Inorganic irritant poisons
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Arsenious oxide-sankhya, somlakhar or arenic trioxide ——most toxic
Arsenic disulphide / red arsenic
Arsenic trisulphide-Yellow arsenic
Copper arsenite-sceele’s green
Copper acetoarsenite-paris green
Arsenic salts
Inhibits ATP formation by combining with the mitochondiral enzymes of sulfydryl group especially pyruvate dehydrogenase and certain phosphates leading to uncoupling of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation.
inhibits transformation of thiamine inot acetyl coa and succinyl coa
inhibits cellular glucose uptake, gluconeogenesis and fatty caicd oxidation further preventing the formation of ateyly coa
MOA of arsenic
120-200mg
1-2days
Fatal dose of arsdenic

Clinical features of acute arsenic poisoning
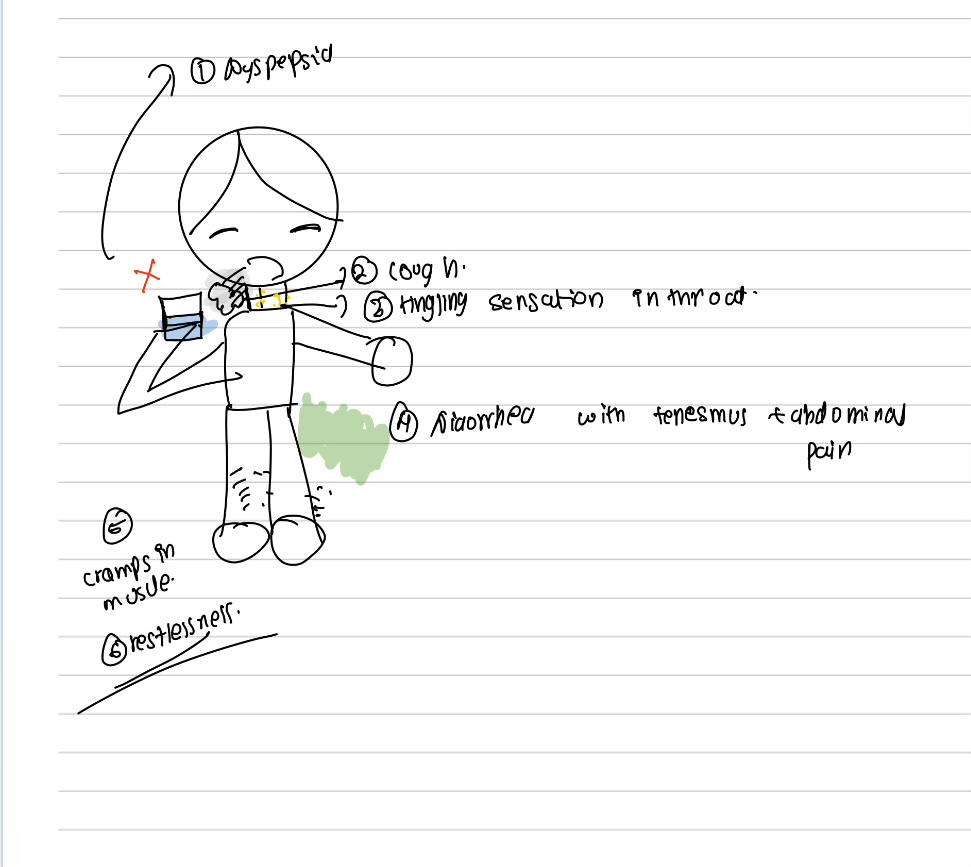
Subacute arsenic poisoning
Rain drop pigmentation, Mee’s lines,Flexor eczema, painless perforation of nasal septum, bone marrow depression, peipheral neutopathy resembling sensorymototr type as in gullian bares syndrome, weakness of the extensor muscles leading to foot drop and wrist drop.
