AP Psychology: Unit 3 Sensation and Perception
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
1
New cards
transduction
converting one form of energy into another
ex. our brain converts vibrations into sound
ex. our brain converts vibrations into sound
2
New cards
sensation
the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment
3
New cards
perception
the process of organizing and interpreting sensory information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events
4
New cards
bottom-up processing
\
sensation is experienced first and works its way up to the brain (sense first, then perceive)
ex. the rose example
sensation is experienced first and works its way up to the brain (sense first, then perceive)
ex. the rose example
5
New cards
top-down processing
constructs perceptions from sensory input by drawing on your experiences an expectation (perceive first, then sense)
ex. The Forest Has Eyes
ex. The Forest Has Eyes
6
New cards
psychophysics
the study of relationships between the physical characteristics of stimuli, such as their intensity, and our psychological experience
7
New cards
thresholds
levels that we are able to recognize sensory information
8
New cards
Gustav Fechner
studied our thresholds
9
New cards
absolute threshold
the level of stimulation necessary to recognize a particular stimulus 50% of the time
10
New cards
subliminal threshold
below your absolute threshold of perceptions
ex. subliminal messages
ex. subliminal messages
11
New cards
priming
unconscious associations that predispose one's perception, memory, or response
12
New cards
difference threshold
the minimum difference between two stimuli required for detection 50 percent of the time
13
New cards
Weber's Law
sensory differences have a minimum percent not constant amount
ex. to note the difference of the weight of two objects they have to differ by 2%
ex. to note the difference of the weight of two objects they have to differ by 2%
14
New cards
sensory adaptation
diminished sensitivity as a consequence of a constant stimulation
ex. walking into your house after a vacation it has a distinct smell
ex. walking into your house after a vacation it has a distinct smell
15
New cards
gestalt
an organized whole. Emphasized our tendency to integrate pieces of information into meaningful wholes
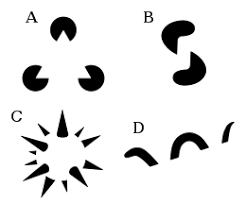
16
New cards
schema
a concept or framework that organizes and interprets information (basically an understanding of something)
17
New cards
accommodation
adapting our current understandings (schemas) to incorporate new information (adjust)
ex. a child who believes all four legged furry black and white animals are cows has to change their understanding when they see a dalmatian
ex. a child who believes all four legged furry black and white animals are cows has to change their understanding when they see a dalmatian
18
New cards
assimilation
interpreting our new experiences in terms of our existing schemas
ex. a child sees a cow has four legs and is black and white. that child now thinks everything with four legs and is black and white is a cow
ex. a child sees a cow has four legs and is black and white. that child now thinks everything with four legs and is black and white is a cow
19
New cards
figure-ground
the organization of the visual field into objects that stand out from their surroundings
20
New cards
visual cliff
a laboratory device for testing depth perception in infants and young animals
21
New cards
depth perception
the ability to see objects in three dimensions although the images that strike the retina are 2D; allows us to judge distance; everyone is born with this
22
New cards
monocular cues
depth cues, such as interposition and linear perspective, available to either eye alone
23
New cards
binocular cues
depth cues, such as retinal disparity, that depend on the use of two eyes
24
New cards
linear perspective
A monocular cue for perceiving depth; the more parallel lines converge, the greater their perceived distance.
