Physics IGCSE - Energy, work and power
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Different types of energy storage
Type of energy | Example |
Chemical | fossil fuels |
thermal | hot water |
kinetic | moving objects |
gravitational | roller coaster at the top |
elastic | stretched elastic band |
nuclear | nucleus of atom |
electrostatic | two opposite charges held apart |
electromagnetic | two opposite poles of 2 magnetic held apart |
Describe how energy is transferred between stores during events and processes of transfer by forces (mechanical work done)
force is applied → moves an object through a distance
Describe how energy is transferred between stores during events and processes of electrical currents (electrical work done)
charges flow (electricity)
Describe how energy is transferred between stores during events and processes of heating and by electromagnetic
energy transferred between hot and cold
Describe how energy is transferred between stores during events and processes of sound and other waves
energy transferred as a wave (e.g. light wave)
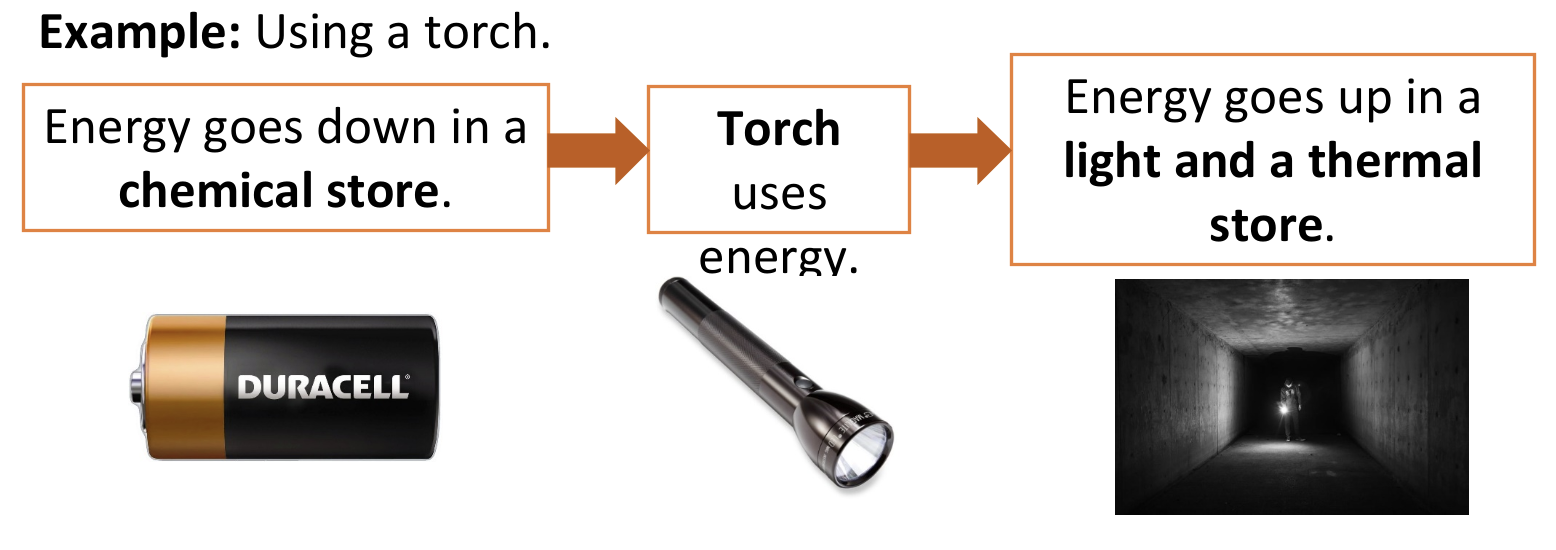
Law of conservation of energy
energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred from 1 form
Apply this law of conservation of energy to simple examples including the interpretation of simple flow diagrams
Gravitational potential energy
- object gains GPE when lifted from ground
- object loses GPE when lowered towards ground
Gravitational potential energy (GPE) formula
