UWORLD GI Principles Step 2 CK
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
___ is the most common complication of PUD.
Hemorrhage
- fluid + blood resuscitation, medical tx, endoscopic intervention
- most stop bleeding spontaneously
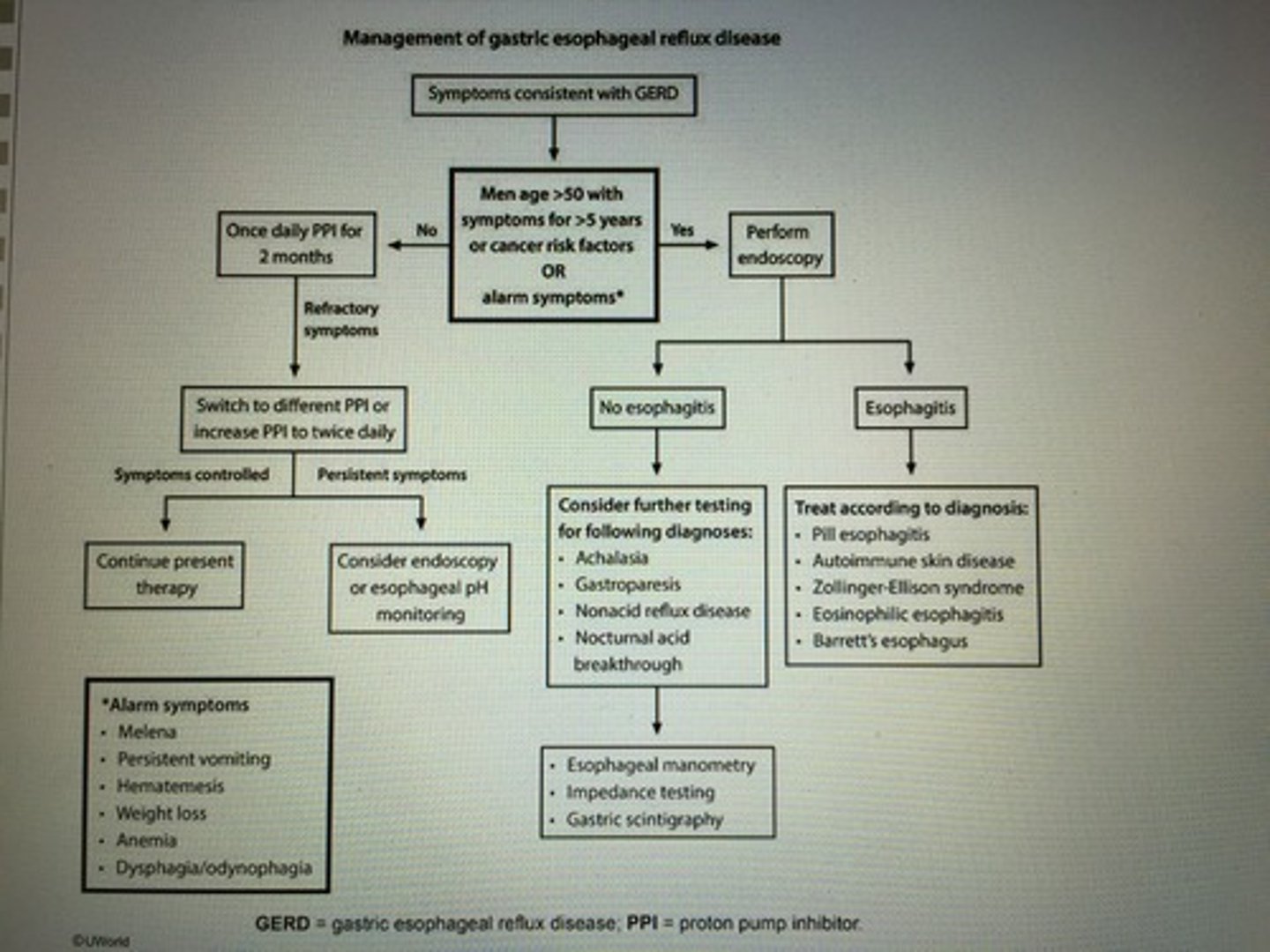
Management of GERD
Rapid INC in transaminases with modest elevations in total bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase. What kind of hepatic injury?
Ischemic hepatic injury -> hypotension due to septic shock/HF
- liver enzymes typically return to normal w/in 1 to 2 weeks
Pt between 15-25 has bloody diarrhea, tenesmus, and cramping as well as wt loss and anemia. Biopsy colon shows mucosal inflammation.
Ulcerative colitis
- sclerosing cholangitis, uveitis, erythema nodosum, spondyloarthropathy
- Routine surveillance with yearly colonoscopies is recommended for pts with UC beginning 8-10 years after dx prevention/early detection colon cancer
1% annual cancer incidence in pts with UC
Pt presents with malabsorption with a hx of living in endemic area (Puerto Rico) for more than 1 mo. Biopsy shows blunting of villi w/ infiltration of chronic inflammatory cells, including lymphocytes, plasma cells, and eosinophils. Pt also has megaloblastic anemia.
Tropical sprue
- malabsorption of vitamin B12 and folic acid => megaloblastic anemia
Signs malabsorption: glossitis, cheilosis, protuberant abdomen, pallor, pedal edema
Hyperactive BS, borborygmi
Dx: small intestinal mucosal biopsy
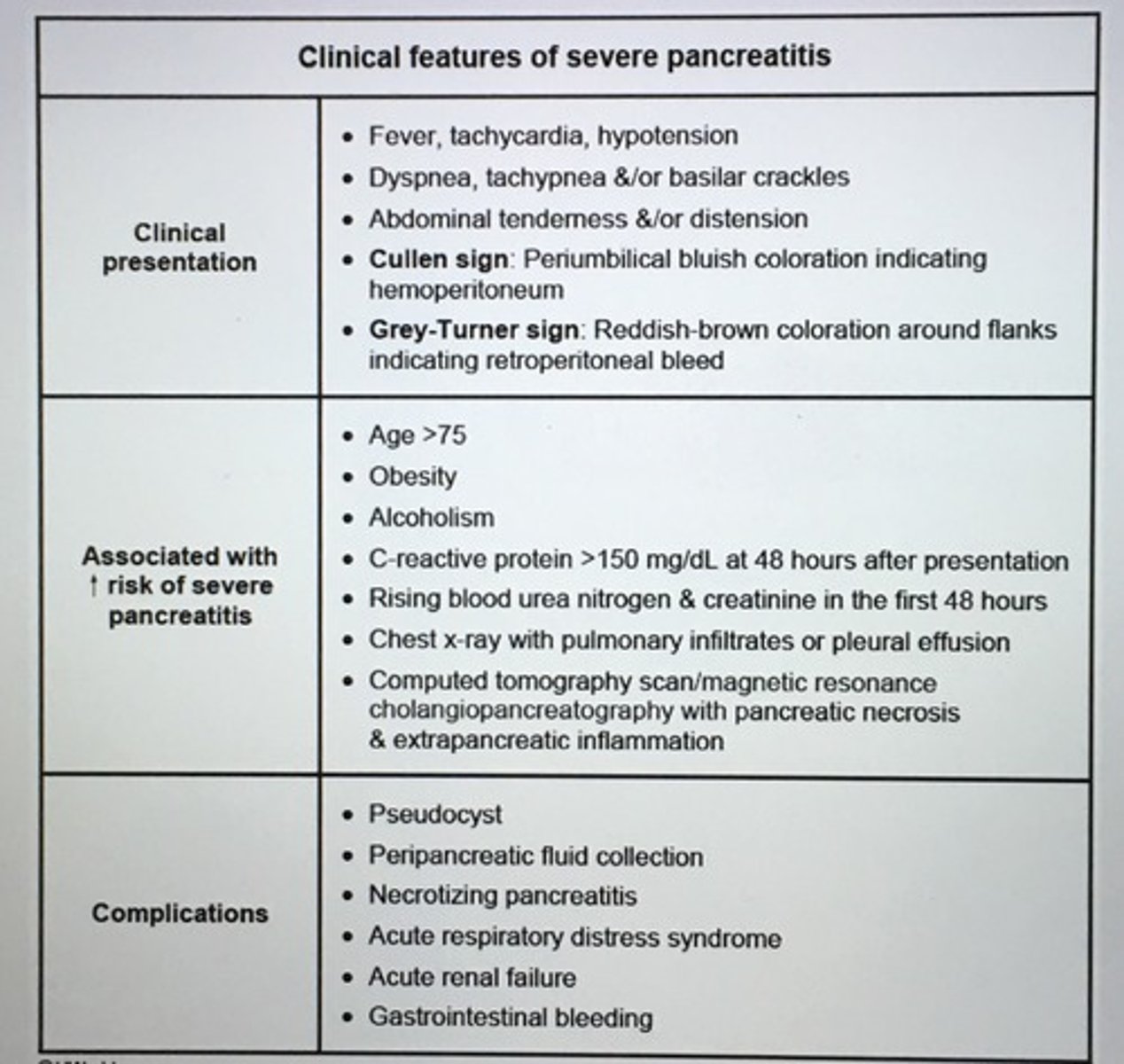
Complications of acute pancreatitis.
Pleural effusion
ARDS
Ileus
Renal failure
Pt presents w/ N/V, epigastric pain, alcohol abuse and gallstones most common cause of acute pancreatitis
Causes acute pancreatitis?
1. Chronic alcohol abuse
2. Gallstones
3. Hyperlipidemia (I, IV, V)
4. Drugs (didanosine, azithroprine, valproic acid)
5. Trauma
6. Iatrogenic (post-ERCP)
Clinical presentation acute pancreatitis?
Dx requires 2 of the following:
- Acute epigastric abd pain often radiating to the back
- INC amylase/lipase > 3 times normal limit
- Abd imaging shows focal or diffuse pancreatic enlargement w/ heterogenous enhancement w/ IV contrast (CT) or diffusely enlarged & hypoechoic pancreas (US)
Other finds:
- N/V, leukocytosis
- Severe disease w/ abd tenderness, fever, tachy, hypoxemia, hypoT
- ALT>150 unit/L-> biliary pancreatitis
___ is persistent abd pain or dyspepsia either postoperatively (early) or months to years (later) after cholecystectomy.
Postcholecystectomy syndrome
- Biliary (retained common bile duct, cystic duct stone) or extra-biliary (pancreatitis, PUD)
- US followed by ERCP/MRCP can establish the dx and guide therapy toward the causative factor
___ multi-systemic illness with arthralgias, wt loss, fever, diarrhea and abd pain in pt that is white man in 4th to 6th decades of life. PAS-positive material in the lamina propria of the small intestine classical biopsy finding.
Whipple's dz (Tropheryma whippelii)
- chronic cough, myocardial or valvular involvement -> CHF or valvular regurgitation
- late stages dementia, CNS findings (supranuclear ophthalmoplegia + myoclonus)
- low-grade fever, pigmentation, lymphadenopathy
Direct toxins to the liver?
Carbon tetrachloride
Acetaminophen
Tetracycline
Amanita phalloides mushroom
Drug-induced liver disease broadly categorize according to morphology?
1. Cholestasis
- Chlorpromazine, Nitrofurantoin, Erythromycin, Anabolic steroids
2. Fatty liver
- Tetracycline, Valproate, Anti-retrovirals
3. Hepatitis
- Halothane, Phenytoin, Isoniazid, Alpha-methyldopa
4. Toxic or fulminant liver failure
- Carbon tetrachloride, Acetaminophen
5. Granulomatous
- Allopurinol, Phenybutazone
Always suspect ___ in young patient with chronic diarrhea, abdominal pain, wt loss.
Crohn's dz
- GI tract esophagus to anus
- Intestinal fistula, strictures, and anal dz
- Labs: Anemia + reactive thrombocytosis
___ presents with sudden onset of fever, RUQ abd pain, vomiting, and leukocytosis.
Acute cholecystitis
- inciting event gallstone obstructing the cystic duct w/ inflammation and infection
- radiate to right scapula
- total bilirubin btw 1-4 mg/dL
Risk factors for cholesterol gallstones?
- Caucasian race
- Obesity
- Rapid wt loss
- Female sex hormones
- Use OCP
- Glucose intolerance
- Hypomotility of gallbladder (pregnancy, adv age, fasting, hypertriglyceridemia, prolonged total parenteral nutrition)
- Malabsorption of bile acids (ileal disease or resection)
- Pharm tx w/ Clofibrates, osteotide, ceftriaxone
Major types of gallstones?
Cholesterol
Pigmented (calcium bilirubinate)
Mixed stones
- normally water-insoluble cholesterol is secreted in bile then converted into soluble micelles by bile acids and lecithin
- if gallbladder hypomotile or there is excess cholesterol in comparison to bile salts, the cholesterol ppt into soluble crystals that form gallstones
Risk factors for formation pigmented gallstones?
Chronic hemolysis (sickle cell anemia)
Chronic biliary tract infection
Parasitic infection
Advanced age
HIGH YIELD: ___ has lower esophageal spinster (LES) that does not relax (high tone). Hypertrophies inner circular muscle with absent or degenerating neurons (ganglion cells) in myenteric plexus.
Achalasia
- manometry: absent peristalsis
- esophogogram shows dilated esophagus with bird's beak narrowing distal esophagus
HIGH YIELD: Manometric studies how high amplitude peristaltic contractions, LES normal relaxation response. Esophagogram normal.
Diffuse esophageal spasm
- chest pain + dysphagia
- associated emo factors and function GI disorders
- Tx: antispasmodics, diet modulation, and psych counseling
HIGH YIELD: ___ loss of distal peristalsis of the esophagus. Fibrosis and complete atrophy of esophageal smooth muscle. LES incompetent (low tone) with time, leading to relax esophagitis and a stricture. Dx.
Scleroderma
- progressive and difficult to tx
Minimal bright red blood per rectrum (BRBPR) most common causes?
Hemorrhoids
Anal fissure
Polyps
Proctitis
Rectal ulcers
Cancer
< 50 y/o, no risk factors, perform office-based anoscopy or proctoscopy
Pt with tumors of the ___ can have abd pain and wt loss, with jaundice and a distended gallbladder on exam. Characteristic finding on imaging include intra-and extra hepatic biliary tract dilation.
Tumor head of the pancreas
- w/ compression pancreatic duct (steatorrhea) and common bile duct (jaundice/icterus), double duct sign
___ characterized by recurrent bouts of upper abd pain, diarrhea/steatorrhea, and wt loss.
Chronic pancreatitis
- pancreatic calcifications on CT or X-ray
Serum ___ are elevated in pancreatic cancer.
