A2 Unit 4.3 & 4.5 Alcohols and Phenols & Carboxylic acids and their derivatives
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
MAKING ALCOHOLS - Fermentation & From Alkenes

Fermentation v Addition Reaction

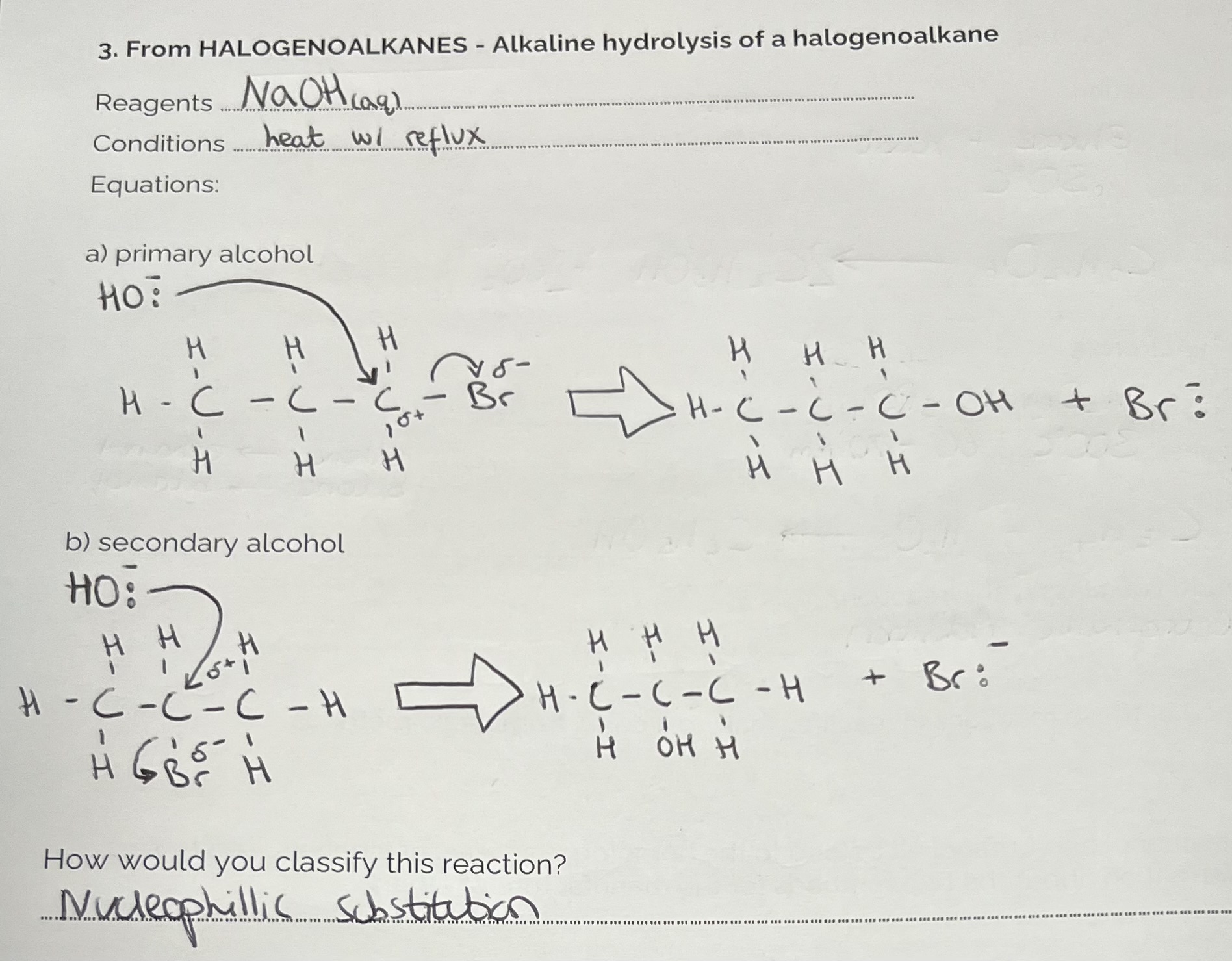
Making Alcohols from Halogenoalkanes
Free Radical Substitution

Making Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds
(Practice questions on pg. 6)

Converting Alcohols to Carbonyl Compounds

Esterification
Esters are sweet smelling.

Converting Alcohols with Ethanoyl Chloride to give esters

Esterification v Ethanoylation

Boiling Points
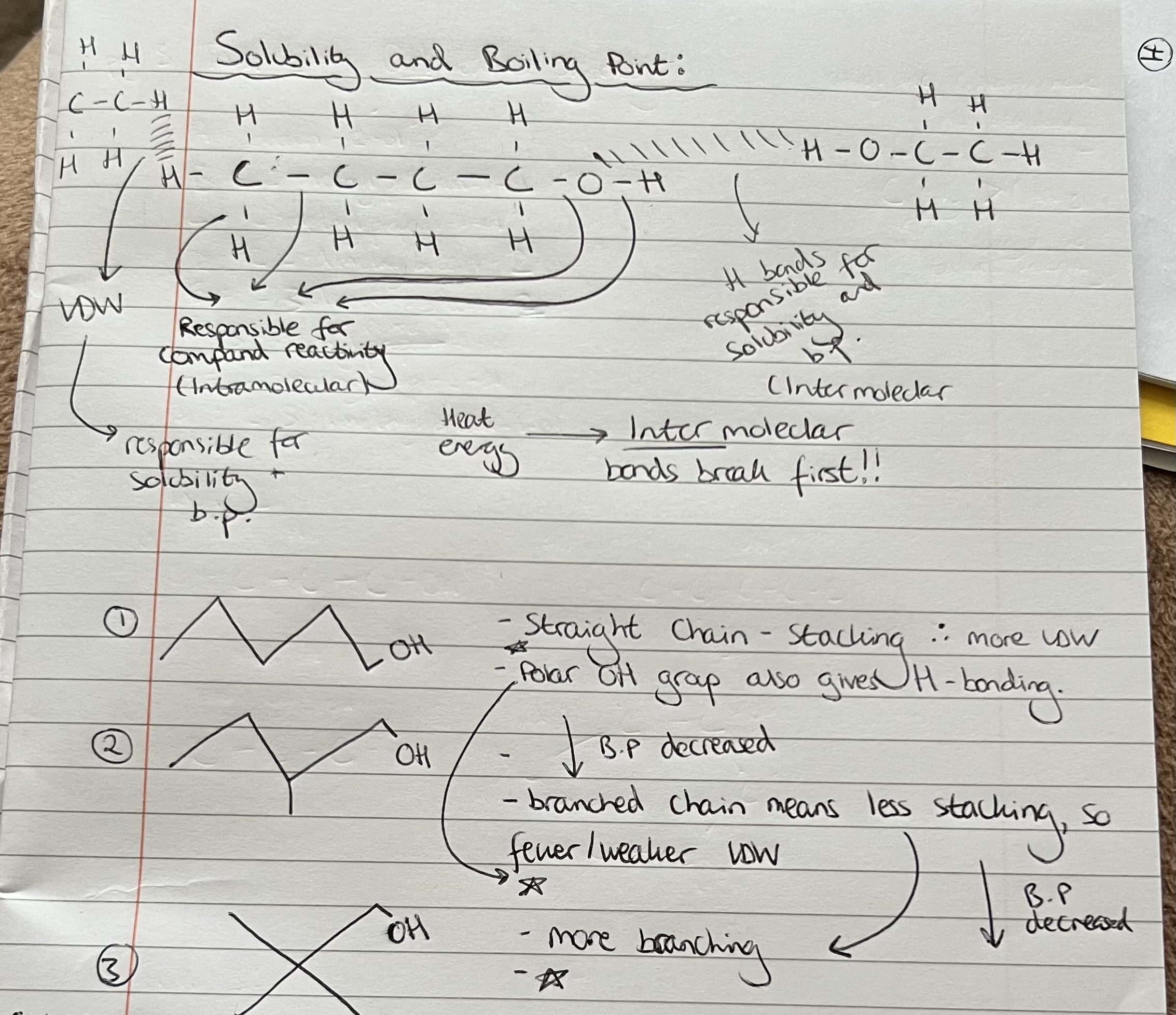
Solubility
Interact not react with H20 molecules. Draw O-H in full.
With ethanol you would observe one layer. With hexan-1-ol you would observe 2 layers as it is less soluble (water on the bottom & hexan-1-ol’ on top)

Converting Alcohols with Hydrogen Halides to give Halogenoalkanes
(Complete questions on pg. 10)

