Fiscal Policy and Its Impact on the Economy
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
Fiscal Policy
refers to changes in federal taxes and purchases that are intended to achieve macroeconomic policy objectives.
Automatic Stabilizers
some forms of government spending and taxes that automatically increase or decrease along with the business cycle
Example of Automatic Stabilizer
Unemployment insurance payments are larger during a recession
Directional Fiscal Policy
refers to intentional actions the government takes to change spending or taxes
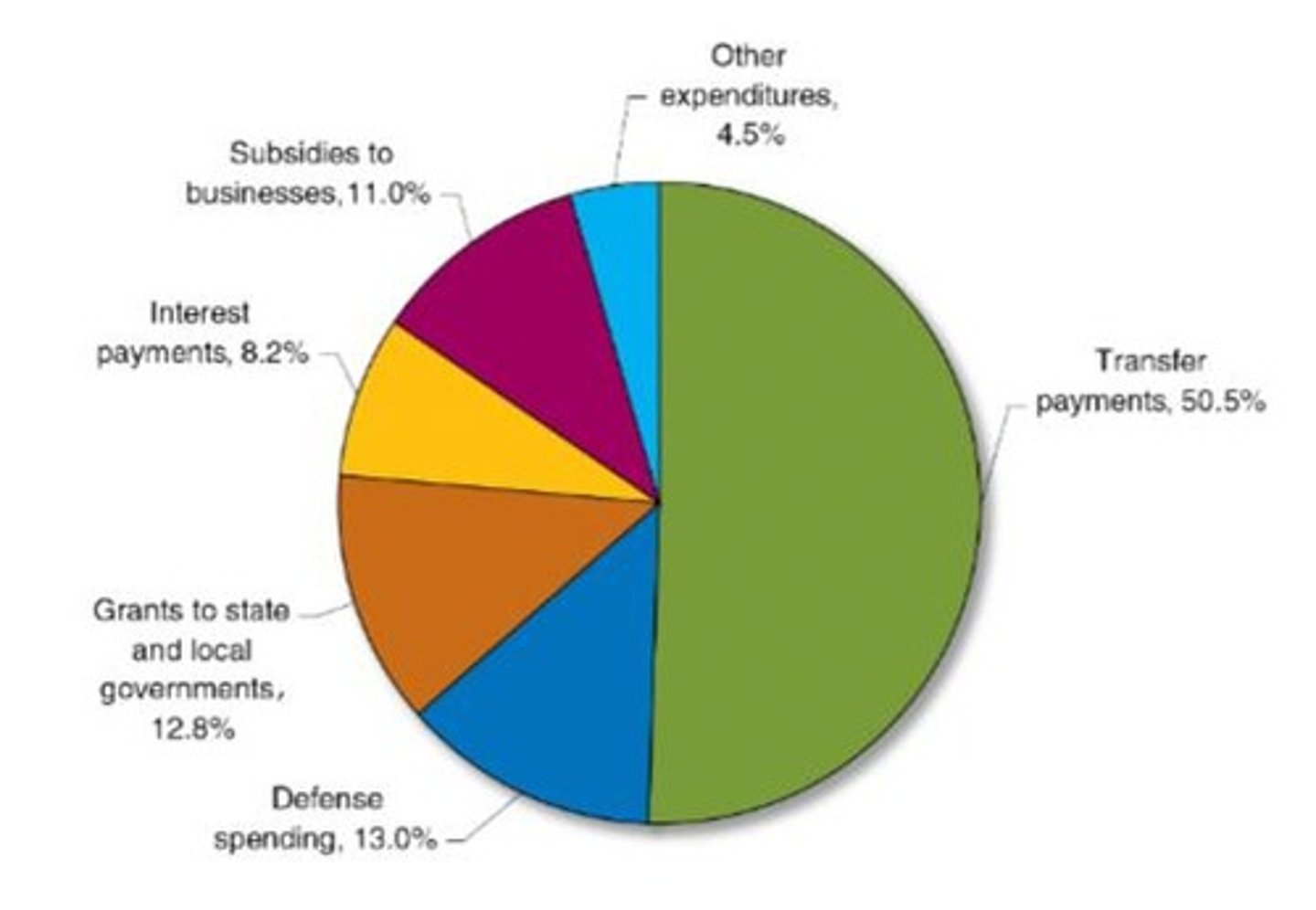
Federal Government Expenditures as a Percentage of GDP
As a percentage of GDP; are now higher than ever - over 30% of GDP
Federal Government Expenditures
purchases consist of defense spending and 'everything else,' like salaries of FBI agents, operating national parks, and funding scientific research.