CA 19-9 (cancer-associated antigen)
- abd pain
- wt loss
- jaundice
w/o sx resection most die w/in 1 year
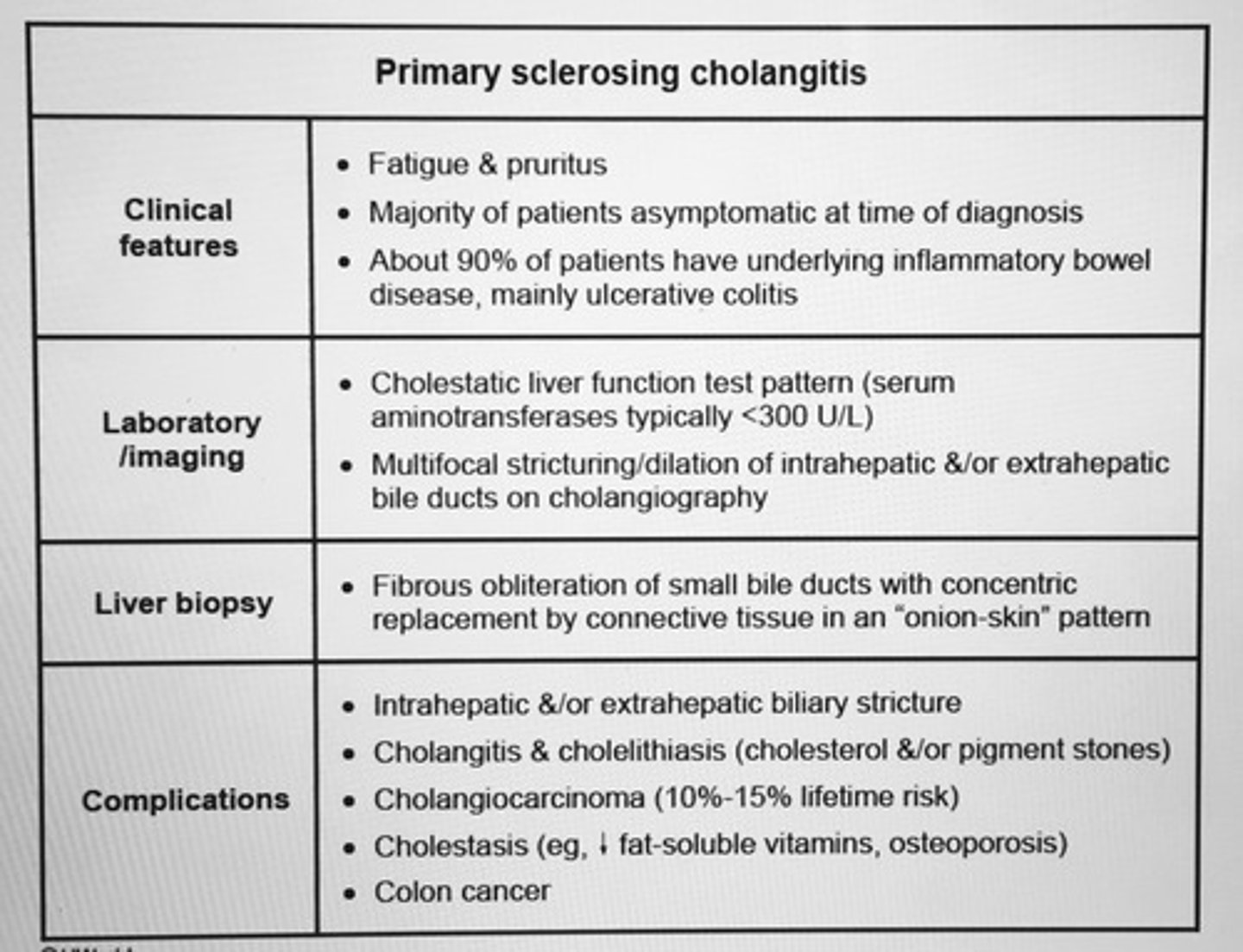
Primary sclerosing cholangitis clinical features, labs, liver biopsy findings, and complications.
GERD predisposed to?
Barrett's esophagus
Erosive esophagitis
Esophageal (peptic) stricture formation (symmetric and circumferential narrowing of the esophagus w/ dysphagia for solids)
Common drugs associated with acute pancreatitis?
1. Diuretics (furosemide, thiazides)
2. Drugs for IBD (sulfasalazine, 5-ASA)
3. Immunosuppressive agents (azathioprine)
4. HIV-related meds (didanosine, pentamidine)
5. Antibiotics (metronidazole, tetracycline)
6. Anti-seizure meds (valproic acid)
CT scan in acute pancreatitis shows?
Swelling of the pancreas w/ prominent peripancreatic fluid and fat-stranding
Dx test of choice for Zenker's diverticulum.
Contrast esophagram
- tx: surgery
Presence of "succussion splash" can indicated ___.
Gastric outlet obstruction
- place stethoscope over upper abd and rock the pts back and forth @ hip
- retained gastric material > 3 hrs after meal generate splash sound, hollow virus filled with fluid and gas
Management of gastric outlet obstruction?
NG suctioning to decompress the stomach
IV hydration
Endoscopy for definitive dx
Diarrhea associated with laxative abuse is?
Watery, INC frequency and volume of stool
- 10-20 BM daily
- Nocturnal BM + painful abd cramps
- Biopsy: dark brown discoloration of the colon w/ lymph follicles shining through as pale patches (melanosis coli) (abuse anthraquinone laxative e.g., bisacodyl)
Major risk factors for pancreatic cancer.
1. Hereditary
- First-degree relative with pancreatic cancer
- Hereditary pancreatitis
- Germline mutations (BRCA1, BRCA2, Peutz-Jeghers syndrome)
2. Environmental
- Cigarette smoking (most significant)
- Obesity, low physical activity
- Nonhereditary chronic pancreatitis
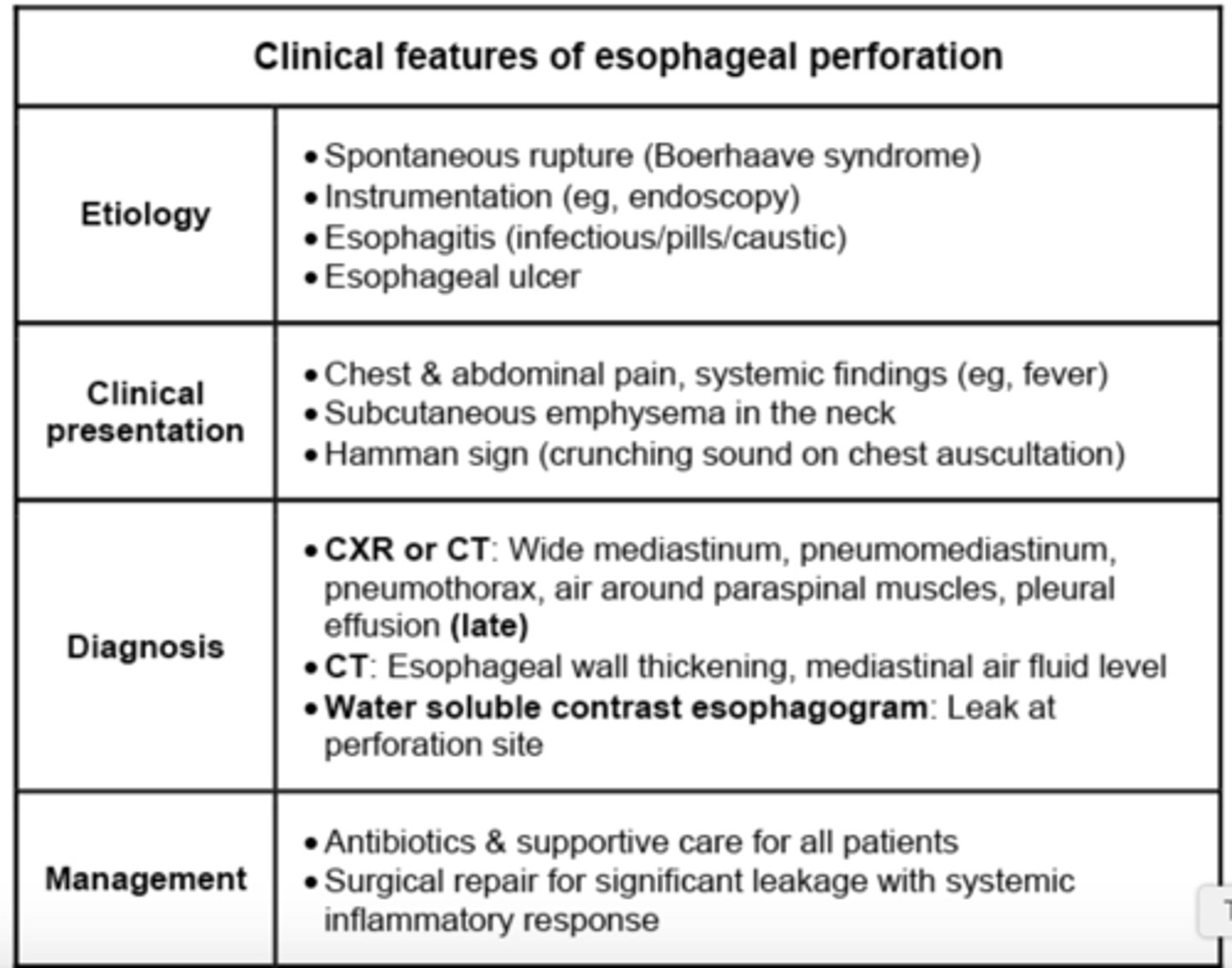
Retrosternal pain and crepitus in the suprasternal notch result from ___, commonly occurs following rupture of the esophagus w/in the mediastinum.
Pneumomediastinum
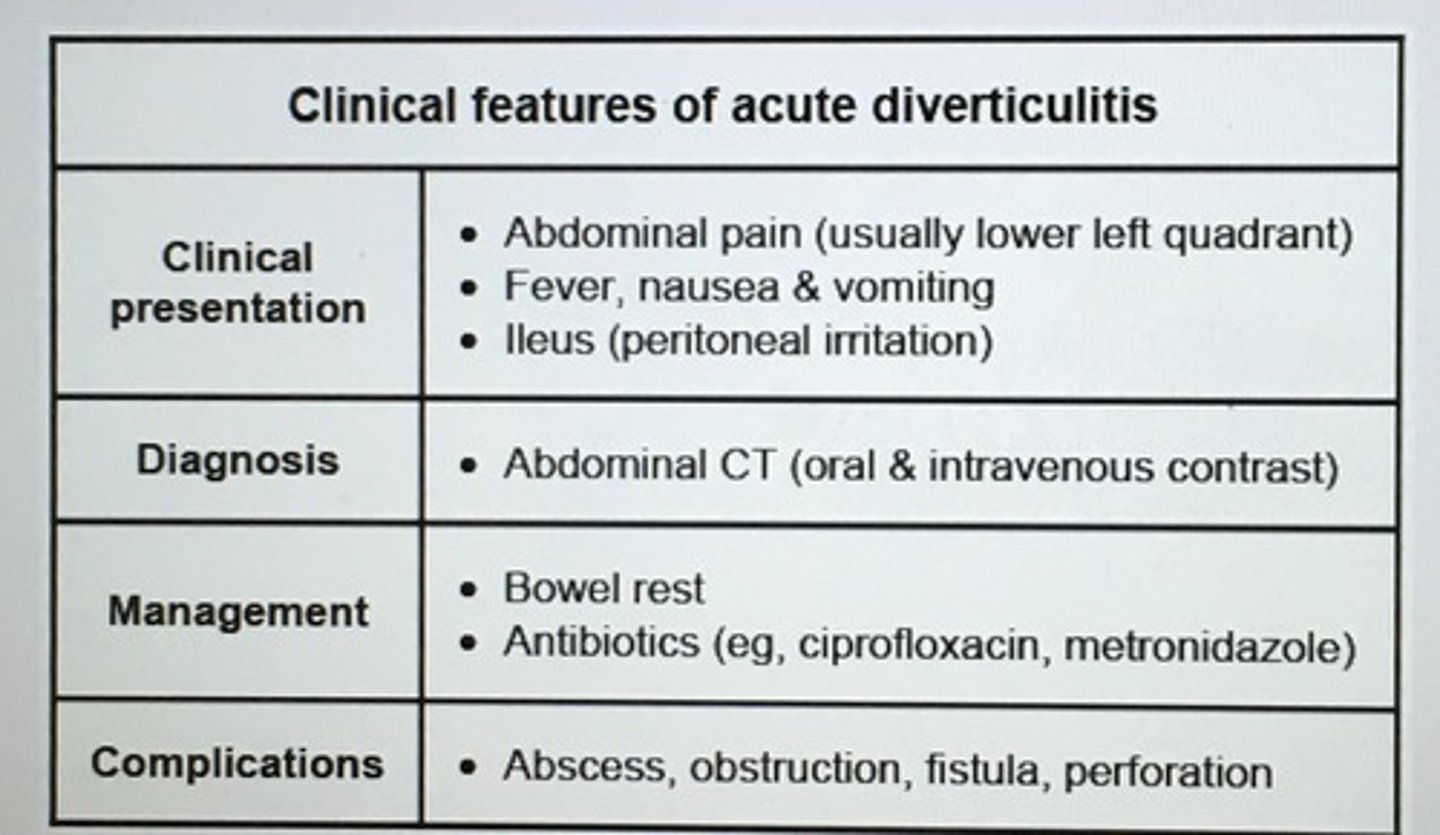
___ is the best test for dx and evaluating the abdomen of pts during an acute episode of diverticulitis.
CT scan
___ antibodies are present in 90% of pts with primary biliary cirrhosis, a chronic liver dz characterized by autoimmune destruction of intrahepatic bile ducts and cholestasis.
Anti-Mitochondrial antibodies
- pruritis, middle aged woman, fatigue, hepatosplenomegaly, xanthomatous lesions eyelids or skin and tendons
- tx: Ursodeoxycholic acid
Stable pts w/o significant comorbid conditions can receive packed red blood cells (PRBC) for hemoglobin < ___g/dL.
Hemoglobin < 7 g/dL
* < 9 for pt w/ symptomatic anemia or ACS with active ischemia
Cryoprecipitate is used as replacement tx for pts with?
Fibrinogen, vWF, or Factor VIII deficiency
FFP is indicated when?
Active bleeding w/ severe coagulopathy
- Liver dx
- DIC
- Supratherapeutic warfarin anticoagulation
FFP: contains all clotting factors and plasma proteins from one unit of blood
When are platelet transfusions started?
Platelet count < 10,000/microL (INC risk of spontaneous hemorrhage)
OR
Active bleeding + platelets < 50,000/microL
Pt has a dark granular pigment in the hepatocytes, INC conjugated bilirubin. INC urinary coprophoryn I. Pigment contains epinephrine metabolites w/in lysosomes.
Dubin-Johnson (benign)
- Sephardic Jews
- Icterus evident (triggers such as illness, pregnancy, OCPs)
___ pt w/ no apparent liver disease who have mild unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia through to be provoked by one of the classic triggers (fasting, stress, illness).
Gilbert's syndrome
Crigler-Najjar syndrome type 1 vs type 2.
Significant unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia
1. Crigler-Najjar syndrome type 1
- AR severe jaundice
- Neuro impairment (kernicterus- bilirubin encephalopathy)
- INC indirect bilirubin 20-25
- phenobarbital, serum bilirubin same
- phototherapy, plasmapheresis short term, liver transplant curative
2. Crigler-Najjar syndrome type 2
- Milder AR
- Lower serum bilirubin < 20
- IV phenobarbital, serum bilirubin reduced
D-xylose test with oral xylose load used to assess the absorptive capacity of the __.
