MGT223 NEW
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
equivalent units
product of number of partially completed units and their percentage of completion with respect to a particular cost.
FIFO method
A method of accounting for cost flows in a process costing system in which equivalent units and unit costs relate only to work done during the current period.
Weighted-Average Method
method of process costing that blends together units and costs from both the current and prior periods.
equivalent units of production (weighted-average method)
the units transferred to the next department (or to finished goods) during the period plus the equivalent units in the department’s ending work in process inventory.
formula for equivalent units (weighted average method)
equivalent units of production units transferred to the next department or to finished goods + equivalent units in ending work in process inventory
activity based costing (ABC)
costing method based on activities designed to provide managers with cost information for strategic and other decisions that potentially affect capacity and therefore fixed costs
overhead cost pools
groups of overhead cost elements.
activity cost pool
bucket in which costs are accumulated that relate to a single activity measure in activity-based costing system.
activity measure
an allocation base in an activity based costing system; ideally, a measure of the amount of activity that drives the costs in activity cost pool; also called a cost driver.
transaction driver
a simple count of the number of times an activity occurs
duration driver
a measure of the amount of time required to perform an activity
unit-level activities
performed every time a unit is produced, proportional to the number of units produced. ex. providing power to run processing equipment, since power tends to be consumed in proportion to the number of units produced.
batch-level activities
performed every time a batch is handled or processed, regardless of how many units are in the batch. for example, the cost of setting up a machine for batch processing.
product-level activities
activities that relate to specific products that must be carried out regardless of how many units are produced and sold or batches run. for example, activities such as designing or advertising a product.
customer-level activities
relate to specific customers and include activites such as sales calls, catalogue mailings and general tech support which are not tied to any specific product.
organization-sustaining activities
activities carried out regardless of which customers are serviced, which products are produced, how many batches are run or how many units are made.
variable cost
Varies, in total, in direct proportion to changes in the level of activity. Is CONSTANT per unit.
fixed cost
Does not vary per unit. (ie the cost of rent is always 2,000 no matter how much is produced)
MOH (manufacturing overhead)
manufacturing costs that cannot be practically traced to a unit of finished goods. consists of indirect materials and indirect labour (ie. supervisors of factory)
sunk cost example
legal costs, paid at the beginning of or during the business
direct material costs (for a company selling computers)
the cost of a hard drive installed in a computer
direct labour costs (for a company selling computers)
the wages of employees who assemple computers from components
manufacturing overhead (for a company selling computers)
depreciation on equipment used to test assembled computers before release to customers, the salary of the assembly shop supervisor
selling and administrative costs
the cost of advertising in the Peel Region Computer User newspaper, sales comissions paid to company's salespeople, salary of company's accountant
is depreciation a fixed cost
yes
examples of opportunity costs
forgone salary at tech company, withdraw of savings
can legal fees paid to incorporate be a differential cost
no, because they have already been incurred and are thus a sunk cost
four functions of managers
planning, directing and motivating, controlling and decision making
planning activities
developing goals and specifying how to achieve them; estimating advertising revenues for a future period, scheduling designated broadcast time slots for games, special programming, news shoes, estimating total expenses for future periods including salaries of news desk anchors
directing and motivating activities
mobilizing people to carry out plans and run routine operations; scheduling news desk anchors for each day’s broadcast news, assigning camera crew employees to cover specific events, reviewing scripts used by news desk anchors, providing performative based incentives based on viewership
controlling
gathering feedback to ensure the plan is being properly executed or modified as necessary; contrasting the actual number of viewers with its projected viewership, comparing actual costs of producing a broadcast with its budget, comparing the advertising revenues earned from broadcasting a sporting event by costs incurred to broadcast at that event
decision making
selecting a course of action from alternatives; determining which news anchor personnel to sign to contracts, identifying and evaluating a new product line to compliment the network’s offering, such as a sport popular in foreign countries, determining which specific games to broadcast in each sport carried by the network.
direct materials
materials that become an integral part of finished product and can conveniently traced to it
indirect materials
small items of material that may become part of an item, but are costly to trace back (ie. glue)
direct labour
factory labour costs that can easily be traced back to individual units of product
indirect labour
factory labour costs of janitors, supervisors, materials handlers and other factory workers that cannot easily be traced to particular products
conversion cost formula
direct labour plus manufacturing overhead (DL + MOH)
prime cost formula
direct material plus direct labour (DM + DL)
what are conversion costs
direct labour costs and overhead costs are incurred to convert materials into finished products
different terms for MOH
indirect manufacturing cost, factory overhead, factory burden
two categories for non-manufacturing costs
marketing or selling costs and administrative costs. note: these are also called period costs
raw (direct) materials inventory
materials used to make a product not yet placed into production
work in process inventory
inventory consisting of units of product only partially complete and will require further work before they are ready for sale to a customer
finished goods inventory
inventory consisting of completed units of product not yet sold to customers
cost of goods sold in a manufacturing company
beginning finished goods inventory + COGM = ending finished goods inventory + cost of goods sold
cost of goods manufactured (COGM)
costs that include the direct materials, direct labour and manufacturing overhead used for the products finished during the period.