Alcohols Practical
Hydroxy compounds (alcohols) i.e propan-1-ol, propan-2-ol etc. have an artifical solvent/ chemical scent and are colourless/ antiseptic.
They are soluble in water (forms one layer). They are all highly flammable - longer chain fuels release more energy and burn for longer (more bonds broken).
As the chain length increases, solubility decreases - greater number of VDW forces. Hydrogen bonds due to polar OH group are less significant/ VDW have greater influence over inter-molecular forces
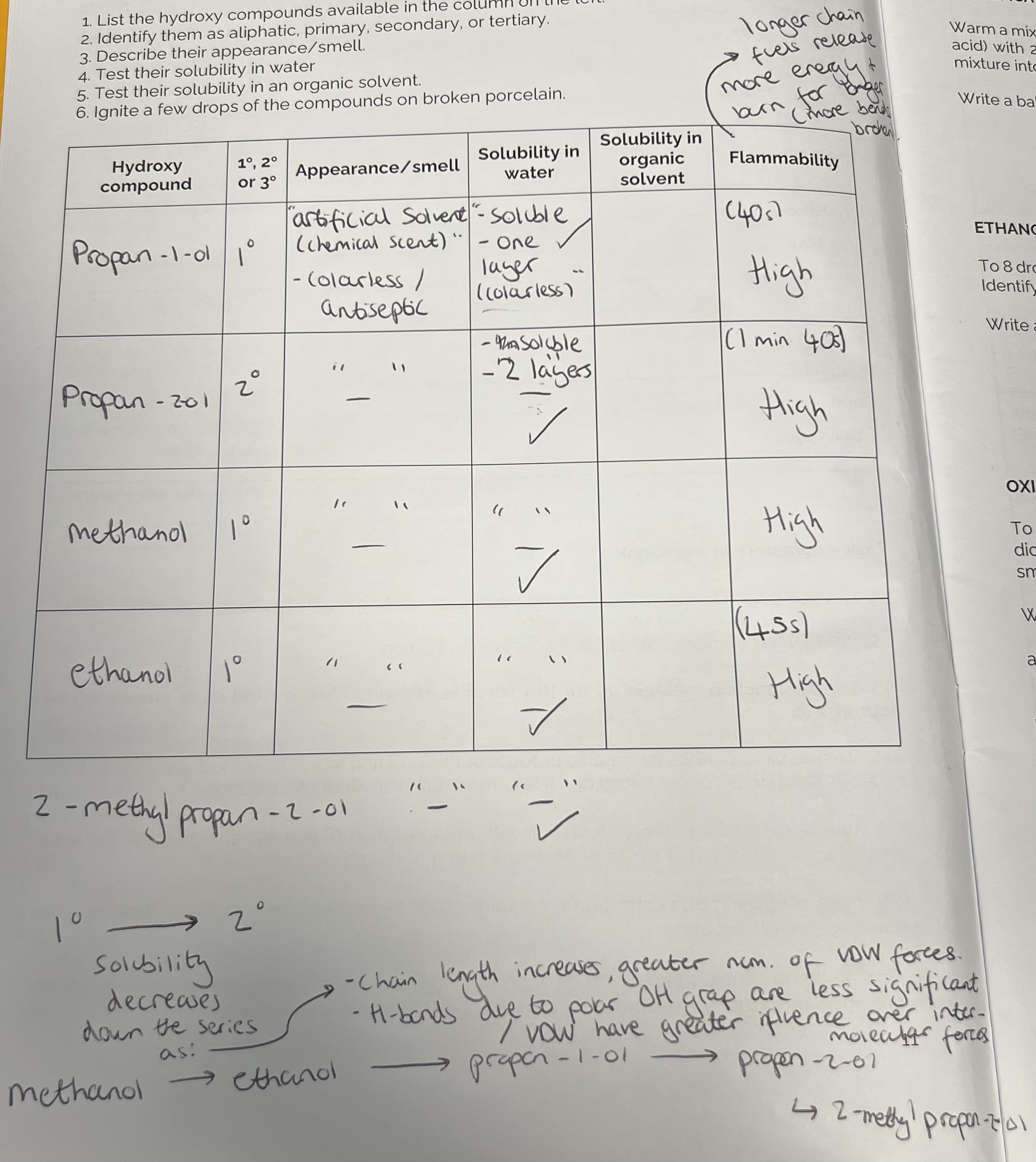
Alcohols Practical 2

Testing for Carbonyl Compounds
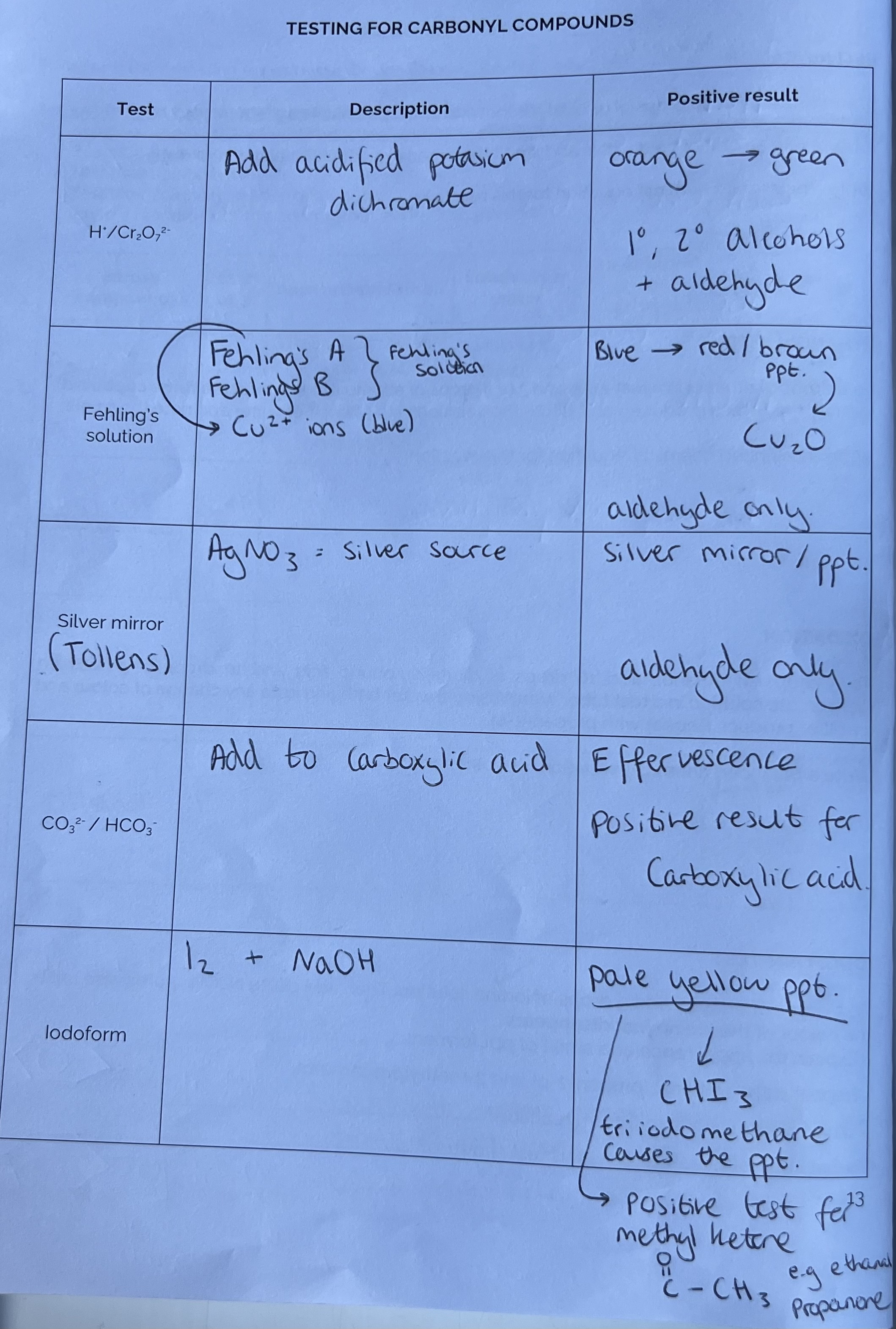
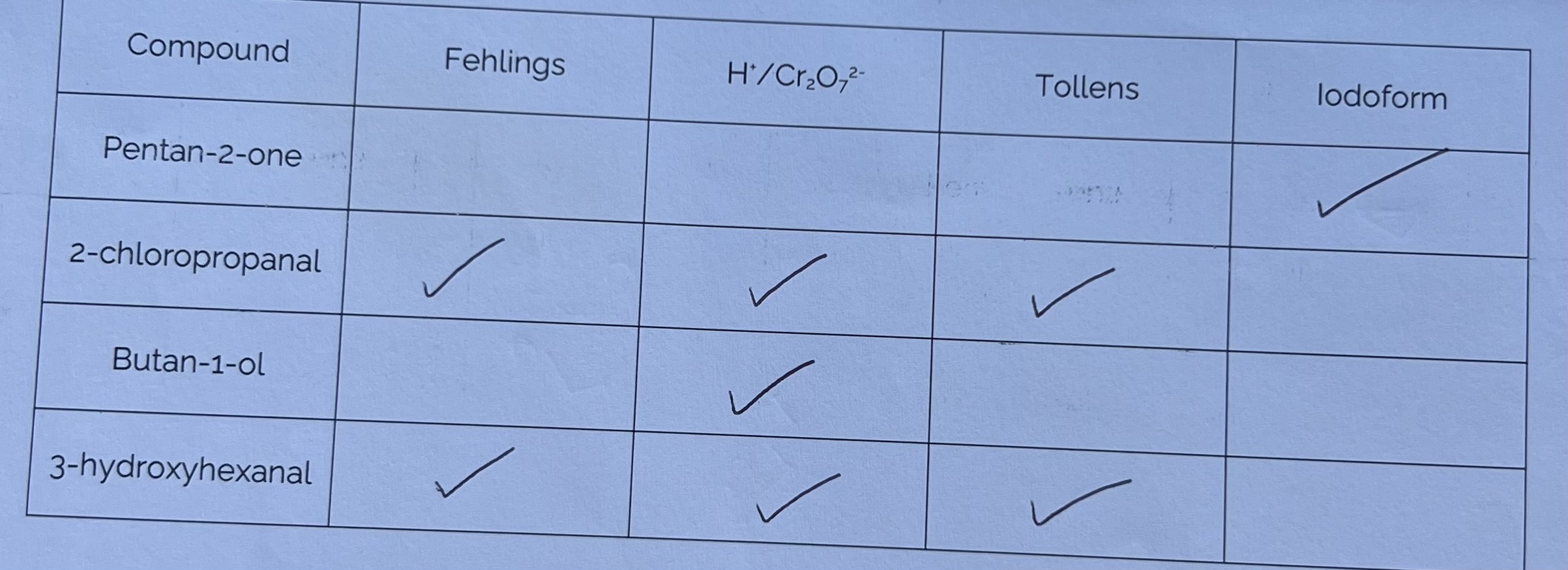
Practice Questions - Testing for Carbonyl Compounds
(Practice questions on pg. 14-16)
Aromatic alcohols - Phenols structure