Proximal small intestine
- D-xylose not absorbed in the intestine, thus excreted in feces, DEC excretion in urine (celiac sprue)
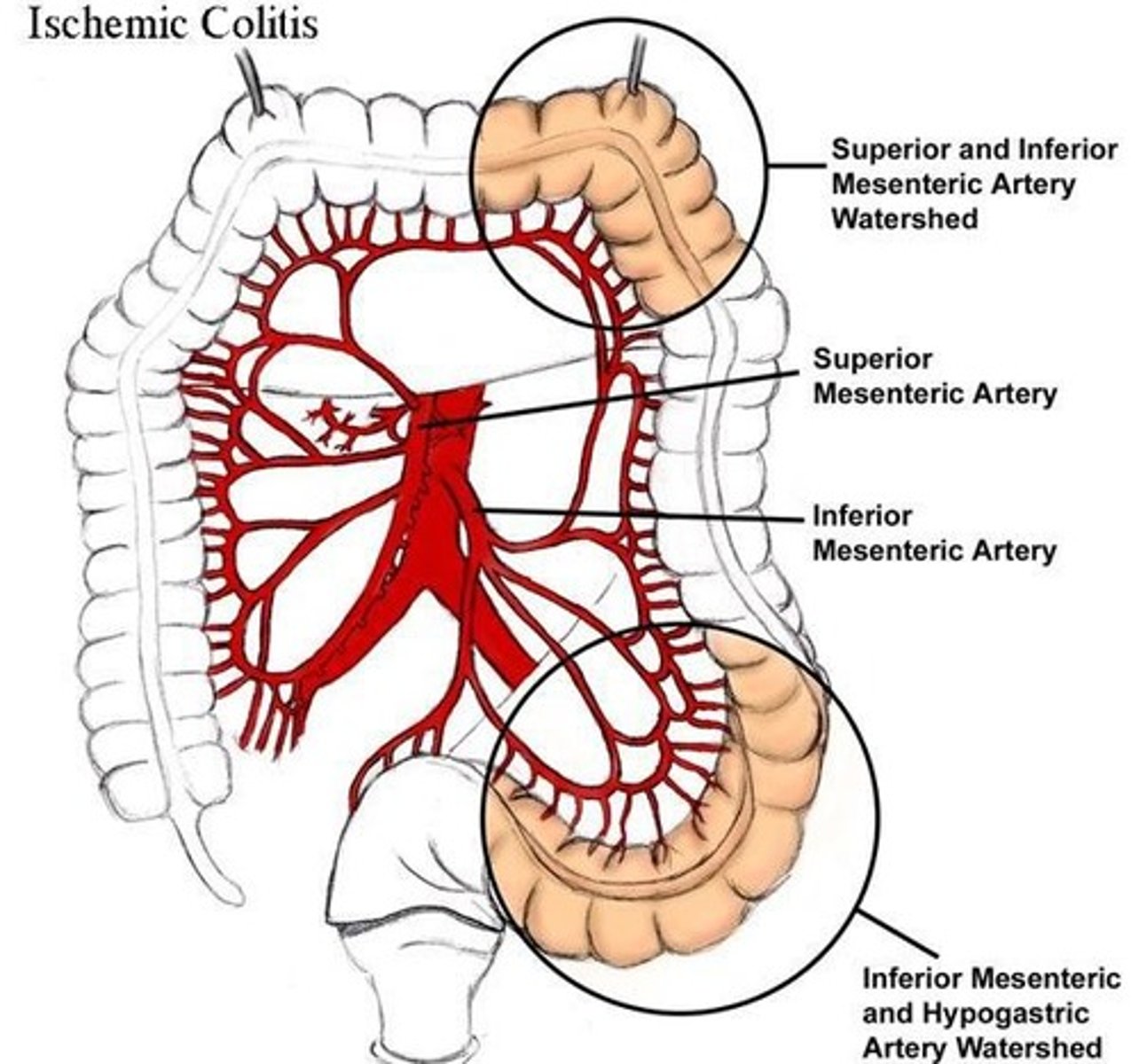
Suspect ___ in pts who have evidence of atherosclerotic vascular dz, present with abd pain followed by bloody diarrhea, and have minimal abdominal exam findings.
Ischemic colitis
- Splenic flexure most common (supplied by end arteries)
- vulnerable to ischemia during systemic hypotension in "water-shed" areas
- X-ray show "thumb printing"
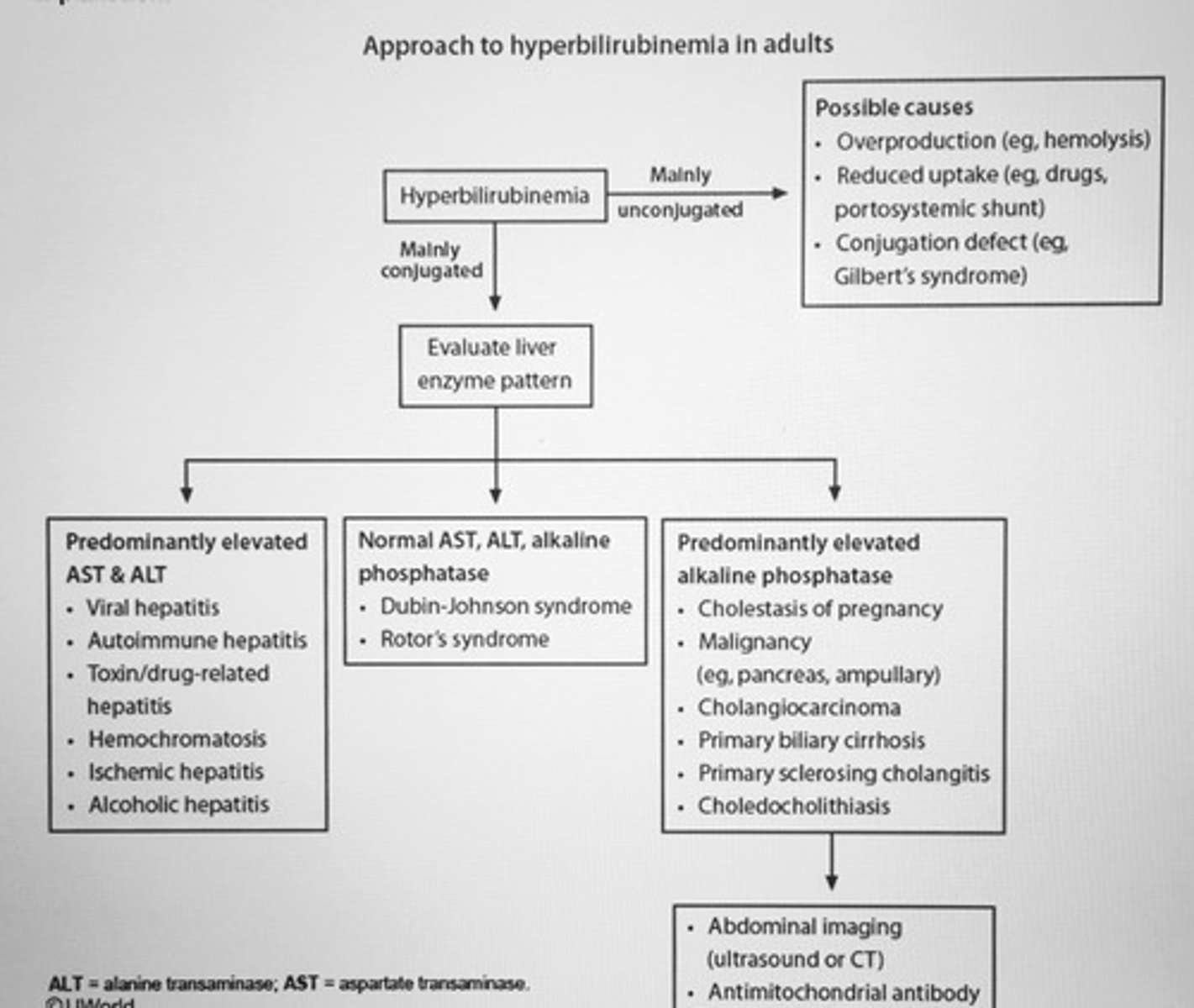
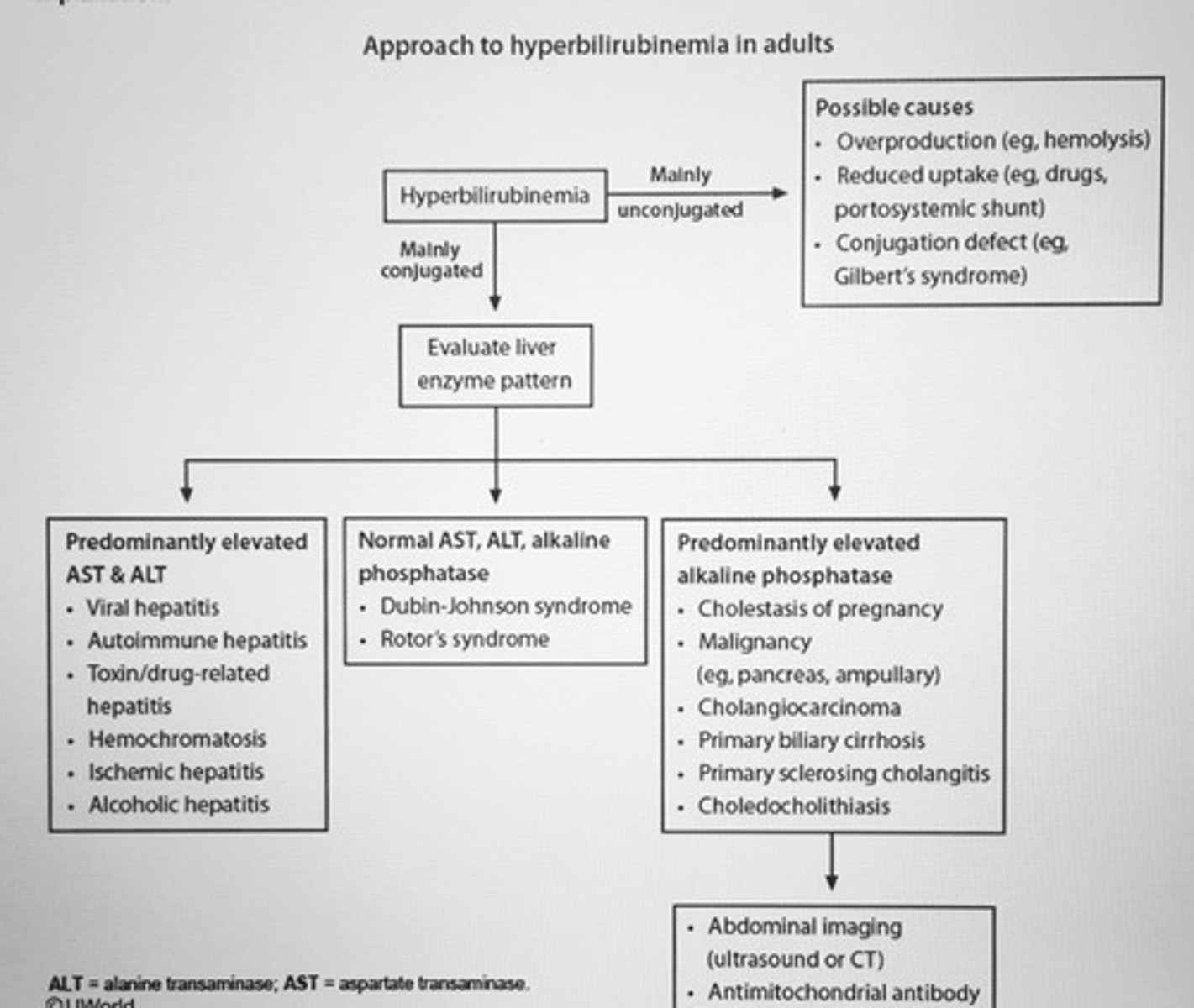
Approach to hyperbilirubinemia in adults algorithm
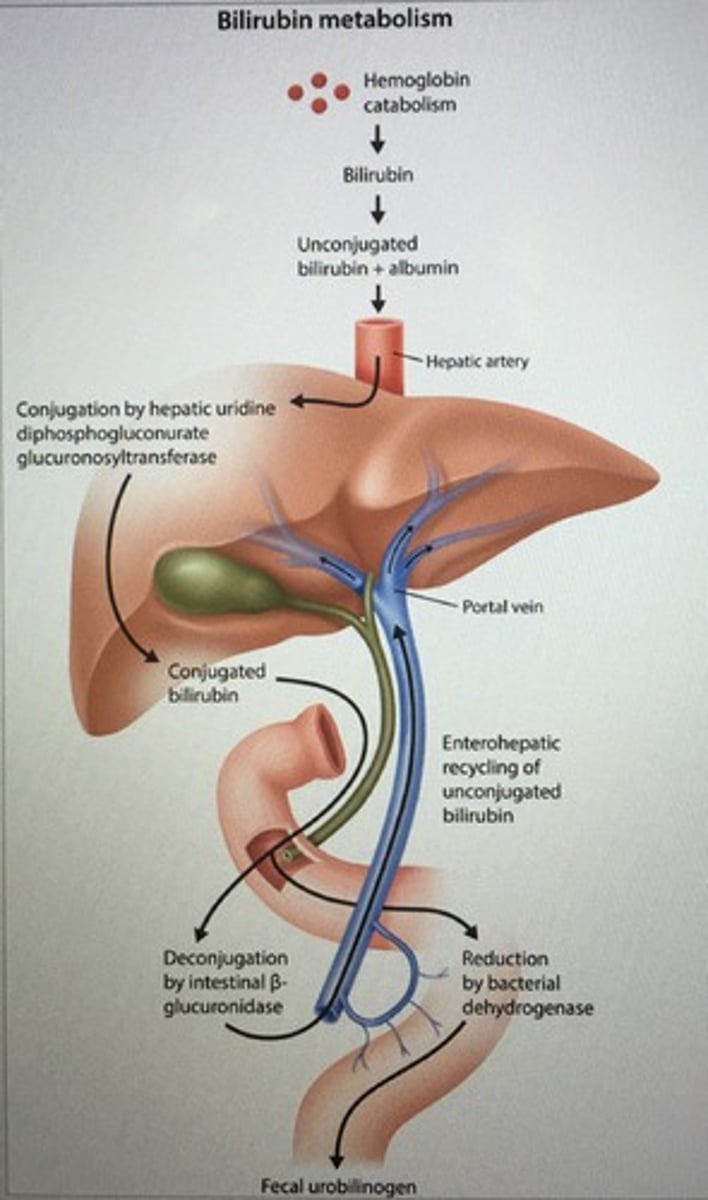
Bilirubin metabolism
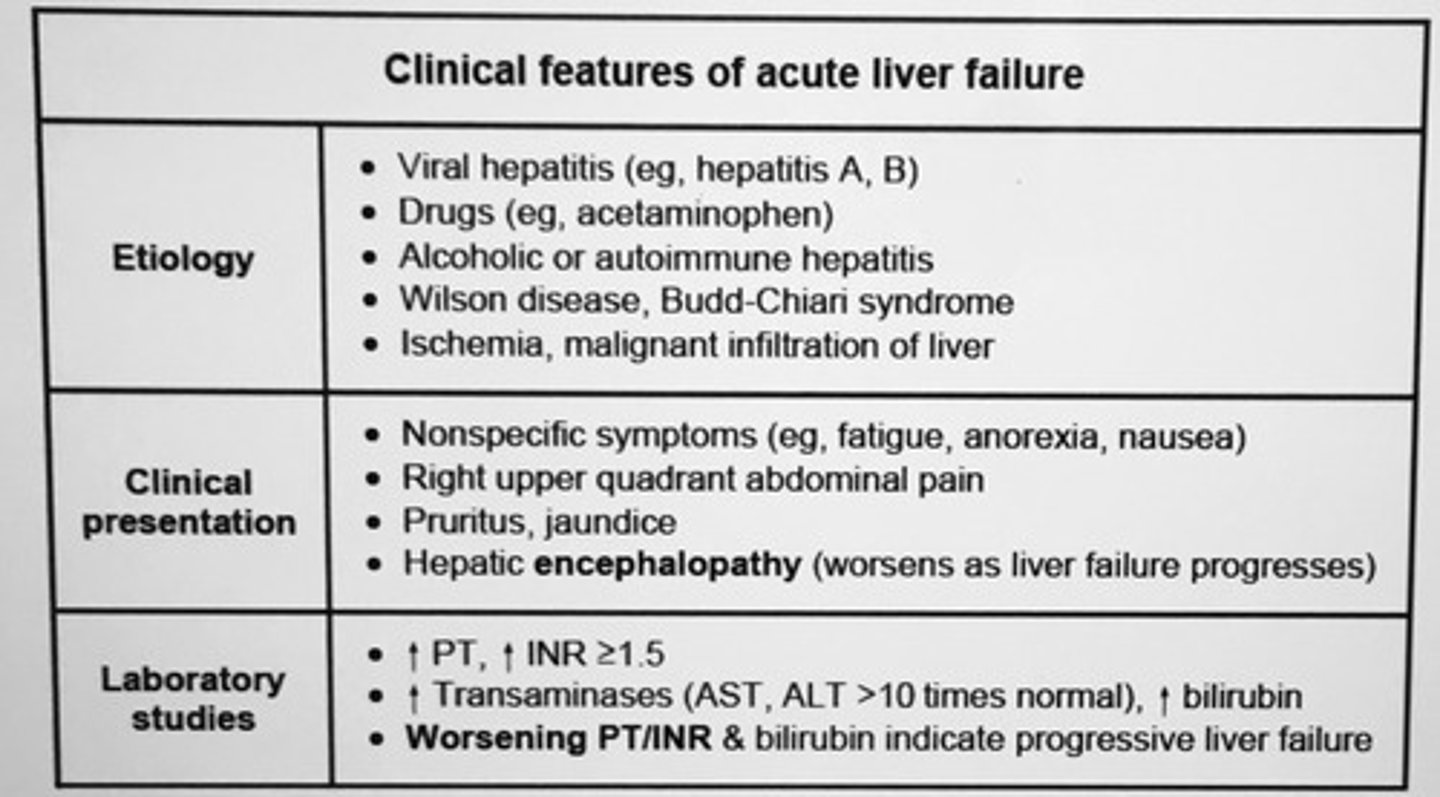
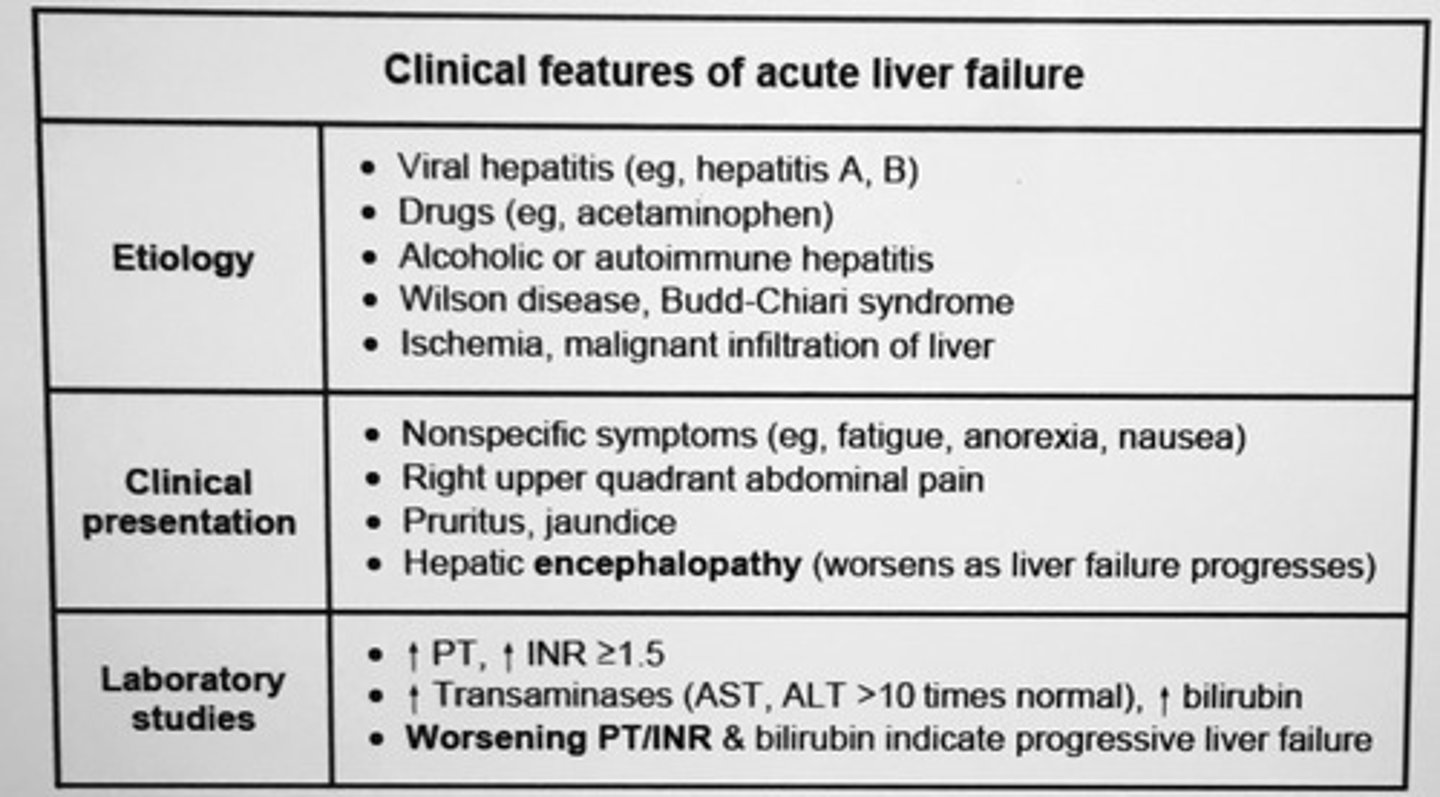
Clinical features of acute liver failure etiology, clinical presentation, lab studies.
