Plant & Animal Science Final Exam
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/37
Earn XP
Last updated 4:33 PM on 12/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
1
New cards
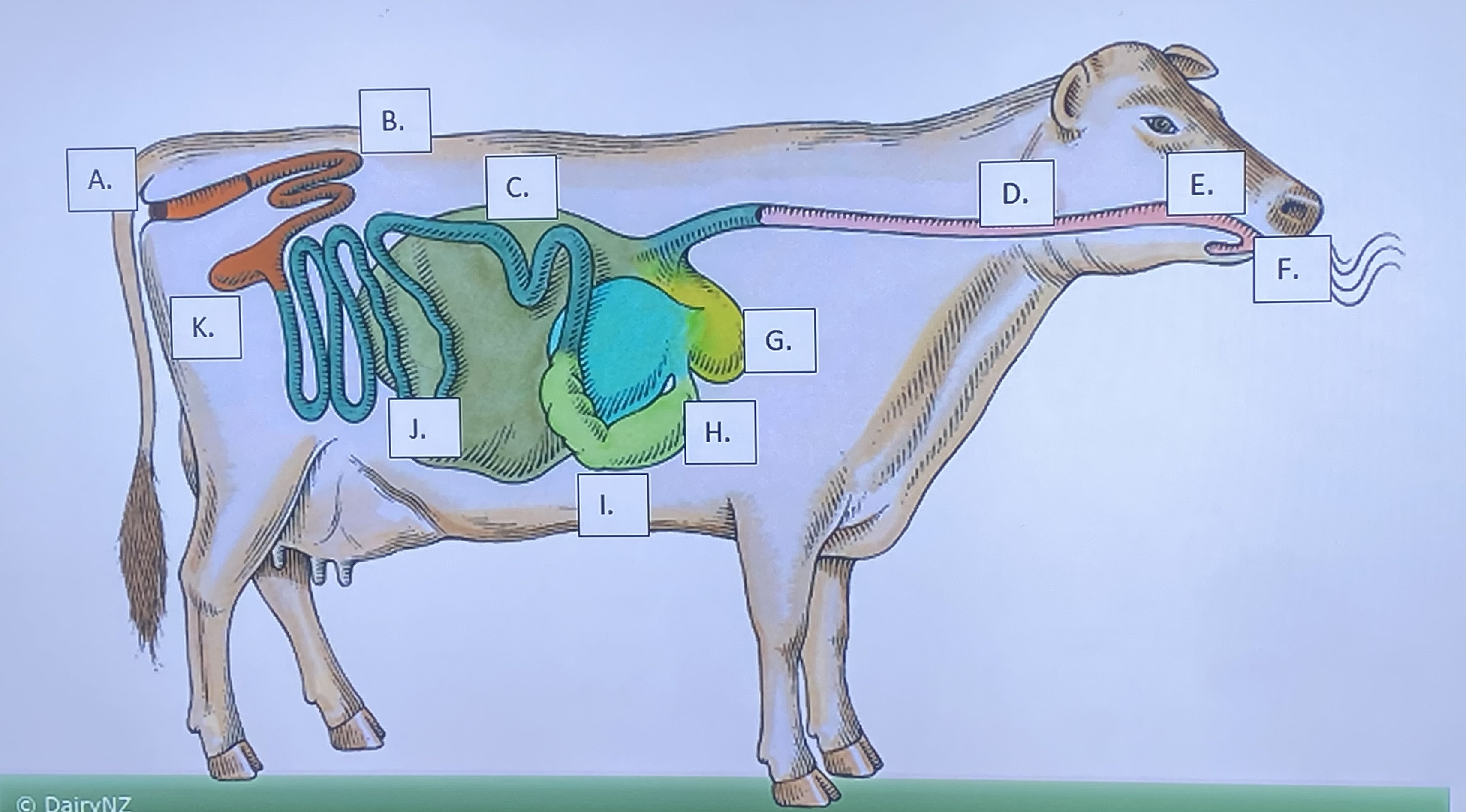
Ruminant - Mouth/Teeth (F)
(Ruminant)
starting point of digestion
\-chemical = saliva
\-mehanial = teeth
starting point of digestion
\-chemical = saliva
\-mehanial = teeth
2
New cards
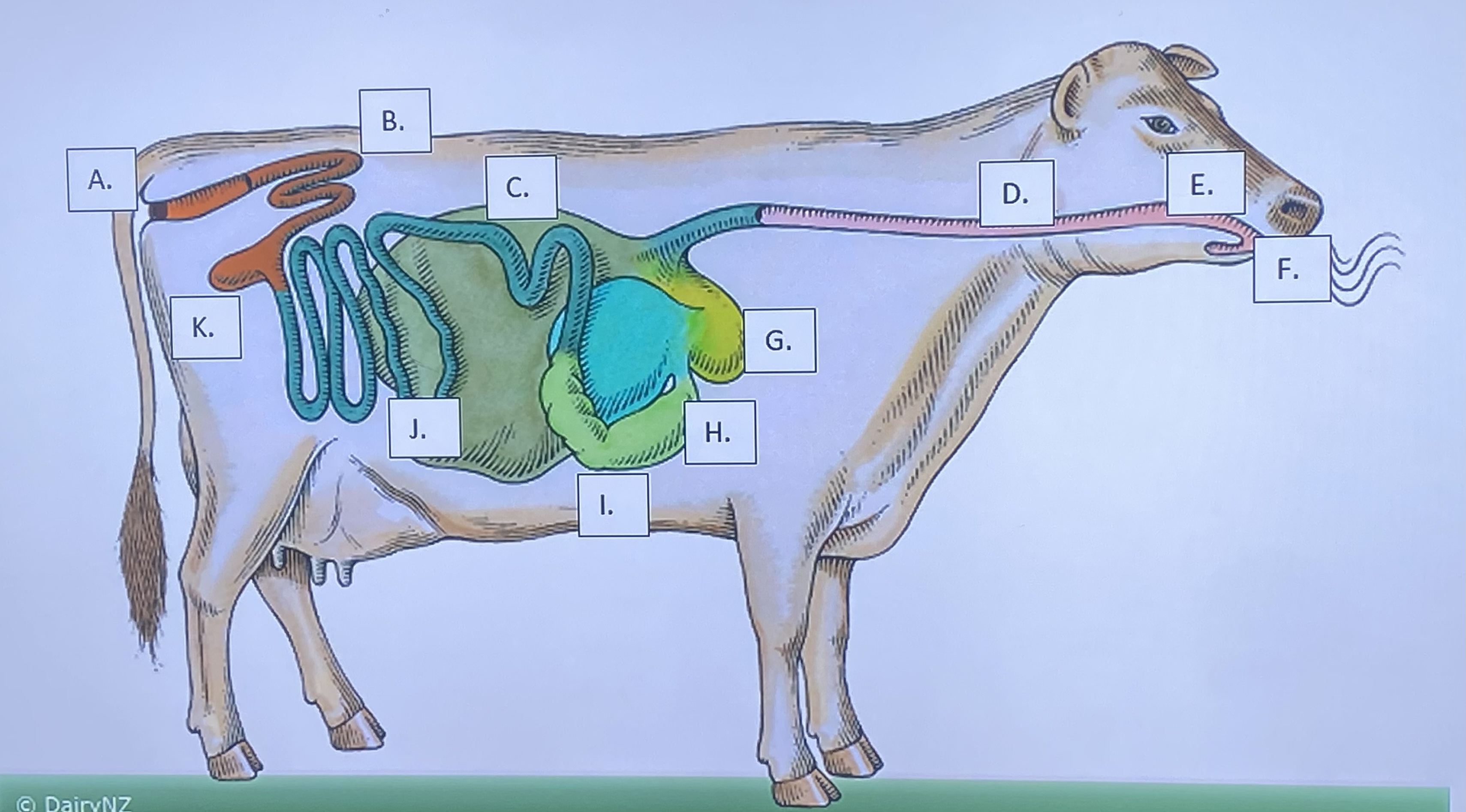
Ruminant - Salivary Glands (E)
(Ruminant)
Secretes saliva to aid in digestion
Secretes saliva to aid in digestion
3
New cards
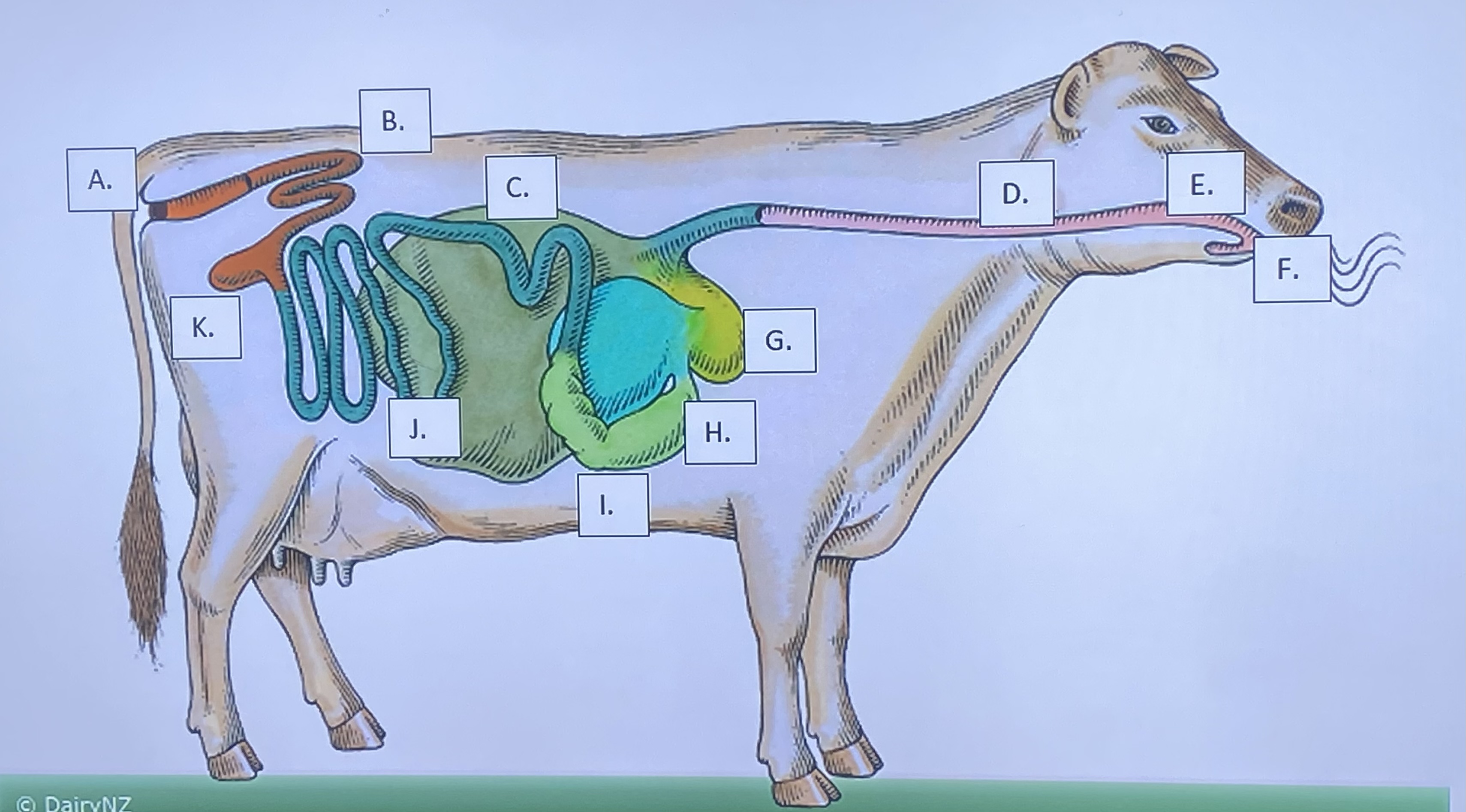
Ruminant - Reticulum (G)
\-honeycomb
\-filter foodstuffs
\-holds foodstuffs
\-site of regurgitation
\-1st compartment
\-filter foodstuffs
\-holds foodstuffs
\-site of regurgitation
\-1st compartment
4
New cards
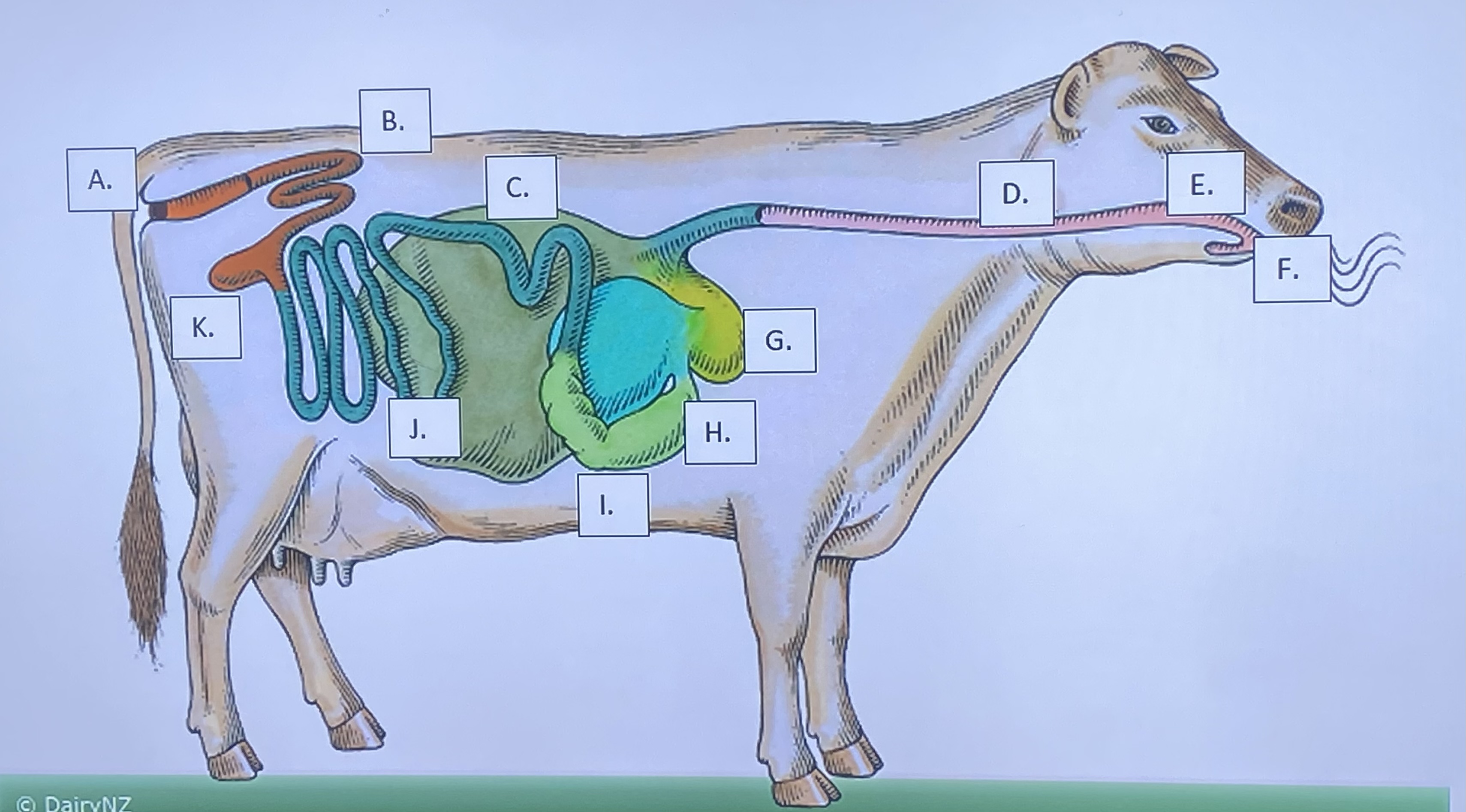
