BIOL2200: Lab Final Exam - Week 13 ALL Lab Slides
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What is the purpose of measuring the zone of inhibition?
To assess how effective an antimicrobial agent is by measuring the diameter of the area where bacterial growth is inhibited
How do you measure the zone of inhibition?
Measure across the center of the clear zone edge to edge, including the disk. If irregular, measure several axes and average
What zone size indicates resistance vs. susceptibility in antiseptic/disinfectant testing?
<10 mm = Resistant (R)
>10 mm = Susceptible (S)
What is a mold?
A multicellular fungus made of hyphae → mycelium
How do molds reproduce asexually?
By producing asexual spores via mitosis; spores are genetically identical and germinate into new colonies.
What are the names of the 3 FUNGI?
Aspergillus (mold)
Penicillium (mold)
Rhizopus (black bread mold)
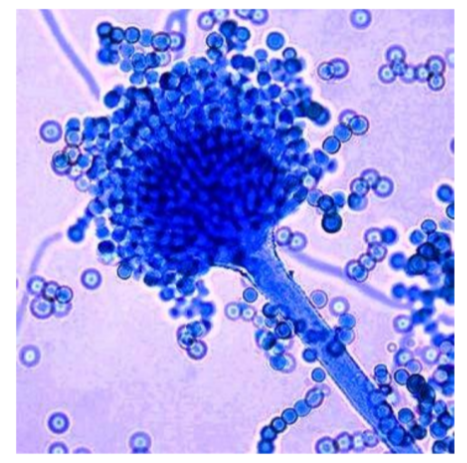
What is the genus name of this organism + and its asexual spore structure?
Aspergillus (mold)
Spore structure: Conidiospores (conidia) — not enclosed in a sac.
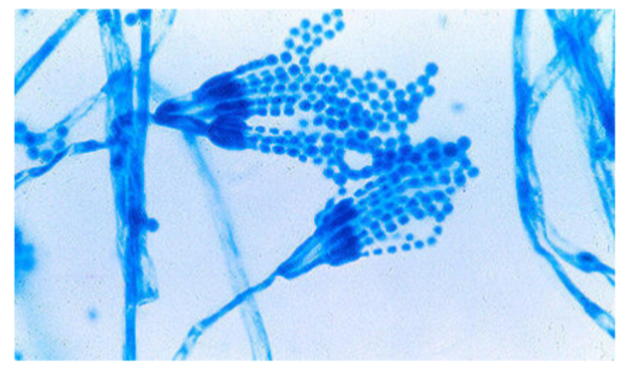
What is the genus name of this organism + and its asexual spore structure?
Penicillium (mold)
Spore structure: Conidiospores (conidia) — spores produced at tips/sides of hyphae, not enclosed in a sac.

What is the genus name of this organism + its asexual spore structure?
Rhizopus (black bread mold)
Spore structure: Sporangiospores — spores enclosed inside a sporangium (sac).
What is the names of the 9 Protozoa Organisms?
Balantidium coli
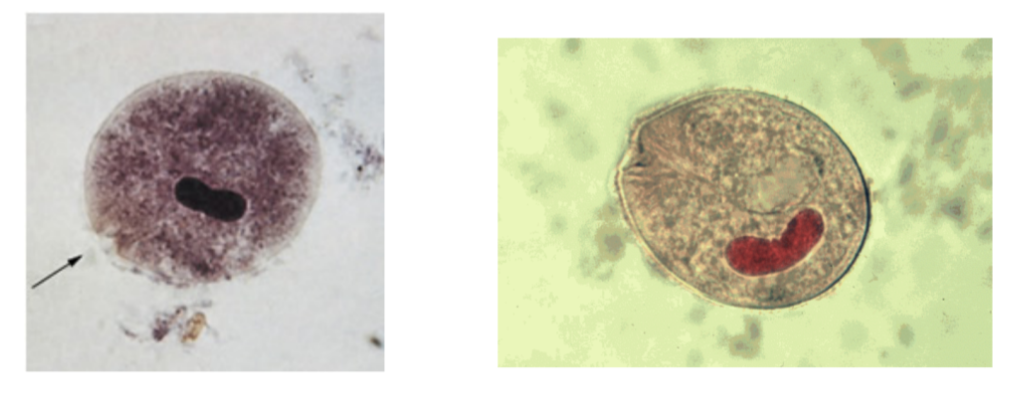
What is the name of this organism?