Features of chronic poisoning
BAL or dimercaprol-3-5mg/kg im 4hrly 2 days, 6 hrly 1 day and 12 hrly for 10 days
Antidote for arsenic poisoning
RIgor mortis early and lasts for longer suration
body is emacitated
putrefaction is delayed
blood tinged vomitus and fecal matter may be present on the clothes.
eyeballs are sunken and skin cyanosed
stomach-edematous, swollen, flea bittenn appearance, red velvety mucosa.
Stomach has mucin covering that may have arsenic particlescongetsion more marked at crest of fugal
Inflammation more at greater curvature posterior part and cardiac endbrain edema necrosis, hemorrhagic encephalitis.
PM findings of arsenic
Lead acetate, carbonate, chromate, monoxide, tetroxide most toxic, sulphide least toixc
Toxic compounds of lead
gasoline
petrol, automobile exhaust, house paints, battery making, steel welding and cutting
Sources of lead poisoning
inghiibts mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation by combining with sulfhydrl group,
inhibits enzymes responsible for heme synthesis—-causing anemia leading to hemolysis
Mechanism of action of lead poisoning
vomitting, constipation, diarrohea, headcahe, lethargy, myalgia,abdominal pain, metallic taste, ataxia, convulsion,coma
features of acute lead poisoning
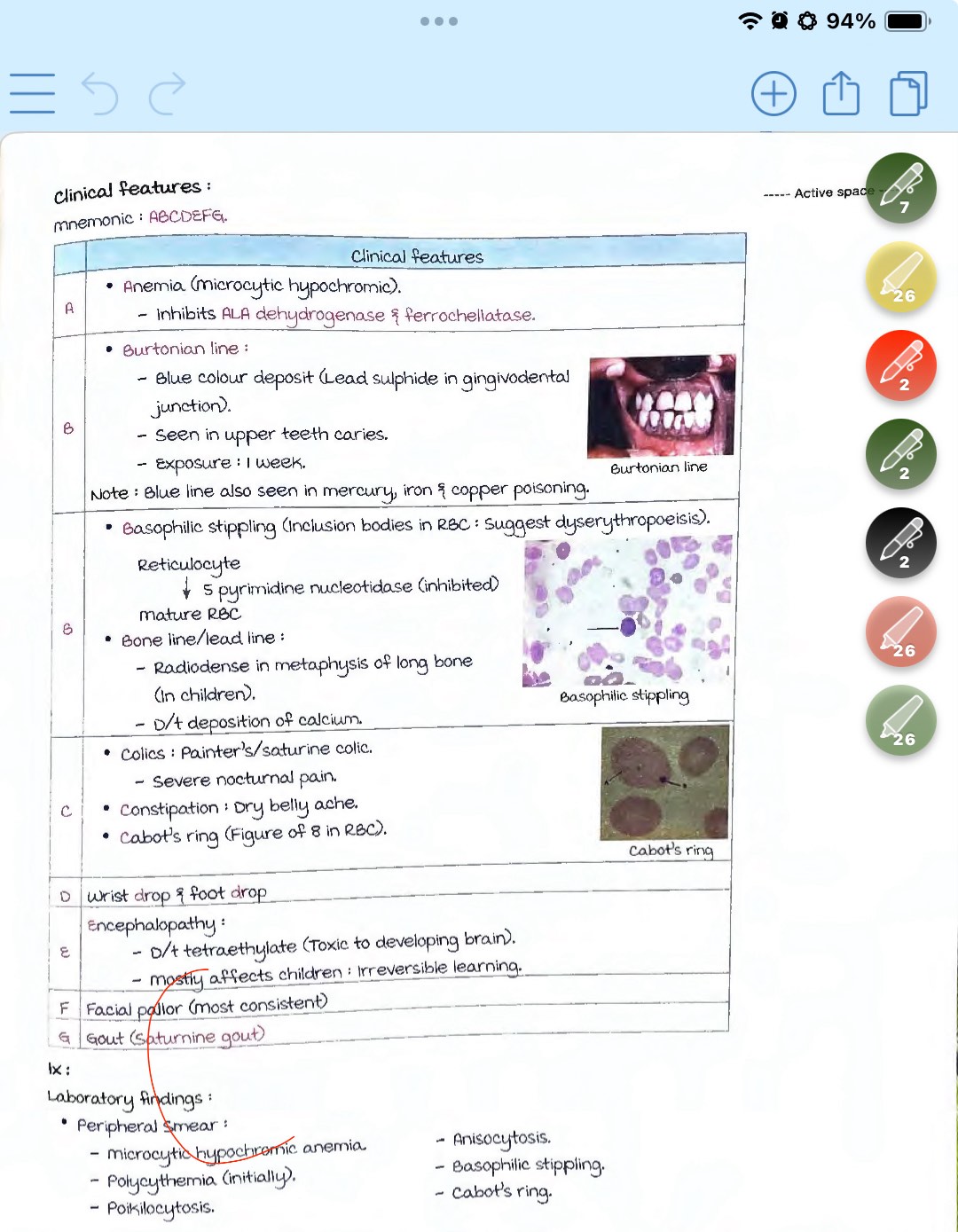
anemia
basophilic stippling
burtonian line due to the deposition of granules in the gingiva, formed due to the formation of lead sulphide from the h2s released from decomposed protein in the mouth
Bone line’lead line -deposition of lead in the epiphyses of growing long bones.