Ruminant - Rumen (C)
\-fermentation vat
\-not active in early stages of life
\-microbial digestion
\-gas -carpet -80%
\-2nd compartment
\-not active in early stages of life
\-microbial digestion
\-gas -carpet -80%
\-2nd compartment
5
New cards
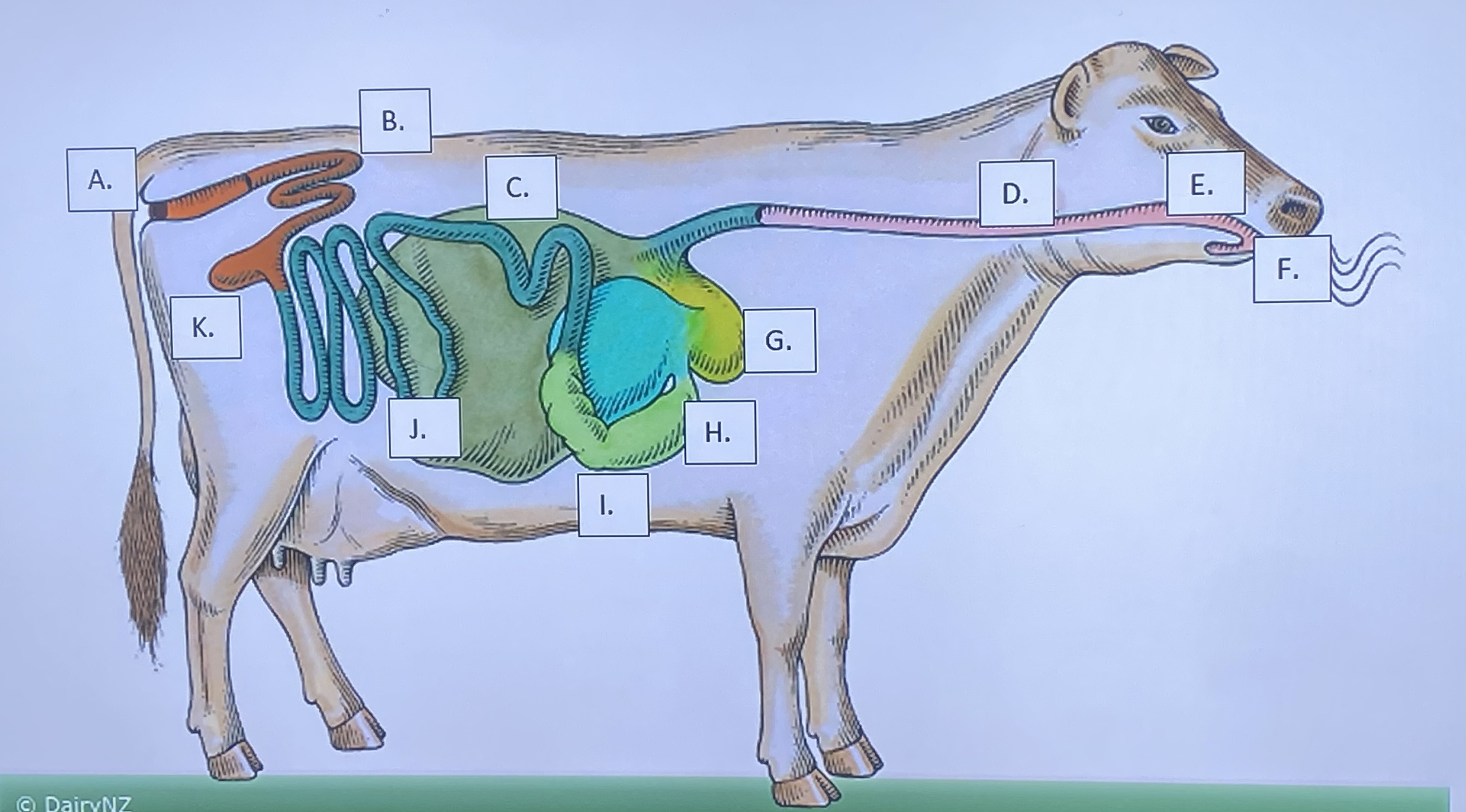
Ruminant - Omasum (H)
\-many folds (book)
\-dries foodstuffs
\-absorbs water & nutrients
\-abnormal for a stomach to absorb nutrients
\-3rd compartment
\-dries foodstuffs
\-absorbs water & nutrients
\-abnormal for a stomach to absorb nutrients
\-3rd compartment
6
New cards
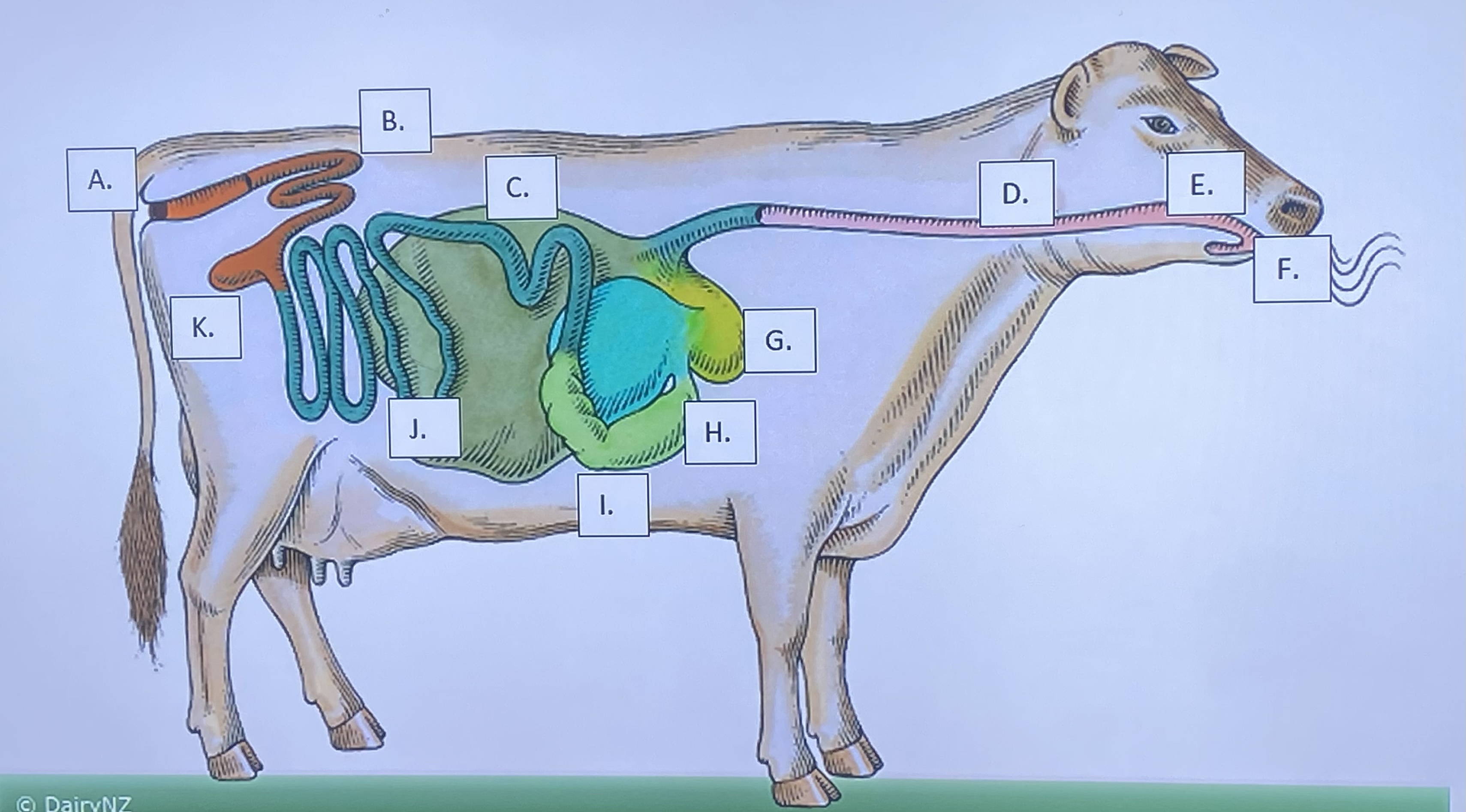
Ruminant - Abomasum (I)
\-“true stomach”
\-acidic digestion
\-hydrochloric acid
\-same as mono gastric
\-pepsin breaks down proteins
\-renin breaks down milk
\-4th compartment
\-acidic digestion
\-hydrochloric acid
\-same as mono gastric
\-pepsin breaks down proteins
\-renin breaks down milk
