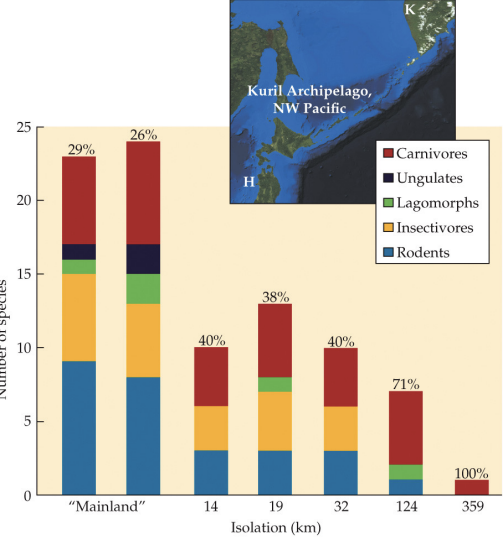
species composition is _____ with the mainlaid
disharmonic
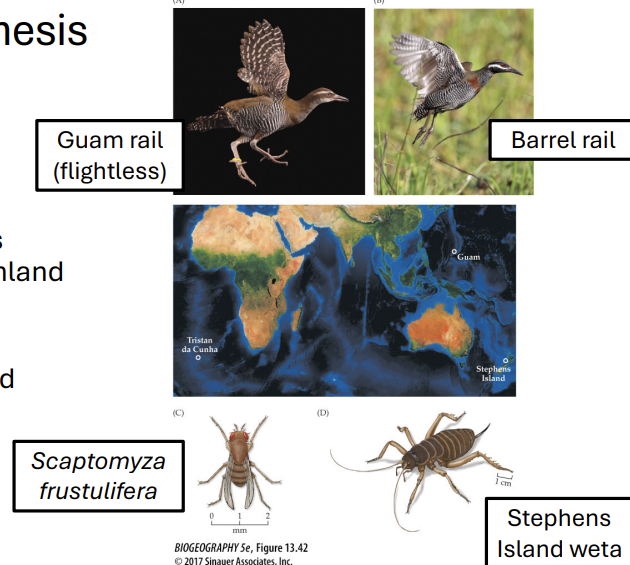
what is island syndrome?
common, yet peculiar features found on island plants and animals
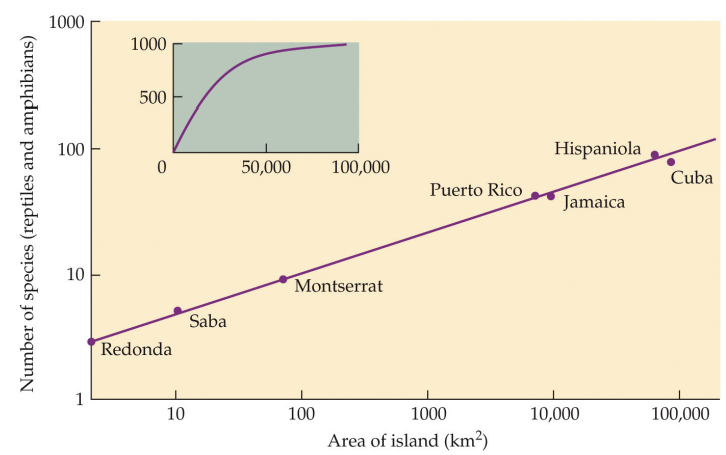
what is an island area?
important for generating habitat diversity
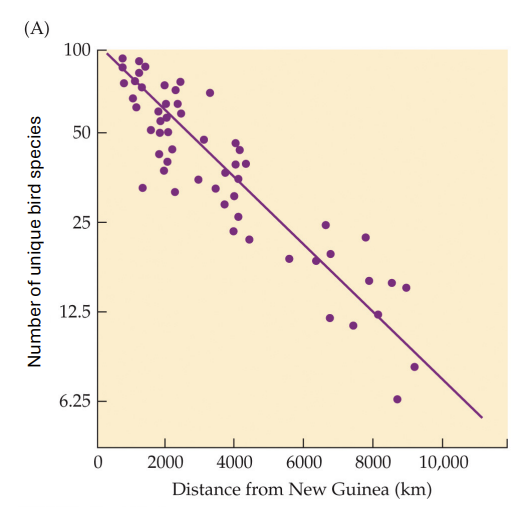
what is island distance?
important for immigration
what is island age?
needed for evolution to play out