Acidity of Phenol

The phenoxide ion

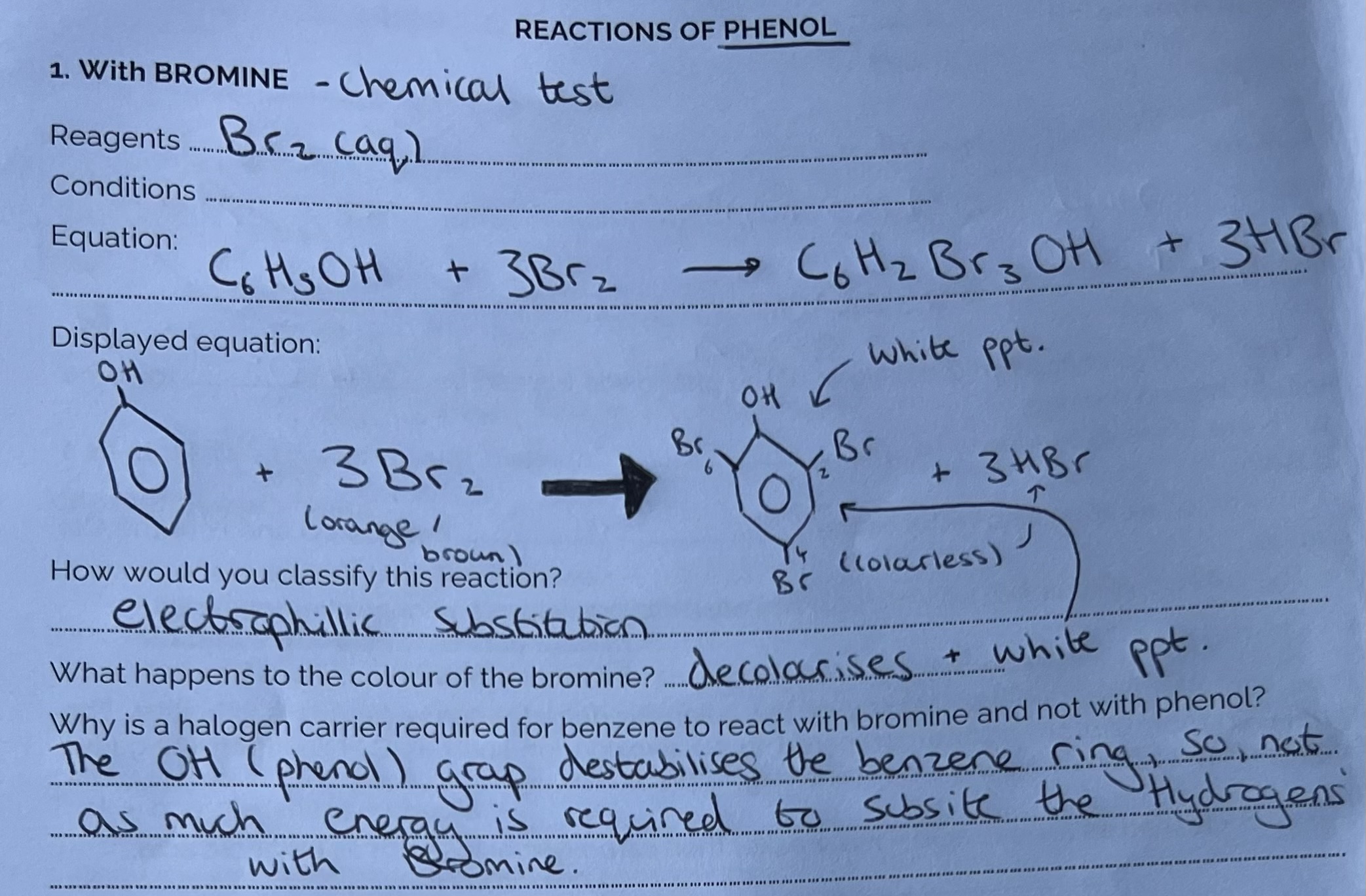
Reactions of Phenol with Bromine
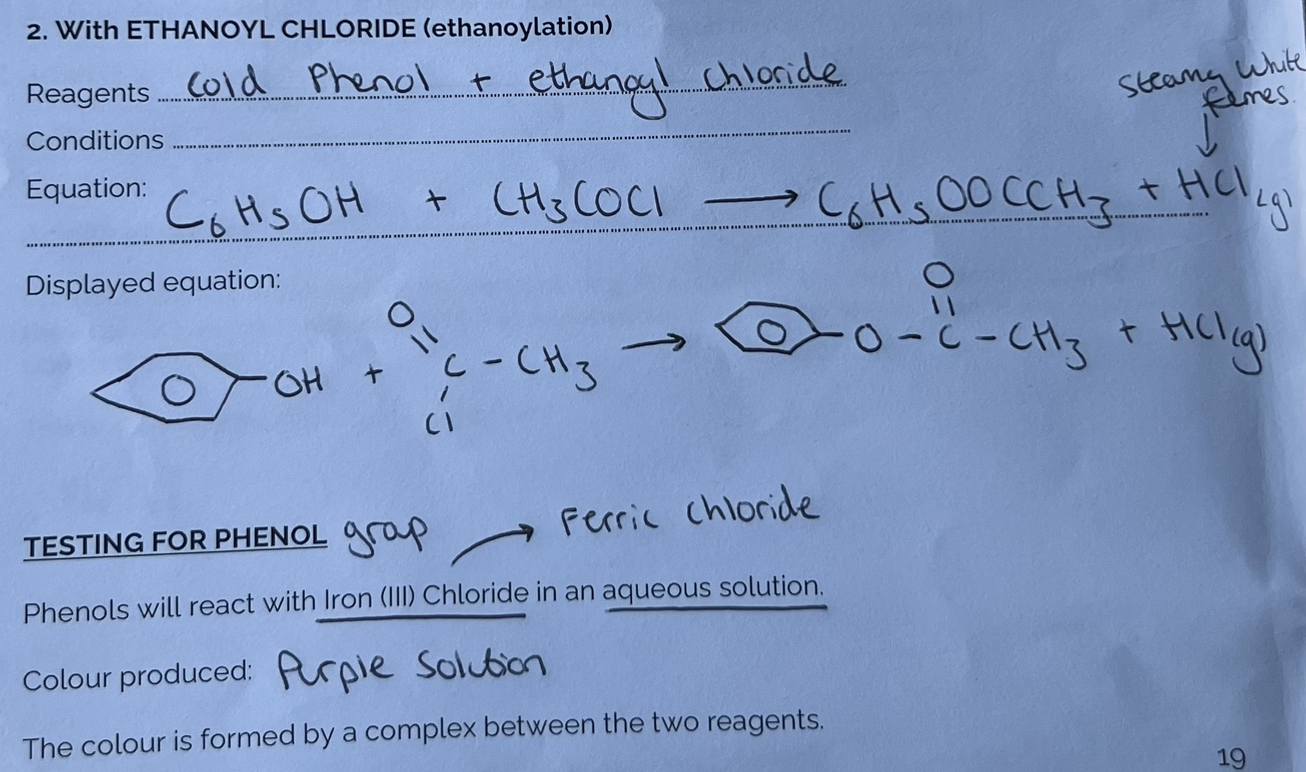
Reactions of Phenol with Ethanol Chloride & Testing for Phenol group
Phenols Practical
Carboxylic Acids
(Practice questions on pg. 23)