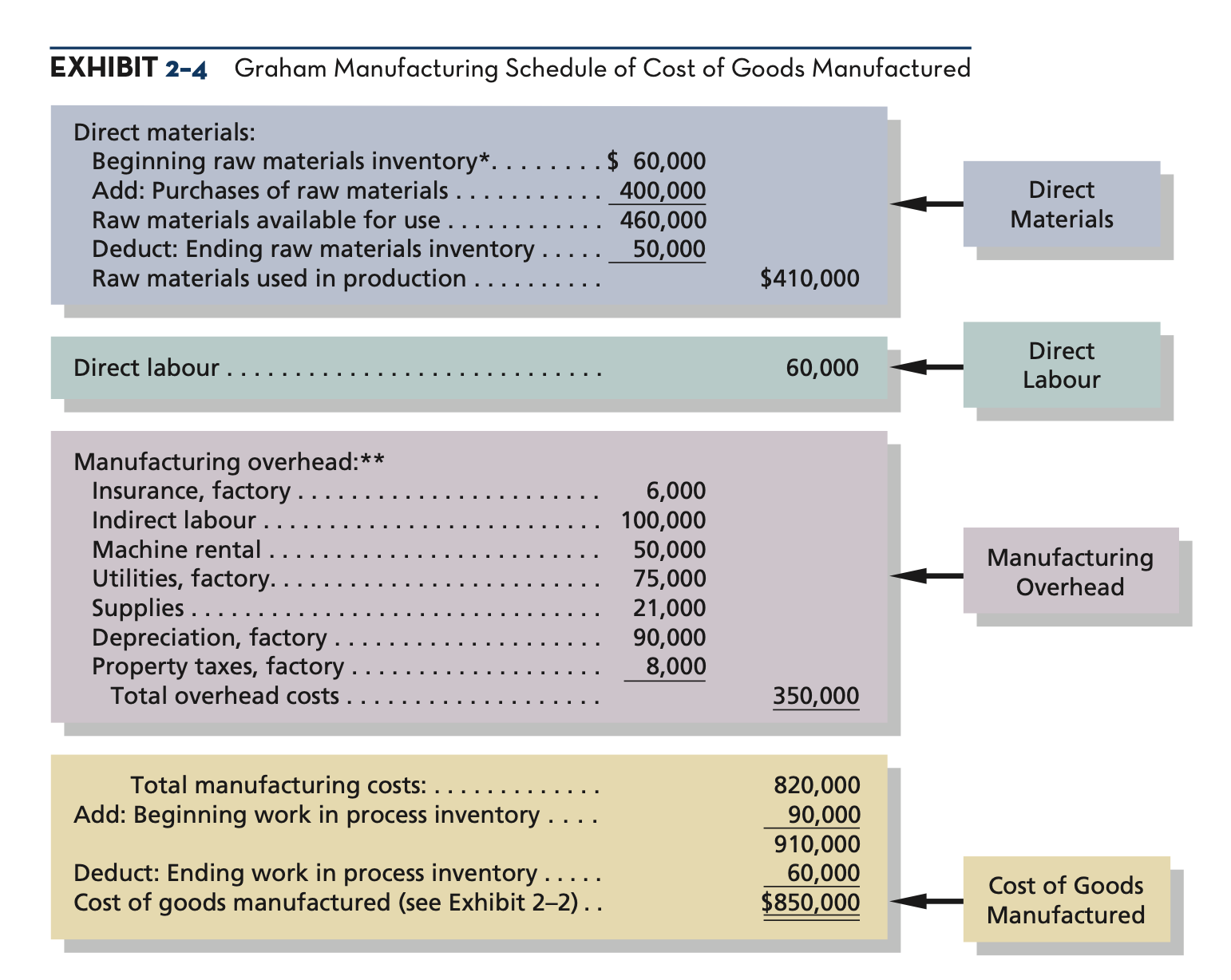
direct/raw materials formula (for schedule of cost of goods manufactured)
beginning raw material inventory + raw materials purchased (NOT used) = raw materials available for use in production - less ending raw materials inventory = raw materials used in production
manufacturing costs formula (for cost of goods manufactured)
direct materials USED (not purchased) + direct labour + manufacturing overhead
work-in process inventory (for cost of goods manufactured)
beginning work in process inventory + total manufacturing costs = total WIP for the period - ending WIP = cost of goods manufactured
cost of goods sold formula
beginning finished goods inventory + cost of goods manufactured = cost of goods available for sale - ending finished goods inventory
preparing a “schedule of cost of goods manufactured”
direct materials
direct labour
manufacturing overhead
work in progress inventory
mixed cost
cost that has both a variable and fixed cost component
what does the fixed portion of a mixed cost represent
the basic minimum cost of having a resource ready and available for use
what does the variable portion of a mixed cost represent
represents the cost incurred for the actual consumption of the resource
schedule of cost of goods manufactured
schedule showing DM, DL, and MOH incurred for a period and assigned to work in process and completed goods
total manufacturing costs
costs that represent the DM, DL and MOH used to perform the production work for finished or unfinished products for the period
two general classifications for costs
manufacturing and non-manufacturing costs
matching principle
costs are recognized as expenses when related revenue is realized
product costs
recorded in inventory before expensed in the period where revenue is recognized. all manufacturing costs are product costs.