Transfer Payments and Federal Expenditures
Around half of federal expenditures are spent on transfer payments, like Social Security, Medicare, and unemployment insurance.
Federal Revenue Sources
- comes from taxes on individual employment: individual income taxes and payroll taxes earmarked to fund Social Security and Medicare
- taxes on firm profits constitute about 5.4% of federal receipts
- remained of revenue comes from excise taxes, tariffs on imports, and other fees from firms and individuals
Budget Shortfall for Social Security and Medicare
- Through 2092, the budget shortfall for these programs is estimated to be enormous: almost $16.8 trillion (in present value terms)
True or False: A change in government purchases directly affects aggregate demand?
True
Does a change in taxes have an indirect or direct effect on aggregate demand?
indirect: a change in taxes changes income which affects consumption
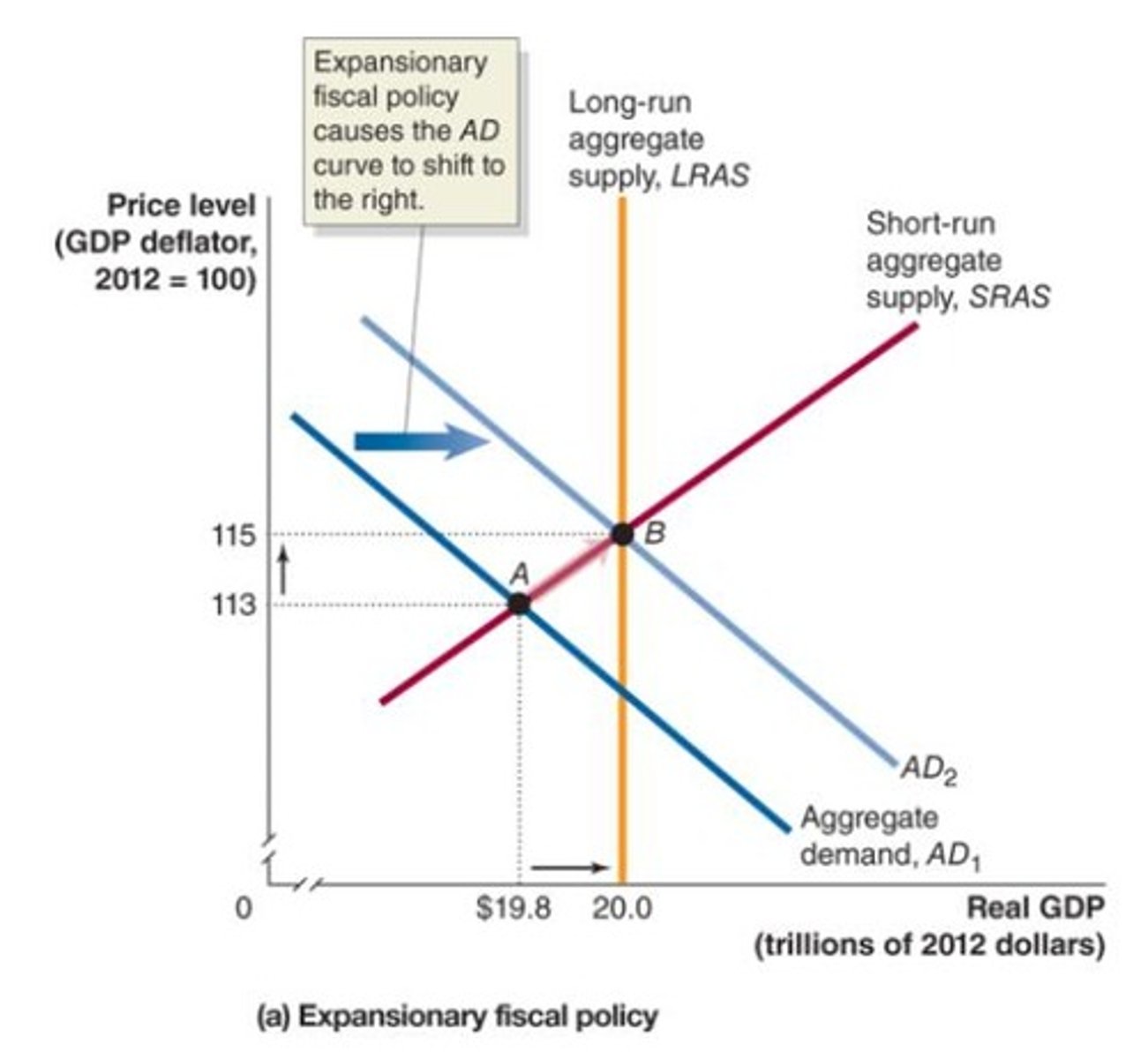
Expansionary Fiscal Policy
involves increases in government purchases or decreasing taxes
- if government believes real GDP will be below potential GDP
- decreasing unemployment
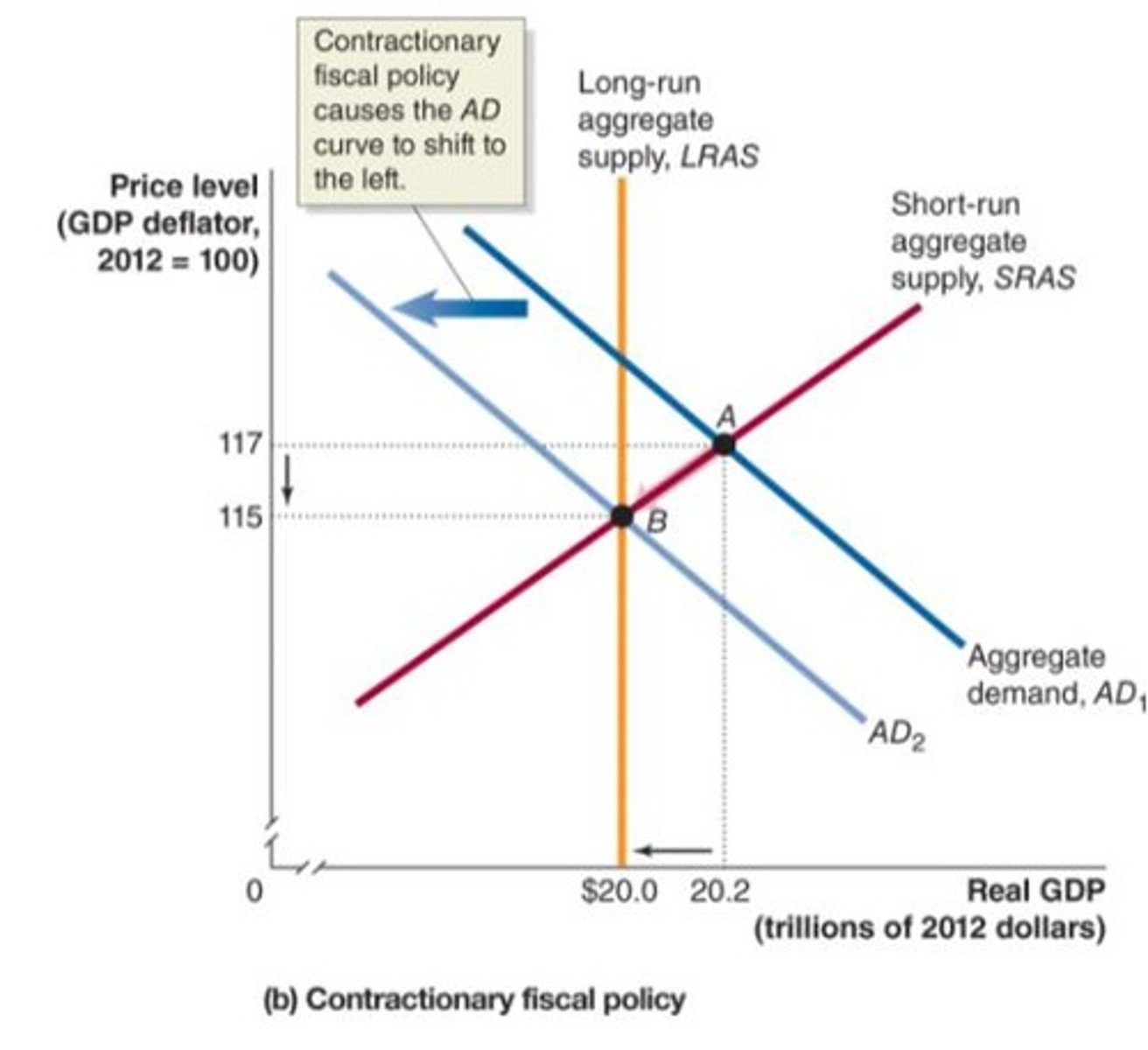
Contractionary Fiscal Policy
involves decreasing government purchases or increasing taxes
- if government believes real GDP will be above potential GDP
- decreasing inflation
Countercyclical Fiscal Policy
refers to the use of government spending and taxation policies to counteract fluctuations in the business cycle
ex) if in a recession, the government issues expansionary fiscal policy to increase government purchases or cut taxes so real GDP and the price levels rise (goes against the business cycle of recession)
Ceteris Paribus
everything else is staying the same, including monetary policy.