\-4th compartment
7
New cards
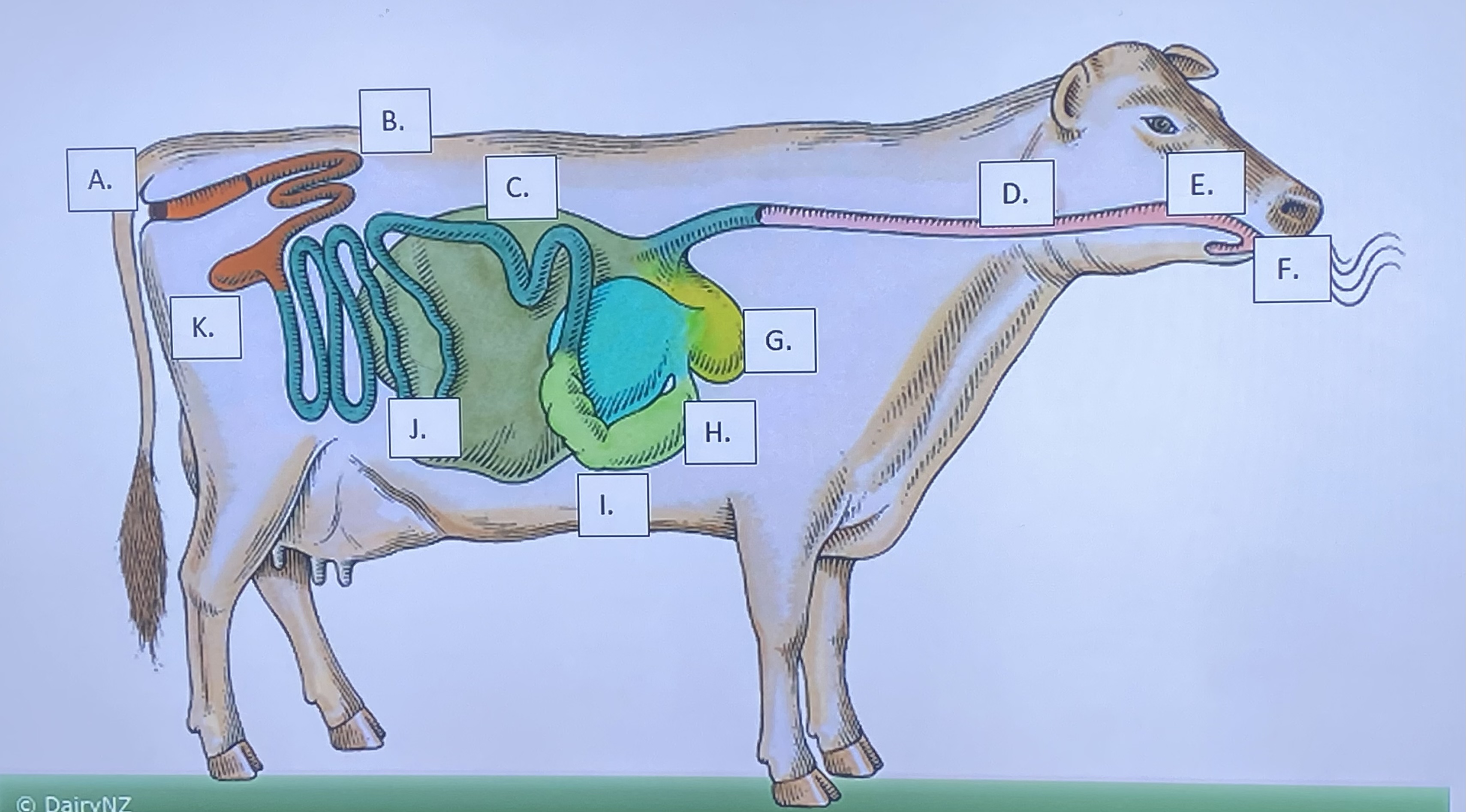
Ruminant - Large Intestine (B)
-absorbs water to send to blood stream
-formation of feces
-formation of feces
8
New cards
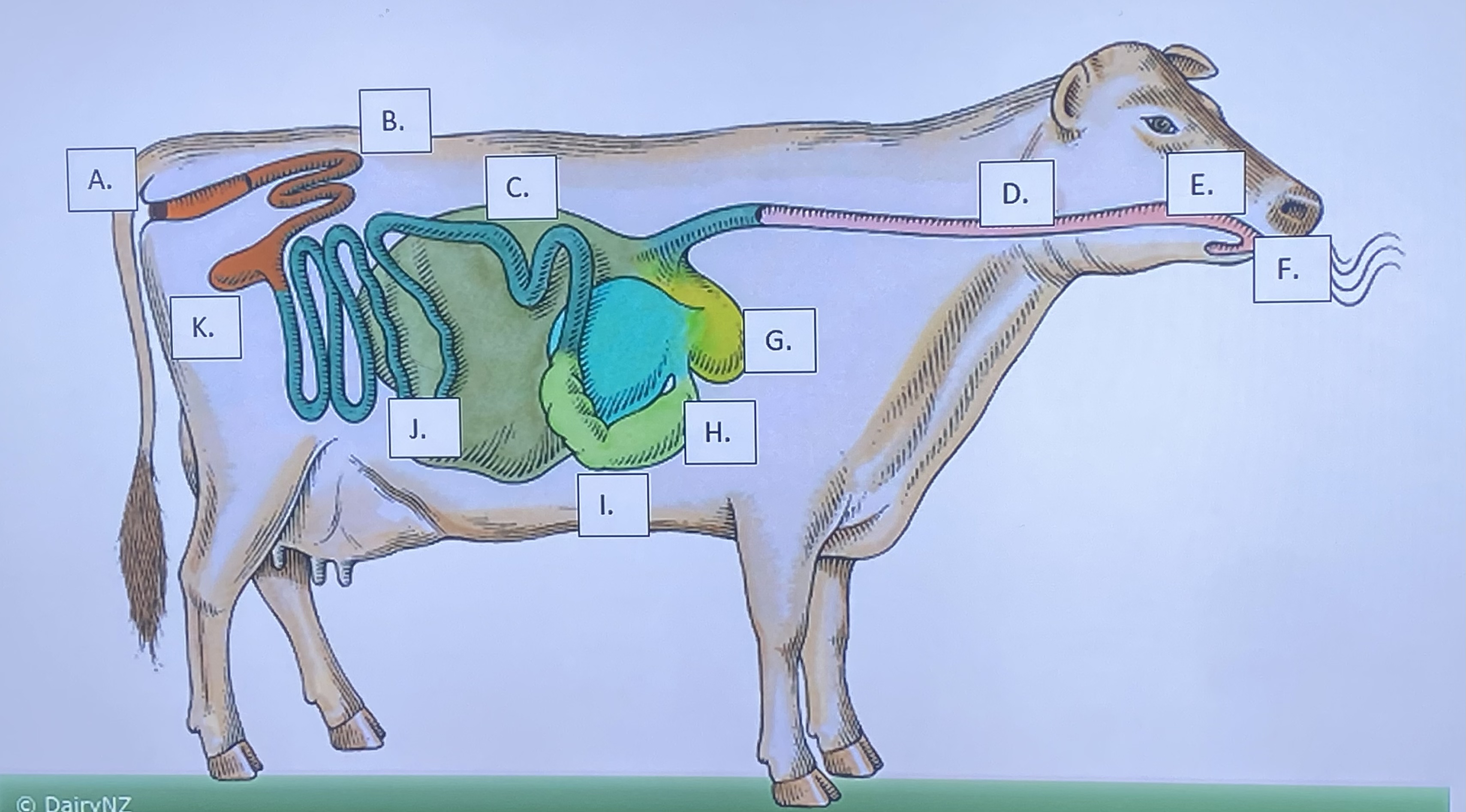
Ruminant - Small Intestine (J)
(Ruminant)
\-absorption of nutrients
\-main site
\-absorbs to the bloodstream
\-3 sections (Dw about them)
\-absorption of nutrients
\-main site
\-absorbs to the bloodstream
\-3 sections (Dw about them)
9
New cards
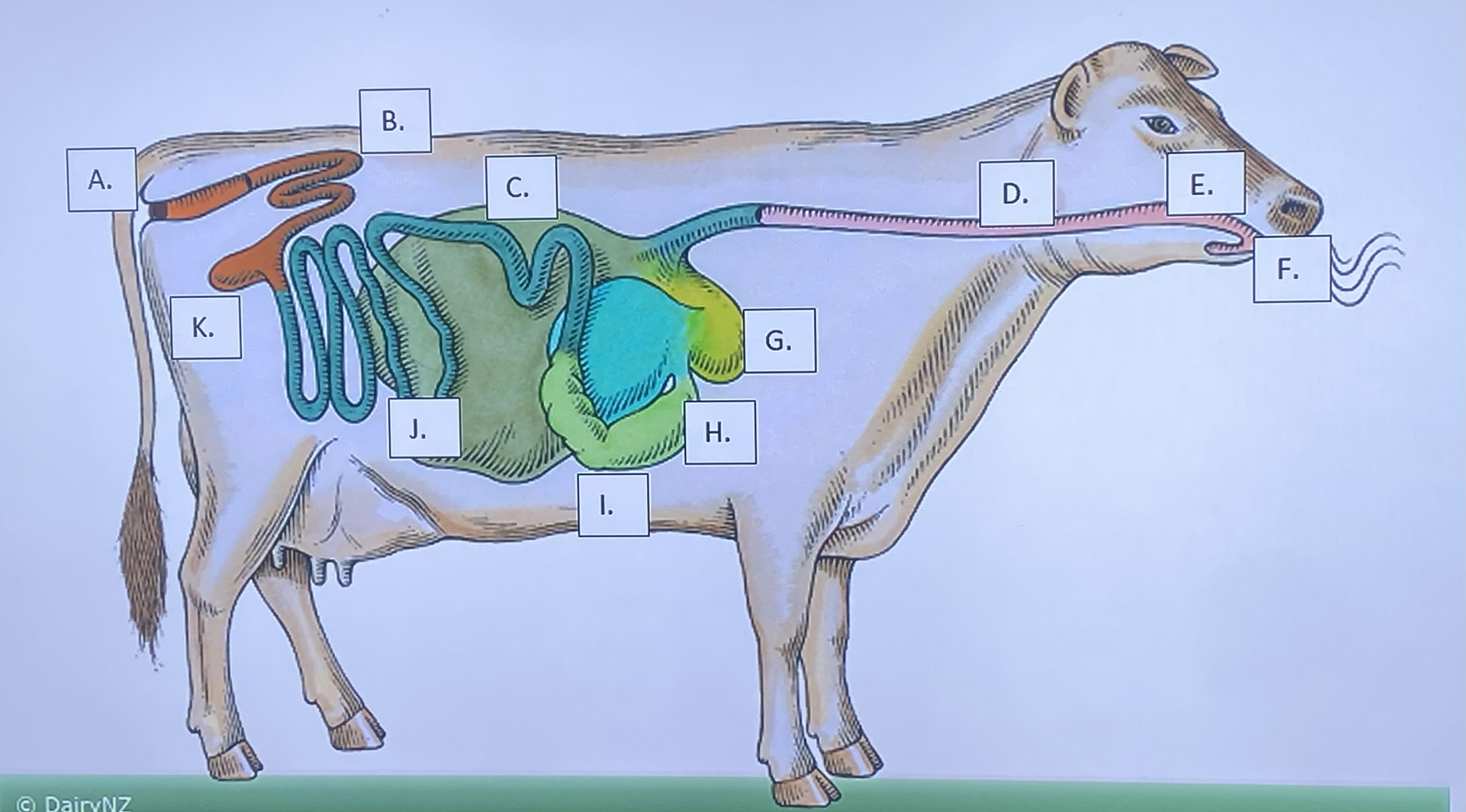
Ruminant - Cecum (K)
-helps break down fiber
-full function still unknown
-full function still unknown
10
New cards
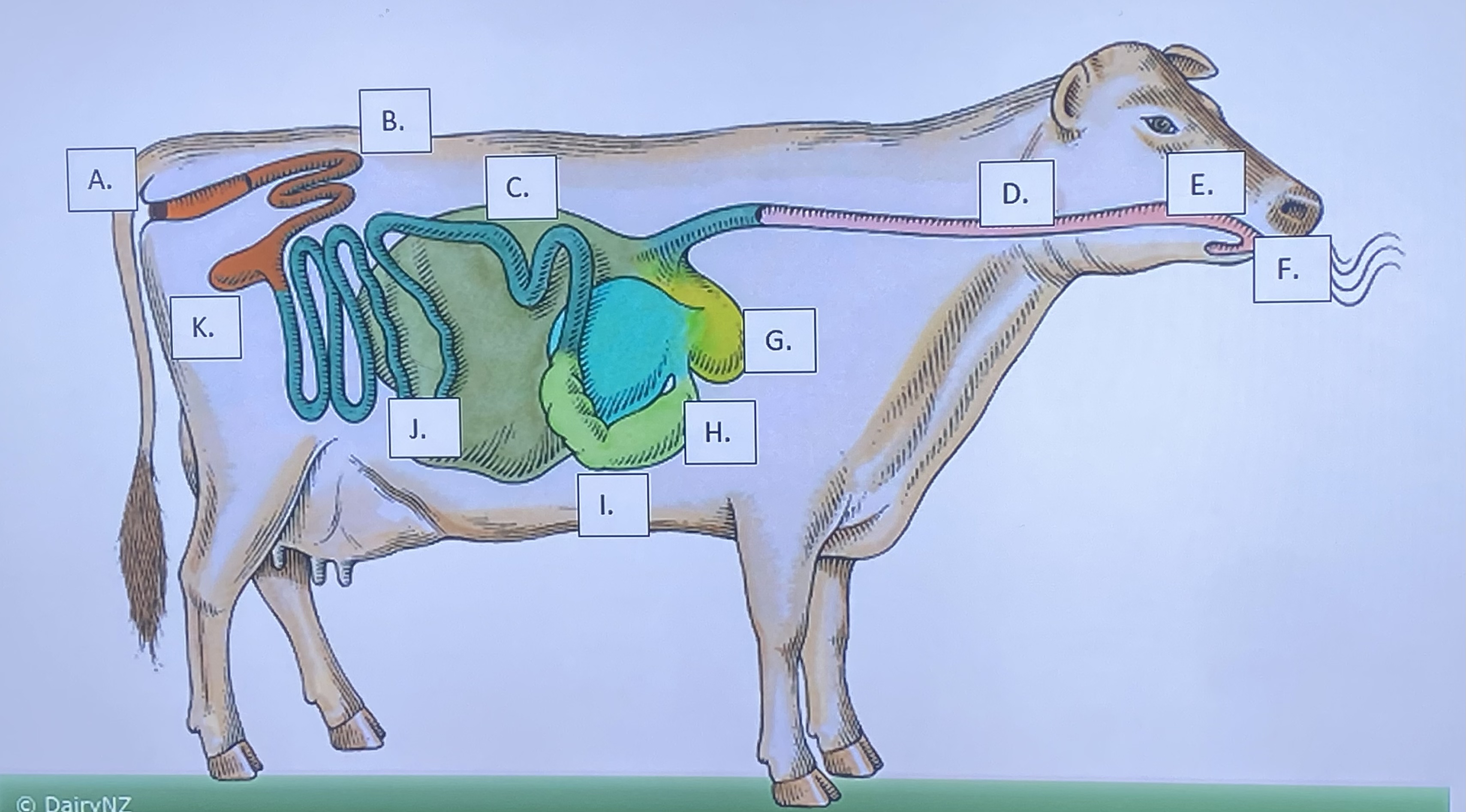
Ruminant - Anus (A)
(Ruminant)
\-excretes fecal matter
\-excretes fecal matter
11
New cards
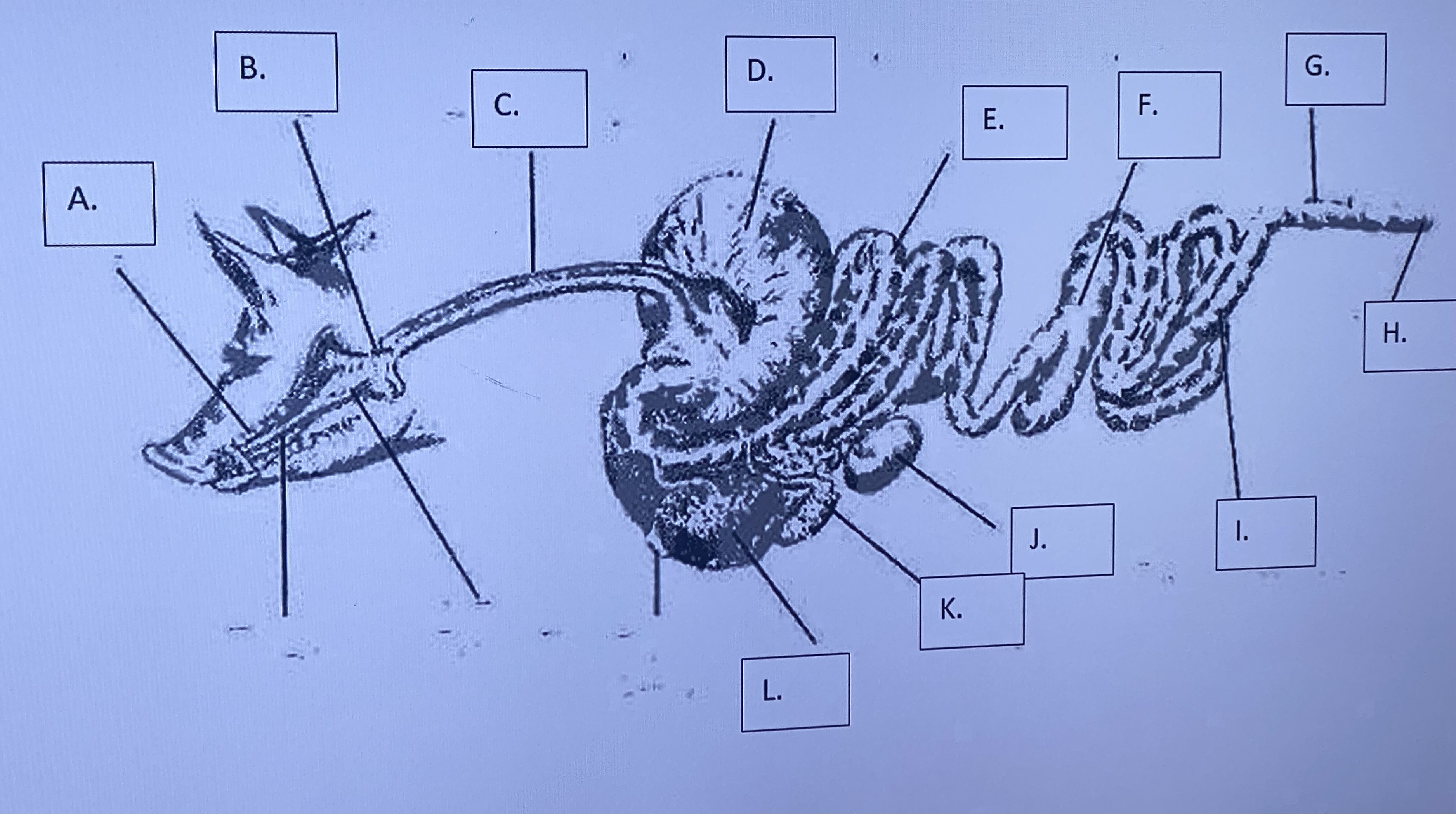
Monogastric - Mouth/Teeth/Tounge (A)
(Monogastric)