GPE (J) = mass (kg) x gravitational acceleration (m/s2) x change in height (m)
Ep = mgΔh
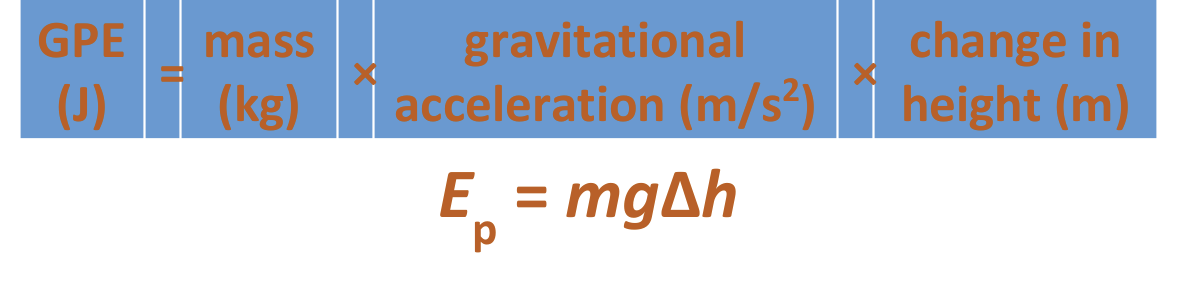
Kinetic energy formula
Kinetic energy = ½ x mass x velocity2
Ek = ½ mv2
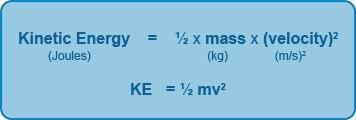
Work done = energy transferred
Work done
- product of force and distance moved in the direction of force
- measure of amount of energy transferred against resistive force
Work done formula
Work done (J) = force (N) x distance moved in direction of the force (m)
W = Fd = ΔE
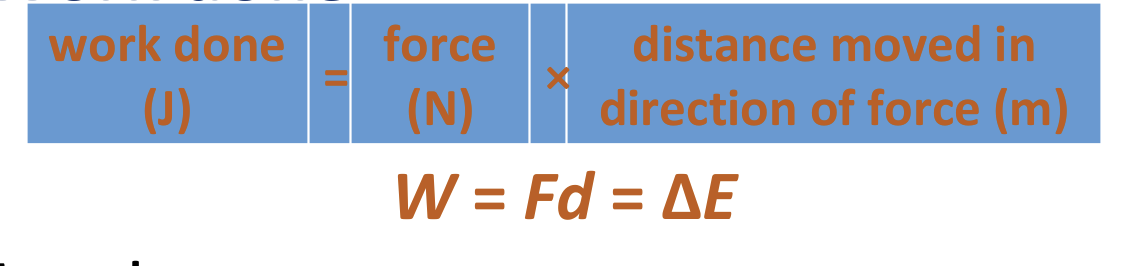
Non - renewable
source cannot be replenished within human lifetime
Renewable
source easily replenished within human lifetime
Types of renewable and non - renewable energy
Non - renewable | Renewable |
Nuclear fission | sun/solar |
Fossil fuels | wind |
wave | |
tidal | |
hydroelectric | |
geothermal | |
biofuel |
Examples of renewable and non - renewable energy
Energy | Examples |
Nuclear fission | heat released from nuclear fission heats water → creates steam for turbine |
Fossil fuels | generated in power plant → fuel is burned in boiler → steam to turn turbine |
sun/solar | converts sunlight into electricity |
wind | kinetic energy from win to turn blades → connected to rotor → drives generator |
wave & tidal | convert kinetic energy of water → into mechanical energy → drives generator |
hydroelectric | water flows through dams → spins turbine |
geothermal | uses heat from earth’s core to create steam → steam spins turbine |
biofuel | burned to heat water in boiler → steam that drives turbine to generator |