what is community assembly?
the non-random accumulation of non-equivalent species
dispersal filter question:
can the species reach the location?
environmental filter question:
can the species tolerate abiotic conditions?
biotic filter question:
can the species coexist with other species?
human activity creates _____?
islands of habitat in a sea of developed land
what does human activity lead to in island conservation?
hostile environments and conservation implications (need natural preserves)
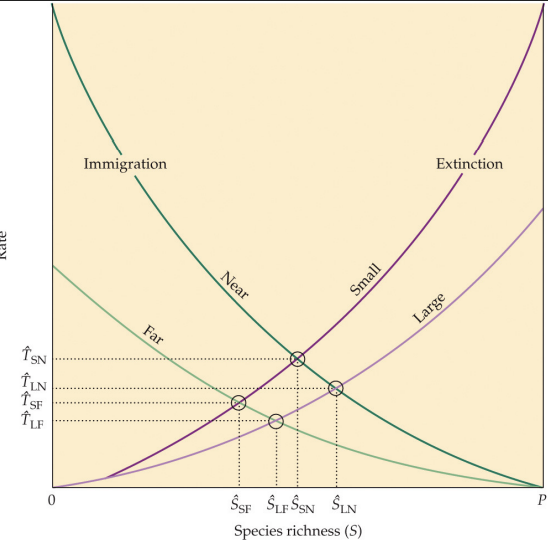
what is the equilibrium theory of island biogeography?
the number of species on an island is determined by a balance between new species arriving (immigration) and existing species dying out (extinction)
near islands have more species than far islands (high immigration)
large islands have more species than small islands (low extinction)

what are two examples of the equilibrium theory?
florida keys - cleared islands of insects using methyl-bromide
krakatoa - volcanic eruptions on small island cleared all plants and animals
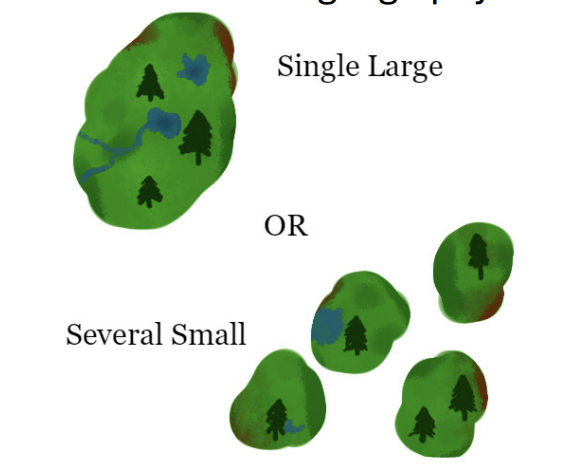
what is SLOSS?
single large of several small (long running debate about the best way to design protected areas)

what is an example of a success story?
gray wolf reintroduction in yellow stone
15 in 1995, 17 in 1996
prey foraging behaviors changed (they ate most of the vegetation)
changed local biodiversity and river patterns

what is an example of a failure story?
invasive and non-native species (cats)

cats:
cats globally contributed to many extinctions of small birds and mammals
one of the world’s worst invasive species
islands are natural ways scientists can understand ____ , ____ , and ______.
evolution, speciation, and biogeographic principles.
what are the 3 key factors determining species richness and diversity?
island area, distance from mainland, and island age
how does dynamic equilibrium impact island communities?
dynamic equilibrium explains how the balance between immigration and extinction determines the number of species on an island.
how do island biogeography theories apply to conservation?
habitat fragmentation (building of roads, farms, cities, etc.) creates “islands” requiring corridors and strategic preserve design
how do invasive species impact islands?
invasive species pose major threats to island ecosystems due to endemic species’ and their lack of evolved defenses