Common caused of vanishing bile duct syndrome?
- Primary biliary cirrhosis (MCC)
- Failing liver transplant
- Hodgkin's dz
- g-v-host dz
- Sarcoid
- CMV
- HIV
- Medication toxicity
Vanishing duct syndrome, progressive destruction of intrahepatic bile ducts, ductopenia
Porcelain gallbladder results from the intramural deposition of ___ , is usually diagnosed on abdominal imaging, is associated with an INC risk of ___, and requires ___.
Calcium salts
Gallbladder carcinoma
RESECTION
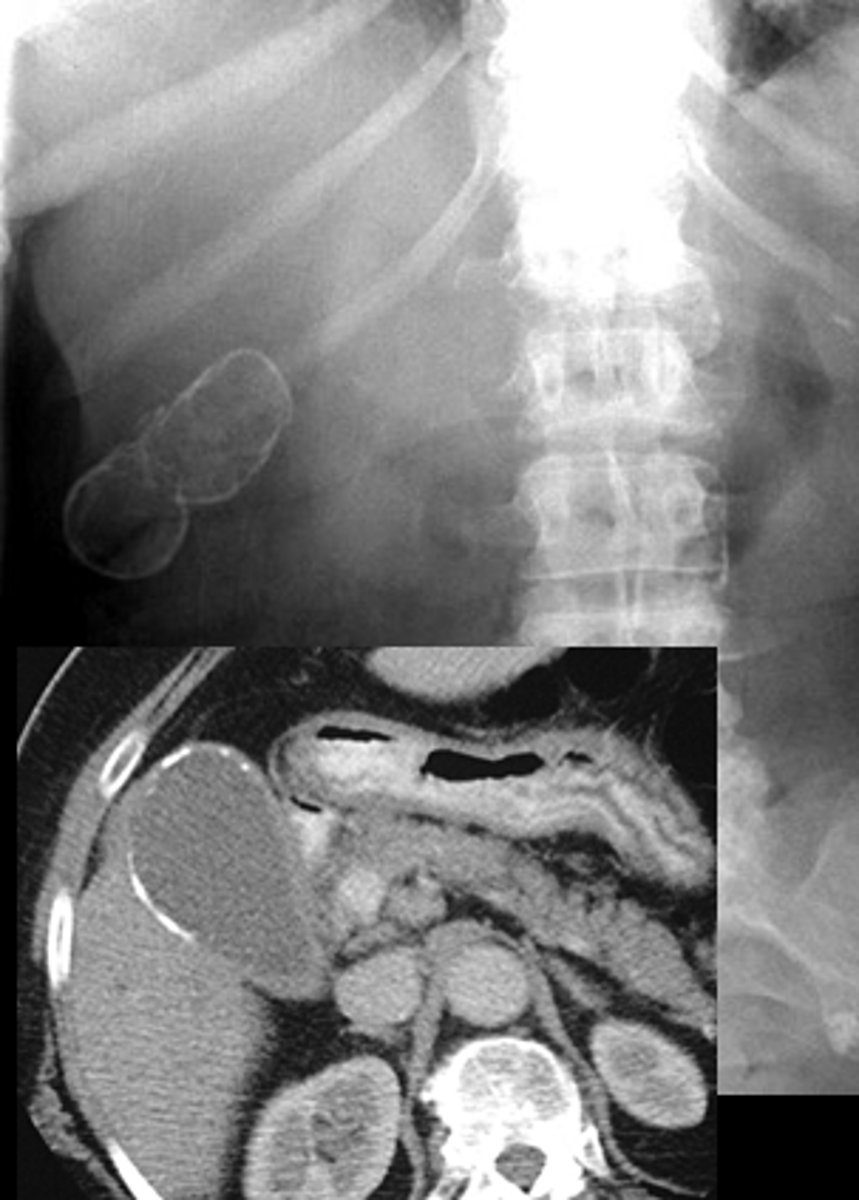
Classic PE findings in pancreatic carcinoma.
Nontender but palpable gallbladder at the R costal margin in a jaundiced patient (Courvoisier's sign)
L supraclavicular adenopathy (Virchow's node) pt with metastatic dz
Which imaging modality is the most sensitive and specific for diagnosis of pancreatic carcinoma.
Abdominal CT
Dysphagia
Severe pain
Heavy salivation
Mouth burns
Which poison?
Caustic poisoning
- does not cause alteration in consciousness
- damage is result of necrosis of tissue that lines GI tract
- severe case, perforation of the stomach or esophagus can occur causing peritonitis and mediastinitis
___ is the most common source of liver metastases
Colorectal cancer
- as blood from the colon moves through the portal circulation directly to the liver
- colonoscopy diagnostic step localizes tumor and provides tissue dx
*lung and breast also mets to liver but less common than GI malignancies
Management of gallstones.
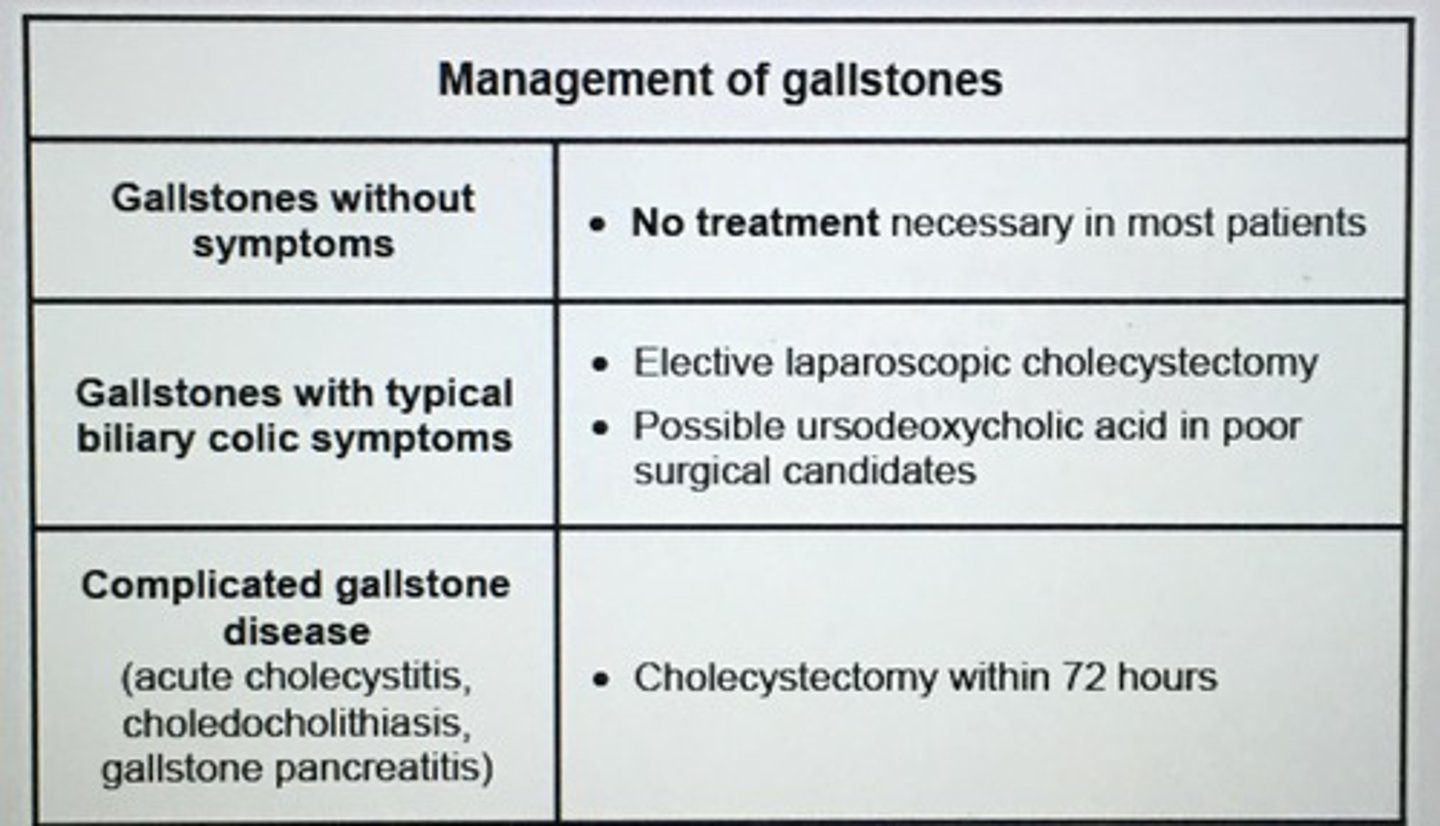
Acalculous Cholecystitis
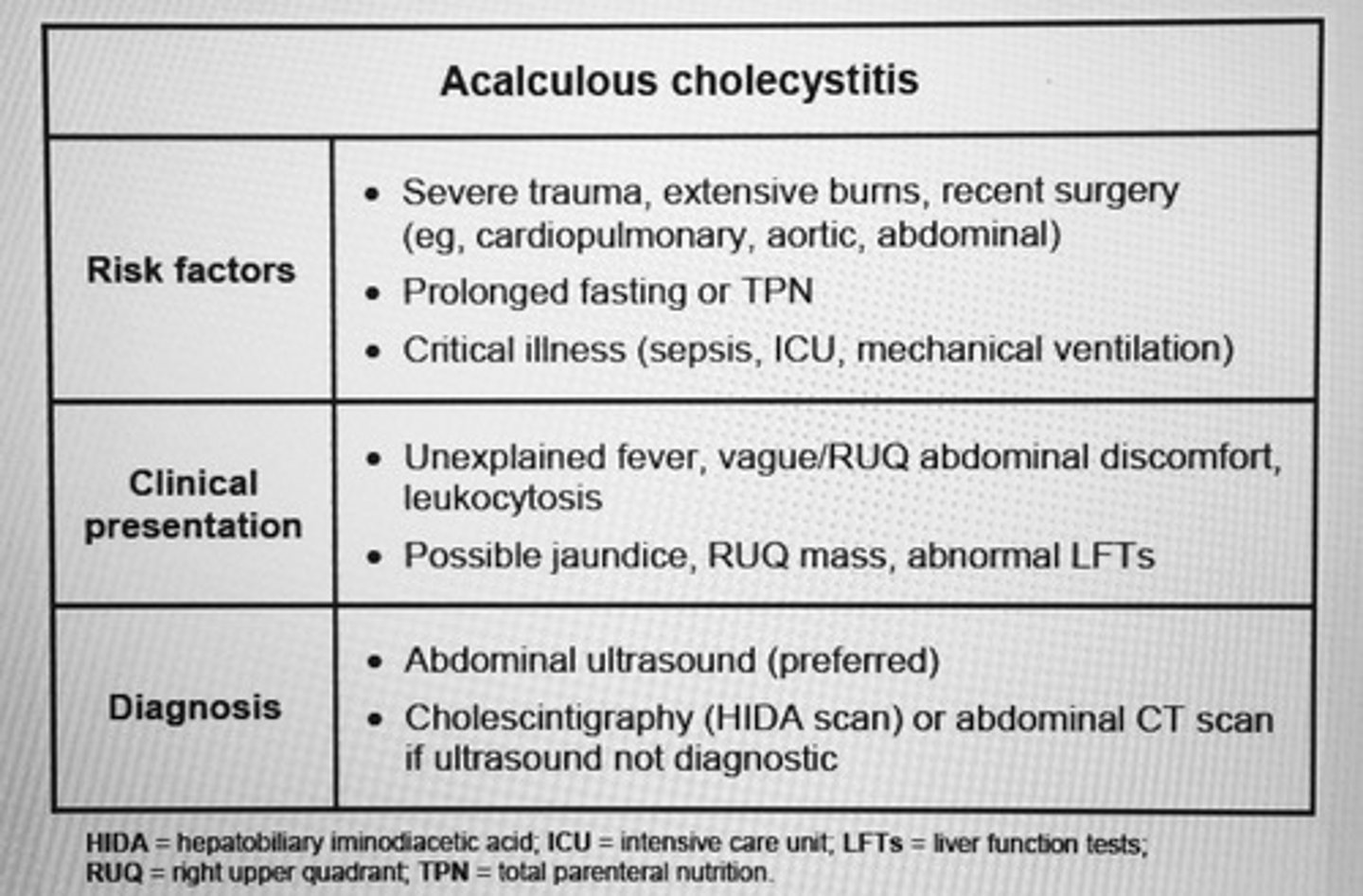
Acute cholangitis
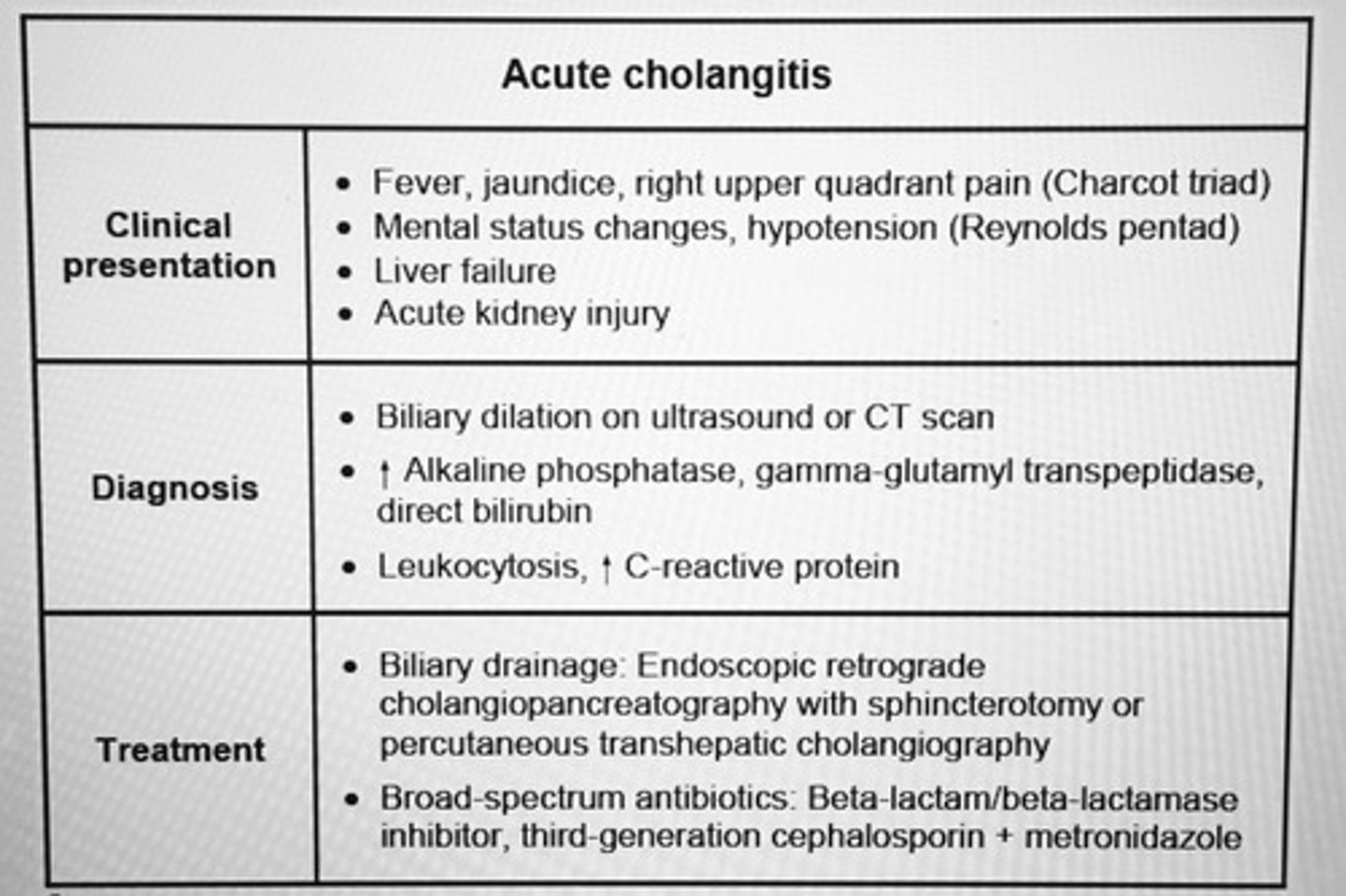
Chronic mesenteric ischemia