- "holding everything else constant"
- used to isolate the effect of one variable by assuming that all other relevant factors remain unchanged
ex) "If the price of apples increases, the quantity demanded will decrease." This means: Assuming nothing else changes (like consumer income or the price of oranges), an increase in price will lead to a decrease in demand.
Dynamic Aggregate Demand and Supply Model
Our model of fiscal policy so far is static: it assumes long-run potential GDP does not change and that the price level is constant.
Inflation Control
Contractionary fiscal policy is not really causing prices to fall; it's causing inflation to be lower than it otherwise would have been
Fiscal Policy Response to Recession
In a recession, expansionary fiscal policy can increase government purchases or cut taxes.
Fiscal Policy Response to Inflation
In rising inflation, contractionary fiscal policy can decrease government purchases or raise taxes.
Expansionary Fiscal Policy in the Dynamic Model
- federal government projects that aggregate demand will not rise enough to maintain full employment so it enacts an expansionary fiscal policy to increase aggregate demand and hopefully full the employment level
- The price level is higher than it would have been without the expansionary fiscal policy
Contractionary Fiscal Policy in the Dynamic Model
- federal government projects that aggregate demand will rise so much that the employment is beyond full employment level, causing high inflation, so it enacts a contractionary fiscal policy to decrease aggregate demand and down to the full employment level
Autonomous increase in aggregate demand
If the government increases its spending on goods and services, then aggregate demand increases immediately
Induced increase in aggregate demand
Increased government spending leading to people receive this as increased income, increasing their consumption spending accordingly
Multiplier effect
The process by which a change in autonomous expenditure leads to a larger change in real GDP.
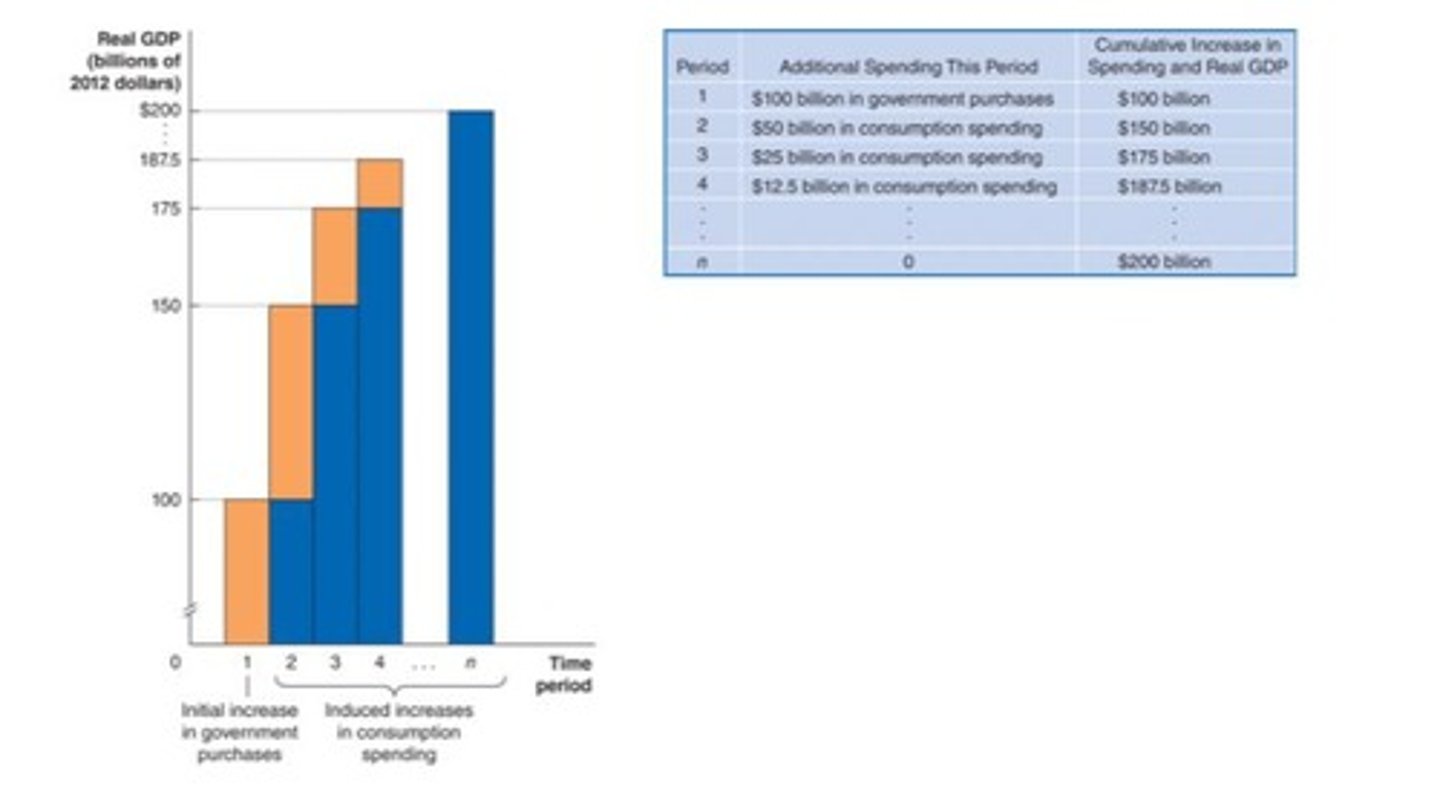
Multiplier size
The magnitude of the multiplier effect, which is necessary to predict the eventual effect of a change in autonomous expenditures.