Physical Properties of the lower Carboxylic Acids
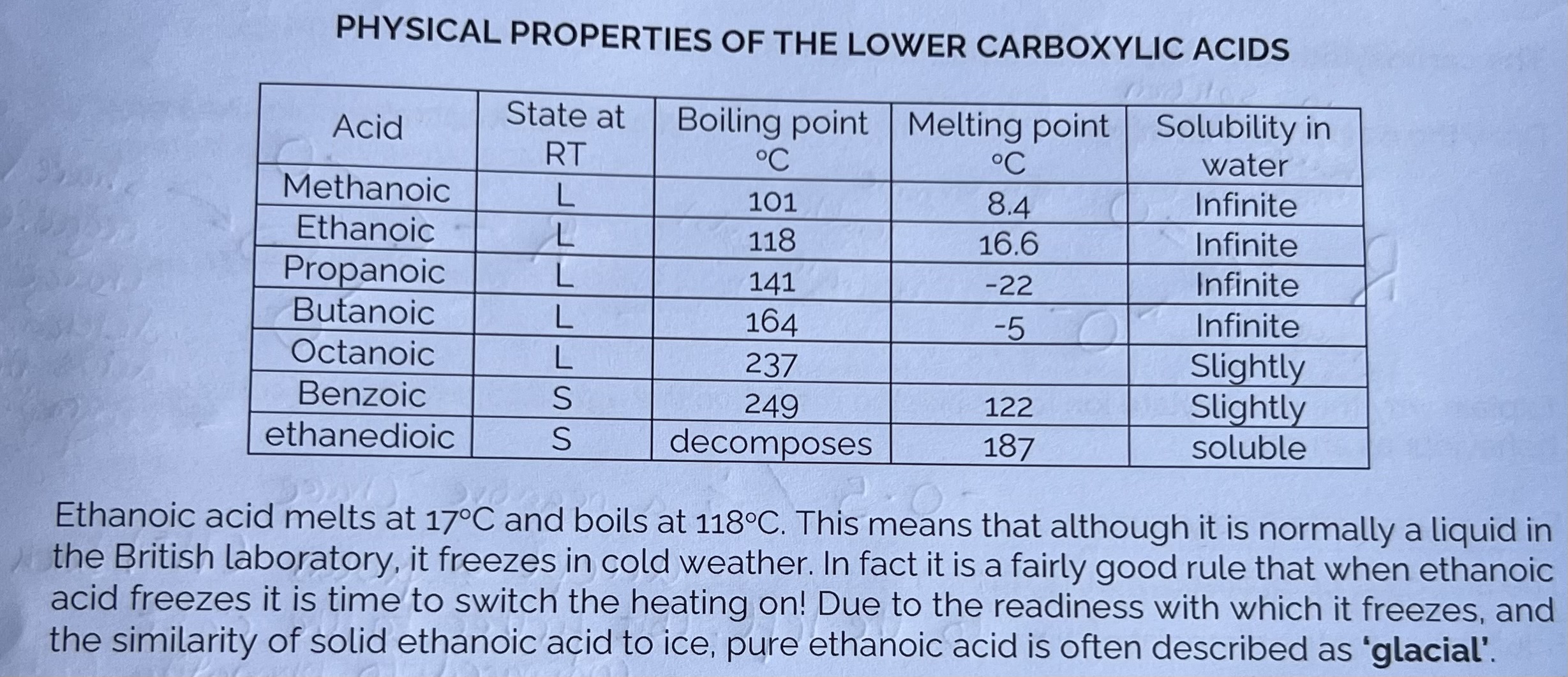
Physical Properties of the lower Carboxylic Acids - Example Questions

Acidic properties of the Carboxylic Acids

The Carboxylate Ion

Making Carboxylic Acids from Alcohols, Aldehydes & Esters (Acid Hydrolysis)