Shunting of blood away from the small intestine to meet the INC demand of the stomach
- in patients with atherosclerosis, the celiac or SMA may be narrowed and unable to dilate to maintain adequate blood flow to intestines

Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease

Clinical features of esophageal perforation
Small intestine bacterial overgrowth
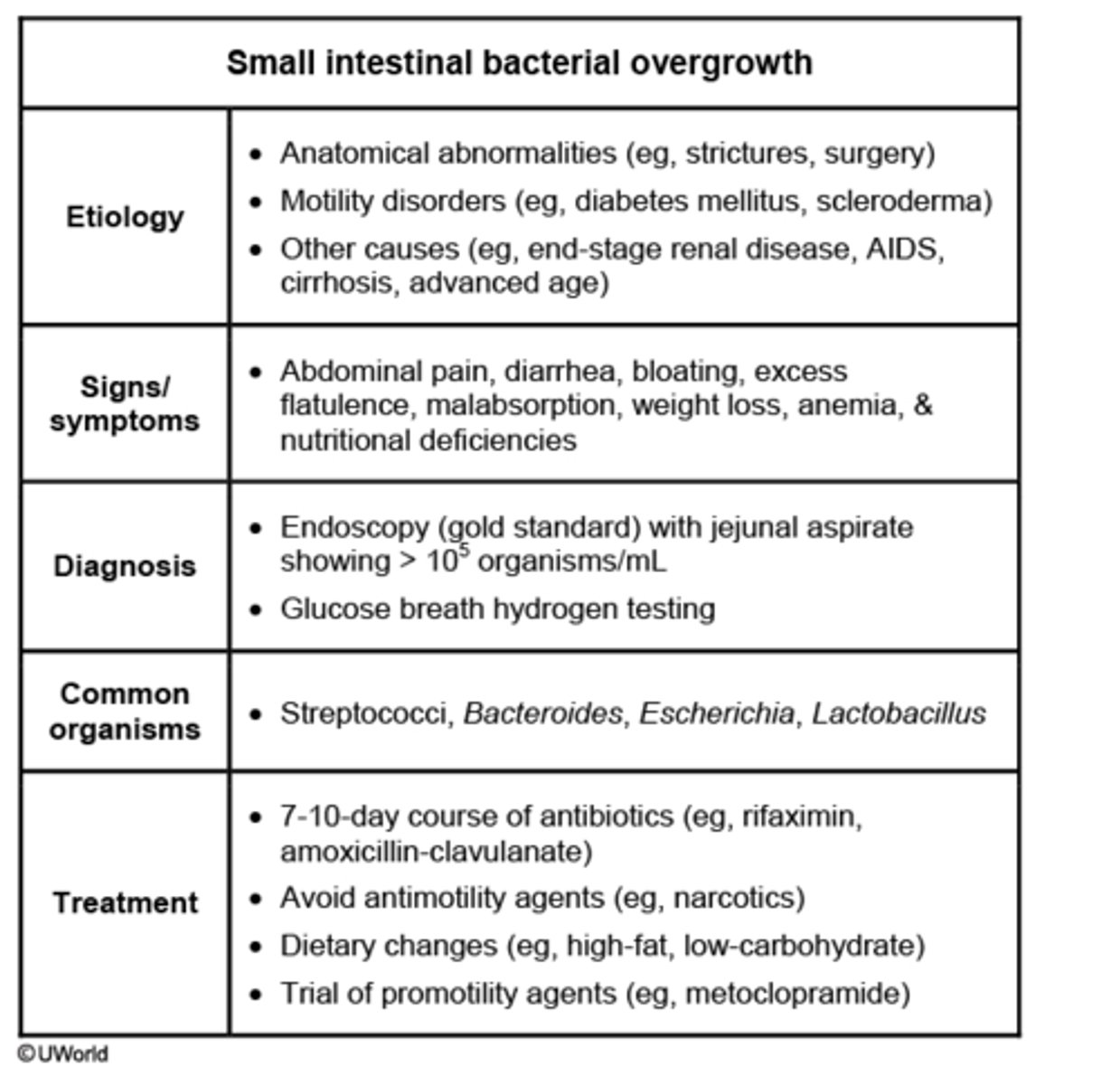
Gold standard diagnosing small-intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO).
Endoscopy with jejunal aspirate showing >10^5 organisms/mL
- presents with abd bloating, flatulence, and diarrhea, deficiency of calcium, vitamin B12, and fat-soluble vitamins
Dx of acute pancreatitis requires which of the following?
2 of the following
- acute epigastric pain radiating to the back
- INC amylase or lipase > 3x normal limit
- abnormalities on imaging consistent with pancreatitis (US if suspect gallstone pancreatitis)
Clostridium difficile colitis treatment algorithm
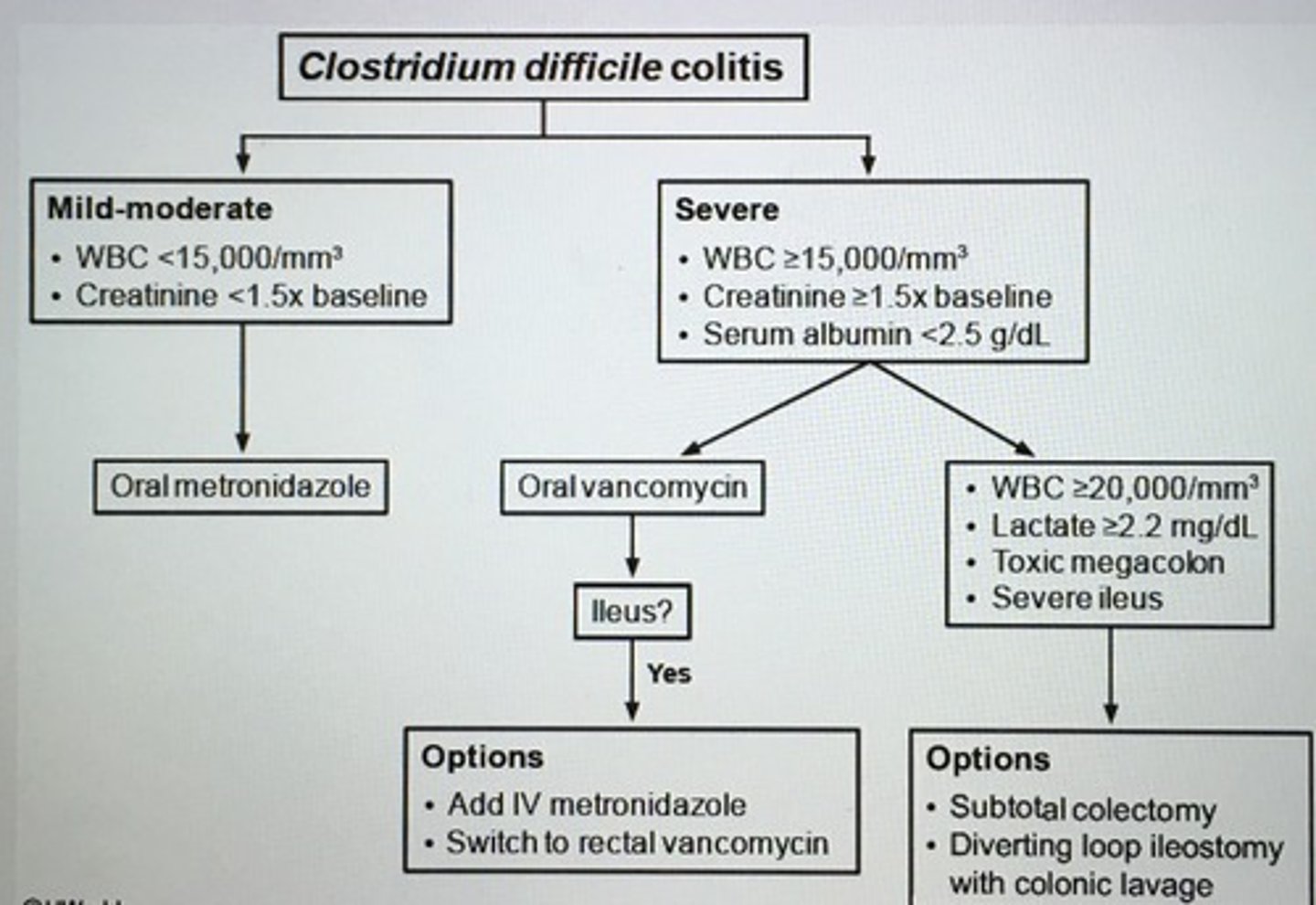
___ is a bacterial antibiotic that is usually reserved for recurrent colitis or an initial therapy for patients with severe colitis who cannot tolerate oral vanco.
Fidaxomicin
Clinical features of acute diverticulitis
Tea and toast type diet is associated with ___ deficiency.
Folate
- heat sensitive
- depleted in 4-5 months leading to DEC RBC production and microcytic anemia
Approach to hyperbilirubinemia in adults
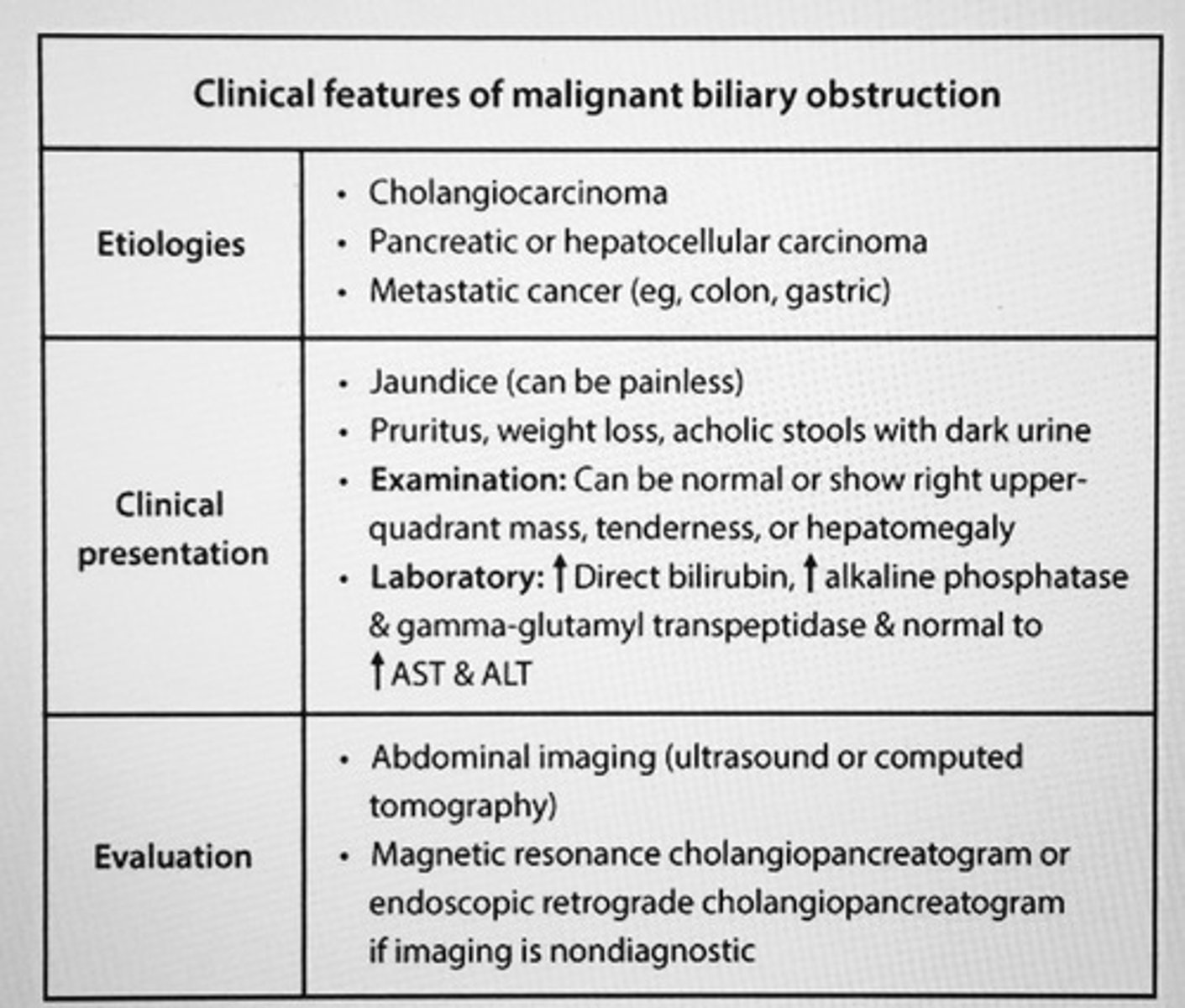
Clinical features of malignant biliary obstruction
In gastric adenocarcinoma, tumor staging at the time of diagnosis determines prognosis and treatment options. ___ is the initial staging modality.