The Multiplier Effect of an Increase in Government Purchases
The multiplier effect associated with an increase in government purchases, which leads to a larger increase in real GDP
ex) over time, a $100 billion increase in government purchases will result in an additional $100 billion in induced consumption spending
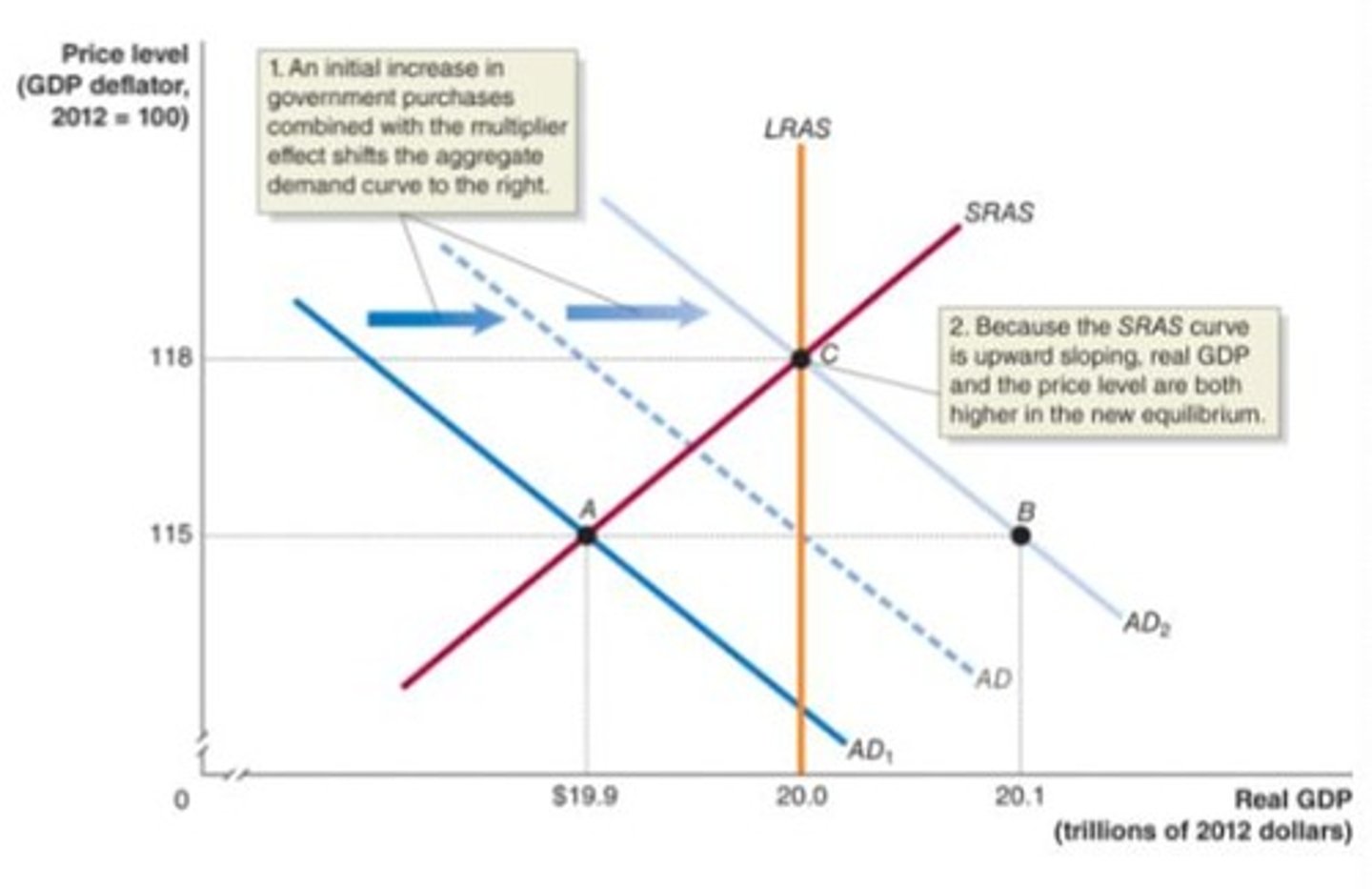
Government Purchases Multiplier
(Change in equilibrium real GDP)/(Change in government purchases)
Tax multiplier
A negative number that indicates the decrease in equilibrium real GDP resulting from an increase in taxes and vice versa
(Change in equilibrium real GDP)/(Change in Taxes)
- expect it to be smaller (in absolute value) than the government purchases multiplier
Transfer payments
Spending by the federal government for which it doesn't receive a good or service in return
ex) $1,400 checks received by many people following the American Rescue Plan in March 2021
Effect of transfer payments
An increase in transfer payments raises household disposable income, increasing consumption spending and having a positive multiplier effect.
Transfer Payments Multiplier
(Change in equilibrium real GDP)/(Change in transfer payments)
Tax multiplier application
The tax multiplier applies to changes in the amount of taxes, without changes in tax rates.
Making Work Pay Tax Credit
A $400 reduction in taxes for working individuals ($800 for households) enacted in 2009 and 2010.
Decreasing tax rates
increases disposable income, leading to increased consumption spending and increases the size of the multiplier effect
Aggregate demand increase
An increase in aggregate demand that results in a rise in real GDP and an increase in the price level.
An increase in government purchases and a cut in taxes have a _________ multiplier effect
positive
A decrease in government purchases, and an increase in taxes have a _________ multiplier effect
negative
Short-run aggregate supply curve