\-begins mechanical (teeth) & chemical (saliva) digestion
\-begins mechanical (teeth) & chemical (saliva) digestion
12
New cards
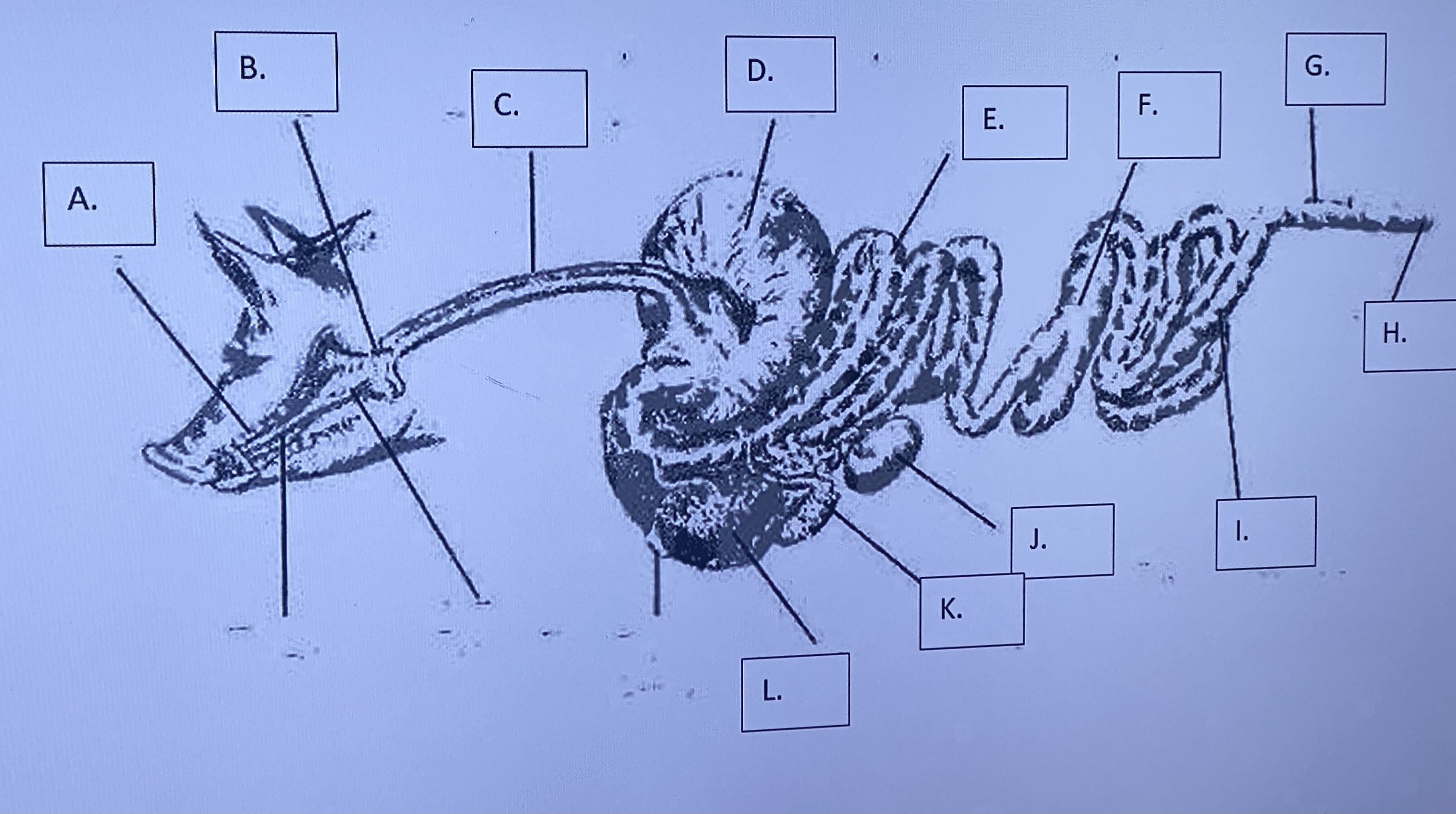
Monogastric - Salivary Glands (B)
(Monogastric)
\-produces saliva, which aids in chem digestion
\-produces saliva, which aids in chem digestion
13
New cards
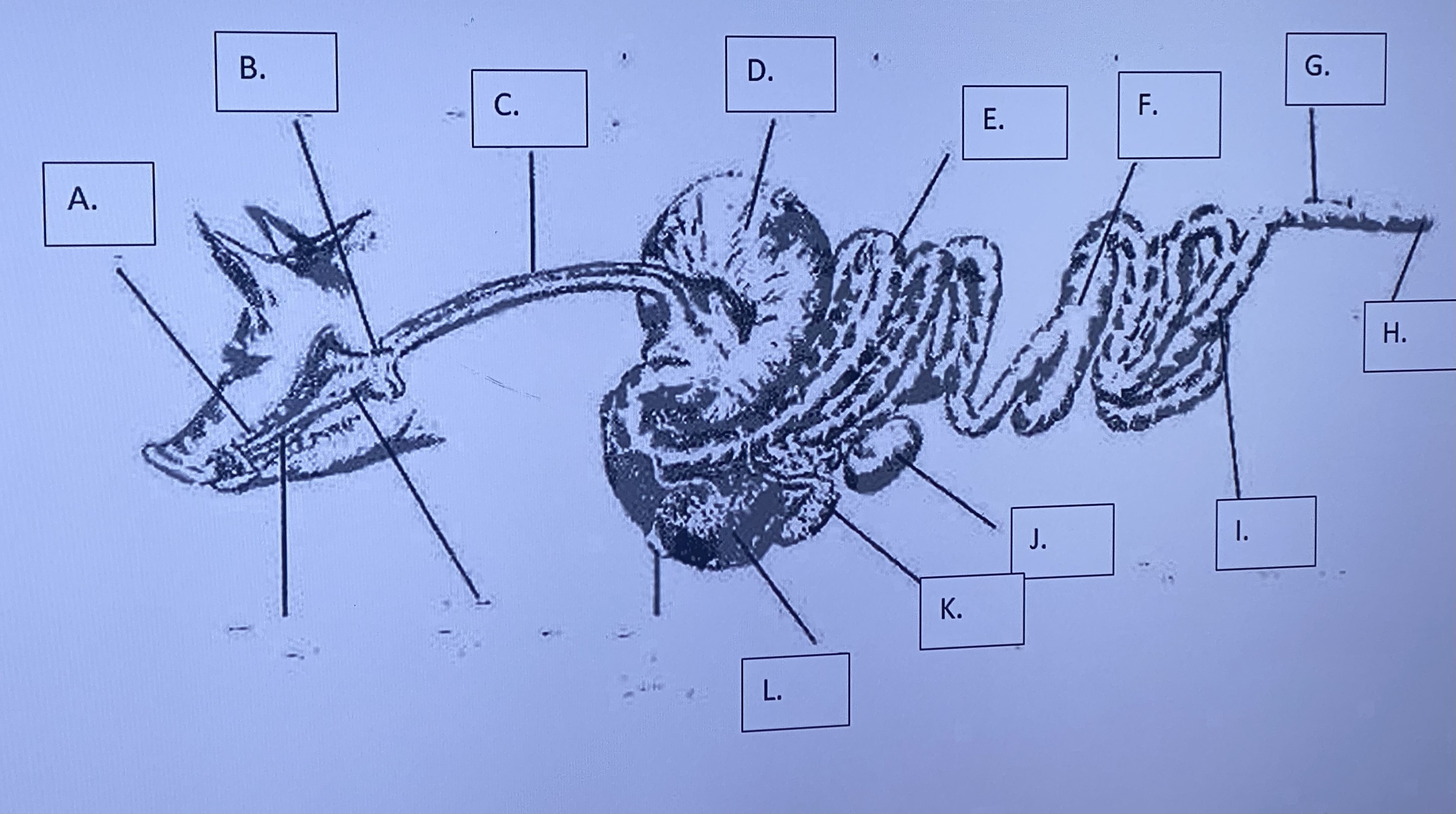
Monogastric - Esophagus (C)
“food tube” - transports food to stomach (moistened by saliva)
14
New cards
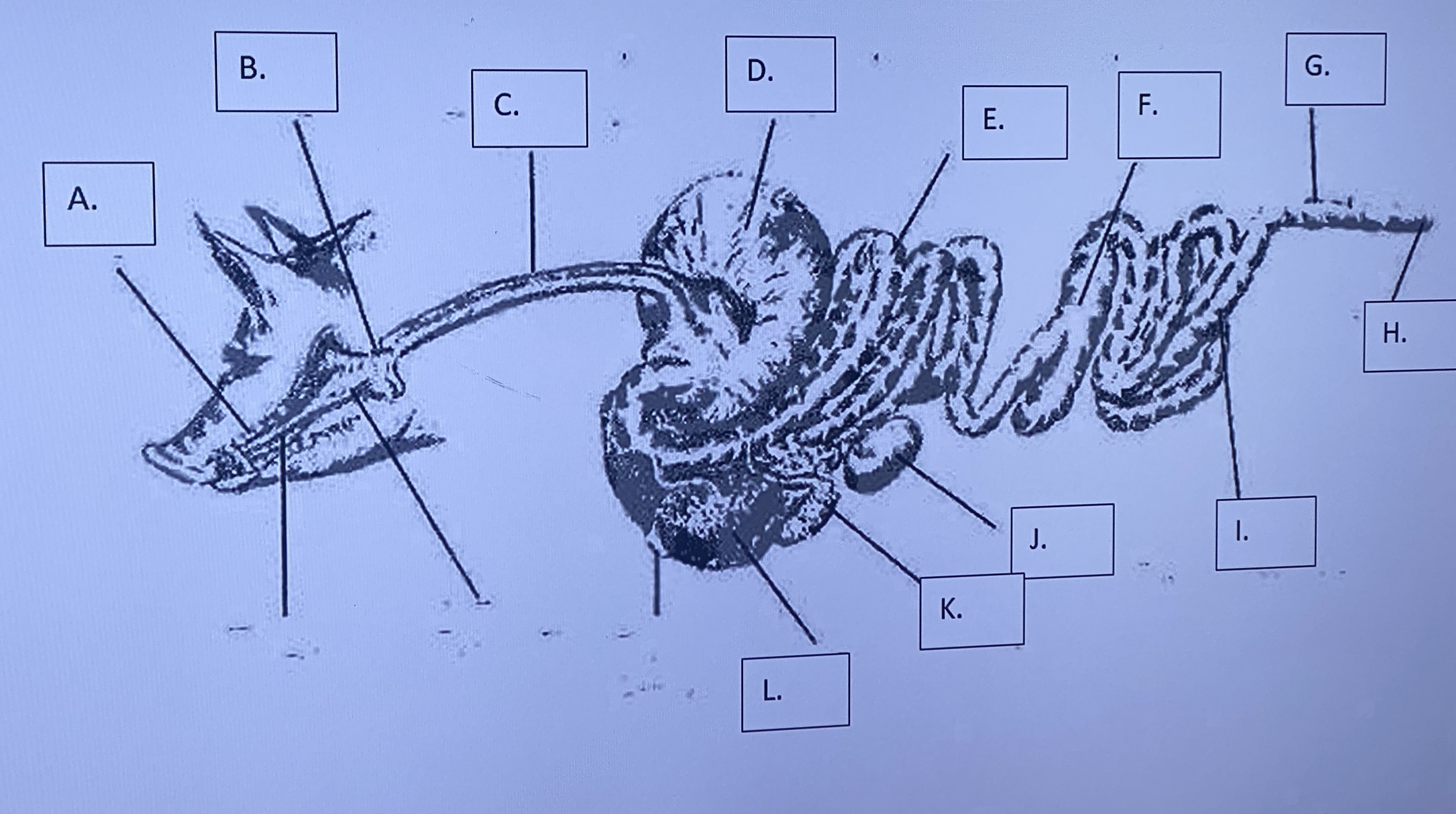
Monogastric - Stomach (D)
- churns & mixes food - uses acidic digestion to break food down further (bottom is lined to protect from digesting itself)
15
New cards
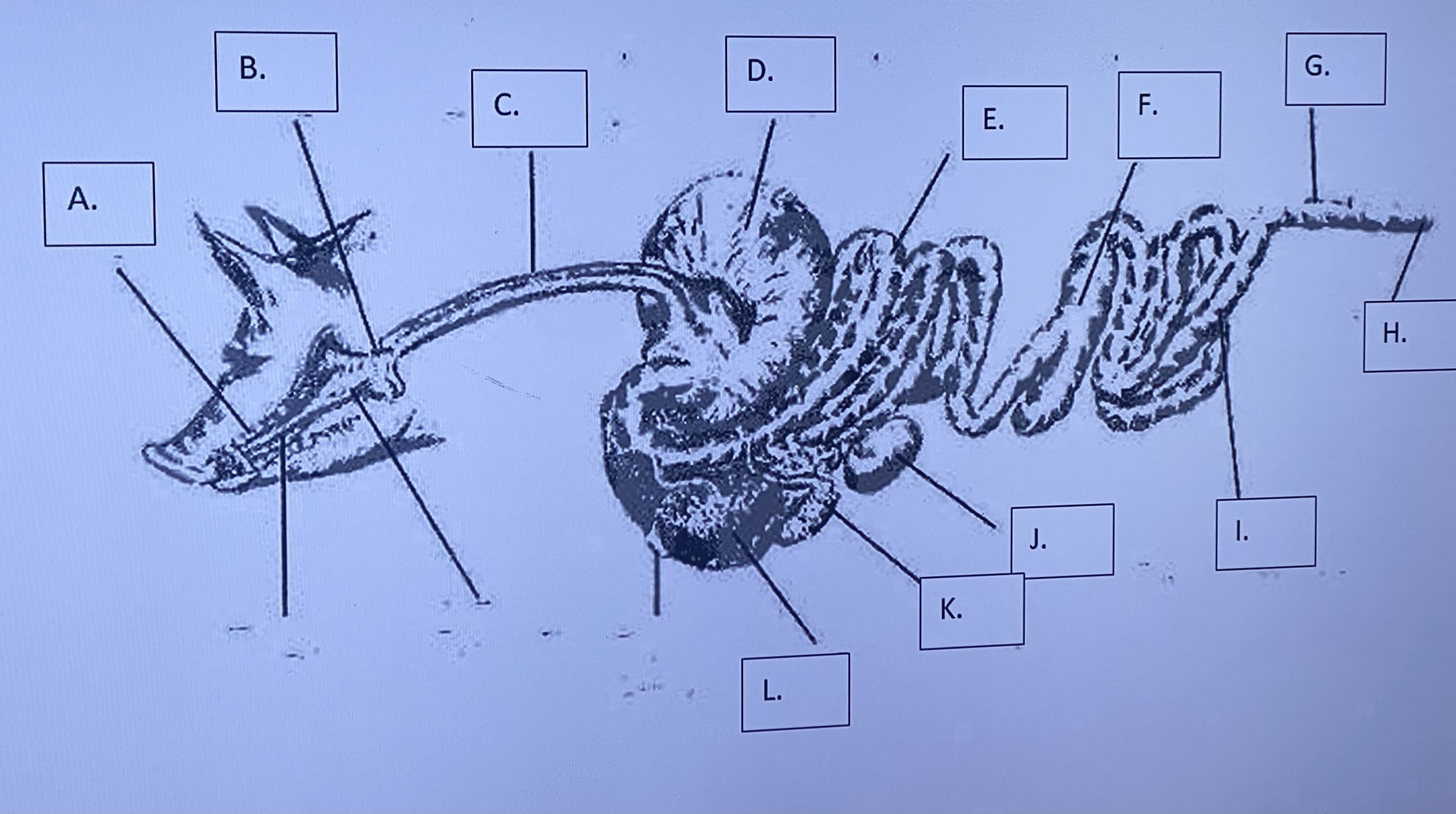
Monogastric - Large Intestine (I)
-absorbs water / dries
16
New cards
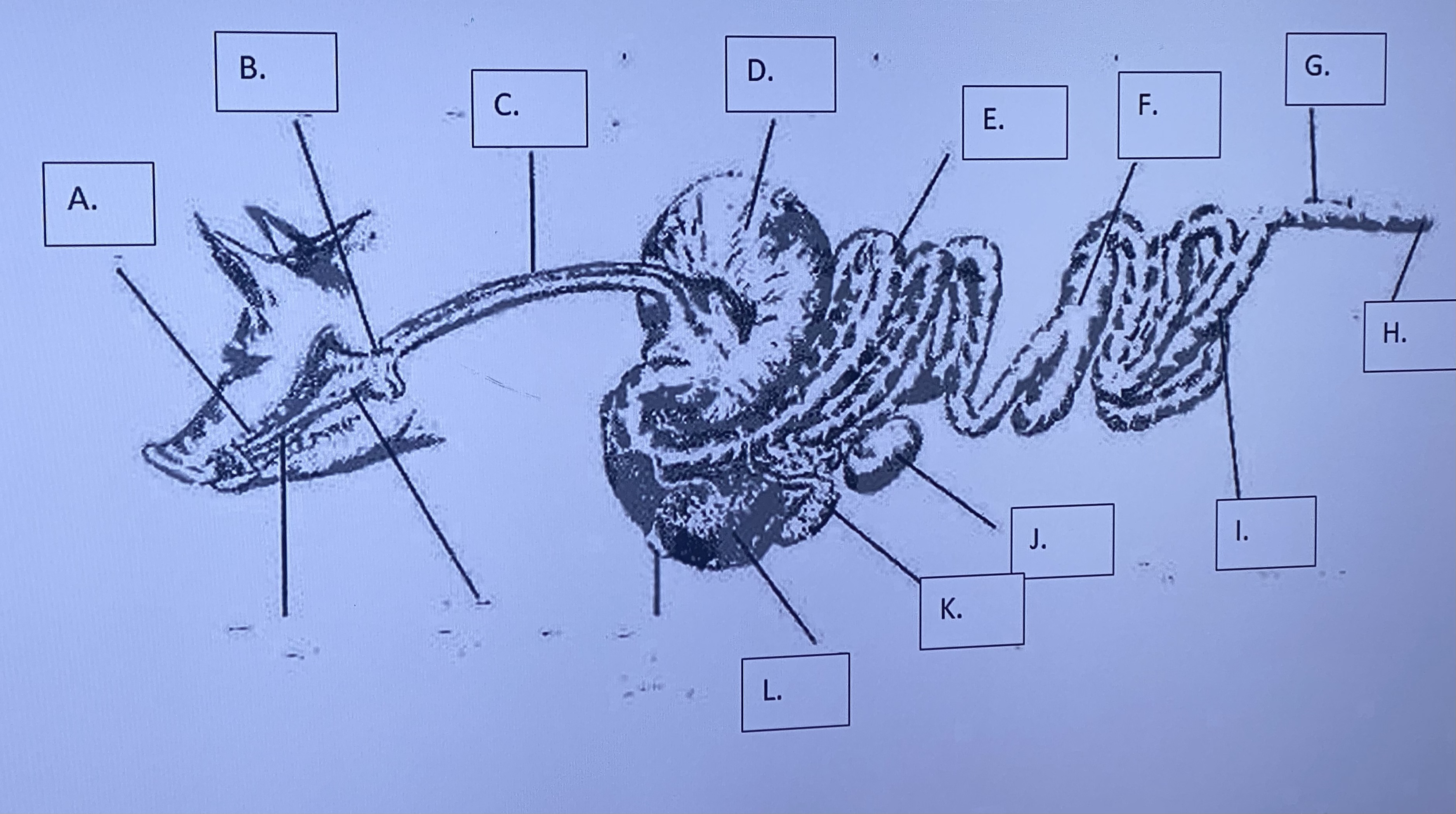
Monogastric - Small Intestine (E)
(Monogastric)
\-does enzymatic digestion and absorbs nutrients