CT scan
Massive doses of aspirin and NSAIDs can cause ___ and upper GI bleeding.
Acute erosive gastritis
- aspirin decreases the protective prostaglandin production, aspirin and alcohol cause direct mucosal injury, leads to decrease in protective barrier -> leak of acid and proteases that penetrate lamina propria -> hemorrhage
Precipitating factors hepatic encephalopathy
1. Drugs (sedatives, narcotics)
2. Hypovolemia (diarrhea, vomiting, diuretics, high volume paracentesis)
3. Excessive nitrogen load (GI bleeding, constipation, high protein diet)
4. Hypokalemia & hypoglycemia
5. Infection (pneumonia, UTI, SBP)
6. Portosystemic shunting (surgical shunts)
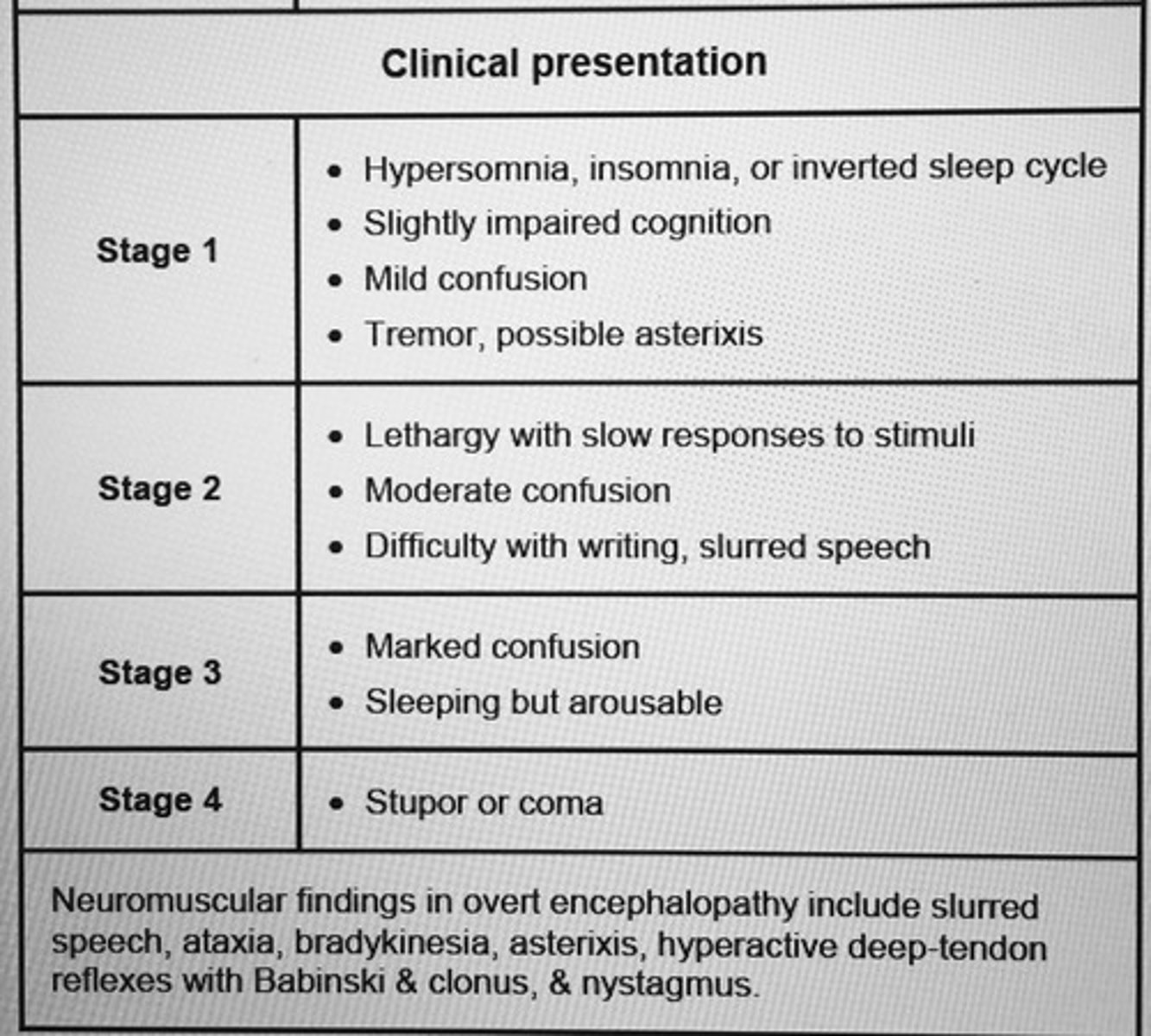
Staging of hepatic encephalopathy
neurotoxins stimulation of inhibitory (GABA) and impairment of excitatory (glutamate) pathways in the brain
Esophageal cancer
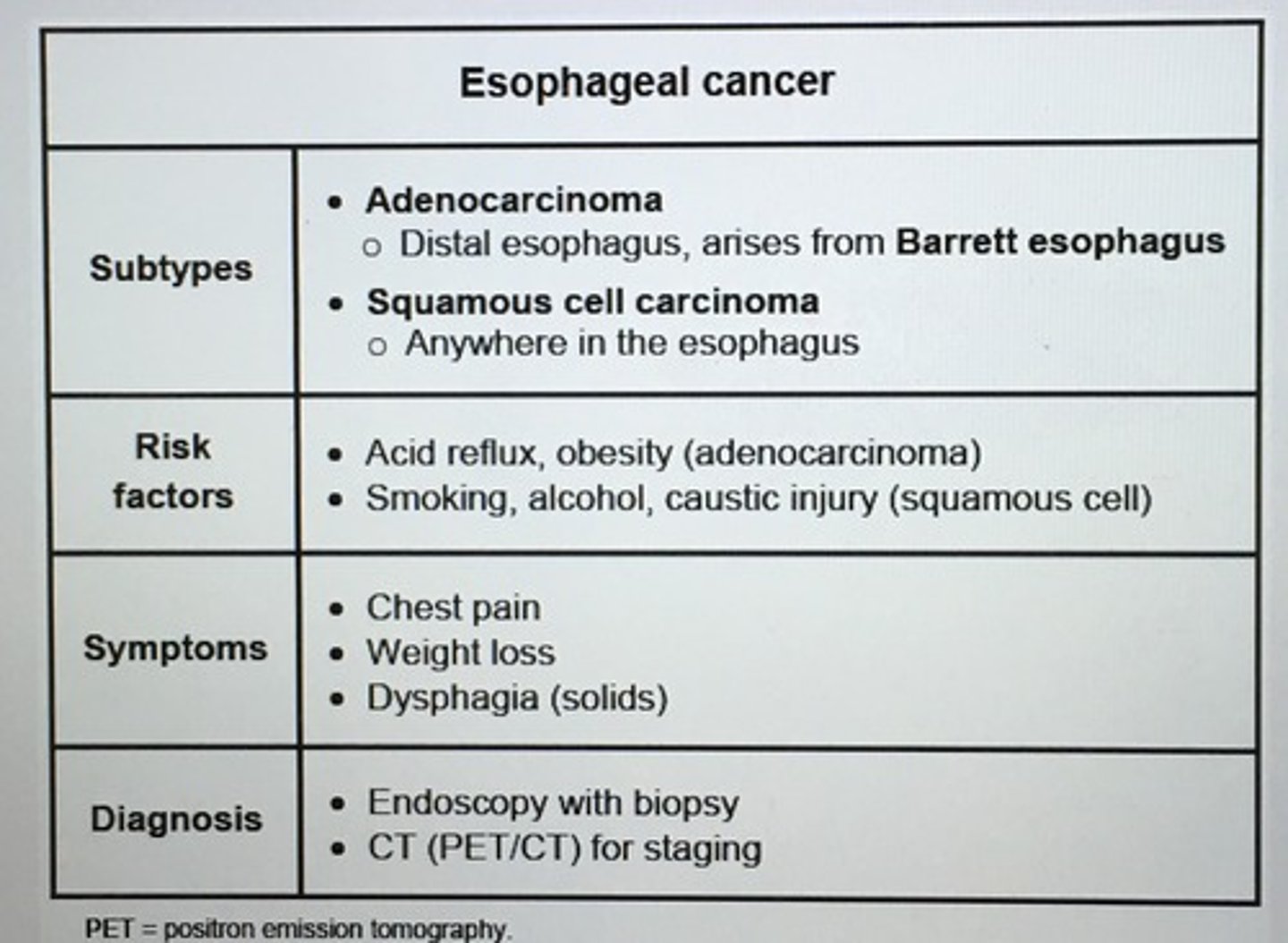
Diagnosis of esophageal cancer requires ___.
Esophageal endoscopy with bx
- young, low risk patient with undetermined esophageal sxs may start with barium esophagram
EGD:
- > 55 years of age
- alarm sxs (wt loss, gross or occult bleeding, early satiety)
Lactose tolerance is characterized by a positive ___ test.
Positive hydrogen breath test
Positive stool test for reducing substances
LOW stool pH
INC stool osmotic gap
NO steatorrhea
Gold standard dx Wilson's disease.
Liver bx that shows quantitative hepatic copper level > 250 mcg/gram dry weight
More commonly, dx confirmed by presence of low serum ceruloplasmic (<20 mg/dL) with INC urinary copper excretion or Kayser-Fleischer rings
Tx Wilson's disease
1. Copper chelators (d-penicillamine or trientine)
2. Oral zinc (prevent absorption)
3. Liver transplant only option for those with fulminant hepatic failure or decompensated liver disease does not respond to pharm
Tx of familial colonic polyposis (FAP).
Mutation APC gene
- a patient with FAP and hundreds of adenomas in the colon has 100% risk of cancer -> elective protocolectomy
Acute pancreatitis by hypotension is through to arise from intravascular volume loss 2/2 ___.
Local and systemic vascular endothelial damage
- > vasodilation, INC vascular permeability, and plasma leak into the retroperitoneum, resulting in systemic hypotension
tx: supportive care with several Liters of IV fluid to replace the lost intravascular volume