Balantidium coli
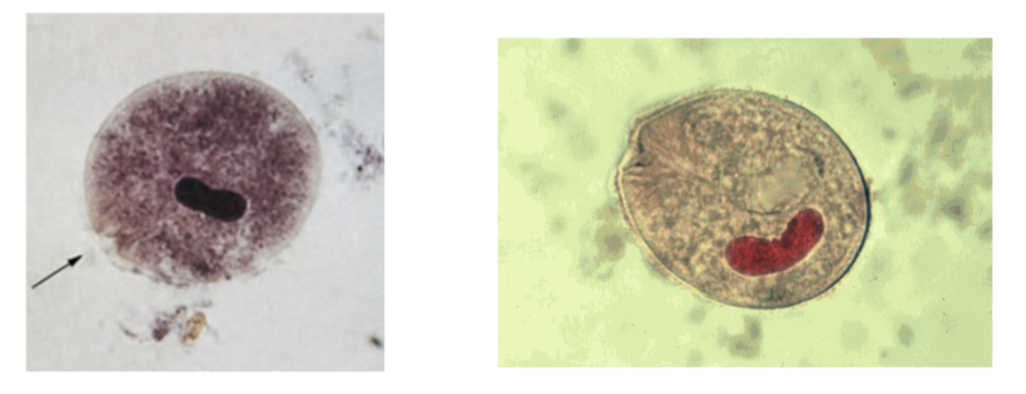
Balantidium coli —
What phylum does it belong to?
What is it’s method of motility?
What disease does it cause?
Phylum: Ciliata
Method of Motility: Cilia
Cysts ingested from contaminated food/water → DIARRHEA
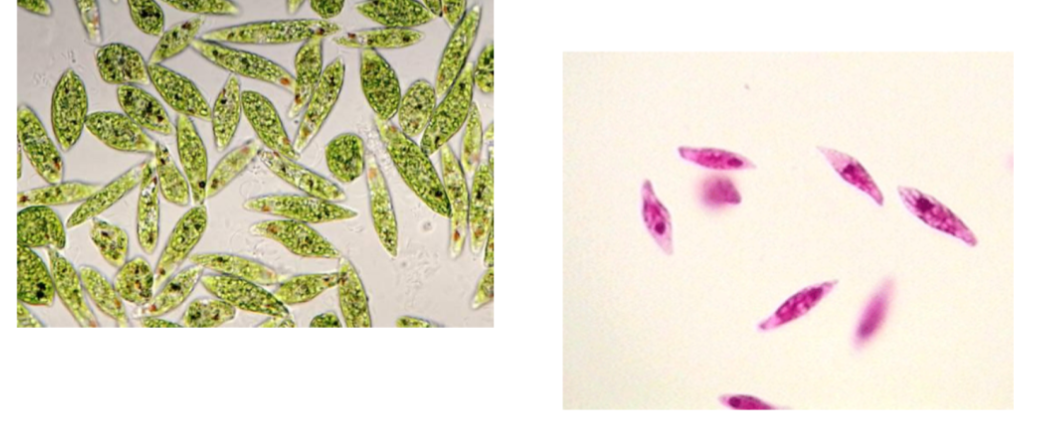
What is the name of this organism?
Euglena
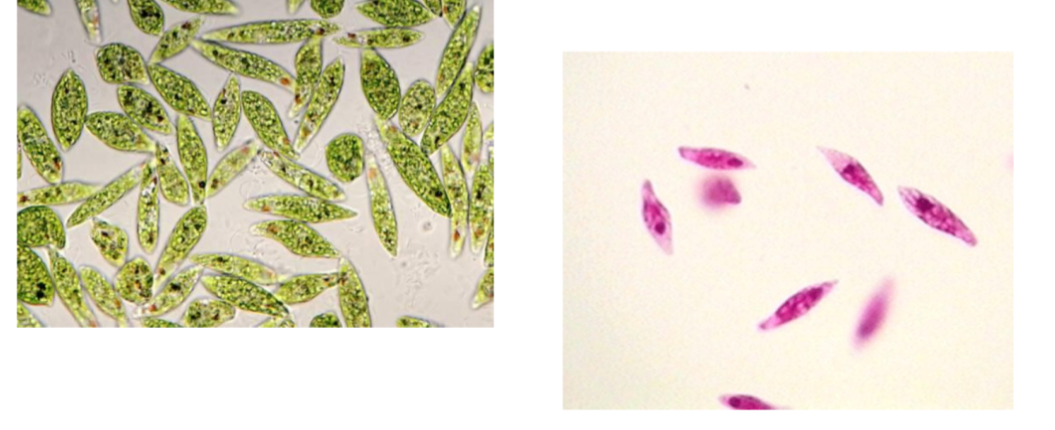
Euglena —
What phylum does it belong to?