\-does enzymatic digestion and absorbs nutrients
17
New cards
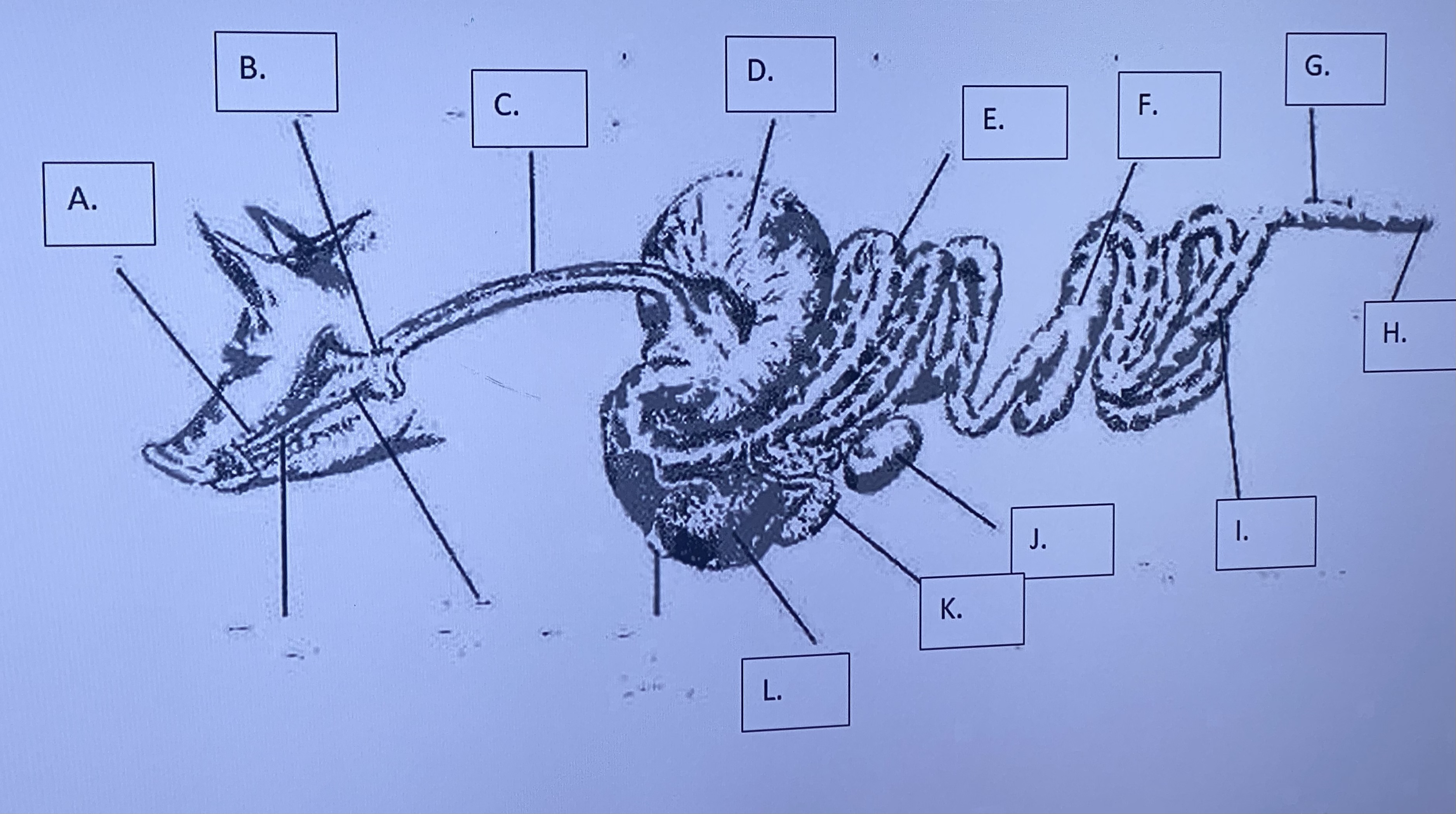
Monogastric - Pancreas (J)
produces & secretes enzymes
18
New cards
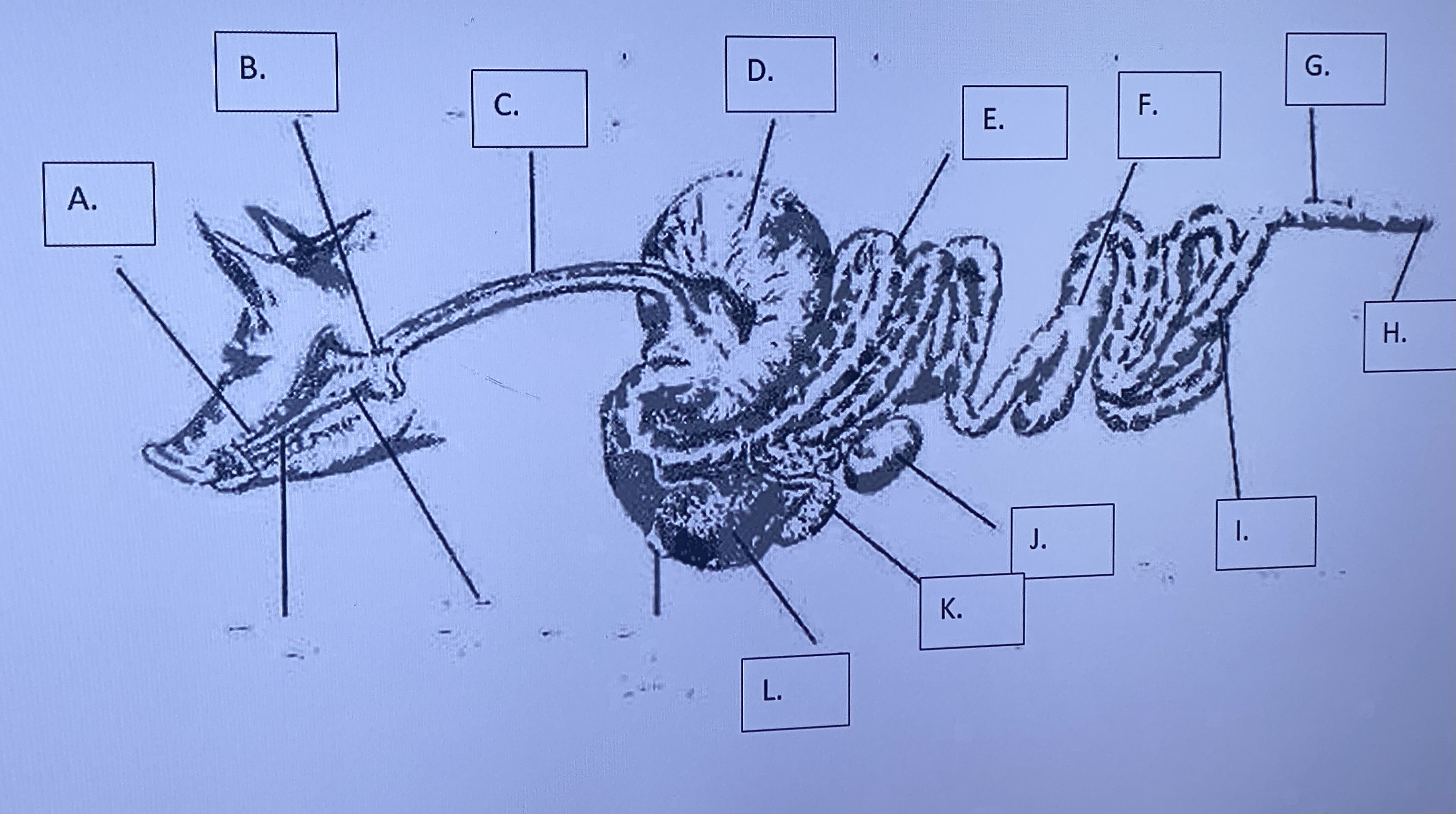
Monogastric - Gallbladder (K)
stores bile
19
New cards
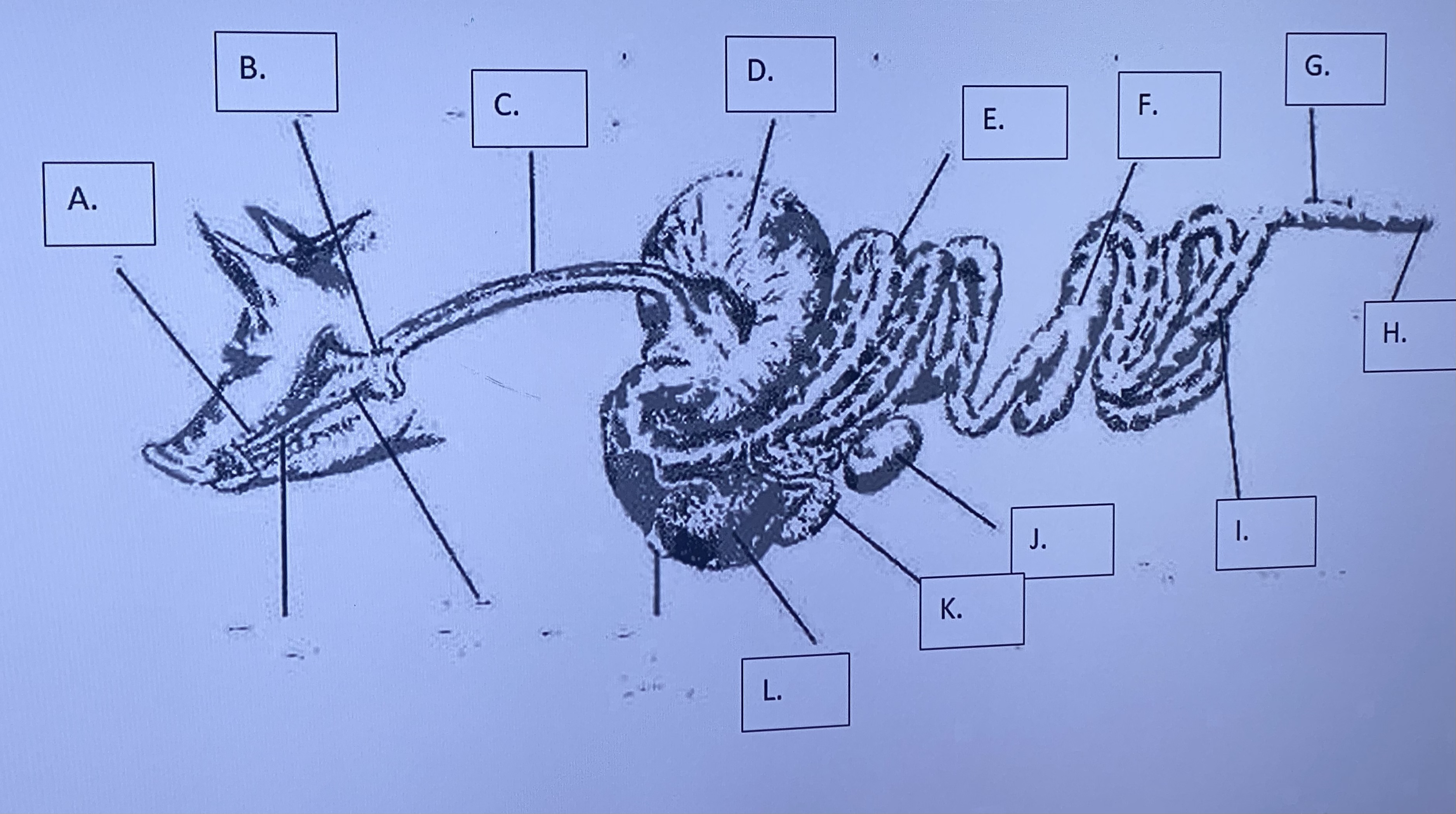
Monogastric - Cecum (F)
no function in most monogastrics; in modified monogastrics (hind-gut fermenters) it ferments roughages (similar to a rumen in ruminants)
20
New cards
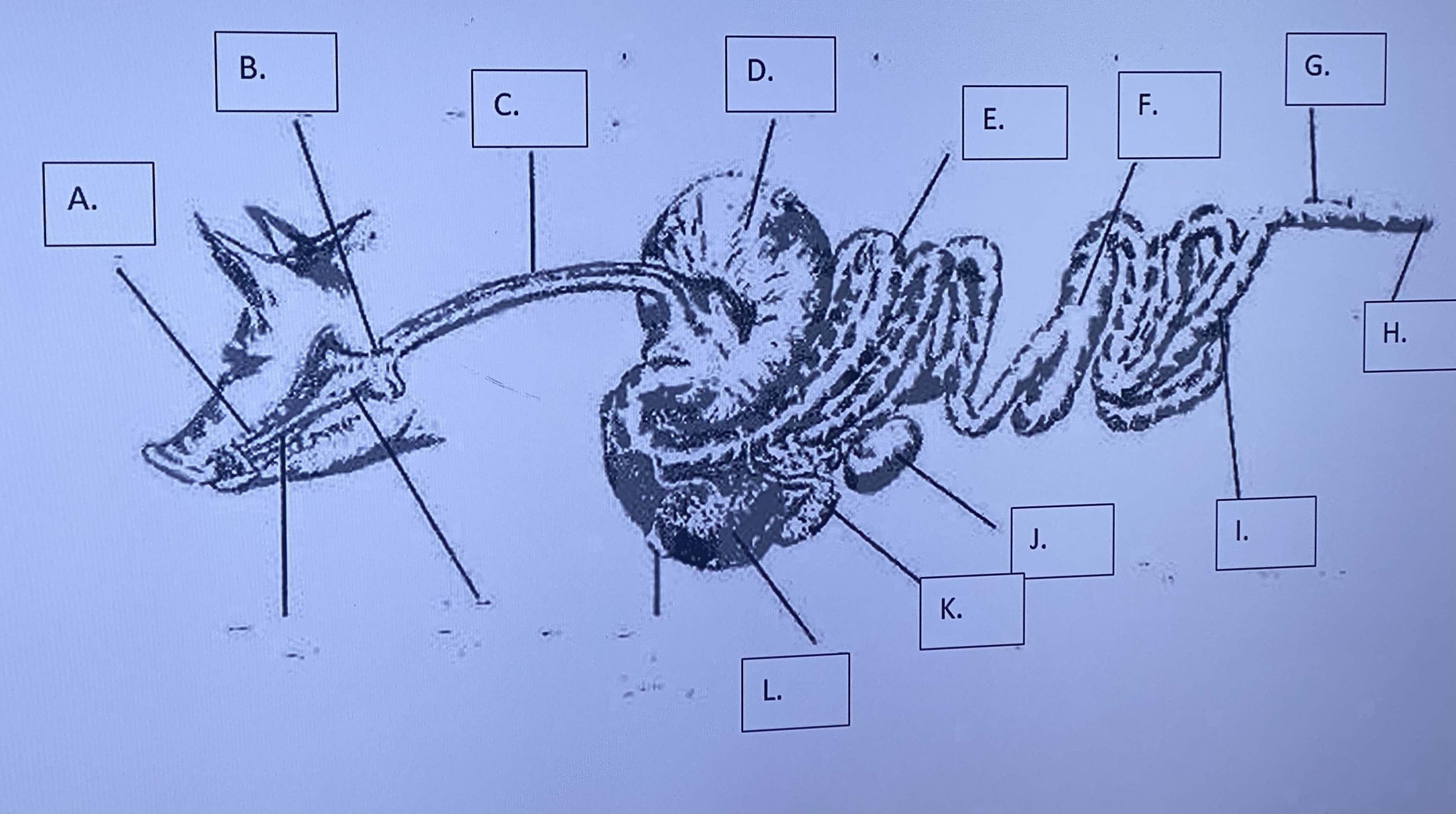
Monogastric - Colon (G)
end of large intestine - storage of fecal matter
21
New cards
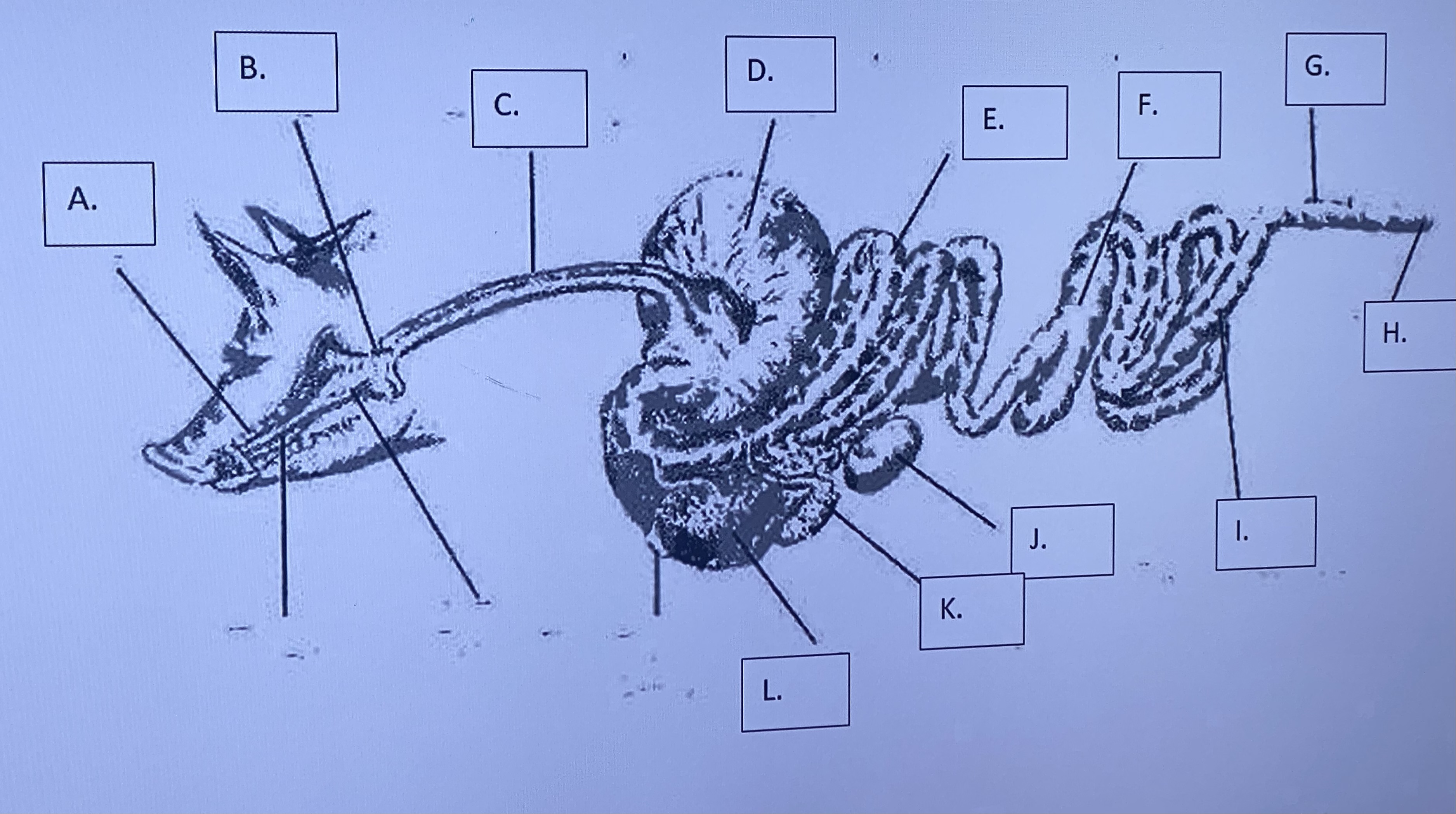
Monogastric - Anus (H)
(Monogastric)
excretes fecal matter
excretes fecal matter
22
New cards
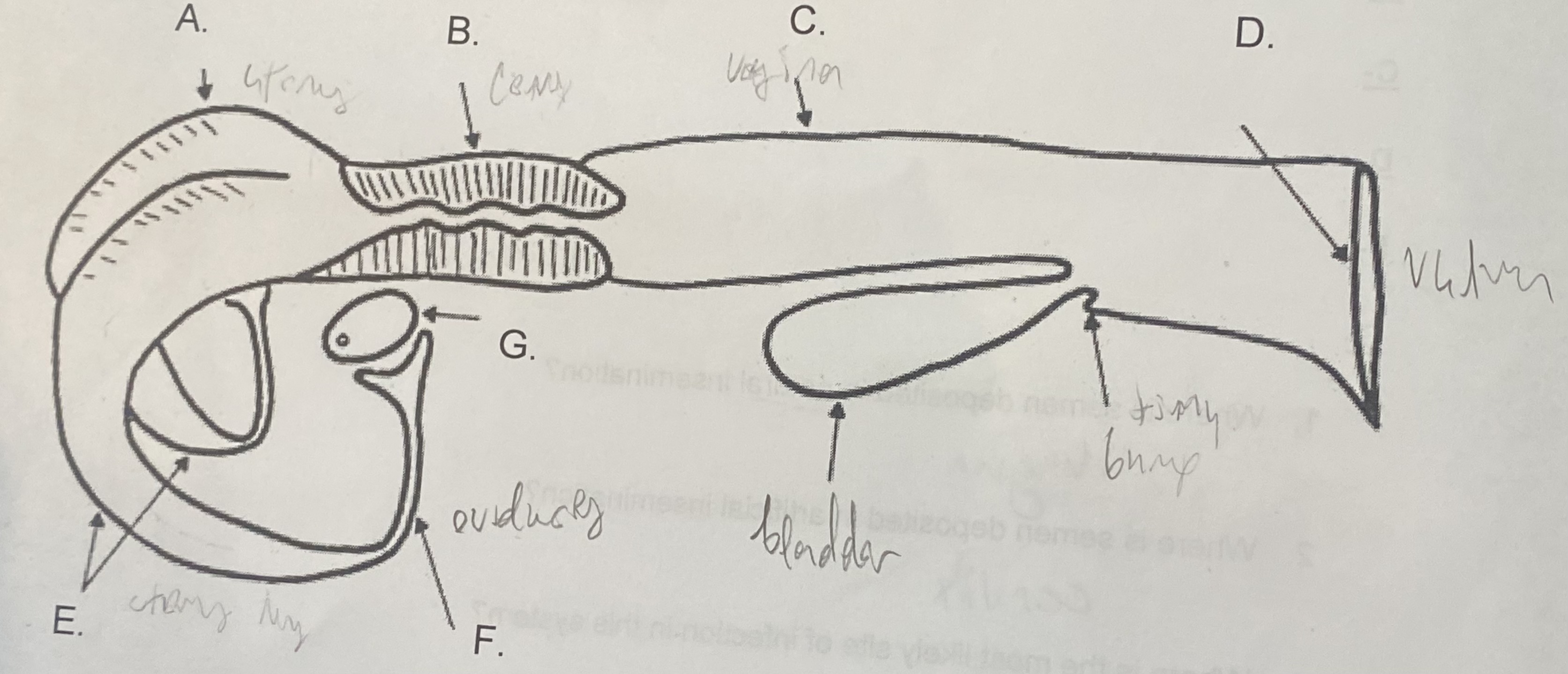
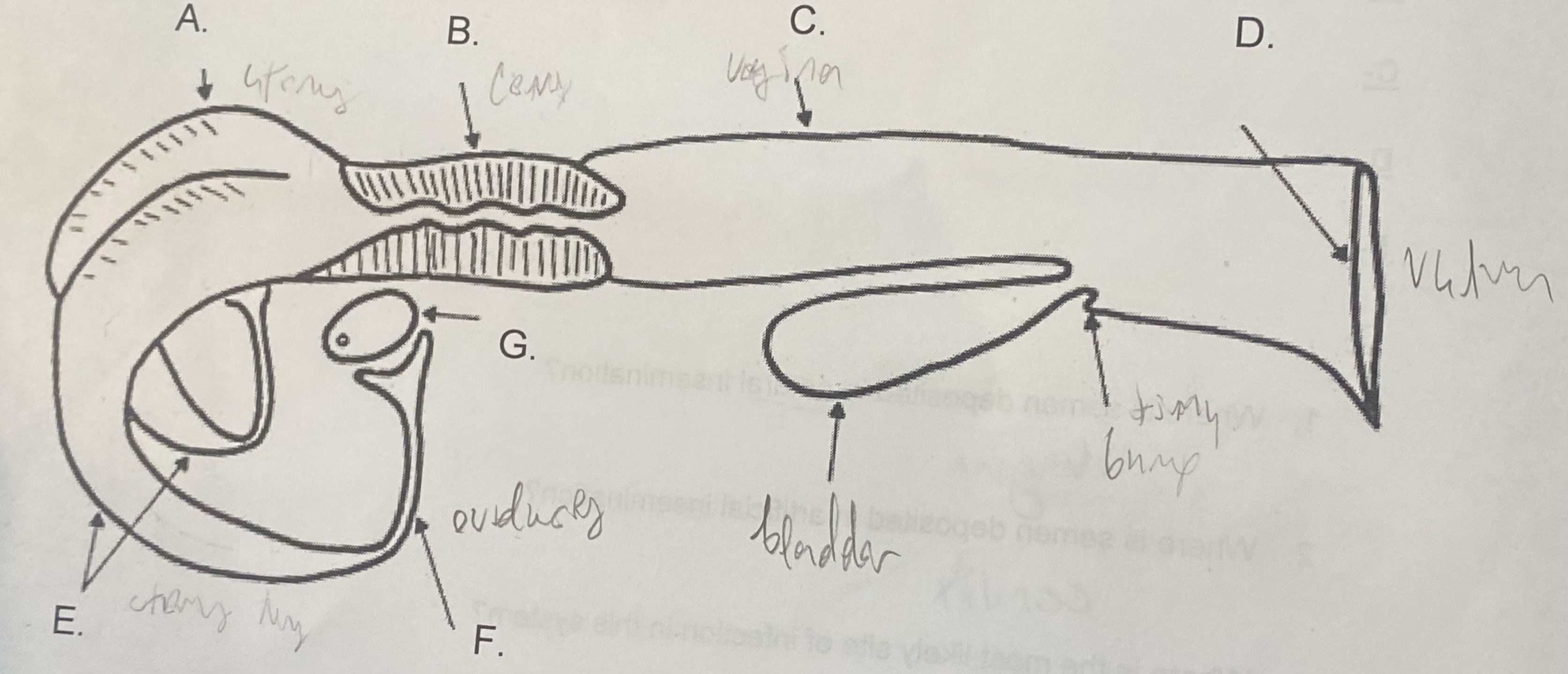
Female - Uterus (A)
-where the egg attaches