A curve that shows the relationship between the price level and the quantity of goods and services supplied in the short run.
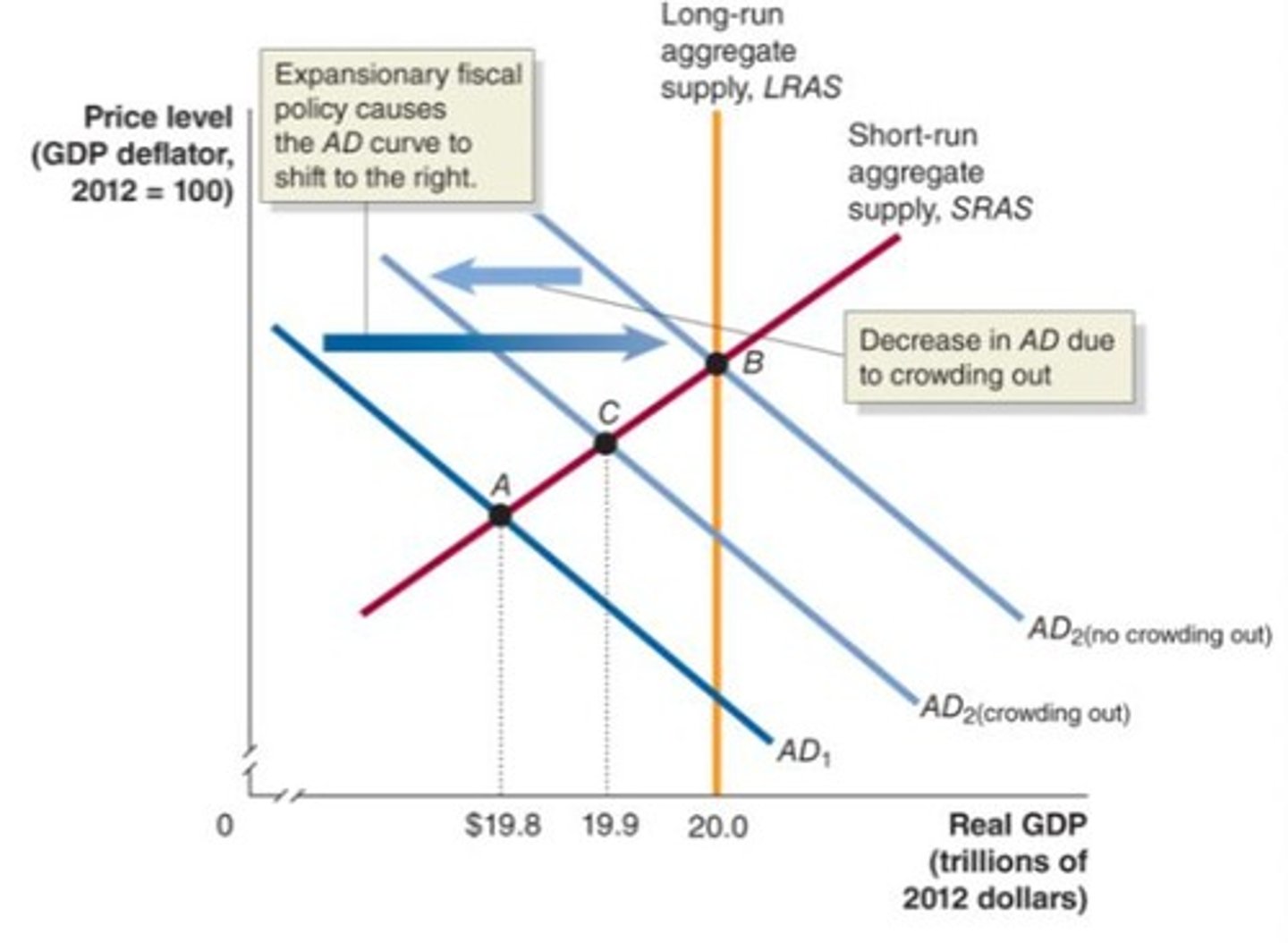
Crowding Out
A decline in private expenditures as a result of an increase in government purchases.
Government borrowing ↑(up) → Interest rates ↑(up) → Private investment ↓(down)
Legislative Delay
Congress needs to agree on the actions, which can delay fiscal policy implementation.
Implementation Delay
Large spending projects may take months or even years to begin, even once approved, delaying fiscal policy implementation
Recession of 2007-2009
The deepest recession in the United States since the Great Depression of the 1930s.
- peak unemployment rate was 10.0%
- decline in real GDP was -4.0%
Temporary Increase in Government Purchases
will cause the demand for money, and hence the interest rate, to rise
- but with higher interest rates, consumption, investment and net exports all fall
Effect of Crowding Out in the Short Run
The initial increase in spending is partially offset by the crowding out, meaning aggregate demand decreases since interest rates rise
Crowding Out in the Long Run
the increase in government purchases will have no effect on real GDP because the reduction in consumption, investment, and net exports will offset the increase in government purchases
Potential GDP
The level of GDP that an economy can sustain over the long term without increasing inflation.
Stimulus Package of 2009
A $840 billion program passed by Congress aimed at boosting the economy during the recession.
Tax Cut
A reduction in the amount of taxes that individuals or businesses must pay, such as the one-time rebate of $95 billion in early 2008.
CBO Estimates
Predictions made by the Congressional Budget Office regarding the economic effects of the stimulus package.
CBO Conclusion of the Stimulus Package