What is it’s method of motility?
What disease does it cause?
Phylum: Euglenozoa
Method of Motility: Flagella (not visible)
Disease: None (non-pathogenic; free-living)
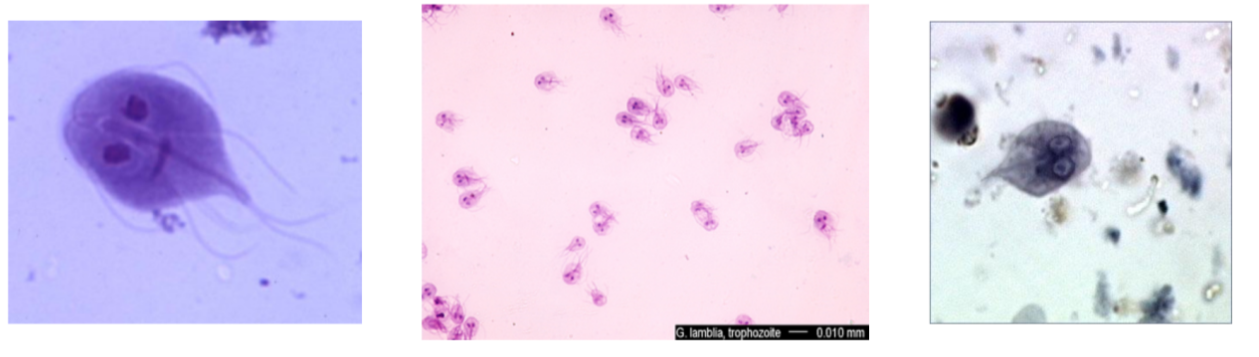
What is the name of this organism?
Giardia lamblia
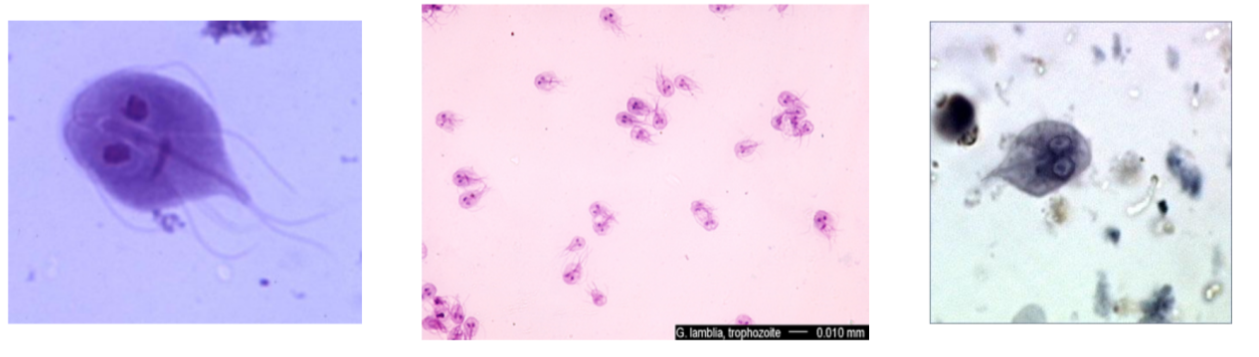
Giardia lamblia—
Describe the shape of Giardia lamblia
What phylum does it belong to?
What is it’s method of motility?
What disease does it cause?