Making Carboxylic Acids from Esters (Alkaline Hydrolysis)
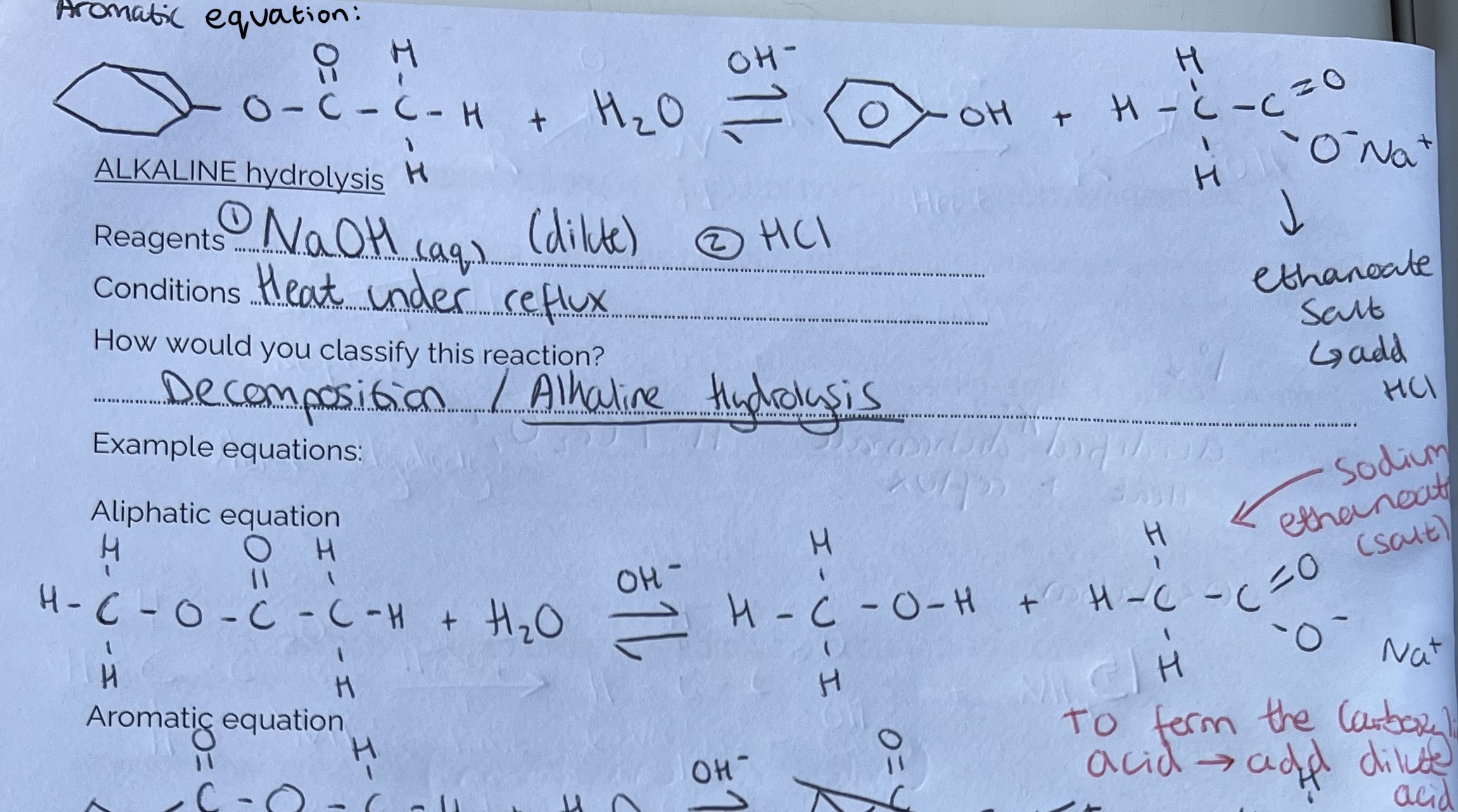
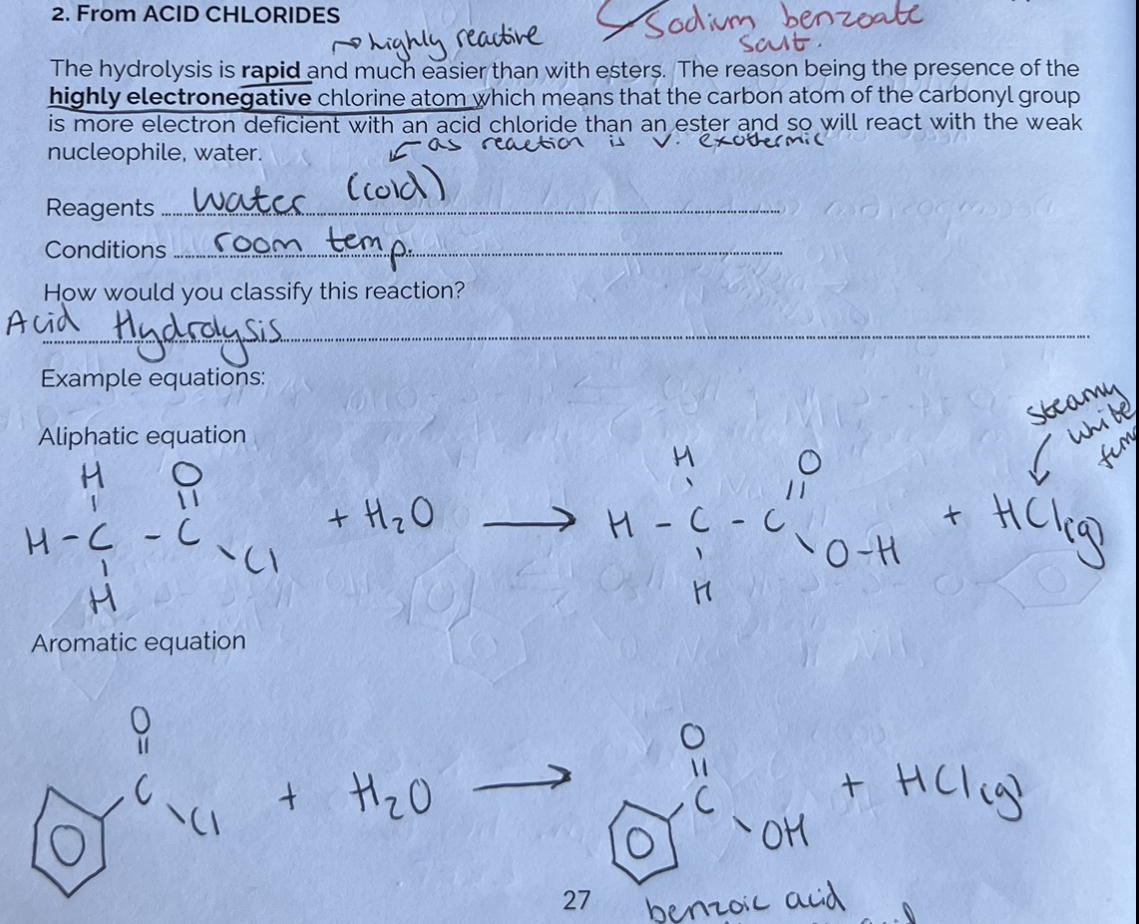
Making Carboxylic Acids from Acid Chlorides
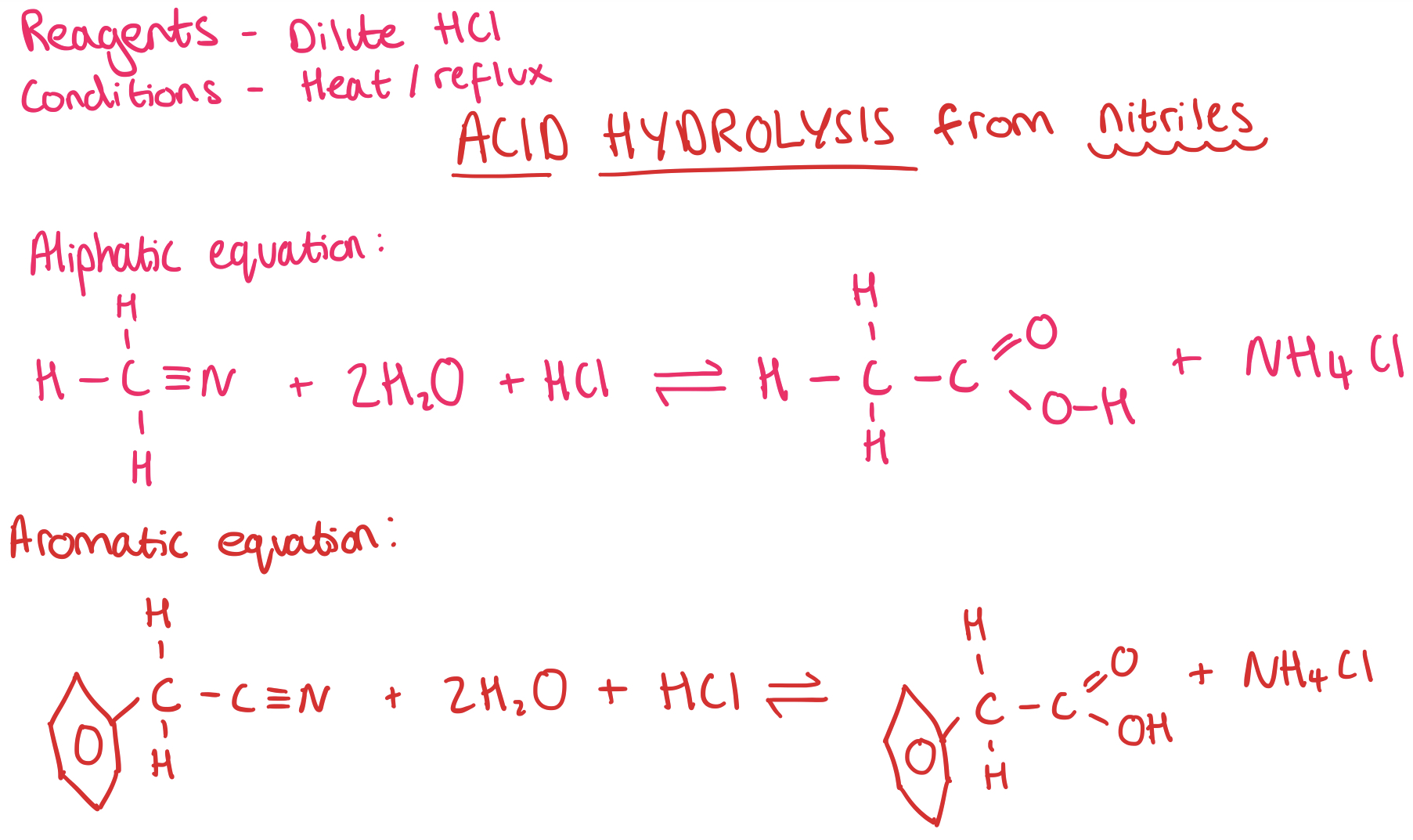
Making Carboxylic Acids from Nitriles - Acid Hydrolysis
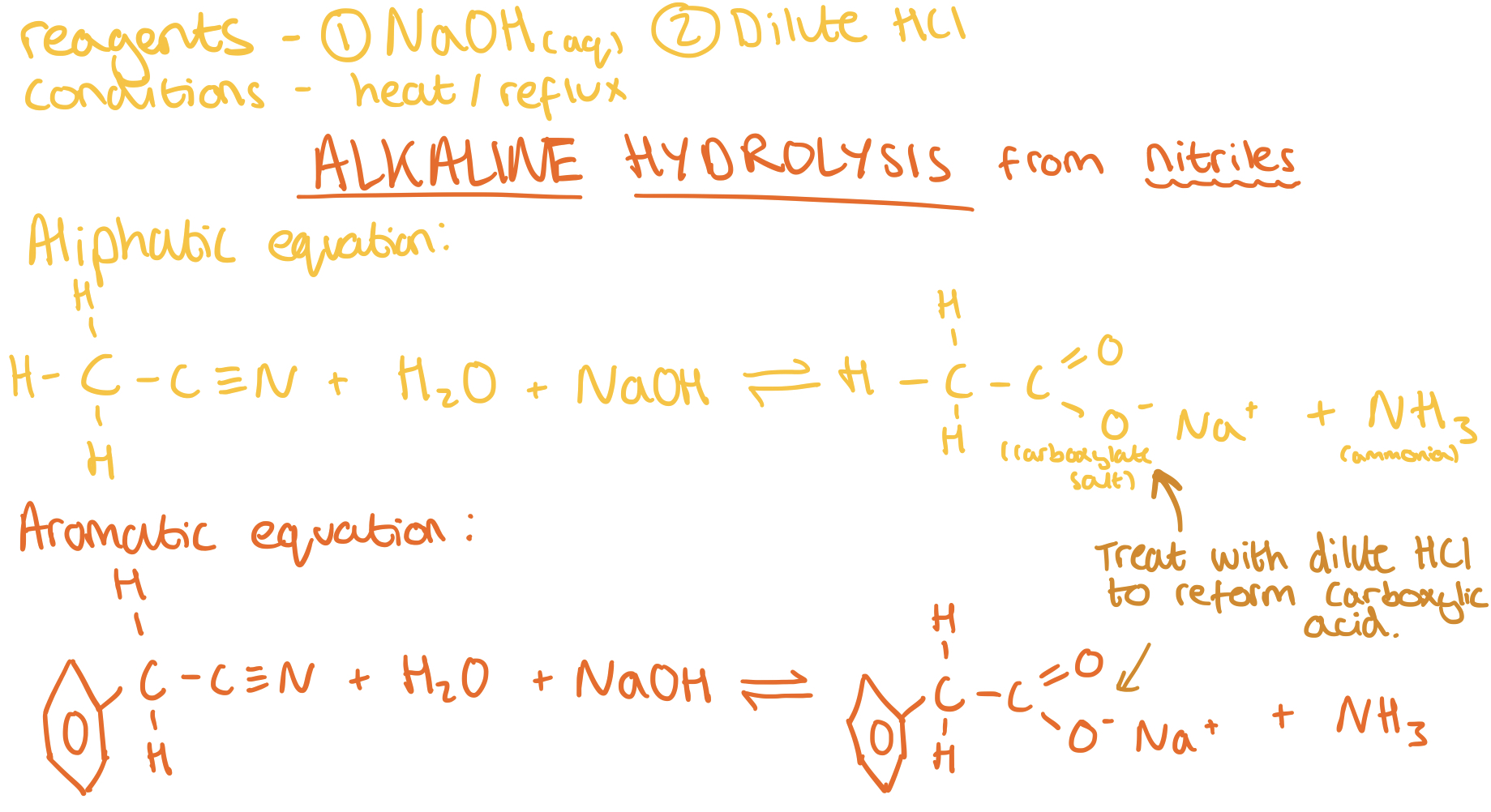