Constipation, Colic of intestine,ureters and BVs , Cabot;s ring -figure 8 in RBCS
Drop-foot and wrist due to the weaknedd of the muscles and degeneration of nerves due to the interference with phosphocreatine metabolism.
Encephalopathy-associated with tetraethyl lead
Face pallor-earliest and most consistent sign
Gout
Features of chronic lead poisoning
Severe poisoning with encephalopathy -BAL-4mg'/kg immediately repeat same dose at 4hourly interval until blood level falls below 8ug/100ml.
then reduce to 12mg/kg/day in 3 divided doses
calcium sodium edta-75mg’kg’day—— reduce to 50 mg
oral chealtion with d penicillamine 10mg /kg/day
if no encephalopathy-reduced doses
moderate ko lagi only edta
mild ko lagi d penicllamine -3omg/kg/day
treatment of lead poisoning
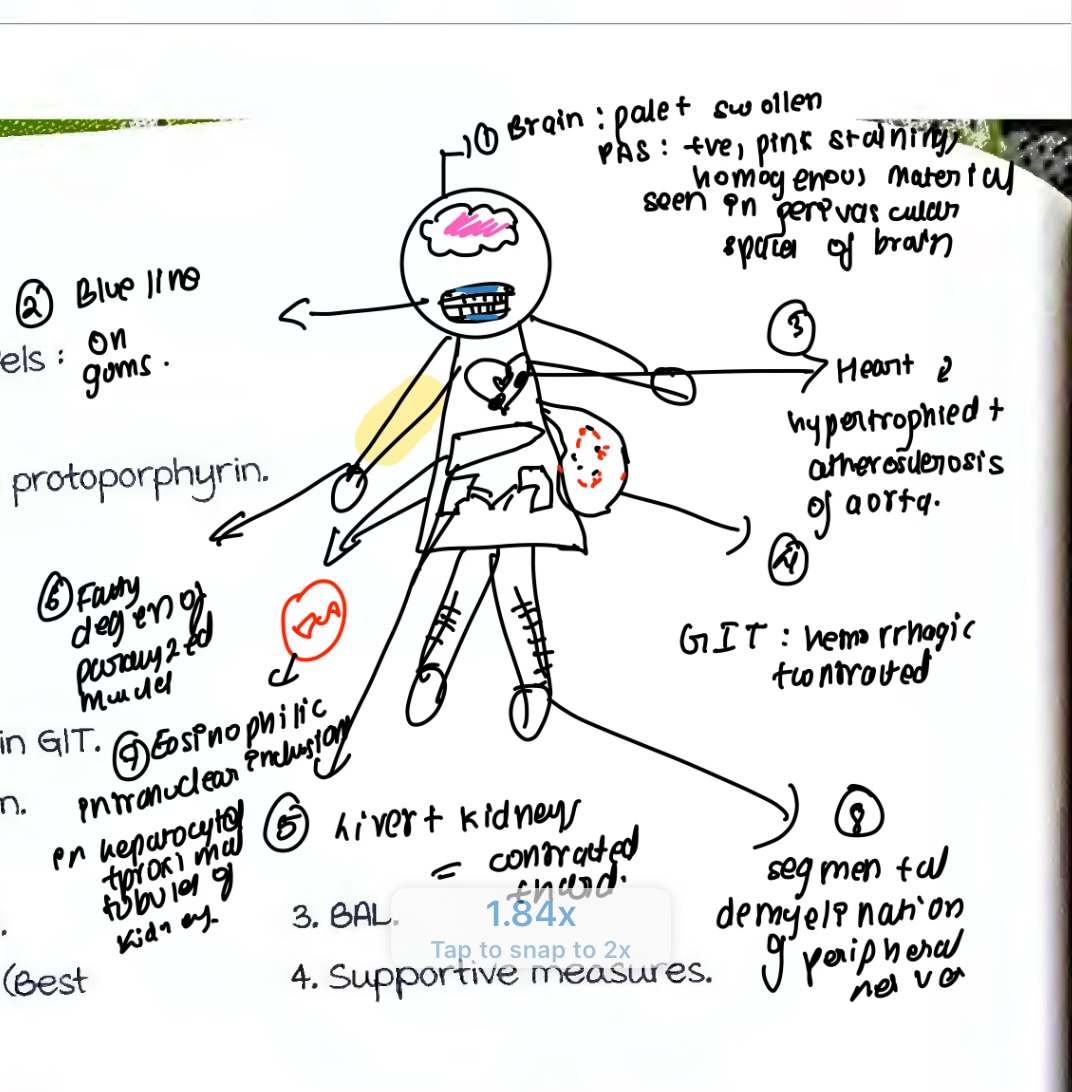
PM finings of lead poisoning
inorganic- mercuric form and mercurous form
mercuric chloride and mercurous chloride mercuric cuphide, cyanide, oxide, iodide.
organic- methyl mercury