-the “womb”
-the “womb”
23
New cards
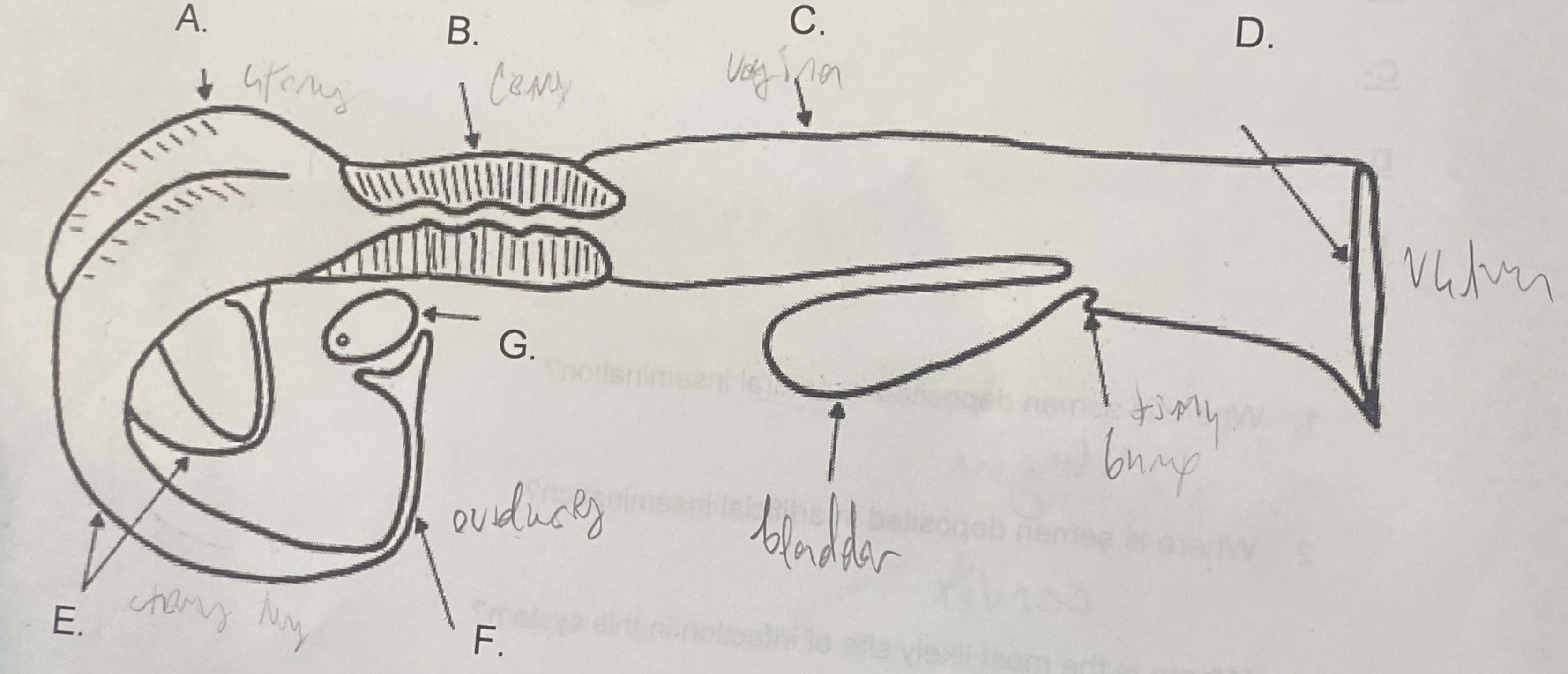
Female - Cervix (B)
\-tight barrier between itself and uterus
\-site of artificial insemination (AI)
\-site of artificial insemination (AI)
24
New cards
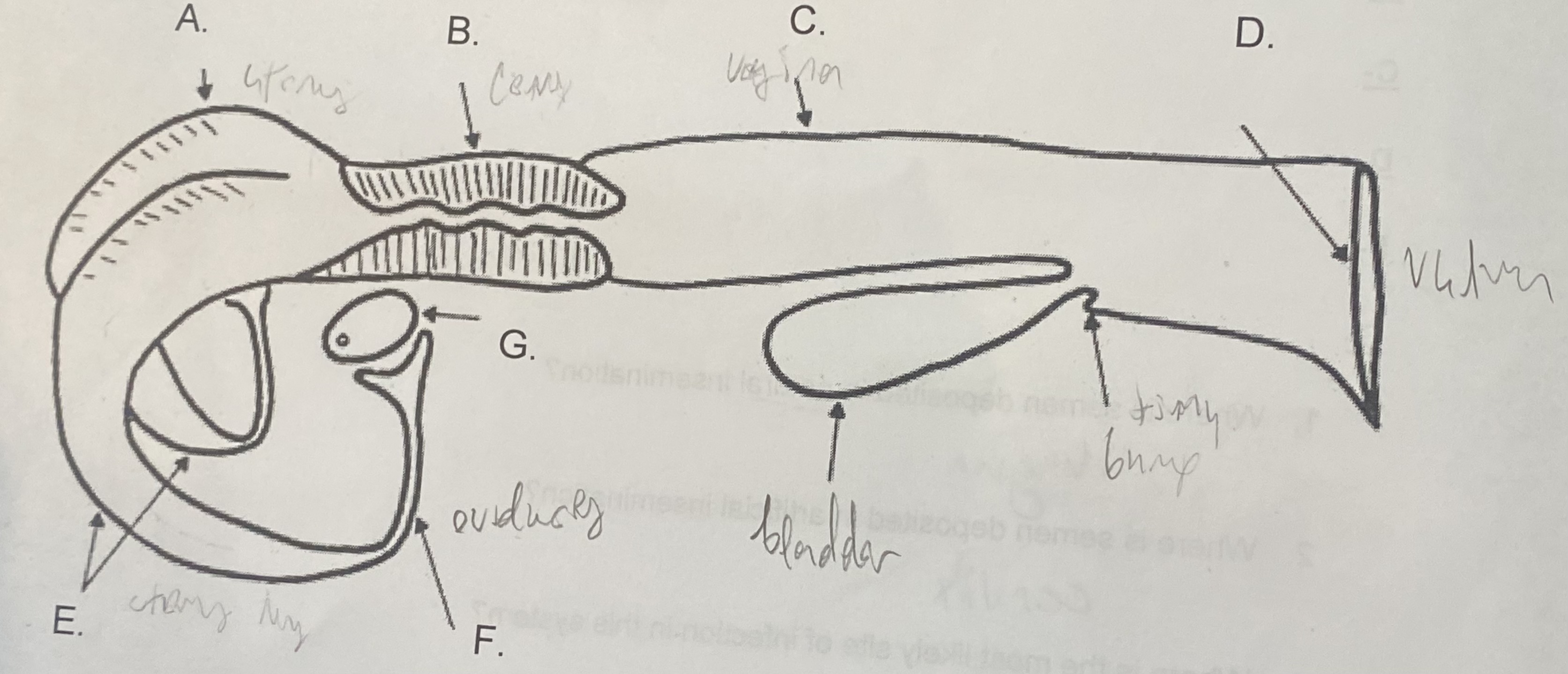
Female - Vagina (C)
-“tube”
-site of natural insemination (NI)
-most common site of infection
-site of natural insemination (NI)
-most common site of infection
25
New cards
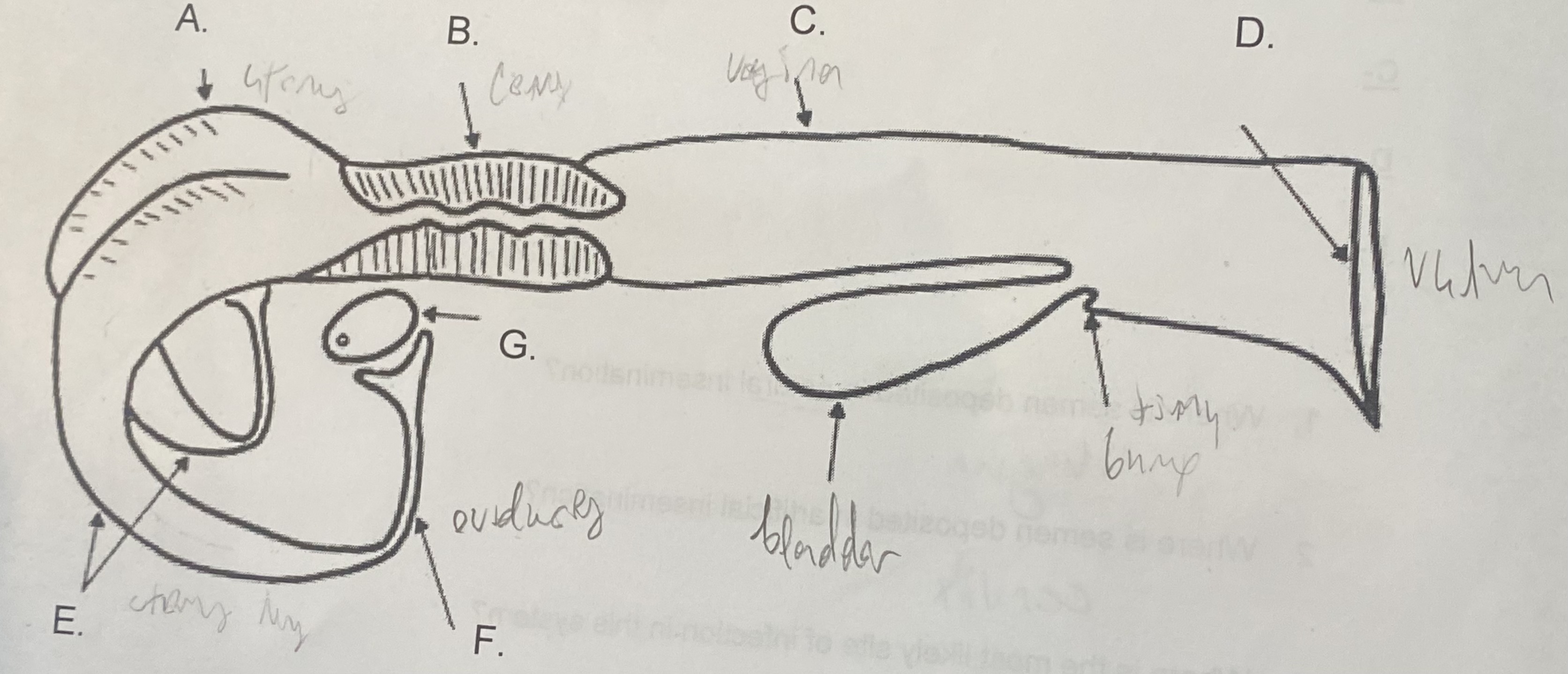
Female - Vulva (D)
-“entryway”
-swells & covers w/ mucus during estrus
-swells & covers w/ mucus during estrus
26
New cards
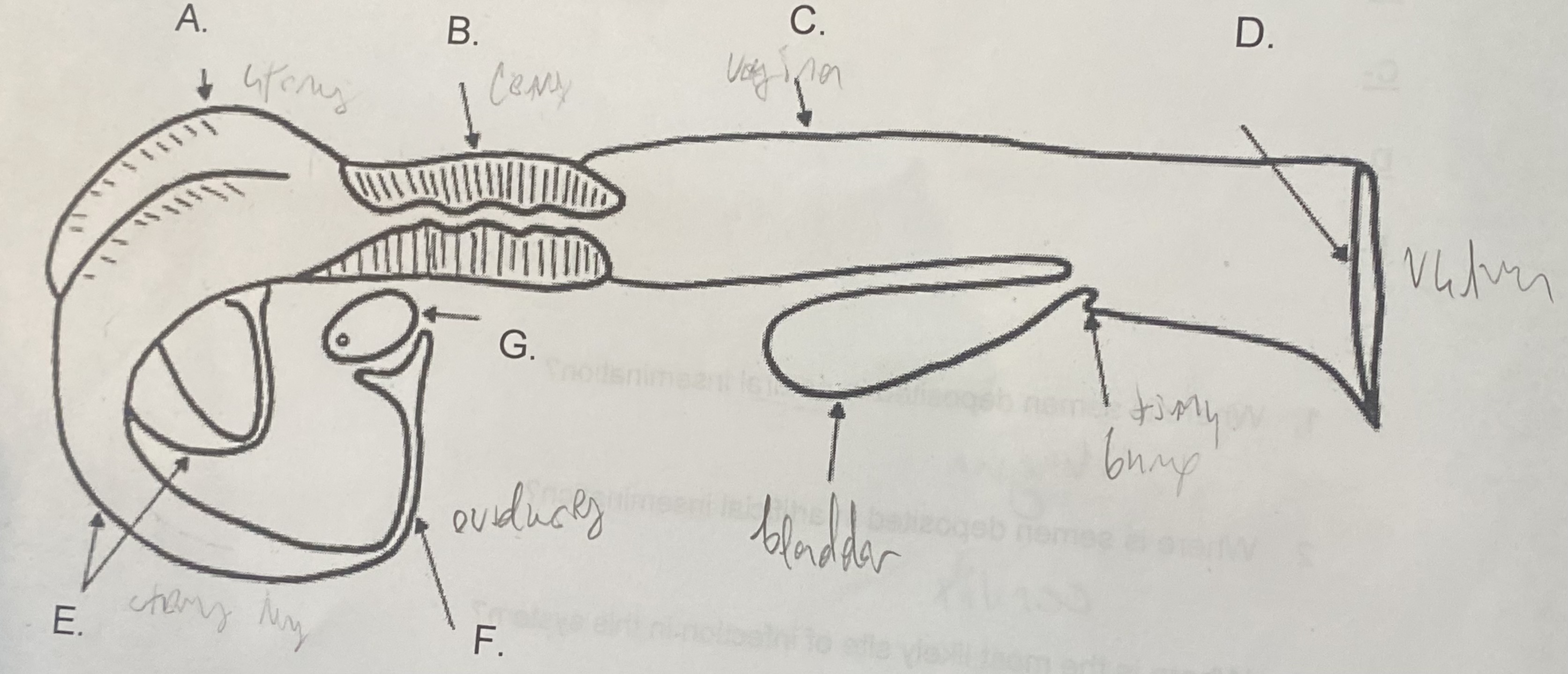
Female - Oviducts (F)
\-where egg is released during corpus luteum
\-path between ovaries and uterine horns
\-path between ovaries and uterine horns
27
New cards
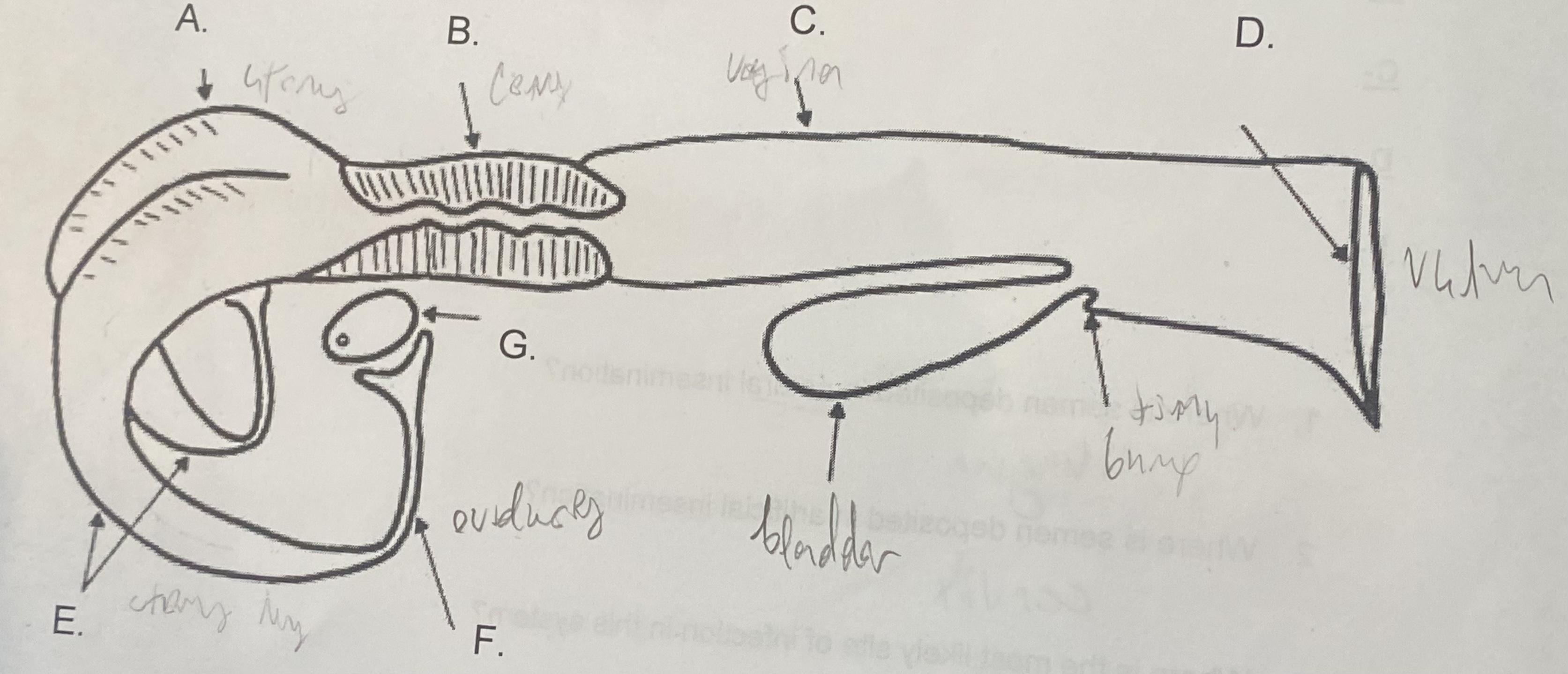
Female - Ovaries (G)