Tear drop shape, two nuclei, multiple flagella hanging off
Phylum: Archaezoa
Method of Motility: Flagella (not visible)
Disease: Severe Diarrhea
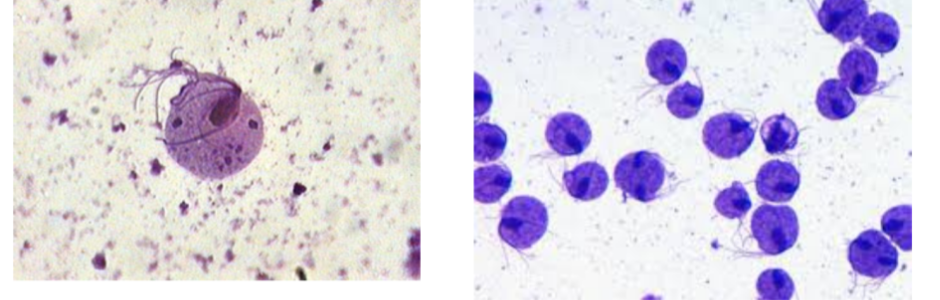
What is the name of this organism?
Trichomonas vaginalis
Trichomonas vaginalis —
Describe the shape of Trichomonas vaginalis
How is it sexually transmitted?
What phylum does it belong to?
What is it’s method of motility?
What disease does it cause?
Big round organism w/ dense nucleus + flagella hanging off
Caused by Protozoan
Phylum: Archaezoa
Method of Motility: Flagella (visible)
Disease: Trichomoniasis/vaginitis
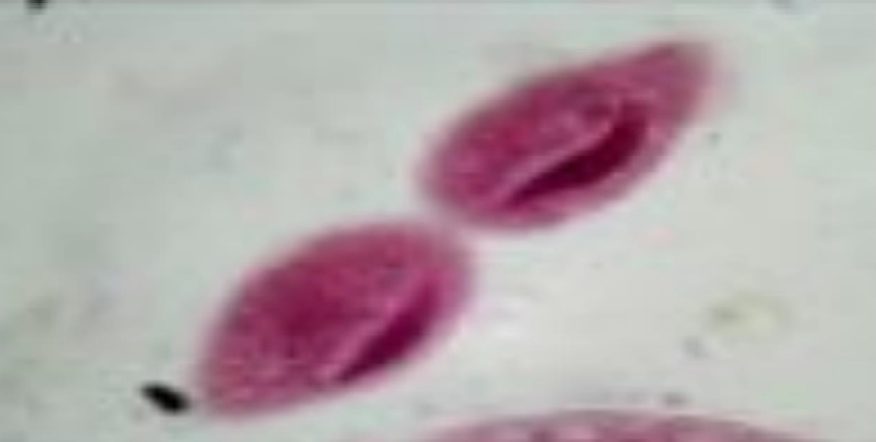
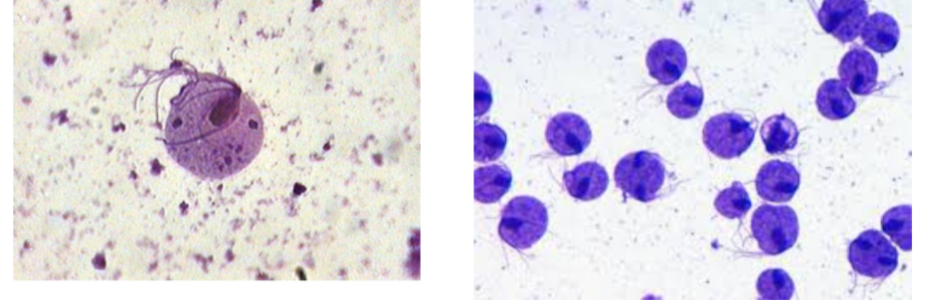
What is the name of this organism?
Paramecium spp.
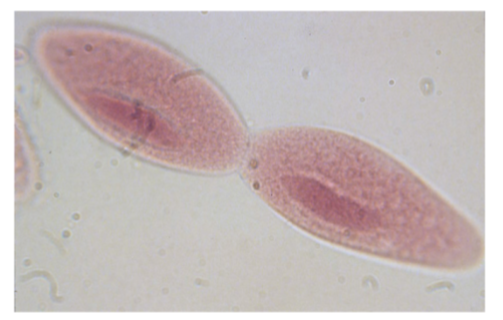
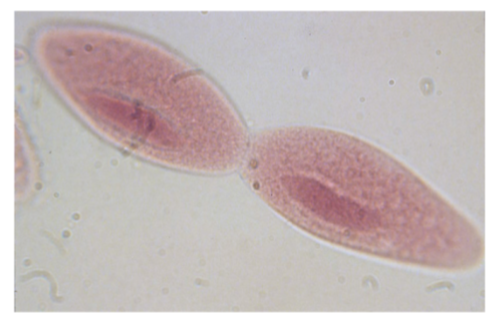
Paramecium spp. —
Identify the type of reproduction.