dimethyl mercury ethyl mercury phenyl mercury
toxic compounds of mercury
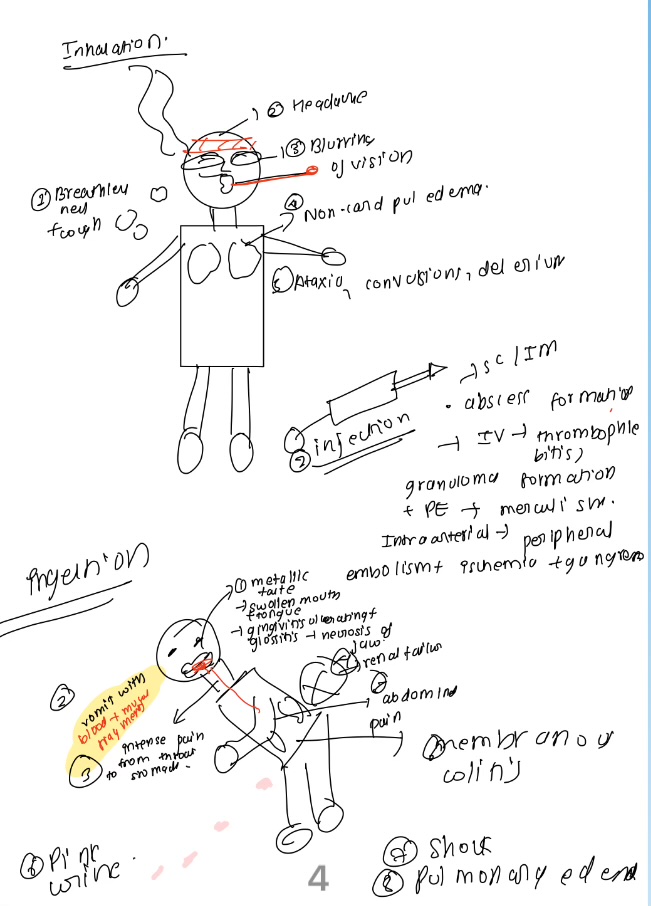
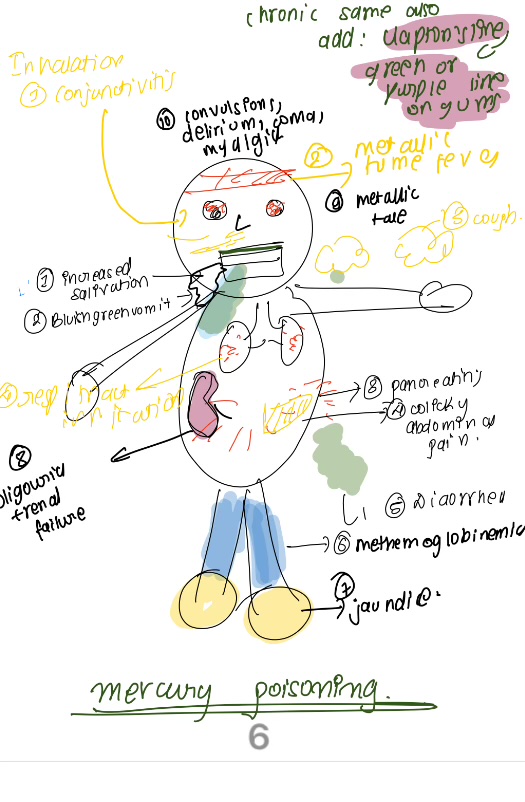
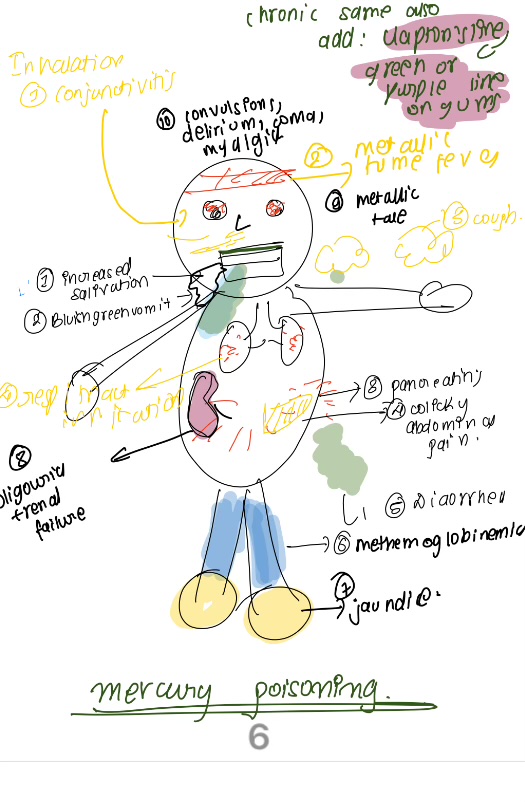
clinical features of merury
Blue MEAT
Blue line, Mercuria lentis, Erethism, acrodynia, tremors
Chronic mercury poisoning is characterised by
Danbury tremors
intially fine ——later coarse and involuntary. termor begins first in the hands, procedes towards the lips and tongue and finally involves the arms and legs.
in advancedd case-hatters shake and glasssblowers shakes. concussion mercularis-severe form of tremors in which no activity is possible.
Tremors associated with mercury poisoning
mercury depositions in the anterior capsule of the lens
on slit lamp examination malt brown reflex is seen.
mercuria lentis
neuropsychiatric disorders present in mercury posioning
characterised by- anxiety amnesia depression, mood instalbility, loss of confiedence, constant blushin, suciede melanchonia, insomina, delusions and hallucination
mad hatters syndrome
Erethism
hypersensitivity reaction isiosyncriatic
characterised by-
paresthesia, pink, puffy, peeling of skin, painful
Acrodynia
minamata disease
hunter rusell syndrome
other disease caused due to hg poisoning
removal of further exposure
demulcents
saline purgatives
oral hygiene
chealting agents
d penicillamine-25-40mg'/kg/day in 4 divided doses in case of children
adult-250mg/kg/day in 4 times a day
DMSA
DMPS
BAL
treatment of mercury posioning
Copper sulphate-blue vitrol
copper carbonate0mountain green
copper subacetate-verdigris
copper asenite-scheels green
copper acetoarsenite-paris green
Copper toxic compounds
copper sulphate-20-30gm
copper subacetate- 15gm
fata period -1-3days
fatal dose of copper
clincial feeatures of copper poisoning
PM findings of copper poisoning
chalcosis bulbi- kayser fleischer ring, sunflower cataract, golden plaques depsoited at posterior pole of retina that reflects with metalic sheen.