25
New cards
interposition
if one object partially blocks our view of another, we perceive it as closer
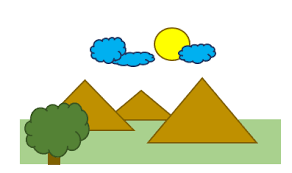
26
New cards
perceptual constancy
our tendency to view familiar objects as unchanging (having the same color, brightness, shape, and size) even as illumination and retinal images change
ex. in a room a red apple is brown, but we still think its red
ex. in a room a red apple is brown, but we still think its red
27
New cards
perceptual adaptation
the ability to adjust or adapt to a change in sensory input
28
New cards
perceptual set
a mental predisposition to perceive one thing and not another (top-down processing)
ex. newspaper photo of "the Lochness Monster" when it actually is just a tree branch, the title makes people see the monster before the branch
ex. newspaper photo of "the Lochness Monster" when it actually is just a tree branch, the title makes people see the monster before the branch
29
New cards
parapsychology
the study of paranormal phenomena, including ESP and psychokinesis
30
New cards
wavelength and its influence on color
the distance from one peak to the next which influences our perception of color
short = blue colors long = red colors
short = blue colors long = red colors
31
New cards
intensity and its influence on color
the amount of energy in a light wave; influences brightness
larger intensity = bright colors small intensity = dull colors
larger intensity = bright colors small intensity = dull colors
32
New cards
cornea
protects the eye and bends light for focus
33
New cards
iris
a colored muscle that adjust light intake
34
New cards
retina
converts light to neural signals to send to the brain
35
New cards
optic nerve
the nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain
36
New cards
fovea
central focal point in retina, cones cluster around it
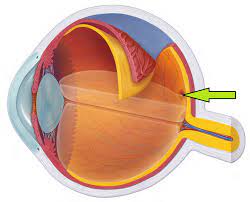
37
New cards
rods
enables black and white (even gray) perception
low spatial activity
sees details
responsible for peripheral vision
low spatial activity
sees details
responsible for peripheral vision
38
New cards
cones
enable color perception
high spatial activity
located in the center of retina
high spatial activity
located in the center of retina
39
New cards
trichromatic theory of color
Also known as the Young-Helmholz Theory of Color; Human eye has 3 types of cone receptors sensitive to different; People see colors because the eye does its own "color mixing" (blue/short; green/medium; red/long)
40
New cards
opponent processing theory of color
States we have three types of receptor cones and they each handle a pair of colors (red/green, yellow/blue, and black/white). If one sensor/color is firing, it slows the other from firing. The theory does a good job at explaining afterimages.
41
New cards
hammer, anvil, stirrup (ossicles)
the three small bones in the middle ear that relay vibrations of the eardrum to the inner ear
42
New cards
frequency
the number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time
43
New cards
pitch
a tone's experienced highness or lowness; depends on frequency
44
New cards
cochlea
a coiled, bony, fluid-filled tube in the inner ear through which sound waves trigger nerve impulses
45
New cards
semicircular canal
structures in the inner ear that are responsible for the sense of balance
46
New cards
basilar membrane
contains hair cells that bend and trigger nerve cells whose axons form auditory nerves, located in the cochlea
47
New cards
kinesthesis
the system for sensing the position and movement of individual body parts
48
New cards
vestibular sense
the sense of body movement and position, including the sense of balance
49
New cards
nociceptors
sensory receptors that detect hurtful temperatures, pressure, or chemicals
50
New cards
gate-control theory
the spinal cord contains a neurological "gate" that blocks pain signals or allows them to pass on to the brain. the "gate" is opened by the activity of pain signals traveling up small nerve fibers and is closed by activity of larger fibers or by information coming from the brain
51
New cards
influences of pain
biological, psychological, social-cultural
52
New cards
taste receptors
chemical receptors on the tongue that decode molecules of food or drink to identify them (tastebuds)
53
New cards
sensory interaction
the principle that one sense may influence another
ex. when the smell of food influences its taste
ex. when the smell of food influences its taste
54
New cards
olfaction
sense of smell
55
New cards
steps to process light
1. Light enters eye and causes reaction in rods and cones
2. Chemical reaction activates bipolar cells
3. Bipolar cells activate ganglion cells, whose axons form the optic nerve. Optic nerve transmits info to visual cortex.
56
New cards
steps to process smell
1. Odor molecules bind to odorant receptors
2. Olfactory receptor cells send electrical signals to olfactory bulb
3. Olfactory bulbs form olfactory nerve which takes info to the brain
57
New cards
steps to process sound
1. Outer ear channels the sound waves through auditory canal to the eardrum -outer ear
2. Ear drum vibrations are sent through hammer, anvil, and stirrup to cochlea -middle ear called ossicles
3. .Cochlea vibrates as well causing ripples in fluid that fills the tube. These ripples cause more ripples in the basilar membrane.
4. Hair cells in basilar membrane bend and trigger nerve cells, whose axons form auditory nerve
5. Auditory nerve takes it to the auditory cortex to be processed and stored
58
New cards
feature detectors
nerve cells in the brain that respond to specific features of the stimulus, such as shape, angle, or movement
59
New cards
blind spot
the point at which the optic nerve leaves the eye, creating a "blind" spot because no receptor cells are located there
60
New cards
synesthesia
describing one kind of sensation in terms of another ("a loud color", "a sweet sound")
61
New cards
selective attention
the focusing of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus
62
New cards
change blindness
when people fail to detect changes to the visual details of a scene
63
New cards
inattentional blindness
failing to see visible objects when our attention is directed elsewhere
64
New cards
extrasensory perception (ESP)
the controversial claim that perception can occur apart from sensory input; includes telepathy, clairvoyance, and precognition