-holds egg supply (finite)
-releases egg during ovulation
-releases egg during ovulation
28
New cards
Female - Uterine Horns (E)
-between ovary & uterus
-length/development determines reproductive capability (size of litter)
-length/development determines reproductive capability (size of litter)
29
New cards
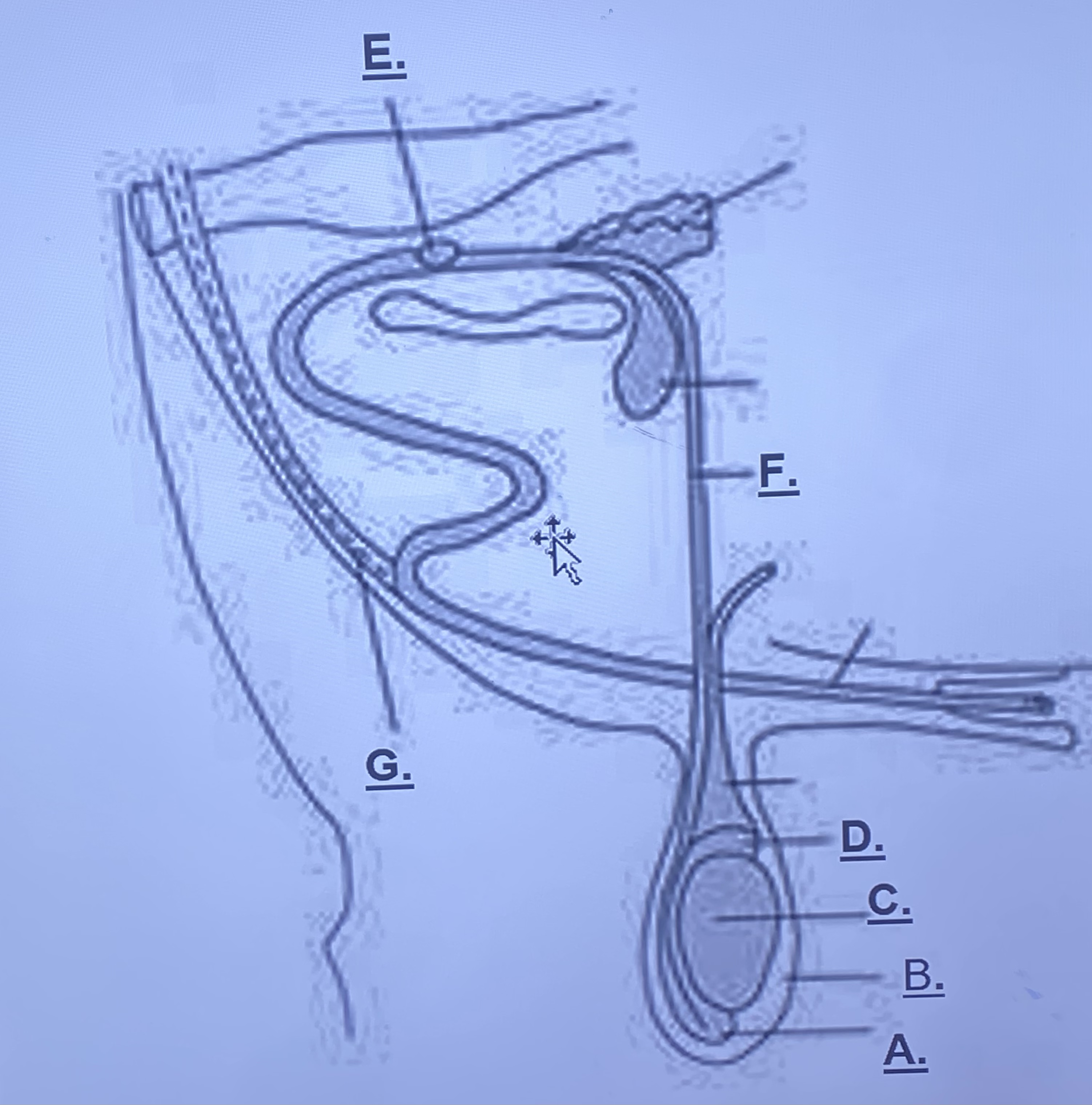
Male - Scrotum (B)
outside skin, protects testes slightly from outside world. rises and lowers based on temperature
30
New cards
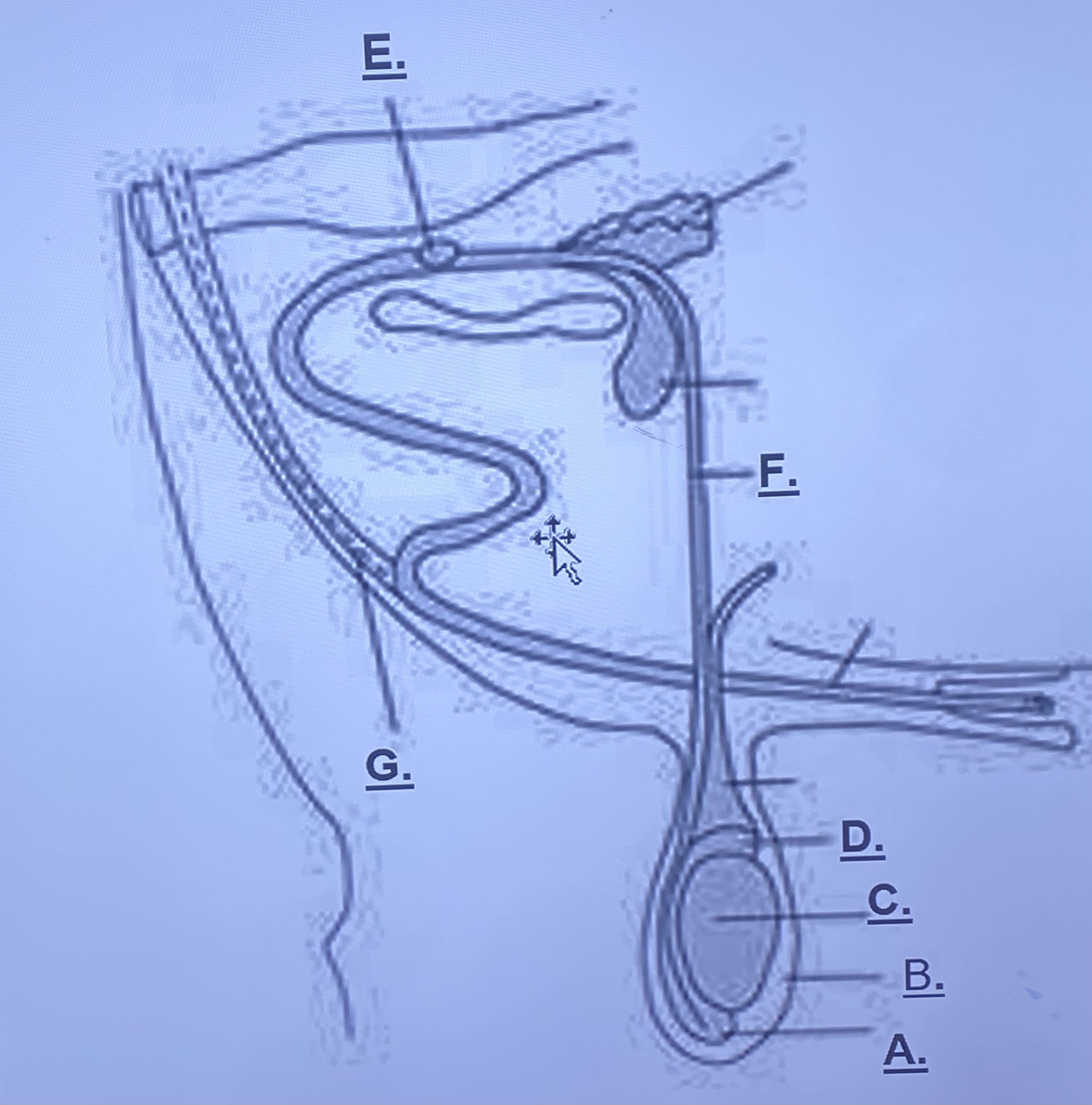
Male - Testicle (C)
produces spermatozoa
31
New cards
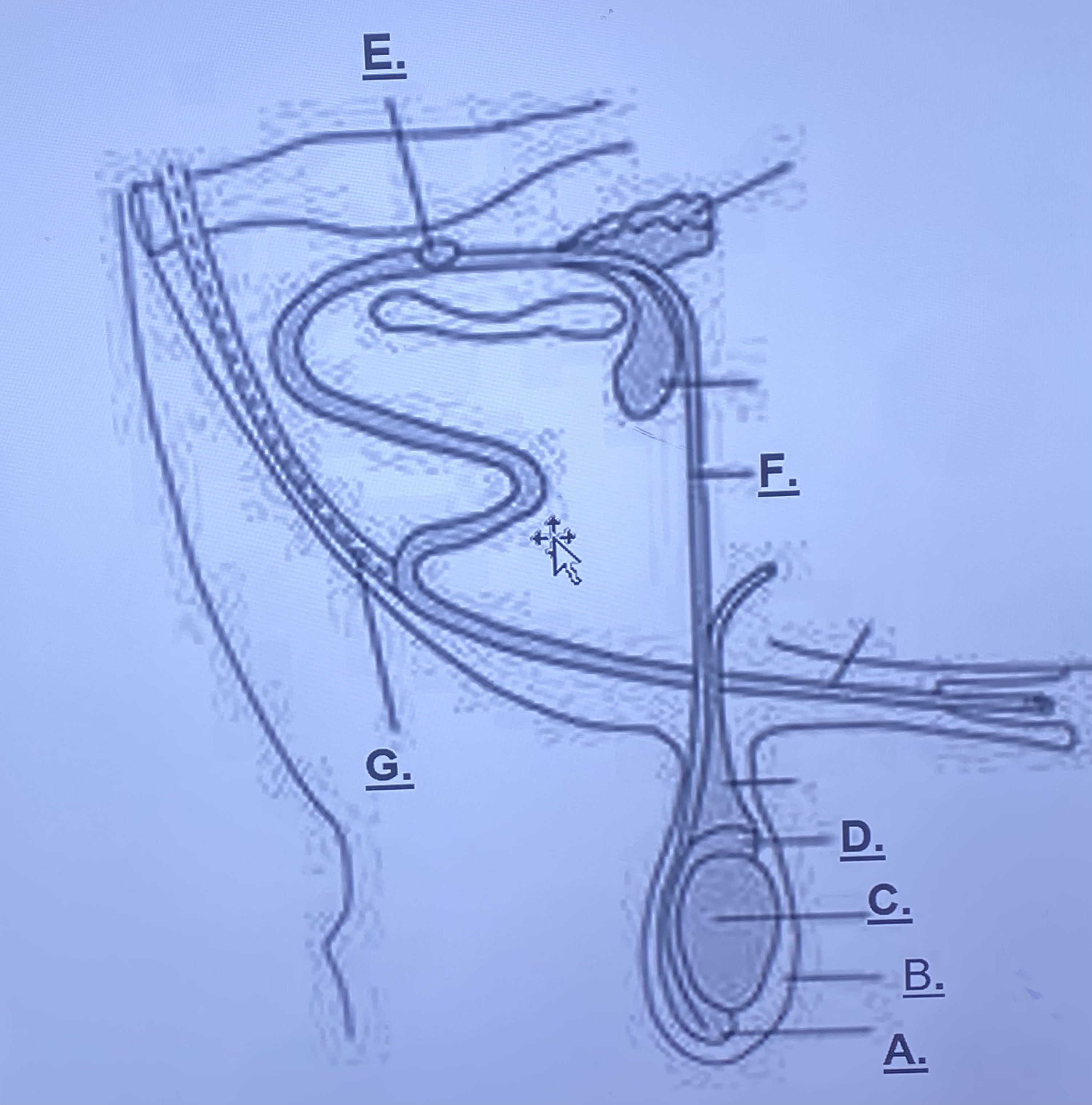
Male - Head of Epididymus (D)
stores immature sperm cells
32
New cards
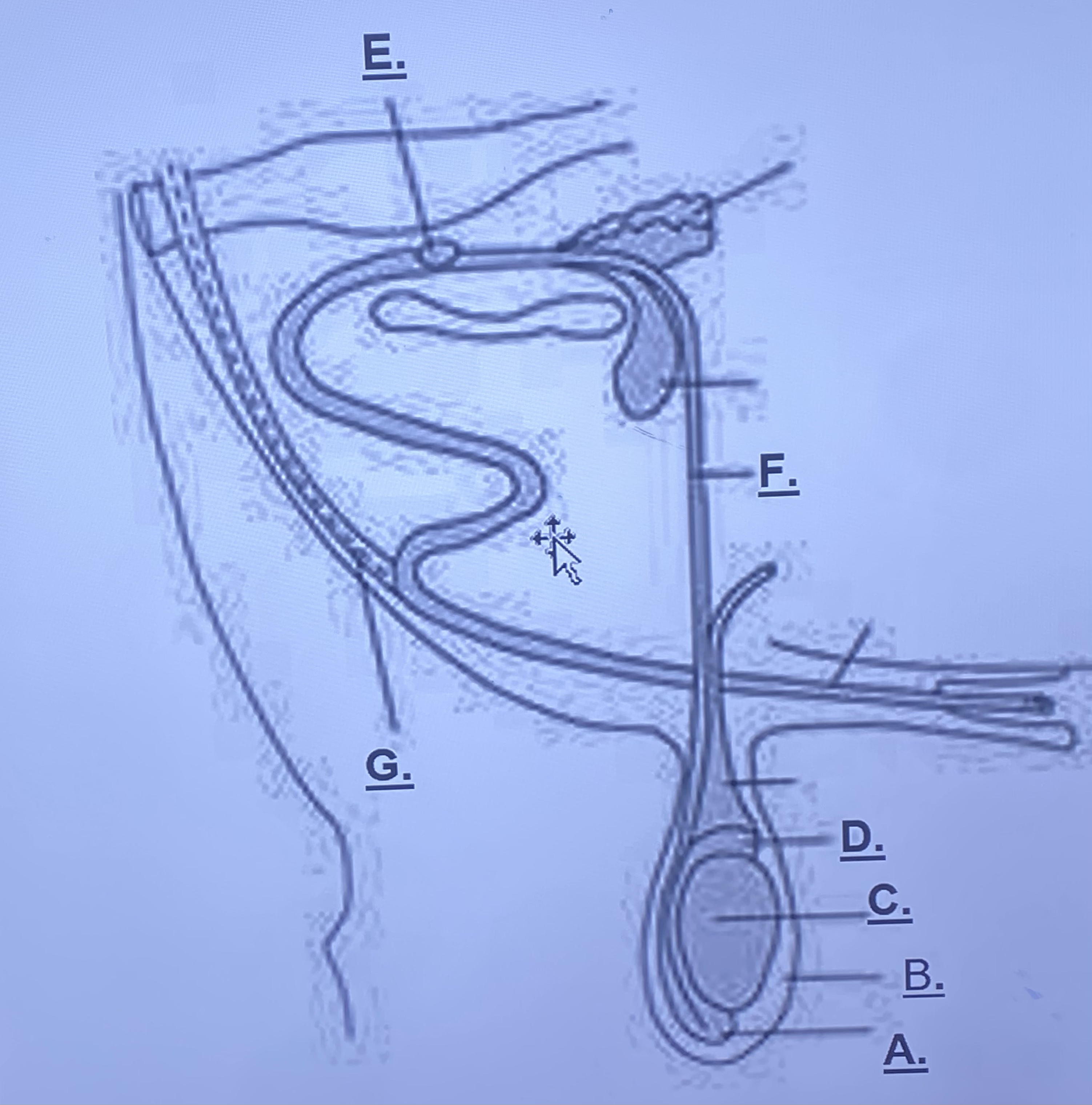
Male - Tail of Epididymus (A)
stores mature sperm cells
33
New cards
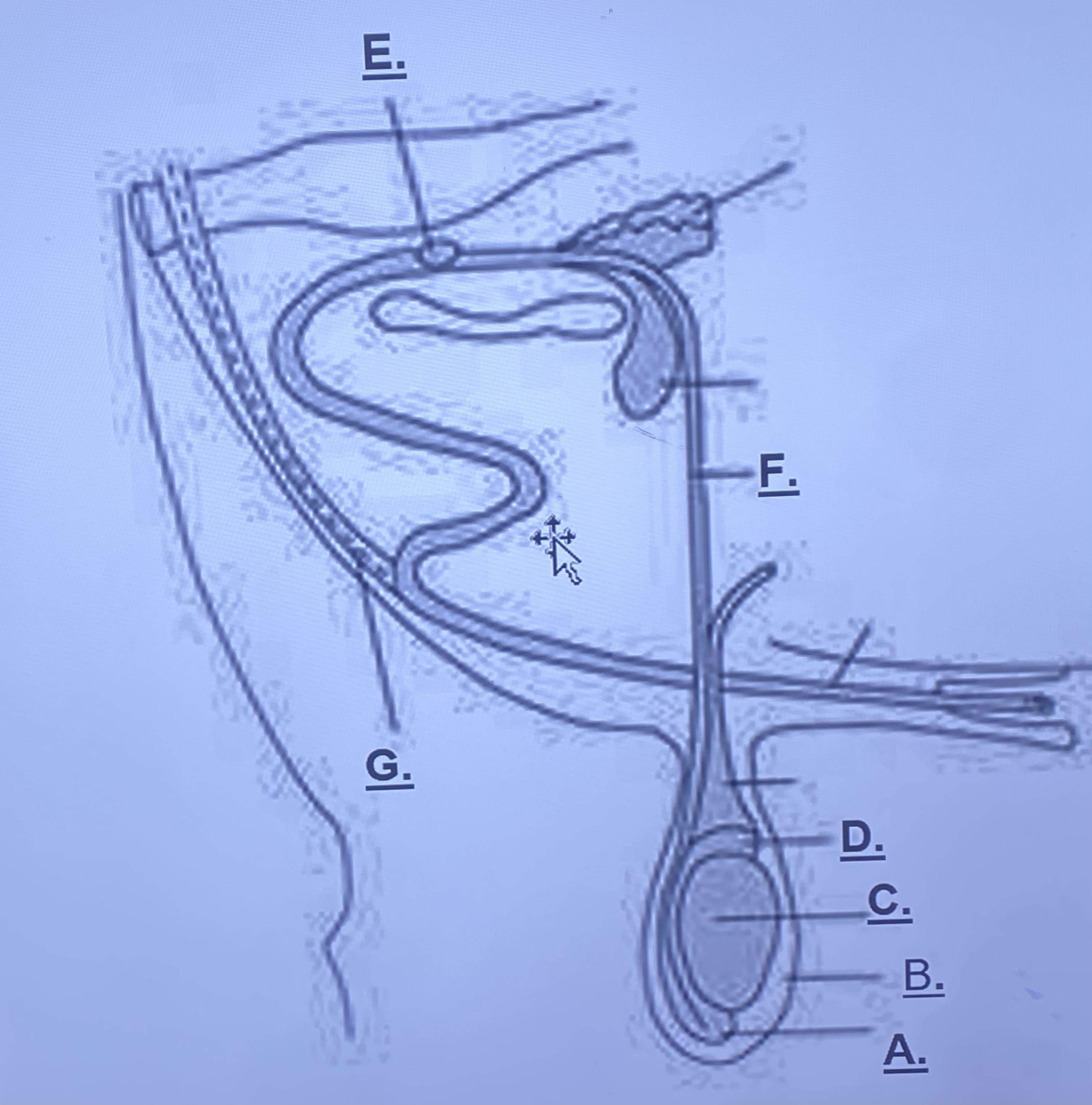
Male - Prostate Gland (Unlabeled)