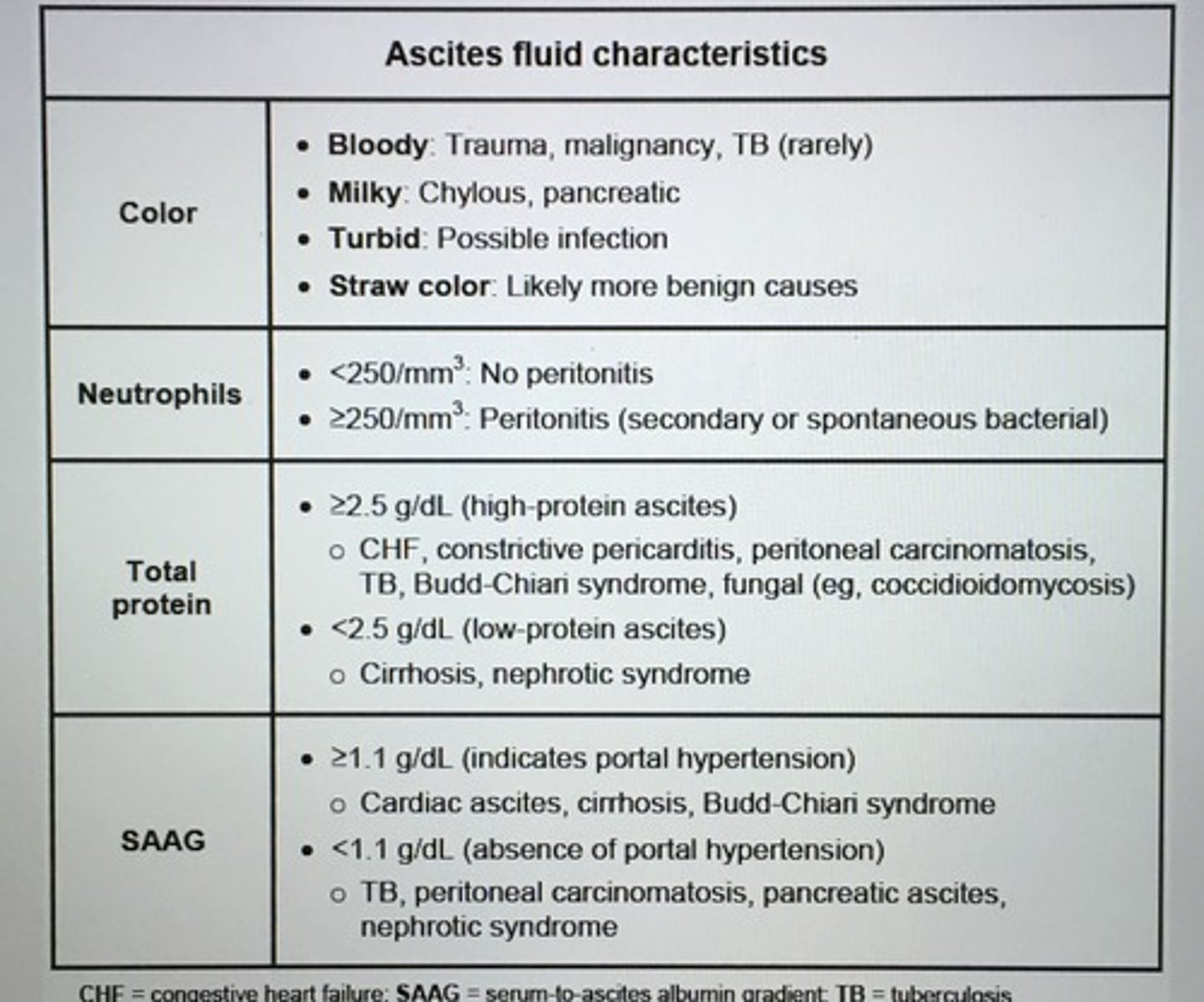
Ascites fluid characteristics
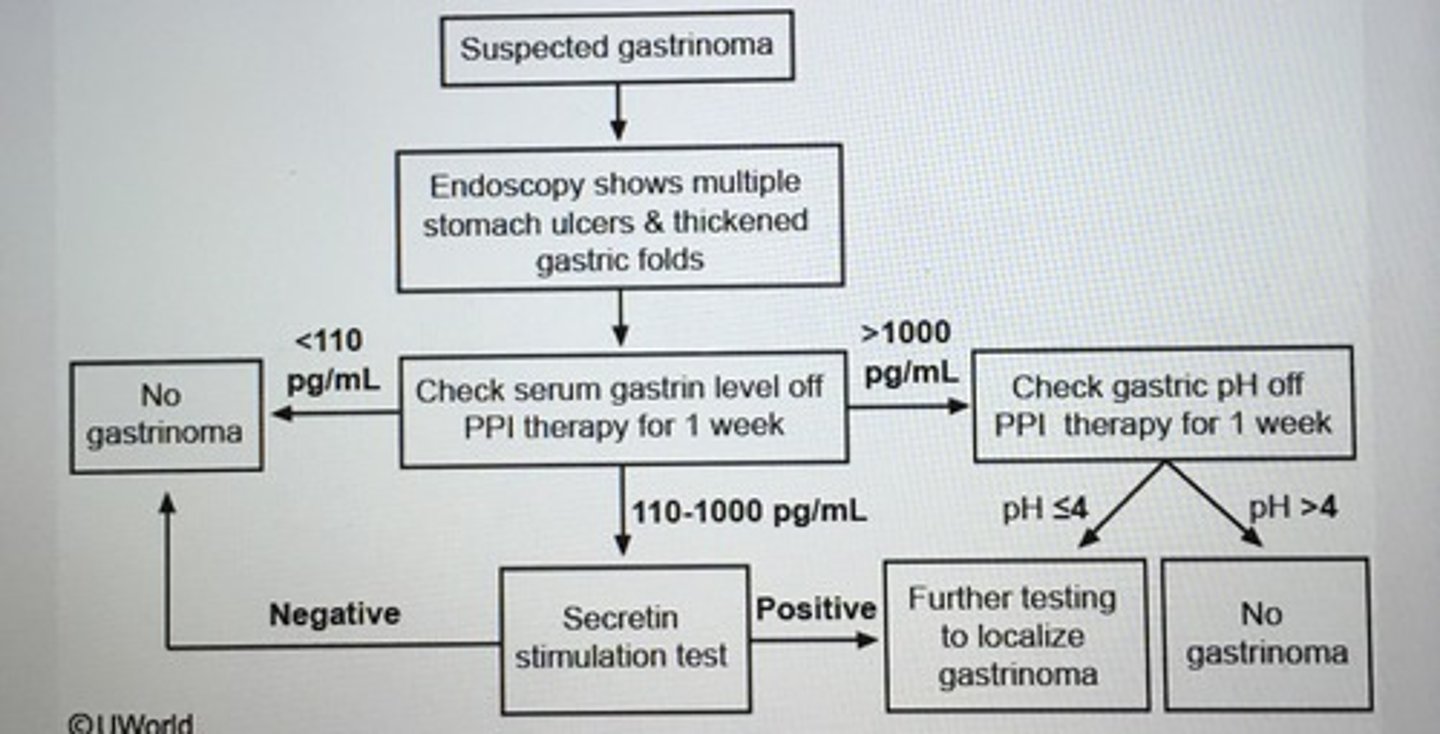
___ should be suspected in patient with multiple stomach ulcers and gastric folds on endoscopy.
Gastrinoma (Zollinger-Ellison syndrome)
- fasting serum gastrin level > 1000 pg/mL
All patient with chronic liver disease should be immunized against ___.
Hep A and B
Common causes of steatorrhea

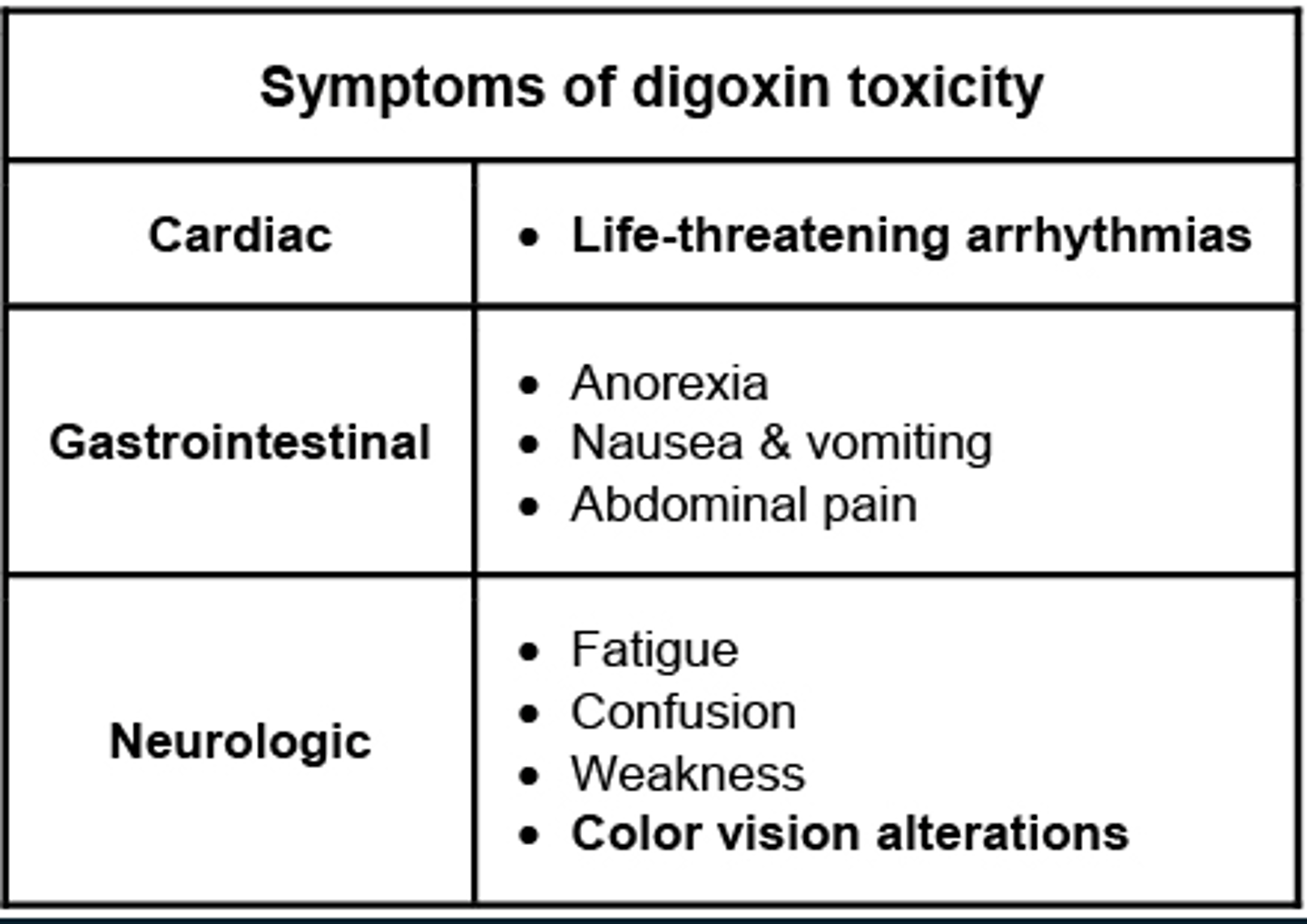
Symptoms of digoxin toxicity.
- DEC digoxin by 25-50% when initiating amiodarone therapy (verapamil, quinidine, and propafenone) INC the serum levels of digoxin
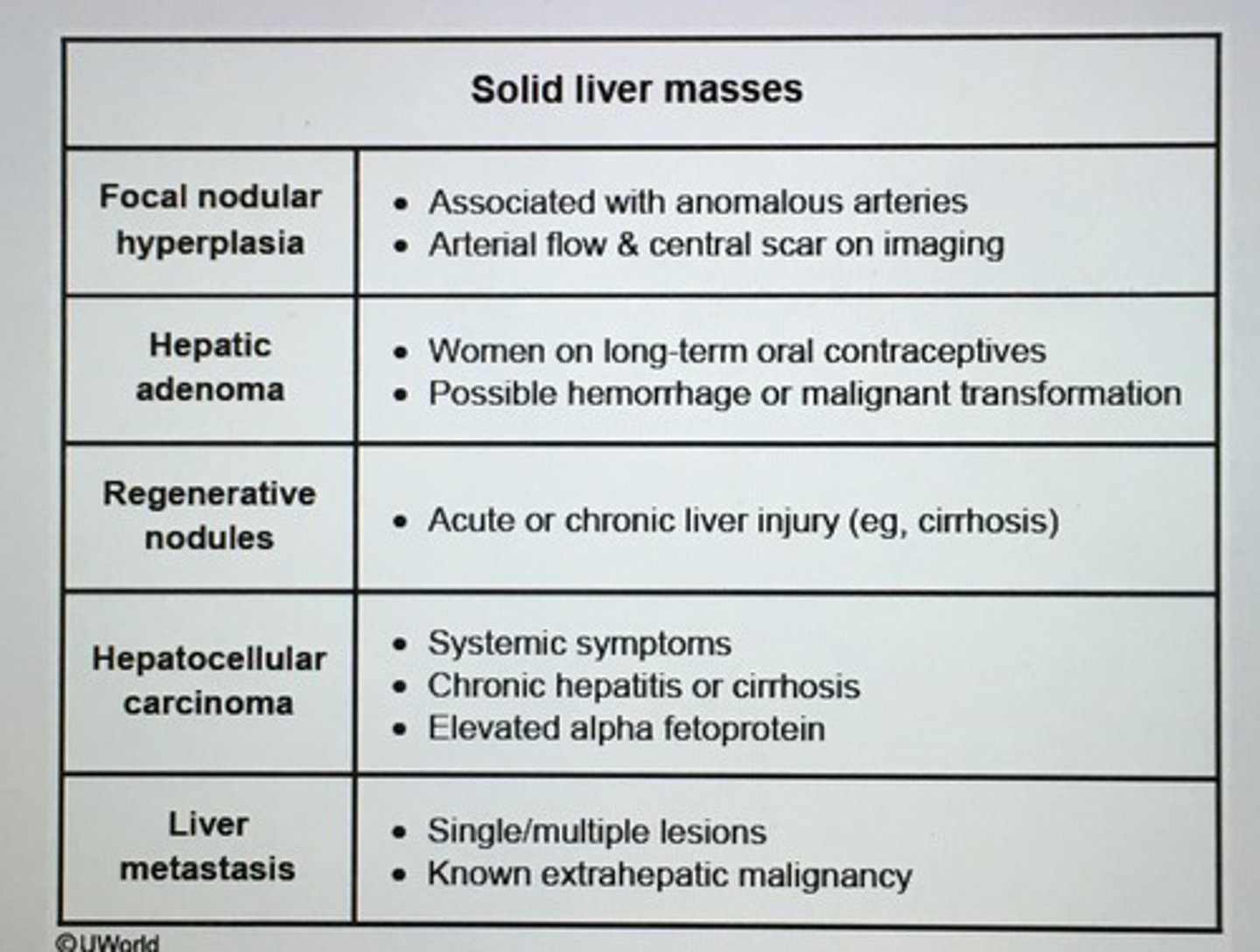
Solid liver masses
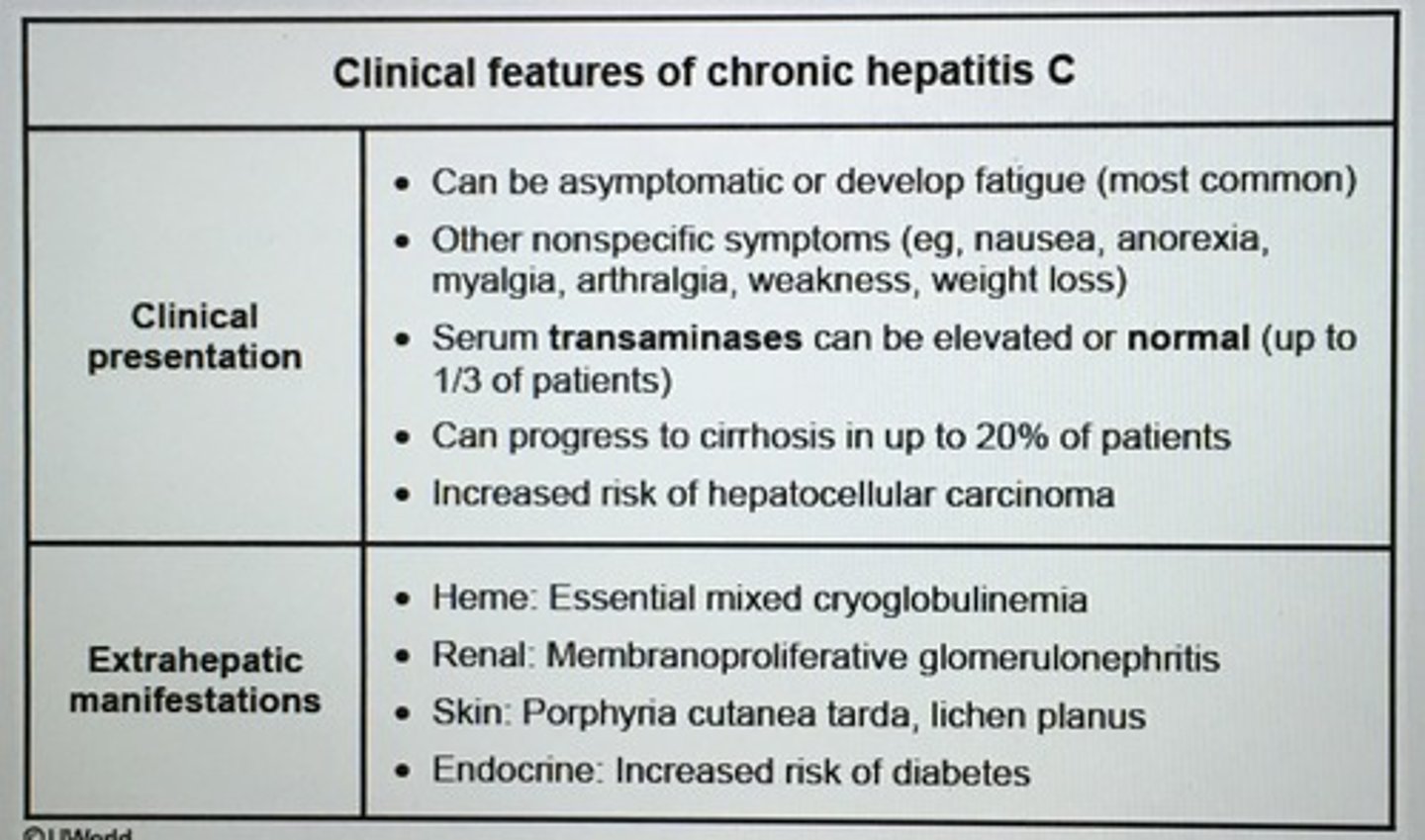
Clinical features of chronic hepatitis C
Porphyria cutanea tarda - fragile skin, photosensitivity, and vesicles and erosions on the dorsum of the hands
Essential mixed cryoglobulinemia: circulating immune complexes that deposit in small or medium vessels and may be associated with low serum complement levels
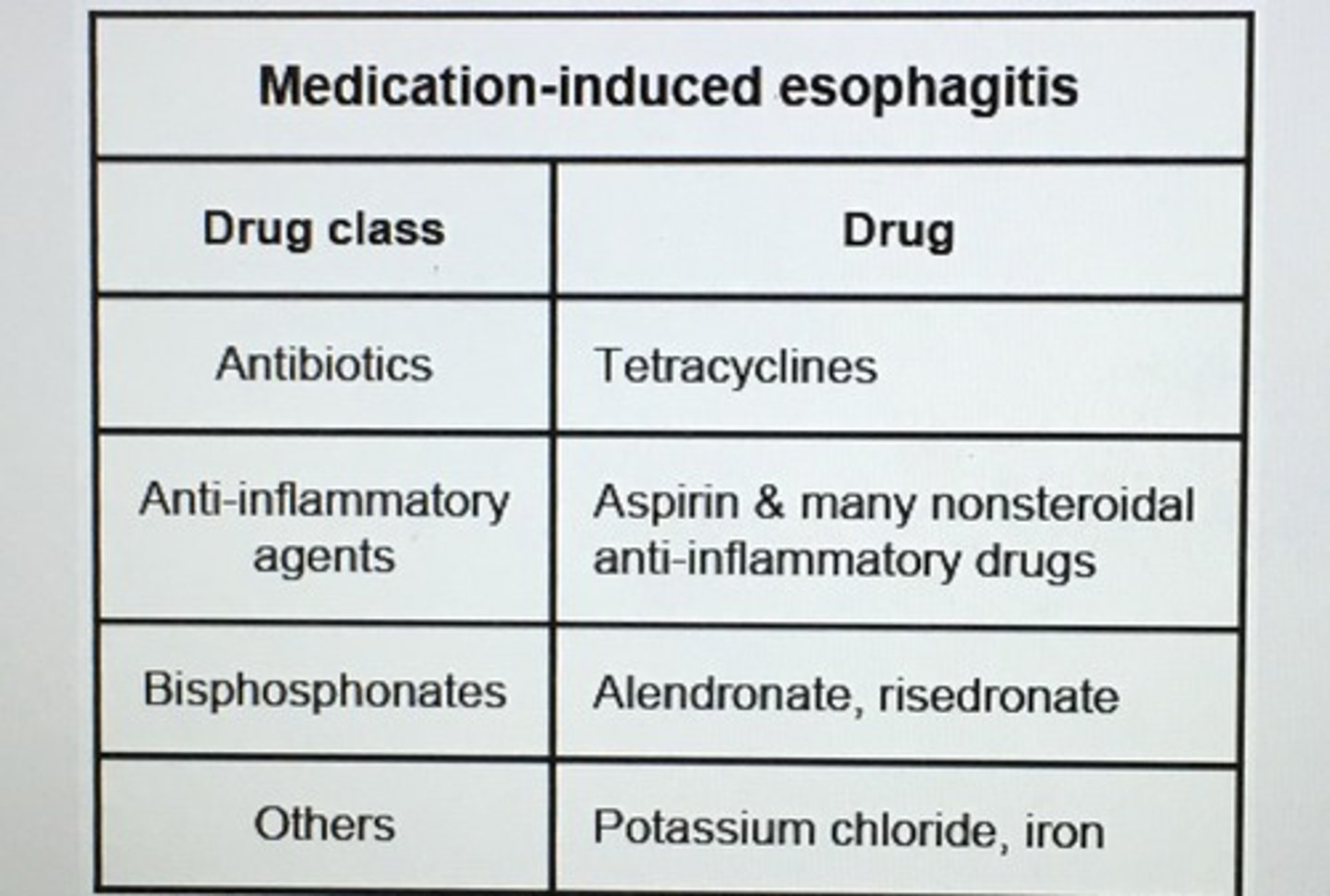
Medication-induced esophagitis
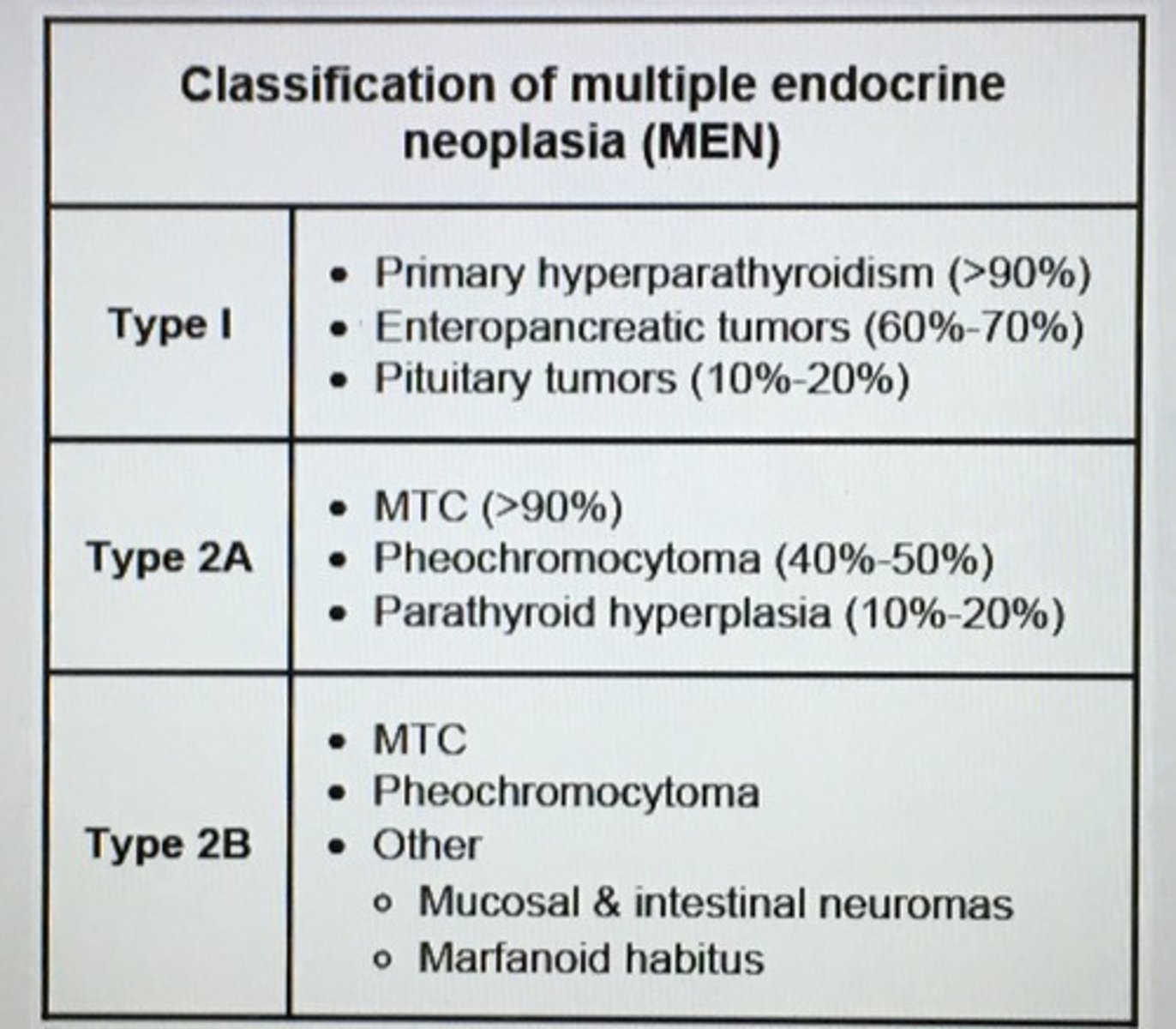
Classification of multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN)
___ is the single most important prognostic indicator in acute liver failure.
PT
Acute liver failure is defined as ___.
Acute onset of severe liver injury with encephalopathy and impaired synthetic function (INR > 1.5) in a patient with cirrhosis and underlying liver disease
* rapidly progressing liver failure can have decreasing transaminases with worsening PT/INR and bilirubin