Binary fission - asexual reproduction
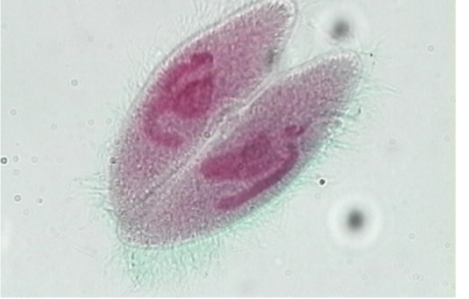
Paramecium spp. —
Identify the type of reproduction.
Conjugation - sexual reproduction
Paramecium —
Describe the type of living + diseases they cause
What phylum does it belong to?
What is it’s method of motility?
Free-living, no disease cause effect in humans
Phylum: Ciliata
Method of Motility: Cilia
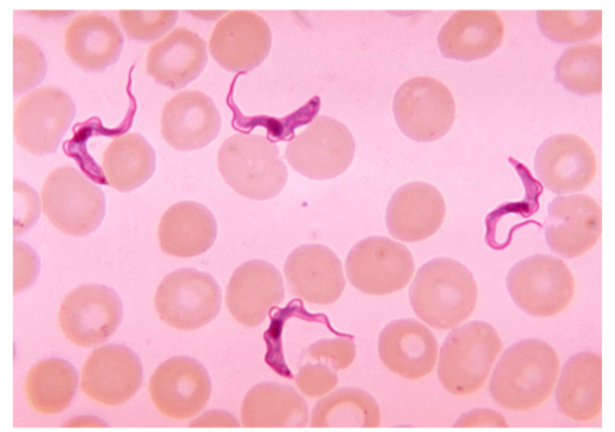
What is the name of this organism?
Trypanosoma brucei
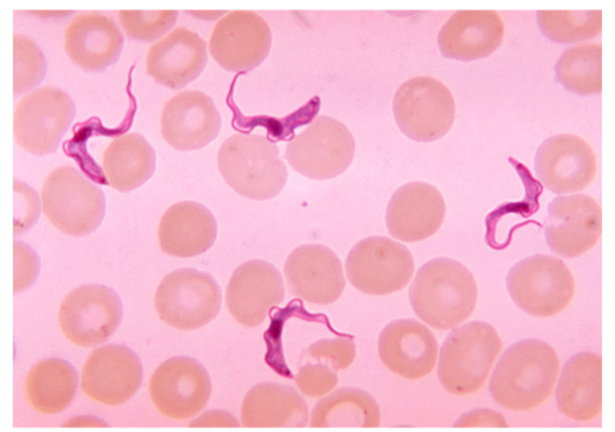
Trypanosoma brucei —
Describe the shape of Trypanosoma brucei
What phylum does it belong to?
What is it’s method of motility?
What disease does it cause?
S shaped squiggles among RBC’S
Phylum: Euglenozoa
Method of Motility: Flagella (not visible)
Disease: African Sleeping Sickness (neurological condition)
What is the name of this organism?
Entamoeba histolytica

Entamoeba histolytica —
Describe the shape of Entamoeba histolytica
What phylum does it belong to?
What is it’s method of motility?
What disease does it cause?
Oval shaped w/ nucleus looks like ring w dot inside
Phylum: Amoebozoa
Method of Motility: Pseudopodia (Pseudopods)
Disease: Diarrhea
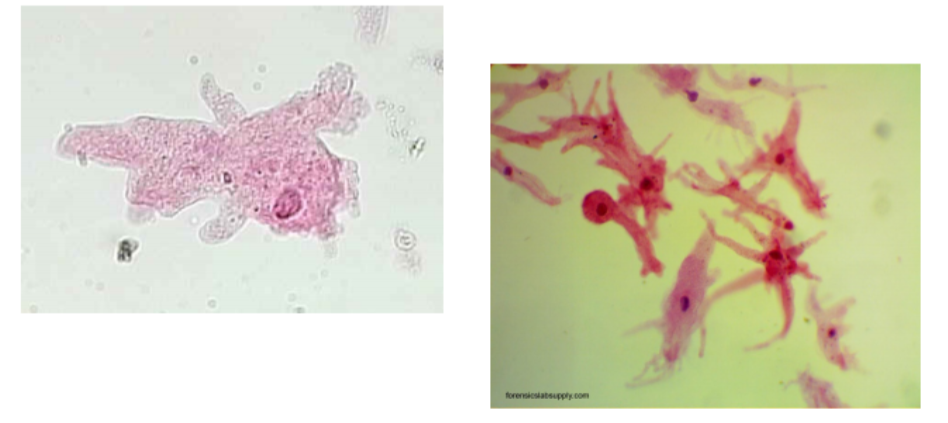
What is the name of this organism?