-adds a buffer solution (change in pH) for sperm cells to survive in female repro. this is what becomes semen
34
New cards
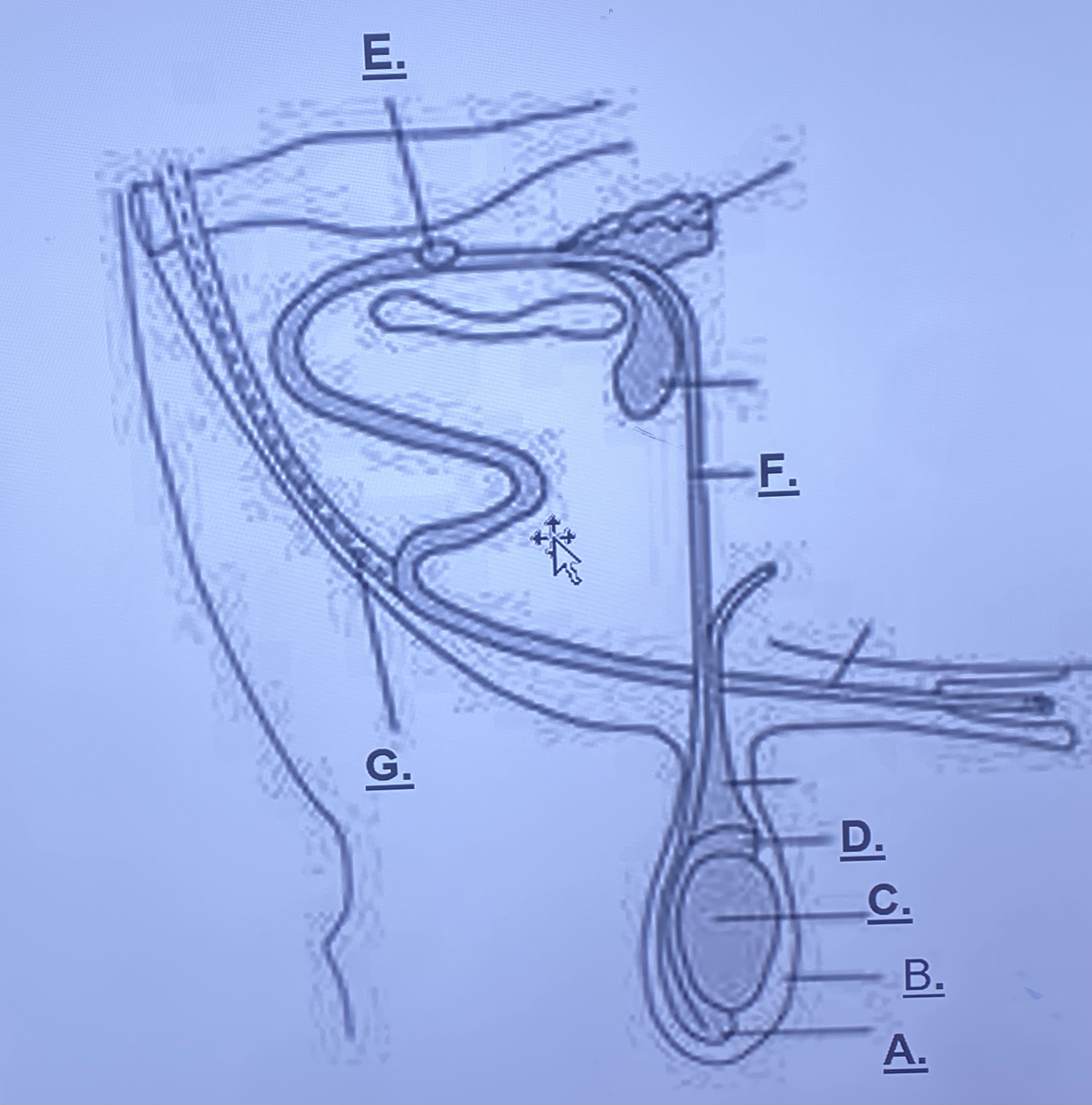
Male - Cowper’s Gland (E)
-cleans remaining urine out of urethra
-“m y q u e e n” (v. sorry to the rest of you this is only for bella and brady)
-“m y q u e e n” (v. sorry to the rest of you this is only for bella and brady)
35
New cards
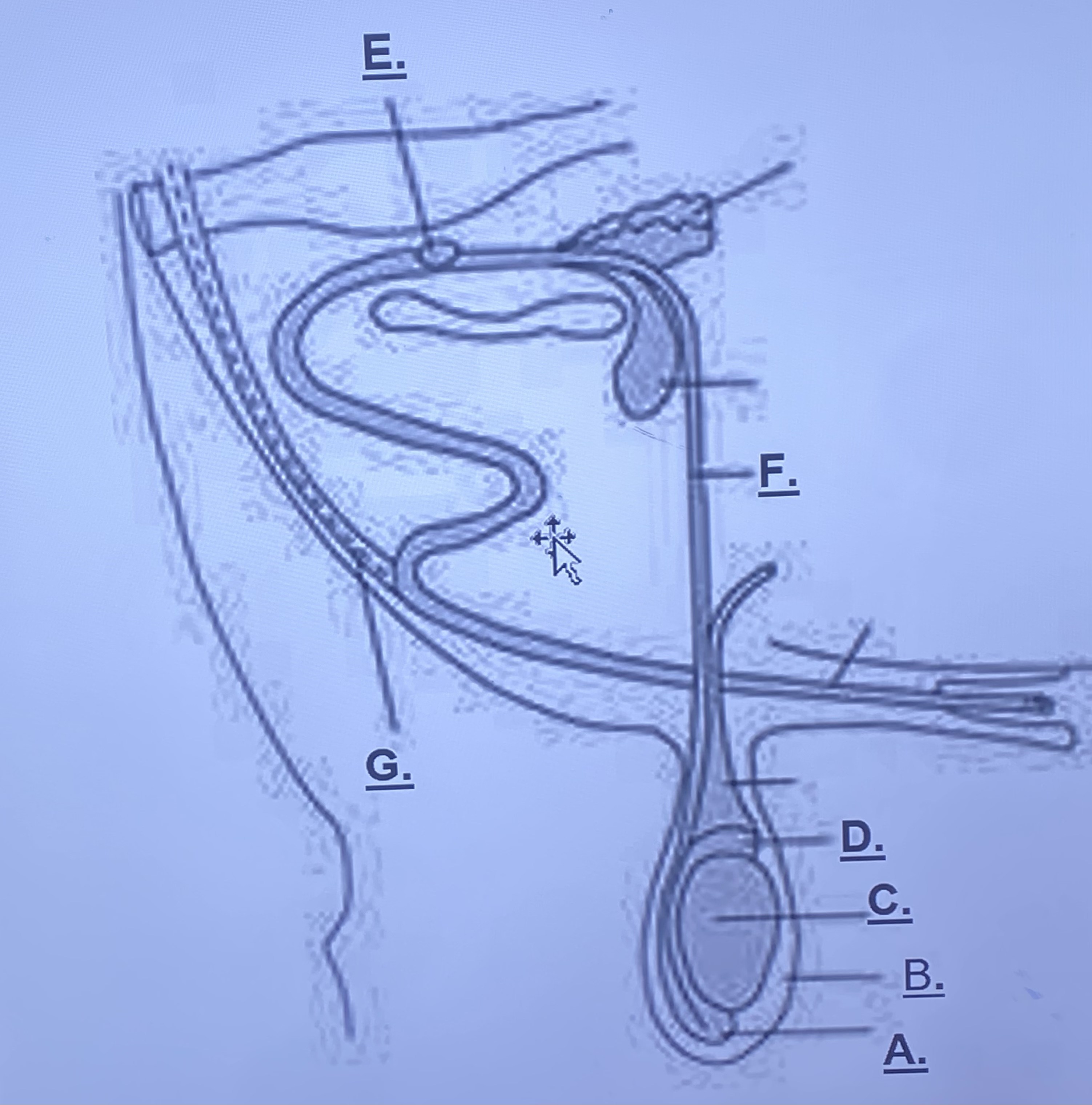
Male - Sigmoid Flexure (Unlabeled)
-fills with blood, enlarges in order to be inserted into a vagina
36
New cards
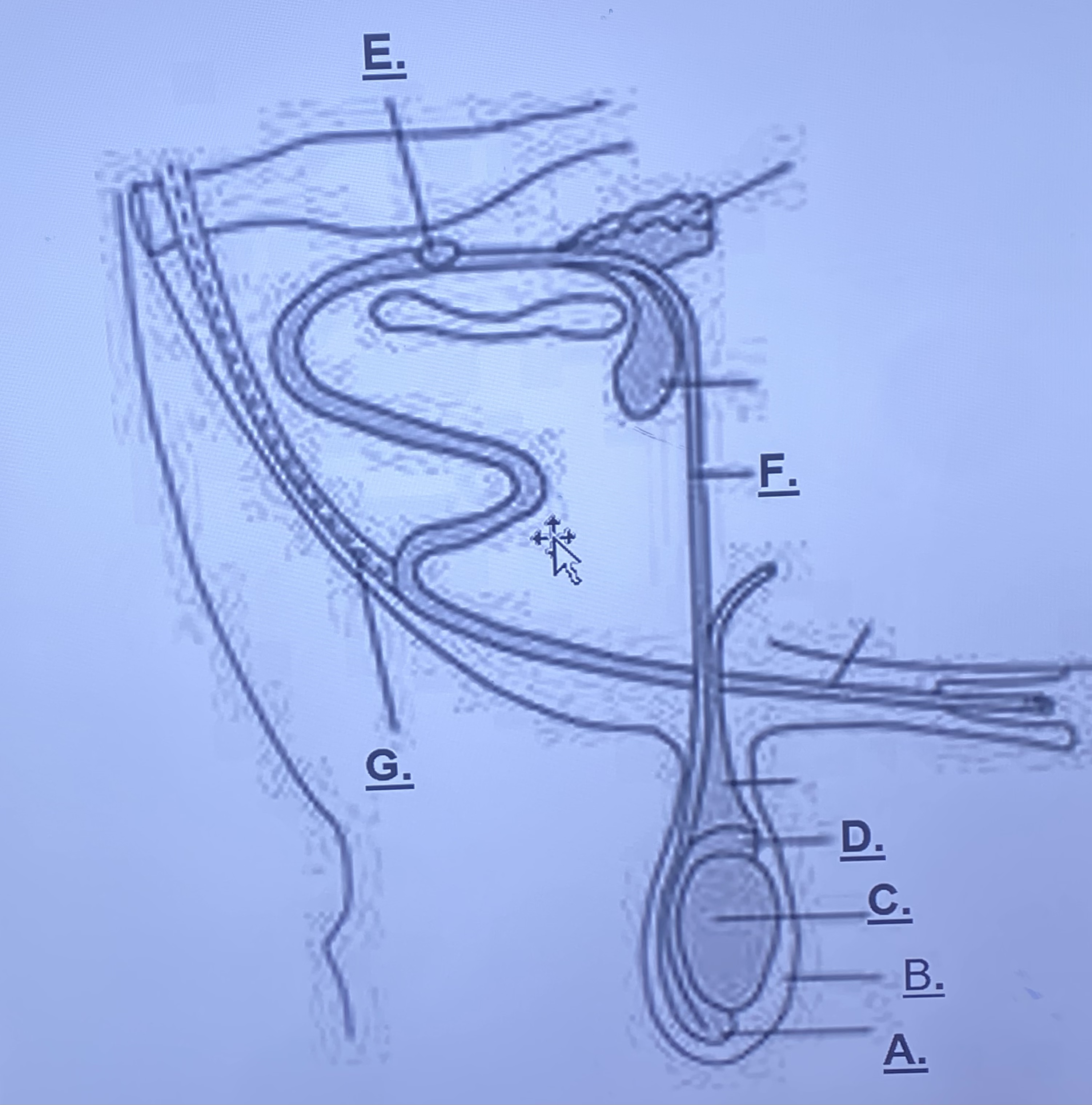
Male - Retractor Muscle (G)
pulls sigmoid flexure back when reproduction is finished
37
New cards
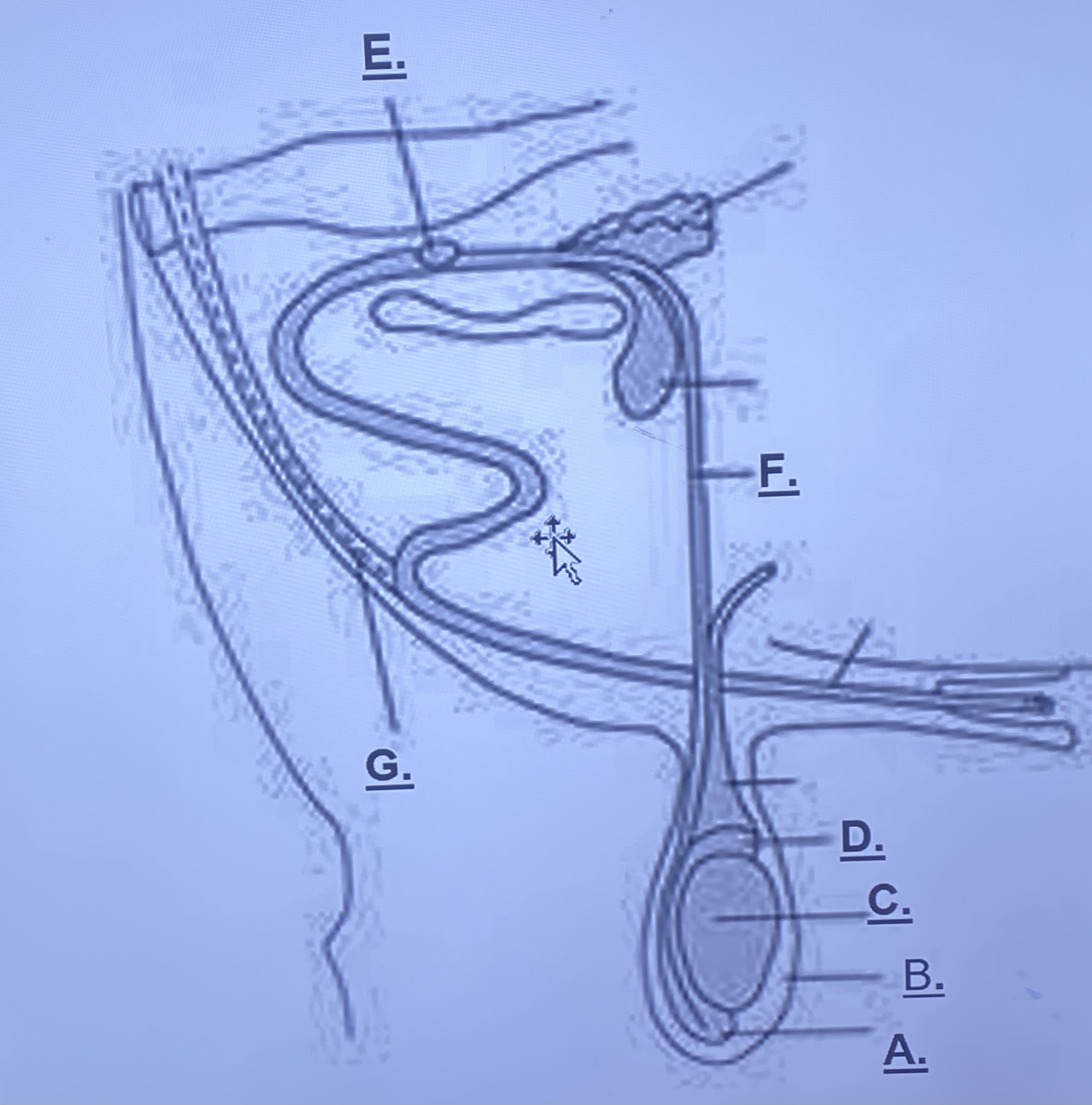
Male - Vas Deferens (F)
transports sperm from epididymis to prostate
38
New cards
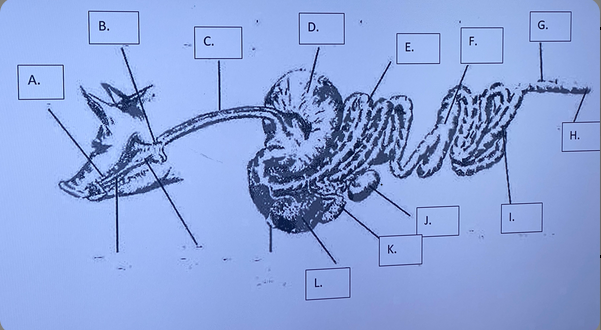
Monogastric - Liver (L)
produces bile