the stimulus package reduced the severity of the recession but did not come close to bringing the economy back to full employment
Economic Recovery
The process of the economy returning to its potential GDP after a recession.
Tax Credits
A reduction in tax liability that can be claimed on a tax return, part of the stimulus package.
Budget deficit
The situation in which the government's expenditures are greater than its tax revenue
Budget surplus
The situation in which the government's expenditures are less than its tax revenue
Do you know whether the federal government is running a budget deficit or a budget surplus currently?
As of May 2025, the U.S. federal government is running a budget deficit. While April 2025 saw a $258 billion surplus, primarily due to strong tax receipts and record customs duties, the cumulative deficit for the first seven months of fiscal year 2025 (October 2024 through April 2025) stands at $1.049 trillion, a 23% increase from the same period the previous year
Automatic stabilizers
are government policies or programs that naturally help stabilize the economy during fluctuations in the business cycle — without any new action by policymakers
ex) unemployment insurance, food stamps, medicaid, etc
Federal budget deficit in 2009
9.3% of GDP
Cyclically adjusted budget deficit or surplus
The deficit or surplus in the federal government's budget if the economy were at potential GDP
- CBO estimated budget deficit in 2009 if real GDP were at its potential would be 7.6% of real GDP
When the federal government runs a budget deficit, it finances its activities by....
selling Treasury securities
Federal government debt / National Debt
The total value of Treasury securities outstanding
- increased dramatically as a percentage of GDP during the two world wars and recessions; now at highest level since 1947 and projected to increase further
Defaulting
Failing to fulfill a financial obligation, such as not making a scheduled payment on debt.
