The Software Process
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:57 PM on 4/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
1
New cards
what is the software process?
a structured set of activities required to develop a software system
2
New cards
what are 3 software process models?
* waterfall model
* prototyping model
* extreme programming XP - part of agile
* prototyping model
* extreme programming XP - part of agile
3
New cards
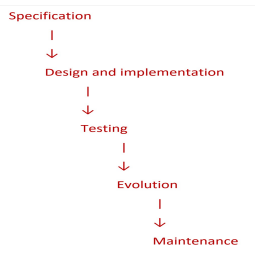
what are the stages in the waterfall model?
4
New cards
what are the benefits of the waterfall model?
* Easy to understand, easy to use
* Provides structure to inexperienced staff
* Milestones are well understood
* Sets requirements stability
* Good for management control (plan, staff, track)
* Provides structure to inexperienced staff
* Milestones are well understood
* Sets requirements stability
* Good for management control (plan, staff, track)
5
New cards
what are the cons of the waterfall model?
* All requirements must be known up-front
* Deliverables created for each phase are considered frozen – inhibits flexibility
* Integration is one “big bang” at the end
* Little opportunity for customer to preview the system
* Until it may be too late
* The Software Crisis existed despite the Waterfall model
* Deliverables created for each phase are considered frozen – inhibits flexibility
* Integration is one “big bang” at the end
* Little opportunity for customer to preview the system
* Until it may be too late
* The Software Crisis existed despite the Waterfall model
6
New cards
what is the software specification stage?
process of establishing what services are required and the constraints on the system’s operation and development
7
New cards
what happens during the software specification stage?
requirements engineering process
* Requirements elicitation and analysis
* Requirements specification
* Requirements validation
Using natural language is often problematic
* Requirements elicitation and analysis
* Requirements specification
* Requirements validation
Using natural language is often problematic
8
New cards
what is the software design and implementation stage?
the process of converting system specification into executable system
9
New cards
what happens during software design?
design a software structure that realises the specification
10
New cards
what happens during software implementation?
translate the designed structure structure into an executable program such as Java
11
New cards
how related are the design and implementation activities?
The activities of design and implementation are closely related and may be inter-leaved e.g. Generating code automatically from UML
12
New cards
what is the software testing stage?
intended to show the system conforms to specification and meets requirements of system customer
13
New cards
what happens during the software testing?
system testing is carried out which involves executing the system with test cases derived from the specification of the real data to be processed by the system
14
New cards
what is the software evolution stage?
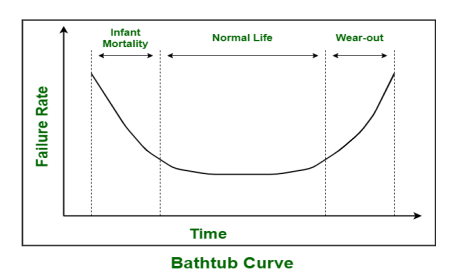
over time the system will change
* infant mortality = high failure rate at the start of release
* normal life = system works well and failure rate plateaus
* wear-out = problems resurface and failure rate rises again
* infant mortality = high failure rate at the start of release
* normal life = system works well and failure rate plateaus
* wear-out = problems resurface and failure rate rises again
15
New cards
what is the software maintenance stage?
consistently maintain system to work how we expect it, fix bugs and add enhancements
16
New cards
what are the 2 types of prototyping?
* throwaway
* evolutionary
* evolutionary
17
New cards
what is the throwaway/ rapid/ closed-ended prototyping?
* Creation of a model that will be discarded rather than becoming part of the final delivered software
* After preliminary requirements gathering, used to visually show the users what their requirements may look like when implemented
* Focus is on quickly developing the model
* Not on good programming practices
* Can be messy
* After preliminary requirements gathering, used to visually show the users what their requirements may look like when implemented
* Focus is on quickly developing the model
* Not on good programming practices
* Can be messy
18
New cards
what are the steps in throwaway prototyping?