Making Carboxylic Acids from Nitriles - Alkaline Hydrolysis
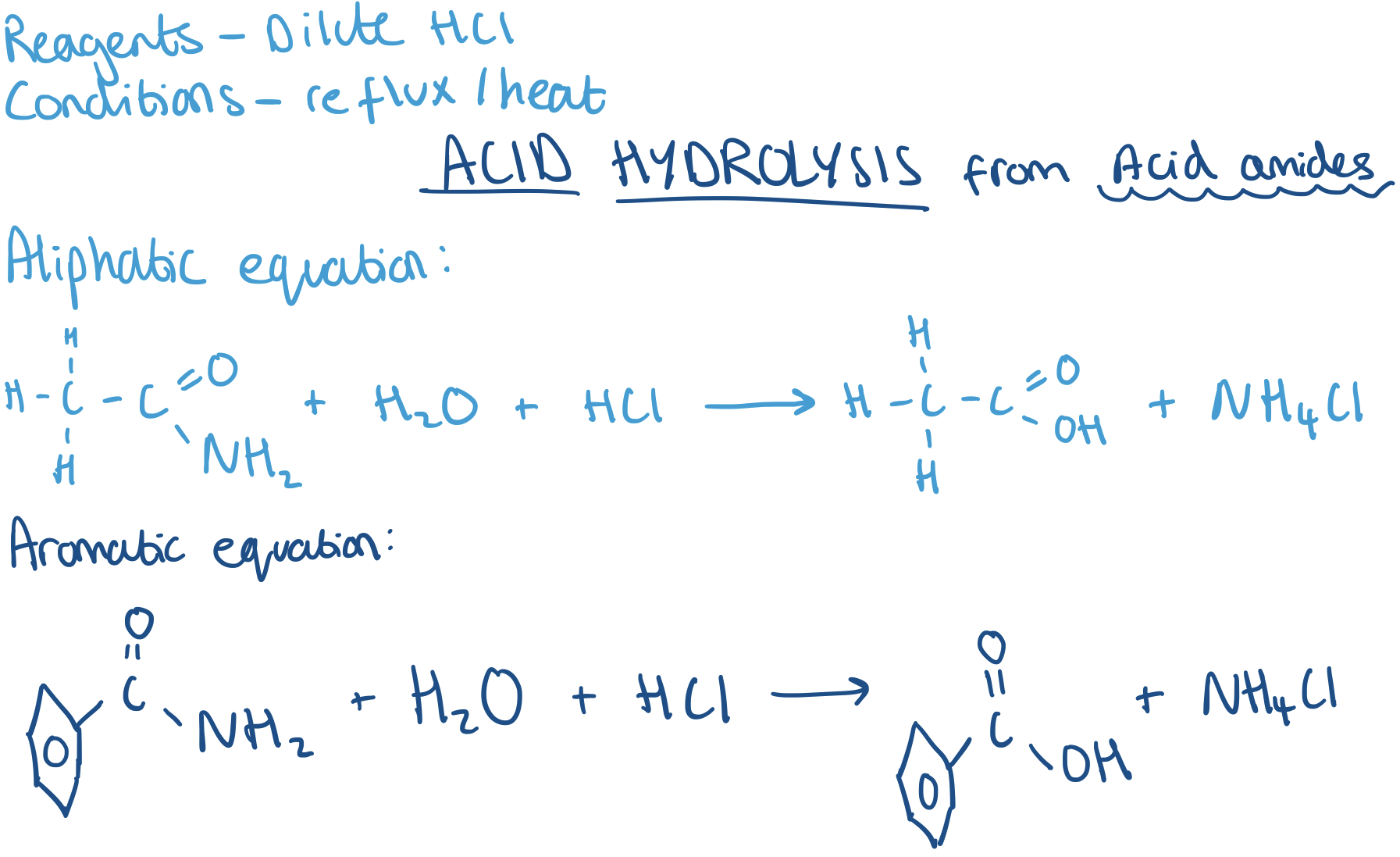
Making Carboxylic Acids from Acid Amides - Acid Hydrolysis
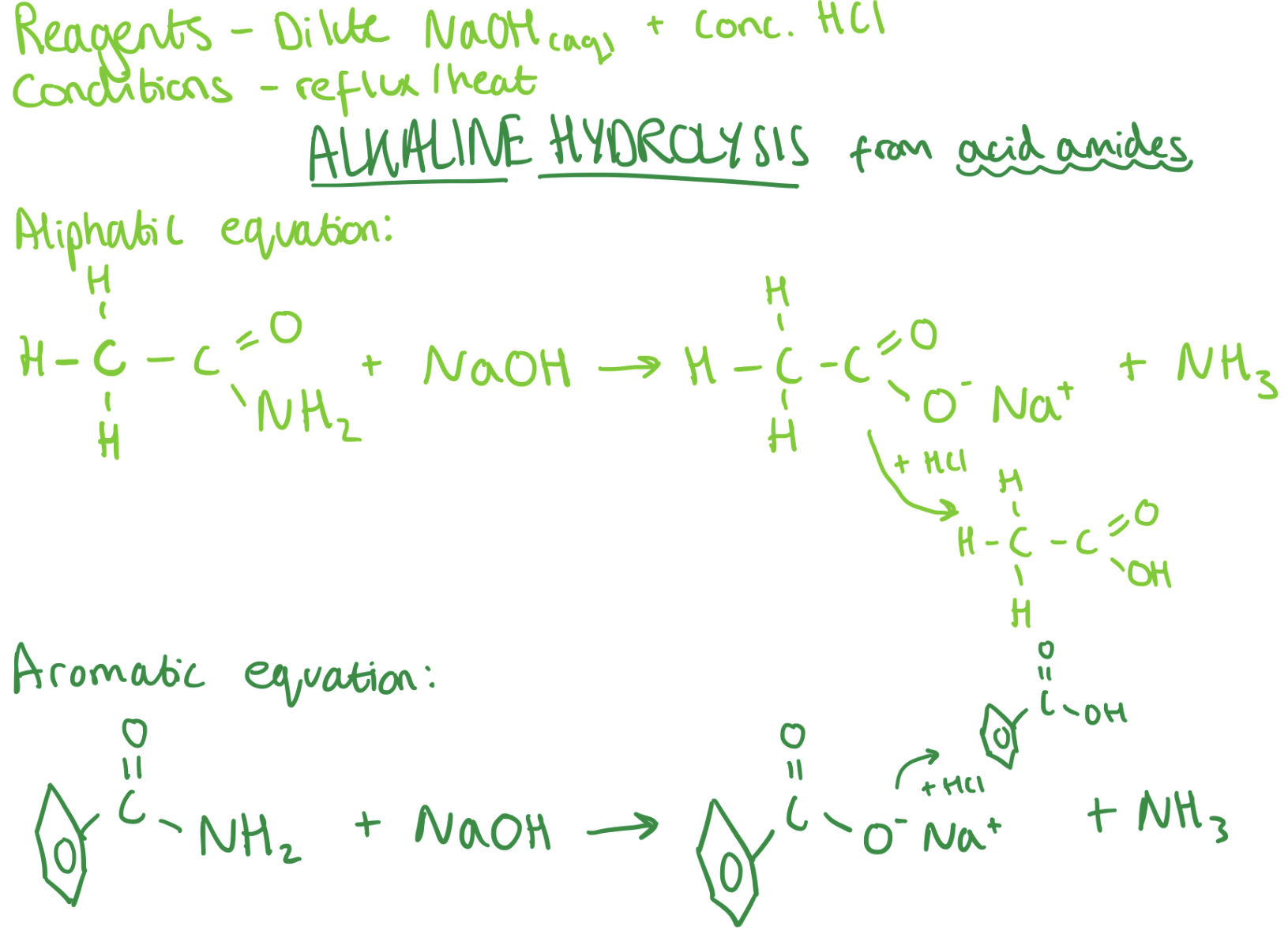
Making Carboxylic Acids from Acid Amides - Alkaline Hydrolysis
Preparation of Aromatic Carboxylic Acids from alkyl benzenes