Amoeba proteus
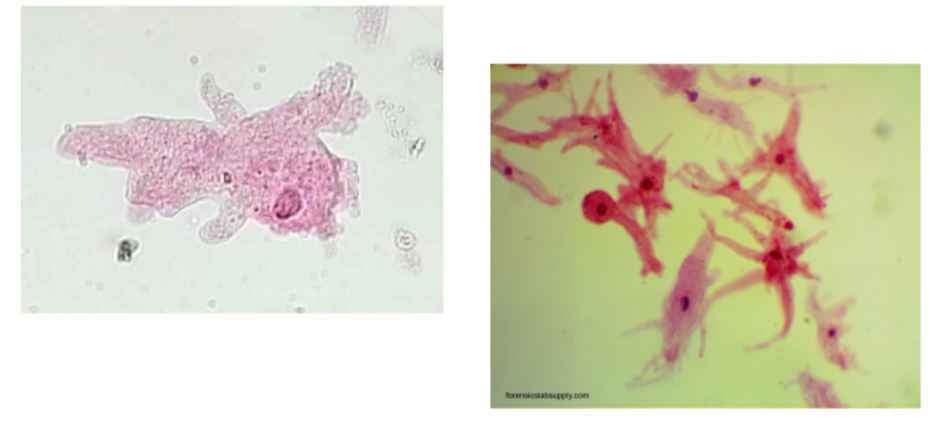
Amoeba proteus —
What phylum does it belong to?
What is it’s method of motility?
What disease does it cause?
Phylum: Amoebozoa
Method of Motility: Pseudopodia (Pseudopods) — finger like projections
Disease: Amebiasis (amebic dysentery) + Acanthamoeba keratitis (eye infection)
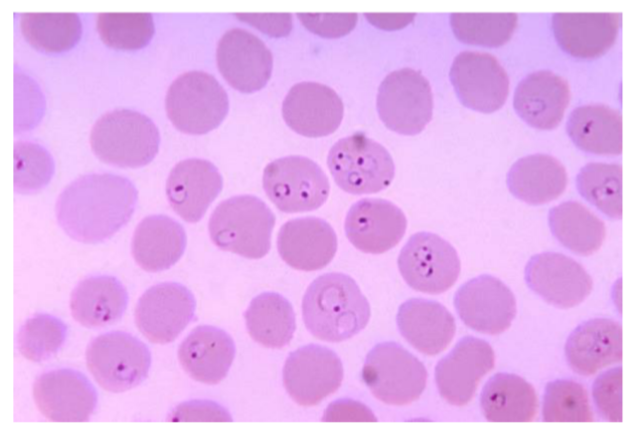
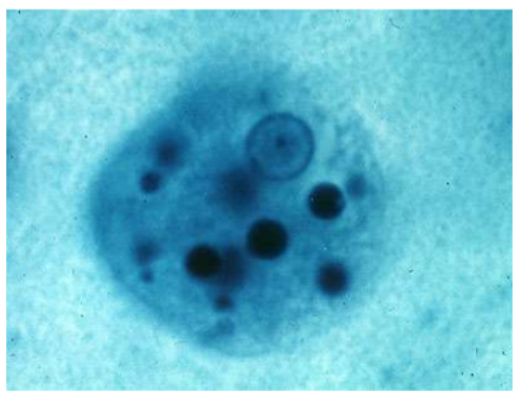
What is the name of this microbe?