1. Write preliminary requirements
2. Design the prototype
3. User uses the prototype
* Specifies/suggests new requirements
4. Repeat if necessary
5. Use the product
6. Then discard it
19
New cards
what is the evolutionary prototyping model?
* Developers build a prototype during the requirements phase
* Prototype is evaluated by end users
* Users give corrective feedback
* Developers further refine the prototype
* When the user is satisfied, the prototype code is brought up to the standards needed for a final product
* Prototype is evaluated by end users
* Users give corrective feedback
* Developers further refine the prototype
* When the user is satisfied, the prototype code is brought up to the standards needed for a final product
20
New cards
when is it best to use prototyping?
* Most beneficial for systems that will have many interactions with end users (use cases) as the greater the interaction between the computer and the user, the greater the benefit of building a quick system for the user to use
* good for designing human-computer interfaces
* good for designing human-computer interfaces
21
New cards
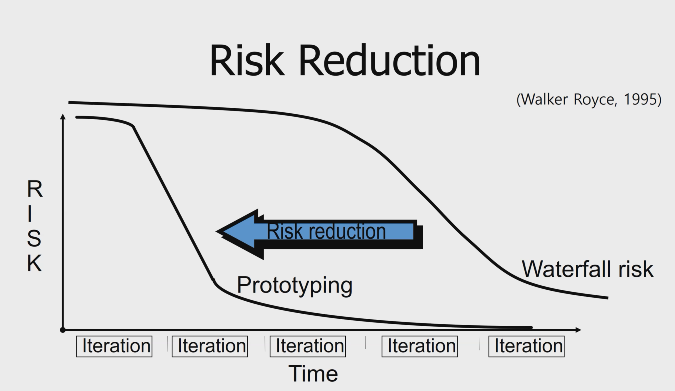
what is the difference between the risk curve for prototyping method and waterfall method?
* prototyping has greatly reduces the risk early on
* waterfall has a higher risk which gradually goes down
* waterfall has a higher risk which gradually goes down
22
New cards
why is it good to use multiple iterations rather than 1 iteration?
* requirements can evolve based on business circumstances and the software needs to support the business and evolve too
* multiple iterations can respond better to change
* multiple iterations can respond better to change
23
New cards
what practices are used during extreme programming?
incremental planning
small releases
simple design
test first design
refactoring
pair programming
collective ownership
continuous integration
sustainable pace
on-site customer
small releases
simple design
test first design
refactoring
pair programming
collective ownership
continuous integration
sustainable pace
on-site customer
24
New cards
what is the incremental planning pinciple?
Requirements are recorded on Story Cards and the Stories to be included in a release are determined by the time available and their relative priority. The developers break these Stories into development Tasks.
25
New cards
what is the small releases principle?
the minimal useful set of functionality that provides business value is developed first. Releases of the system are frequent and incrementally add functionality to the first release.
26
New cards
what is the simple design principle?
Enough design is carried out to meet the current requirements and no more.
27
New cards
what is the test first design principle?
An automated unit test framework is used to write tests for a new piece of functionality before that functionality itself is implemented.
28
New cards
what is the refactoring principle?
All developers are expected to refactor the code continuously as soon as possible code improvements are found. This keeps the code simple and maintainable.
29
New cards
what is the pair programming principle?
Developers work in pairs, checking each others work and providing the support to always do a good job.
30
New cards
what is the collective ownership principle?
The pairs of developers work on all areas of the system, so that no islands of expertise develop and all the developers own all the code. Anyone can change anything.
31
New cards
what is the continuous integration principle?
As soon as work on a task is complete it is integrated into the whole system. After any such integration, all the unit tests in the system must pass.
32
New cards
what is the sustainable pace principle?
Large amounts of over-time are not considered acceptable as the net effect is often to reduce code quality and medium term productivity
33
New cards
what is the on-site customer principle?
A representative of the end-user of the system (the Customer) should be available full time for the use of the XP team. In an extreme programming process, the customer is a member of the development team and is responsible for bringing system requirements to the team for implementation