Converting Carboxylic Acids to Alcohols

Converting Carboxylic Acids to Alkanes (decarboxylation)
(Ignore part highlighted in red)
Decarboxylation means removal of a Carboxylic group and it helps determine structure. The alkane that is produced has a specific melting point, and this value can be compared to data = CH4. Therefore, the Carboxylic acid must have been ethanoic acid.

Converting Carboxylic Acids to Esters

Converting Carboxylic Acids to Acid Chlorides

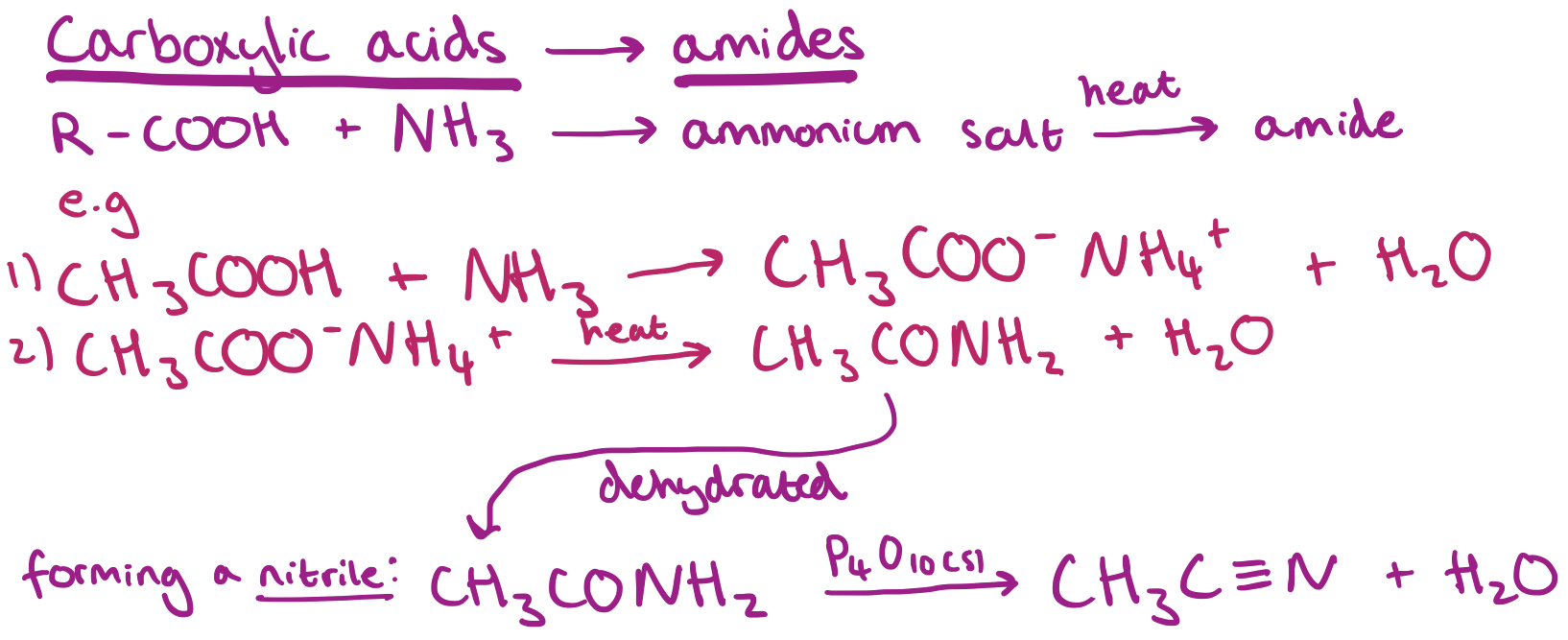
Converting Carboxylic Acids to Amides and onto Nitriles
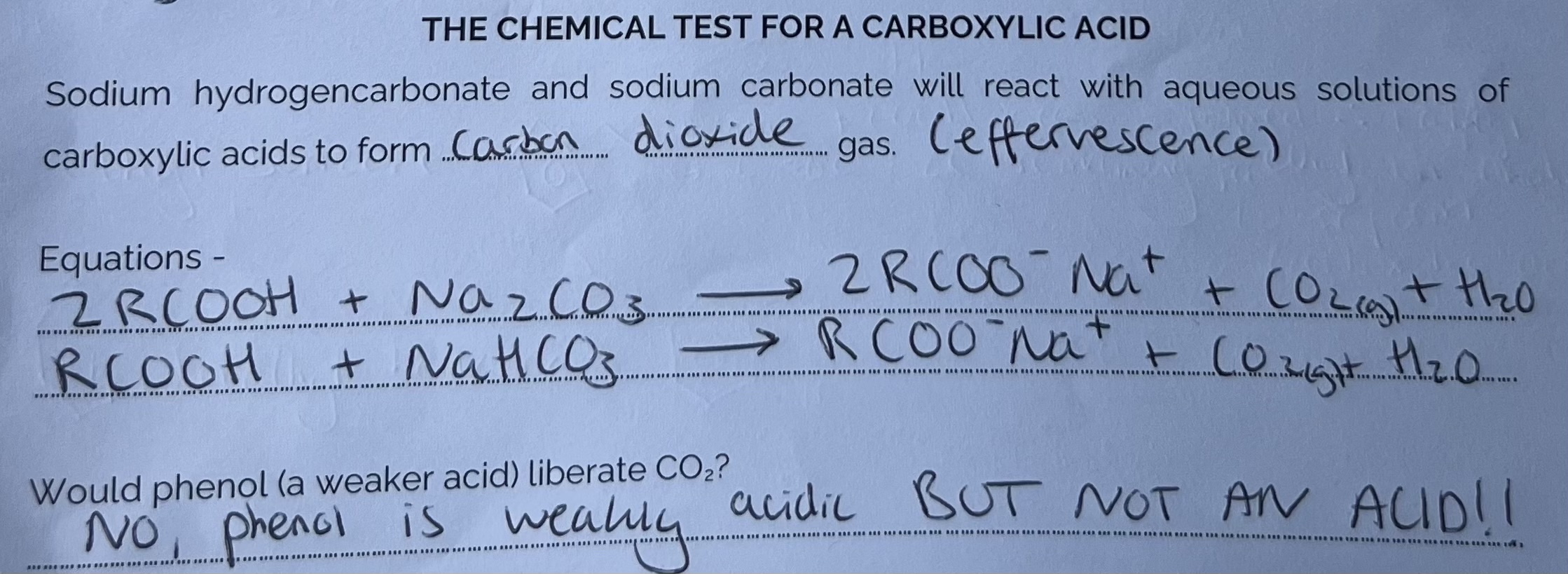
Chemical Test for a Carboxylic Acid
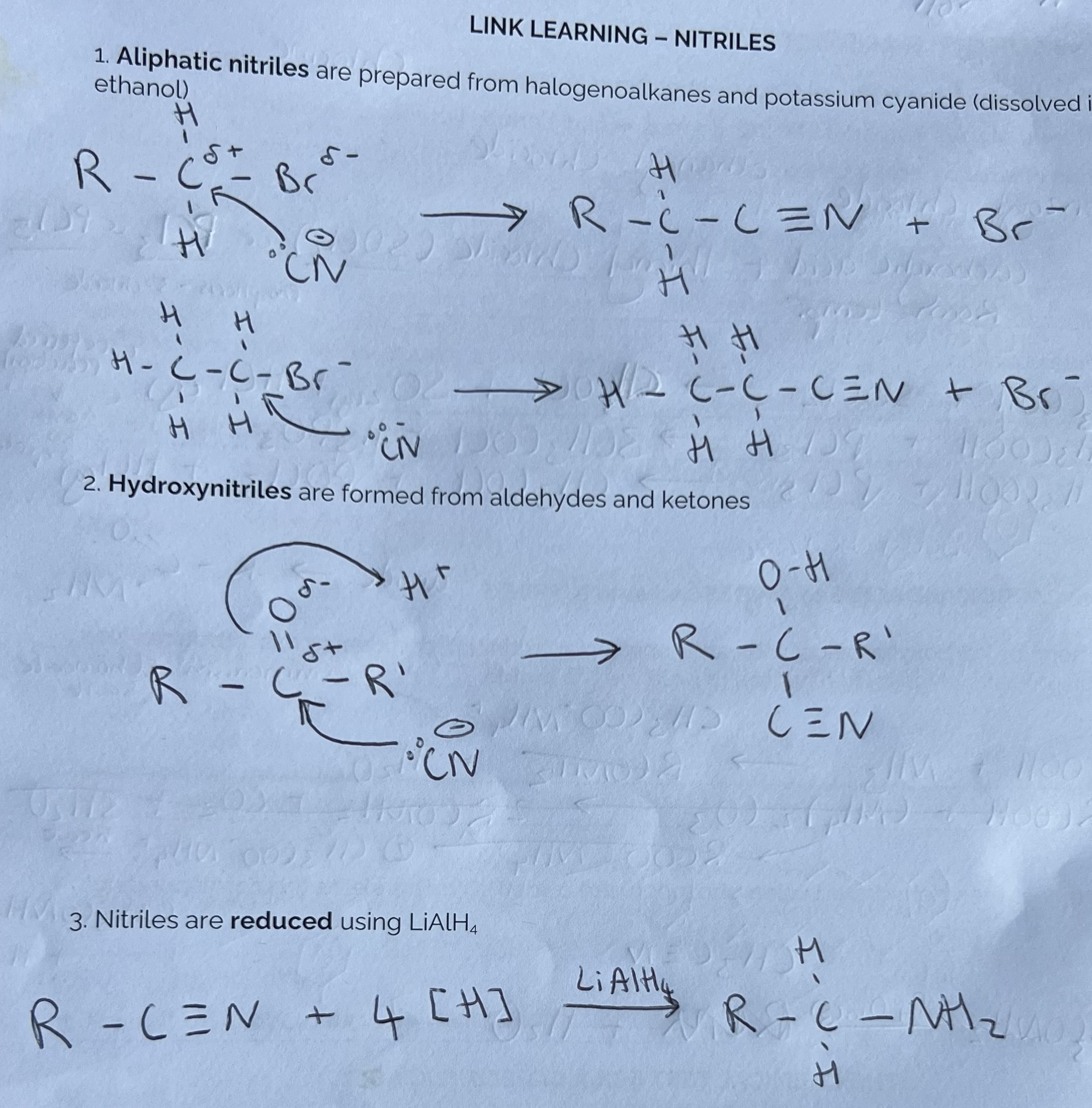
Link Learning - Nitriles
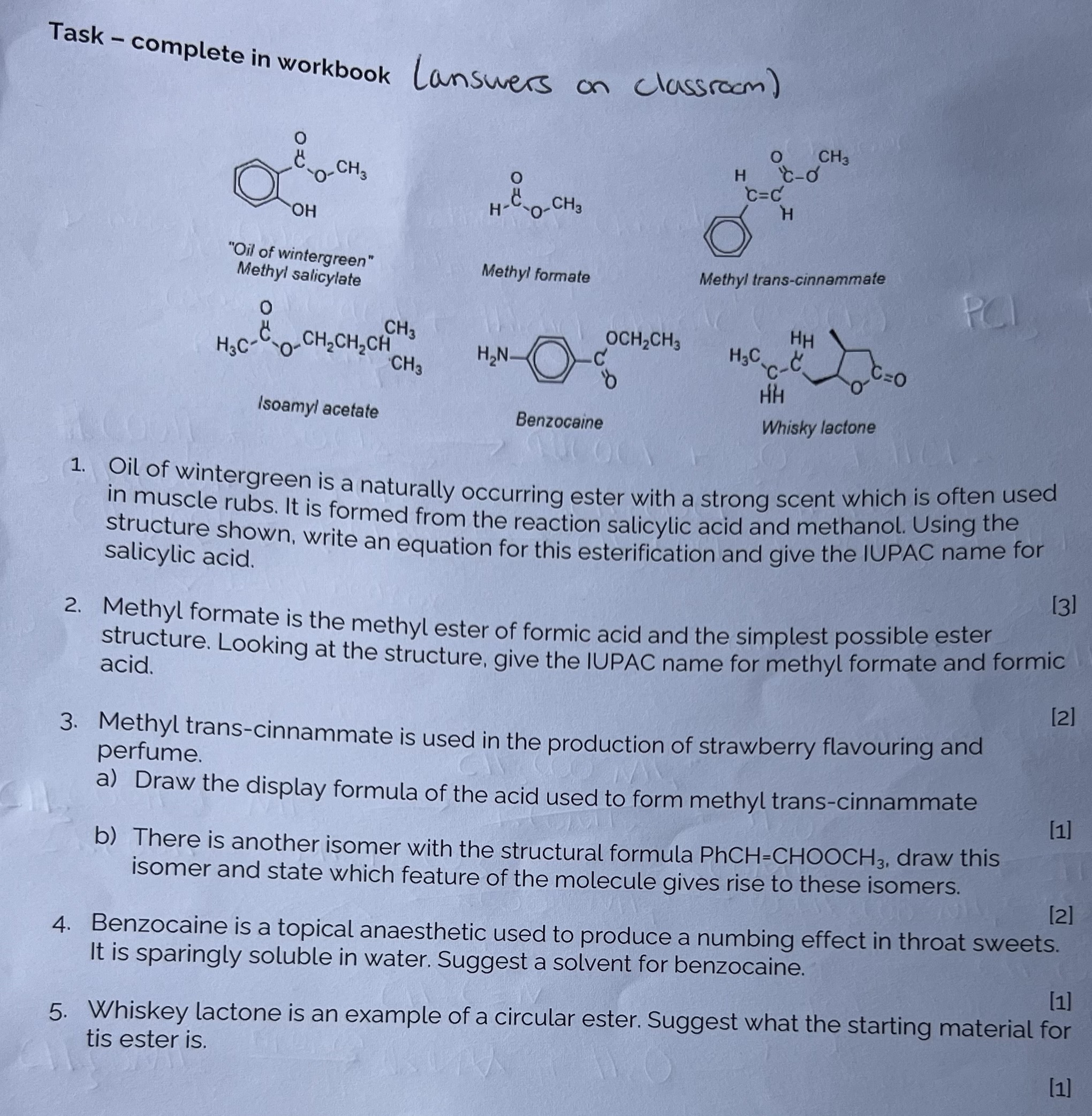
Complete questions on pg. 34
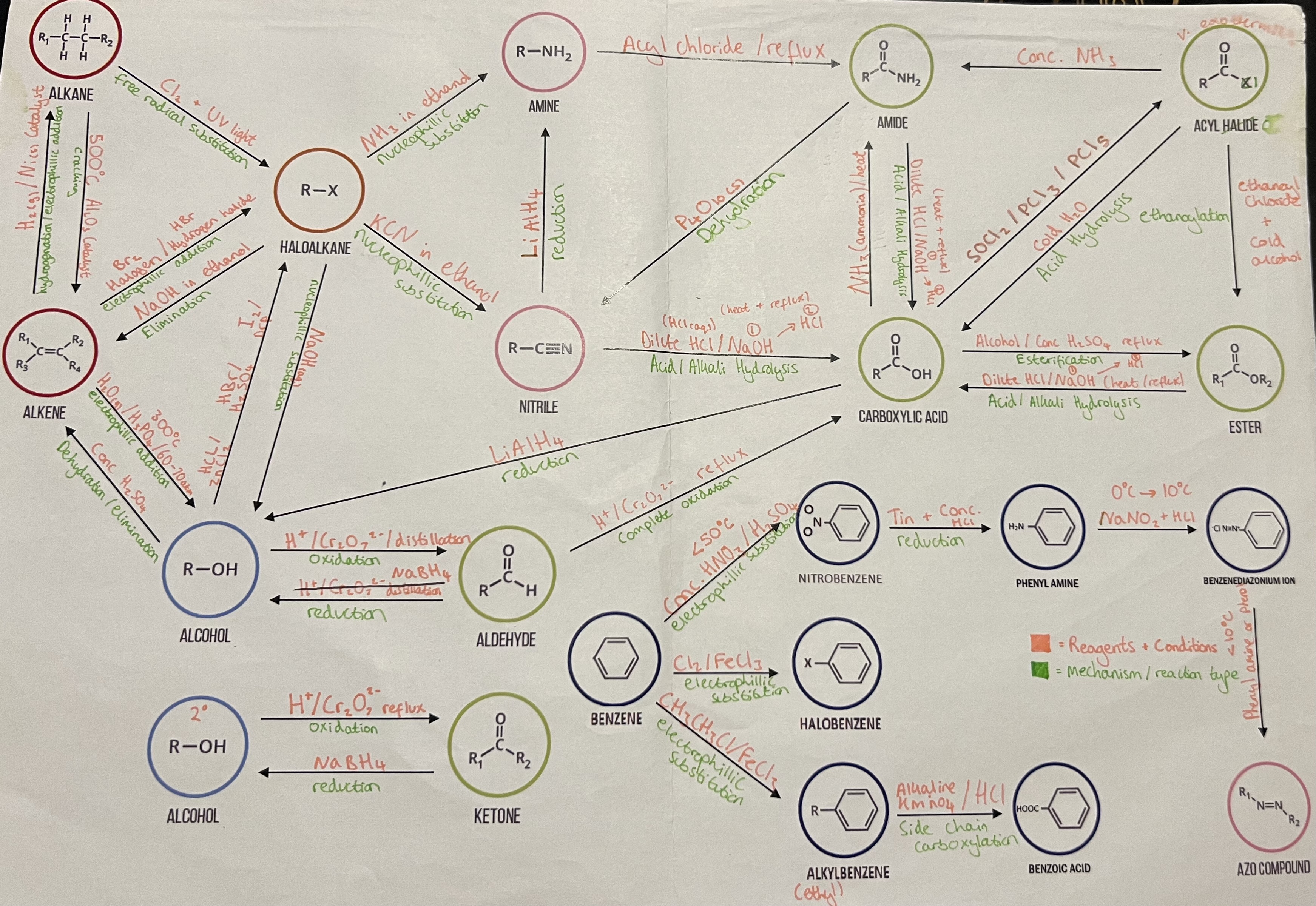
Reaction Summary Sheet