Plasmodium spp
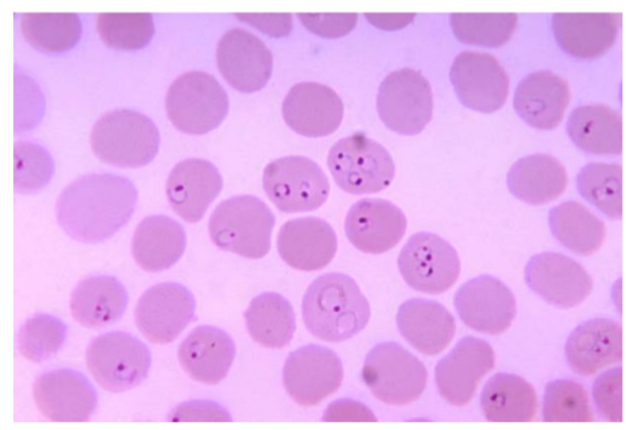
Plasmodium spp —
Describe the structure
What disease does it cause?
How is it transmitted?
What is it’s method of motility?
What phylum does it belong to?
Ring like organism inside RBCS → Causes malaria
Phylum: Apicomplexa
Method of Motility: No Motility
Disease: Malaria
What are the names of the 4 Helminths?
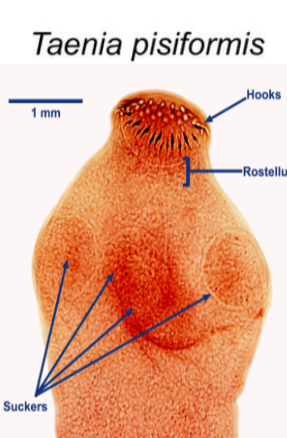
What is the name of this microbe?
Taenia pisiformis
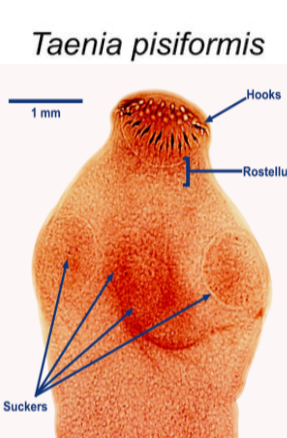
Taenia pisiformis —
What category does it belong to?
What kind of reproduction method does it have?
What disease does it cause?
Category: Cestode (tapeworm)
Reproduction: Hermaphroditic; produces proglottids that release eggs
Disease: Eating raw/undercooked beef, pork, shellfish → causes Taeniasis
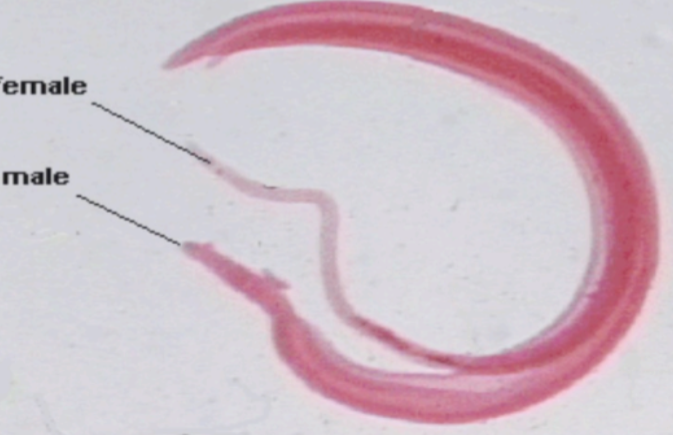
What is the name of this microbe?
Schistosoma mansoni
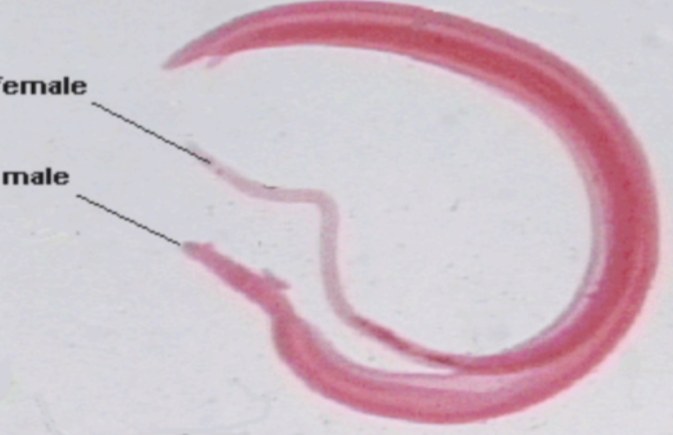
Schistosoma mansoni —
What category does it belong to?