Vineyard sprayerslungs-due to chronic exposure to bordeaux solution(1-2percent copper sulfate solution neutralised with lime)
Copper realted terminologies
potassium ferrocyanide
Antidote for copper poisoning
cadmium
ouch ouch disease or itai disease is casued by
replaces calcium present in the bone-leads to bone softening-osteomalacia
cadmium moa
Thallium poisoning
Poisoner’s poison
forms-thallium acetate, thallium sulphate
BAN
butterfly rash, behavioural change
alopecia with madarosis, aldrich mee’s lines
neuropathy-similar to arsenic
CF
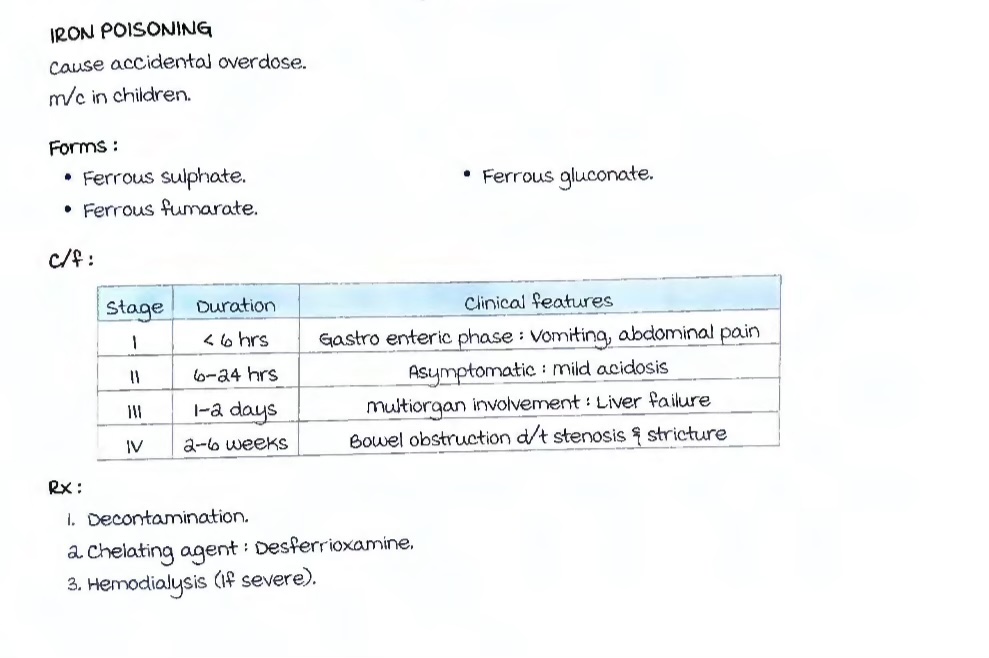
Iron posioning
white- garlicky odour, luminiscent, ocidative, fuming,inflammable, highly toxic