period costs
recorded in the same period they occur. non-manufacturing costs are period costs. includes administrative, marketing or selling costs.
cost object
anything for which costs are desired, including products, customers, job organization sub-units
direct costs
costs that can be directly traced to cost object (DM and DL)
indirect costs
cannot be directly traced to cost object
ending balance of raw materials
beginning balance of raw materials + raw materials purchased - raw materials used
ending balance of work in process
beginning balance of WIP + manufacturing costs in period - cost of goods manufactured
cost driver
activity or factor that causes a specific cost to occur or change, like machine hours, customer orders or production costs
differential cost
differs between alternatives
high-low method
method of separating a mixed cost into fixed and variable elements by analyzing the change in cost between the high and low levels of activity
how to calculate variable cost using high low method
step 1: change in total cost = TC at highest activity level - TC at lowest activity level
step 2: change in activity level = highest activity level - lowest activity level
step 3: (change in total cost / change in activity level) = variable cost per unit
step 4: total cost - variable cost per unit*(Activity level) = total fixed cost
fixed cost element
fixed cost element = total cost - variable cost (* data point)
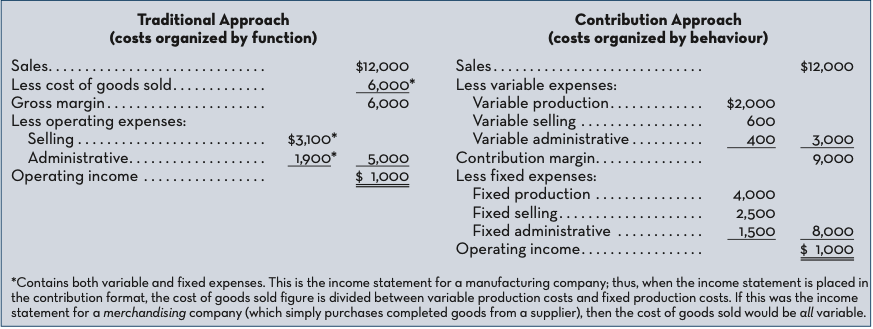
contribution approach
an income statement format where costs are separated into variable and fixed categories
contribution margin
the amount remaining from sales revenues after all variable expenses have been deducted
break-even point
level of sales at which profit is 0. ie. when total sales = total expenses, or total contribution margin = total fixed expenses, or sales - variable expenses - fixed expenses = 0
cost-volume-profit (CVP) graph
the relationships among revenues, costs and level of activity represented in graphic form
equation for profit graph
profit graph = unit CM x Q - fixed expenses, where CM is contribution margin and Q is quantity
contribution margin ratio
the contribution margin as a percentage of total sales.
variable expense ratio
ratio of variable expenses to sales
cm ratio and variable expense ratio relationship
cm ratio = 1 - variable expense ratio
incremental analysis
analytical approach focuses only on items of revenue, cost and volume that will change as the result of a decision
equation method
method of computing break-even sales using contribution format income statement

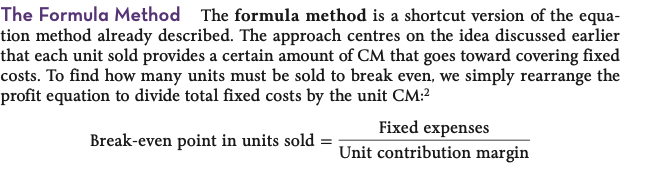
formula method
method of computing the break-even point where fixed expenses are divided by the unit contribution margin
margin of safety
total sales - break even sales
break even point in units
fixed cost / contribution margin per unit
break even point in dollars
fixed cost / contribution margin %
degree of operating leverage
contribution margin / (net) operating income
% change in (net) operating income is determined by
degree of operating leverage x percentage change in sales
net income before taxes
NIBT = NIAT/(1-tax rate)
weight average contribution margin (WACM) per unit
CM per unit of A x % sales of A + CM per unit of B x % sales of B
sales mix
relative proportions in which company’s products are sold. sales mix is computed by expressing the sales of each product as a % of total sales
weighted average contribution margin (%)
total CM/total sales = WACM per unit / WA price per unit
break even sales
fixed cost / weighted average contribution margin (%)
absorption costing
a costing method that includes all manufacturing costs - direct materials, direct labour and both variable and fixed overhead - as part of the cost of a finished unit of producst. also known as full costing