Federal Budget
The government's estimate of revenue and spending for a specific period, typically a fiscal year.
Debt-to-GDP Ratio
A measure of a country's debt compared to its gross domestic product, indicating the country's ability to pay back its debt.
Crowding Out Investment
A situation where increased government borrowing leads to higher interest rates, which in turn reduces private investment.
Infrastructure
The basic physical systems of a business or nation, including transportation, communication, sewage, water, and electric systems.
Modern Monetary Policy
An economic theory suggesting that governments can create money to finance spending without the need for traditional debt.
Aggregate Supply
The total supply of goods and services that firms in an economy plan to sell during a specific time period.
Supply-Side Economics
An economic theory that argues economic growth can be most effectively fostered by lowering taxes and decreasing regulation.
The Long-Run Growth Rate of real GDP depends primarily on:
- the growth in the number of hours worked
- the growth rate of labor productivity as measured by the growth in real GDP per hour worked
CBO's Estimate of Real GDP Growth, 2021-2025
Hours Worked: 0.5
Labor Productivity: 1.3
Real GDP: 1.8
- the sum of the growth rate of hours worked and the growth rate of labor productivity
- predicts the number of hours worked will grow slower than the population
- majority of real GDP growth will result from increasing productivity
Posttax wage
When an individual decides how much to work, he bases the decision on how much an hour of work will increase his ability to consume goods and services
Pretax wage
When a firm decides how many people to employ, it considers how much it has to pay in total for each worker
Tax Wedge
The difference between the pretax and posttax return to an economic activity, which can distort economic incentives.
A large tax wedge....
distorts the incentives of individuals and firms to take part in economic activities, generally resulting in lower levels of economic activity—lower real GDP.
Marginal Tax Rates
The rate of tax applied to the last dollar of income earned, which affects economic behavior.
Individual income tax
a tax on a person's earnings; affects labor supply decisions and returns to entrepreneurship
Corporate income tax
a tax on the value of a company's profits; affects incentives of firms to engage in investment
Tax on dividends and capital gains
- Affects the supply of loanable funds from households to firms, and hence the real interest rate
- also affects the way firms disburse profits
Tax Simplification
The process of making tax laws easier to understand and comply with, potentially leading to increased economic efficiency.
CBO
Congressional Budget Office, a federal agency that provides economic data and budgetary analysis to Congress.
IRS
Internal Revenue Service, the U.S. government agency responsible for tax collection and tax law enforcement.
Long-Run Impacts
The effects of economic policies or conditions that manifest over an extended period, typically years or decades.
CBO predicts the 2017-2027 real GDP growth rate will be...
2.1% growth per year
(in 2007-2017, real GDP grew 1.5% per year)
President Trump proposed several fiscal policy actions to increase real GDP growth to 3% per year. This could happen by...
- increasing the growth rate of hours worked
- increasing the growth in labor productivity
(to achieve President Trump's goal, labor productivity would need to grow at 2.5% per year)
Increasing the growth rate of hours worked involves....
- an increase in population growth
- an increase in hours worked per employee
- an increase in the employment-population ratio
Increasing the growth in labor productivity involves....
- reducing business taxes to increase investment spending
- increasing business startups by reducing regulations and taxes on small businesses
Apprenticeships
Programs that combine on-the-job training with classroom instruction to prepare individuals for a specific trade.
Labor productivity growth rate (2006-2020)
Labor productivity grew at a rate of 1.5% per year
Multiplier formula
A mathematical representation used to determine how changes in government spending or taxes affect overall economic output.
Real GDP
The total value of all goods and services produced in a country, adjusted for inflation.
Balanced Budget Multiplier
If government purchases and taxes are both increased by $10 billion, GDP goes up by $10 billion in the short run.
Marginal propensity to consume (MPC)
The fraction of additional income that a household consumes rather than saves.
Equilibrium condition
Y = C + I + G, where Y is GDP, C is consumption, I is investment, and G is government spending.
Disposable income
(Y - T), the income available to households after taxes.
Marginal propensity to import (MPI)
The fraction of an increase in income spent on imports.
Effect of lower tax rates
Lower tax rates lead to larger multipliers in the economy.
Jerome Powell
The current chairman of the Federal Reserve (FED).
Impact of imports on GDP
A greater propensity to spend on imports results in a smaller government purchases multiplier.