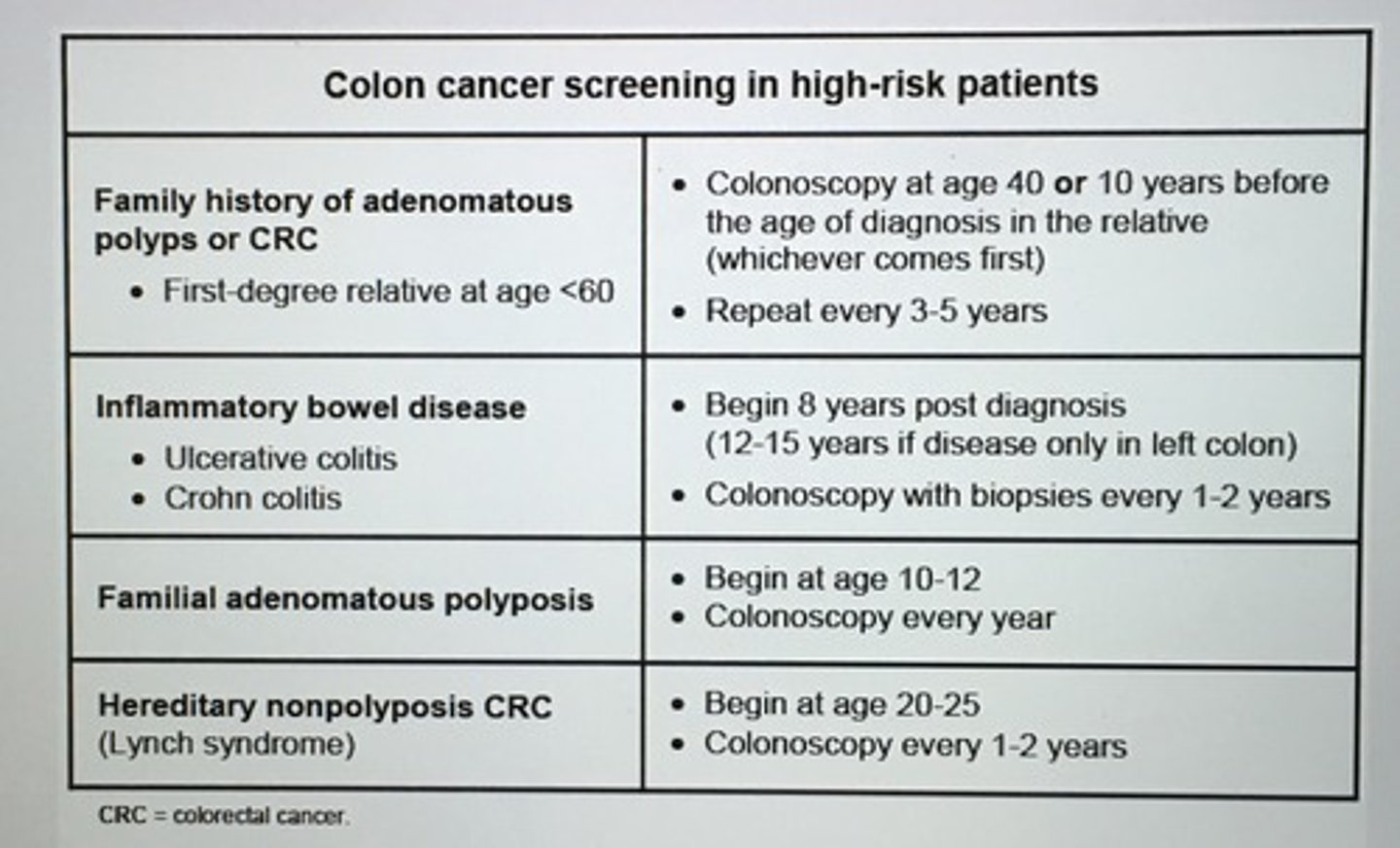
Colon cancer screening in high-risk patients
Anticoagulation with warfarin places patients at risk for hemorrhage. ___ may occur even with supra therapeutic INR. Pt has back pain and sxs of hemodynamic compromise should raise suspicion for ___.
Retroperitoneal hematoma
GI bleeding often have an elevated ___ 2/2 breakdown of hemoglobin and associated hypovolemia.
INC BUN/creatitine ratio
- INC urea production from breakdown of hemoglobin and INC urea reabsorption in the proximal tubule due to associated hypovolemia
Labs in alcoholic hepatitis
1. Elevated AST & ALT < 300 U/L
2. AST: ALT ratio > 2
3. Elevated Gamma-glutamyltransferase, bilirubin, INR
4. Leukocytosis (neutrophils)
5. DEC albumin if malnourished
6. Abd imaging showing fatty liver
7 INC ferritin, acute phase reactant
Only marker for acute HBV infection during the window period.
Anti-HBc
Toxic megacolon diagnosis confirmed with?
Plan abd x-rays and 3 of the following:
- Fever > 38 (100.4)
- Pulse > 120/min
- WBC > 10, 500
- anemia
tx: IV steroids, NG decompression, abx, and fluids
Risk factors: IBD, C. difficile
__ deficiency may result from chronic total parenteral nutrition or malabsorption. Sx alopecia, skin lesions, abnormal taste, and impaired wound healing.
Zinc
- whole grains, beans, nuts
- jejunum
The development of palpable mass in the epigastrium 4 weeks after the onset of acute pancreatitis is highly suggestive of ___.
Pancreatic pseudocyst
- U/S
- only drain if it persists > 6 weeks, > 5 cm, or becomes secondarily infected
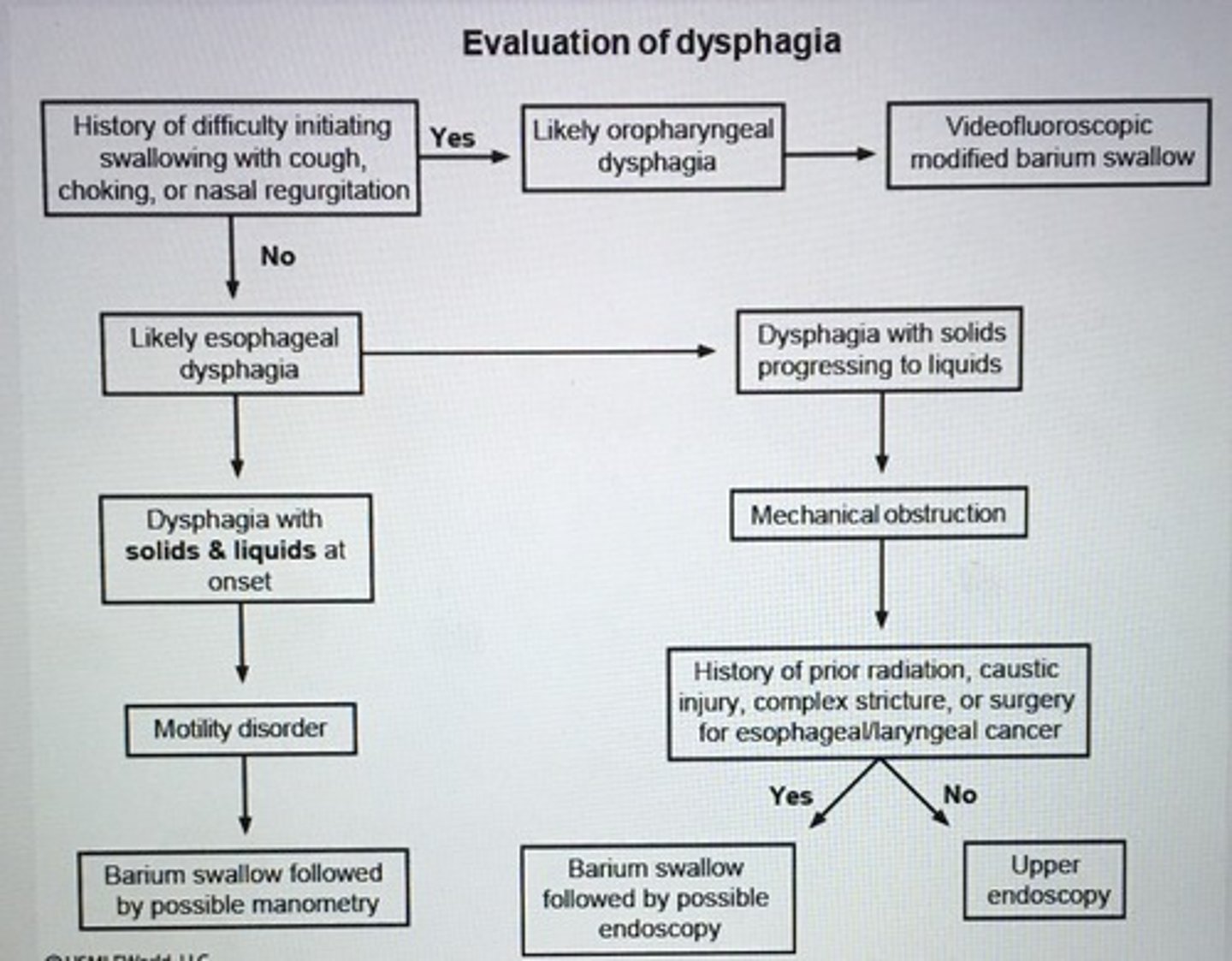
Evaluation of dysphagia.