Advantages and disadvantages of renewable and nonrenewable energy
Advantages | Disadvantages | |
Renewable | - produces no pollutants | - high initial cost - weather dependent - takes up lot of space |
Nonrenewable | - high energy output - cheap to run - reliable | - produces greenhouse gases and other pollutants - finite supply |
Radiation from the Sun is the main source of energy for all our energy resources except geothermal, nuclear and tidal
How the sun’s energy is released
by nuclear fusion in the sun
How is energy released
by nuclear fission in nuclear reactors
Energy efficiency
waste less energy as a proportion of input
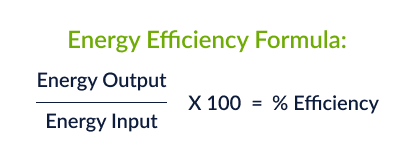
Energy efficiency formula
Efficiency (%) = useful energy output/total energy input × 100%
Energy Efficiency formula (Power)
Efficiency (%) = useful power output/total power input x 100%

Power
work done per unit time/energy transferred per unit time
SIU: watts (W)
1W = 1J/s
Power Formula
power (W) = work done (J)/time (s) = energy transferred (J)/time (s)
P = W/t = ΔE/t
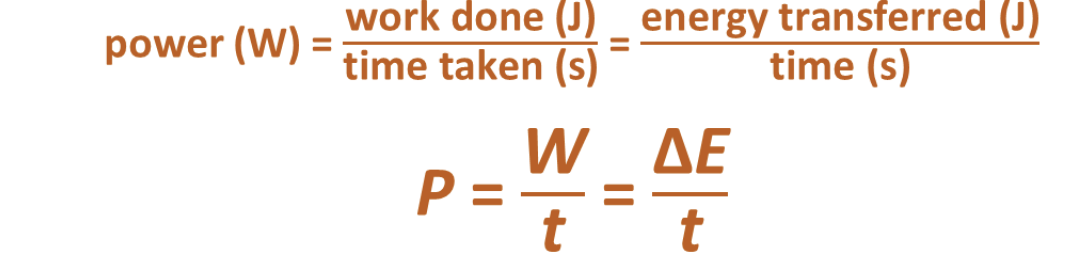
Power formula #2
Power (W) = force (N) x speed (m/s)
P = Fv
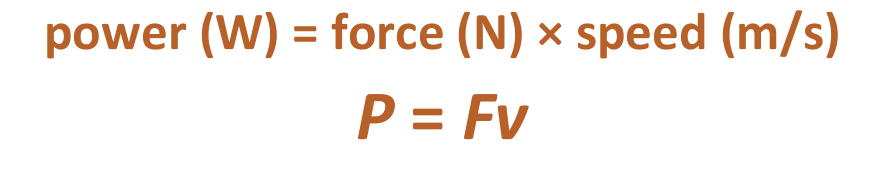
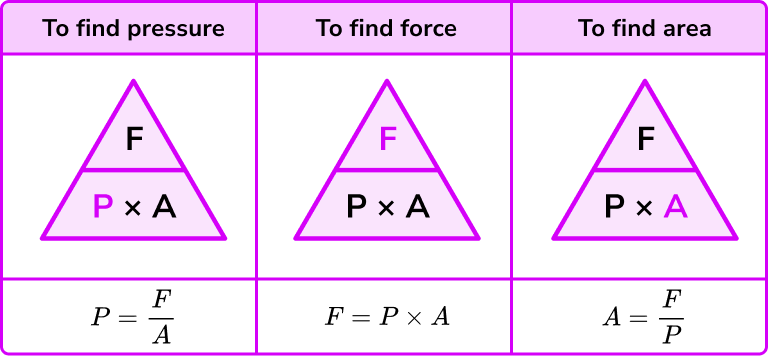
Describe how pressure varies with force and area in the context of everyday examples
the smaller the surface area is → the greater the pressure (e.g a nail of beds on your foot)
Pressure
force per unit area
SIU: pascal (Pa)
Pressure formula
pressure (Pa) = force (N)/area (m2)
p = F/A