Mineralogy midterm
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
a ≠ b ≠ c
α ≠ β ≠ γ ≠ 90°
nothing is equal
a ≠ b ≠ c;
α = β = γ = 90°
all sides unequal, all angles 90
all sides equal
no equal angles
a = b ≠ c
α = β = γ = 90°
rectangle sides, square tops
everything equal
cube
a≠b≠c
α=γ=90°
β≠90°
no sides equal, two right angles
minerals with a different structure but the same composition
-reconstructve
-displasive
-order
-polytypism
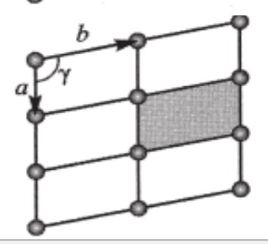
plane lattice
a=b
Y= 90
square
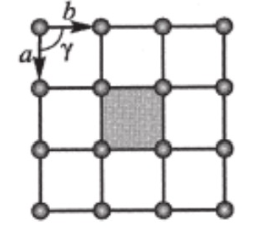
plane lattice
a≠b
Υ=90
rectangle p
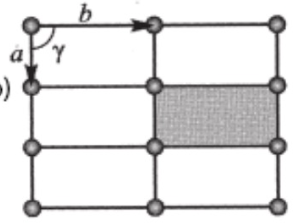
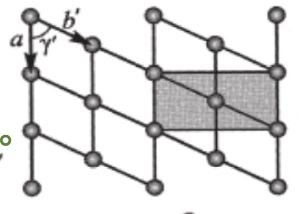
a≠b’ & a≠b
cos(y’)=a/2b & Y=90
rectangle p
a=b & Y=120
hexagonal
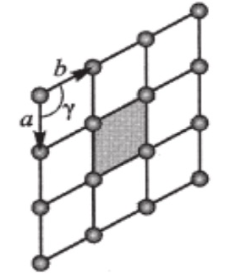
a≠b & Y≠90
oblique
reconstructive polymorphism
major reorganization of the crystal structure- chemical bonds are broken and new bonds are formed
displasive polymorphism
distortion or bending of bond angles-small amount of energy is used, and the reaction is immediate and reversible
order polymorphism
structure remains the same, but cation distribution changes
polytypism
polymorphs differing in stacking of identical sheets or layers
solid solution
mineral structure where specific sites are occupied in variable proportions by two or more different chemical elements because of changing local condition
simple substitution solid solution
substituting cations with same charges
coupled solid solution
substitution where the charge balance is maintained
isodesmic
same strength
mesodesmic
half strength of anion
anisodesmic
different strengths