What kind of reproduction method does it have?
What disease does it cause?
Category: Trematode (blood fluke)
Reproduction: Dioecious (separate sexes); male and female live together in the same bodyDisease: Schistosomiasis – liver damage, abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea
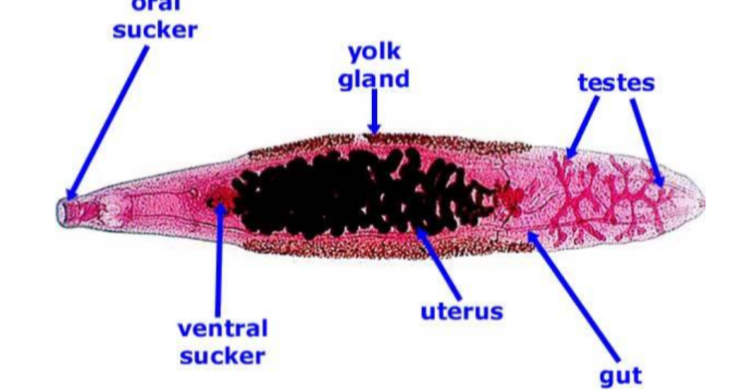
What is the name of this organism?
Clonorchis sinesis (liver fluke)

Clonorchis sinesis (liver fluke) —
What category does it belong to?
What kind of reproduction method does it have?
What disease does it cause?
Category: Platyhelminth - Trematode (liver fluke)
Reproduction: Hermaphroditic - monoecious (both male & female organs)
Disease: Eating undercooked freshwater fish → causes infections (liver or gallbladder) → causes indigestion, fatigue, and diarrhea
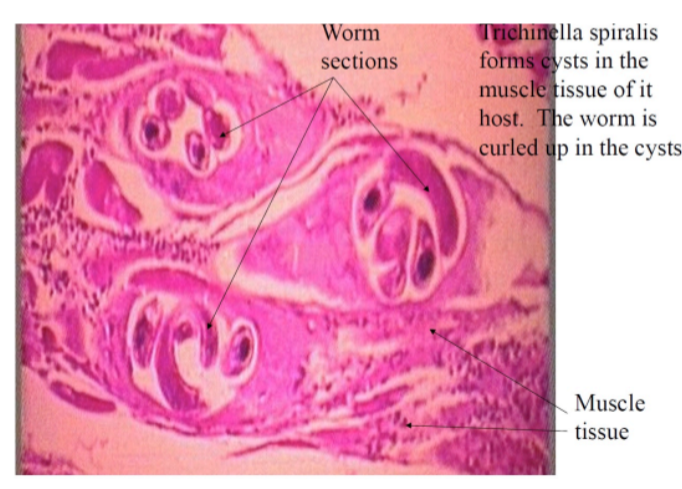
What is the name of this organism?
Trichinella spiralis
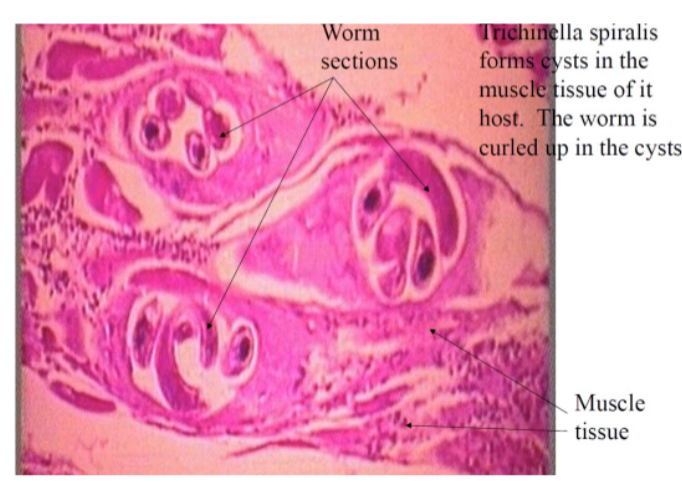
Trichinella spiralis —
What category does it belong to?
What kind of reproduction method does it have?
What disease does it cause?
Category: Nematode (roundworm)
Reproduction: Dioecious; males and females reproduce sexually
Disease: Trichinellosis eating raw/undercookd meat → muscle cysts, fever, nausea, diarrhea, muscle pain