red- sab opposite of white and non toxic
forms of phosphorous
WHite- rodenticide, insecticide, ffertilizers, bombs, smoke screens fireworks
red- matchsticks
Uses of phosphorous
protoplasmic poison and affetts celular oxidation
cardio and heapatotoxic
moa of phosphorous
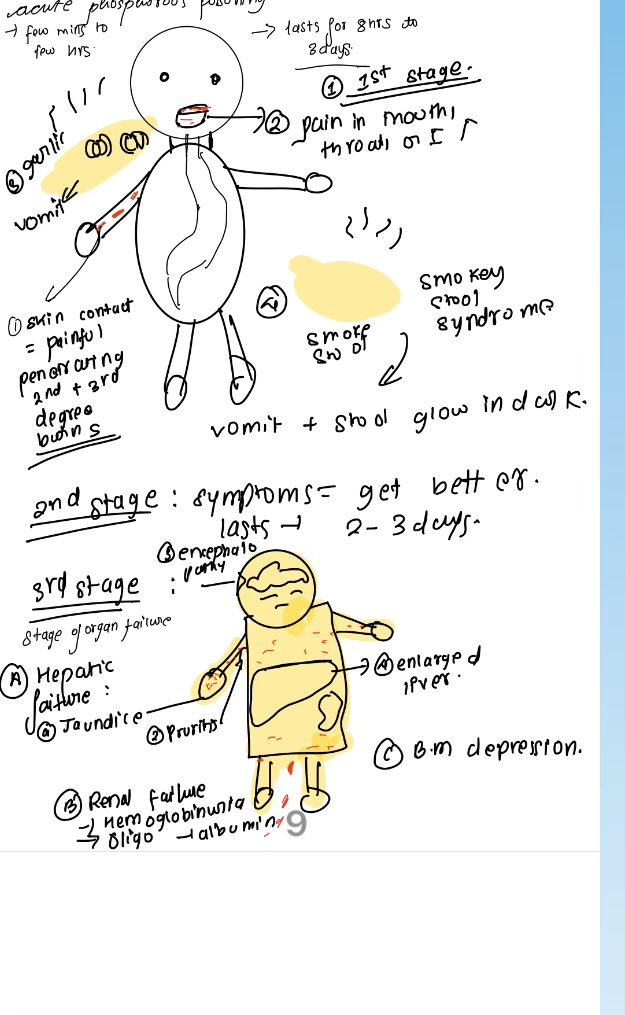
clinical features of phosphorous
similar to acute
phossy jaw or glass jaw- osteomyelitis of the lower jaw. initial toothache, swelling, loosening of teeth.
features of chronic poisoning pf phosphorous
milk, oily or fatty food should not be given as it increases absorption
what should not be done in the treatment of phosphorous poisoning
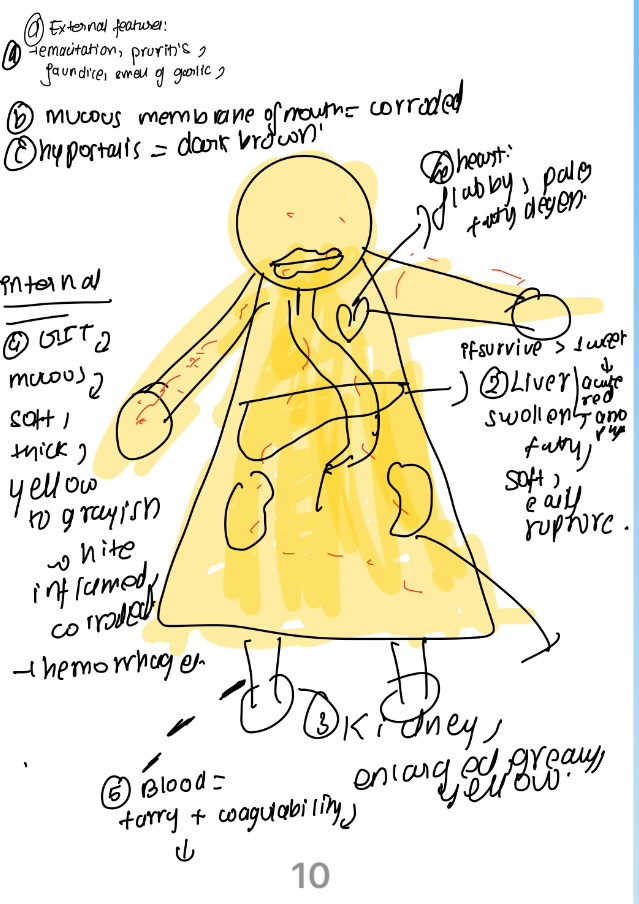
Pm finding of phos poisoning