Exam 3 Psychobiology
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Turner’s syndrome
missing a chromosome on the 23rd pair, marked as XO
characteristic features of webbed neck, abnormal elbows, etc.
Konrad Lorenz
a German etholist who won a Nobel prize, focused on the final form/goal, where things go to
Daniel Lehrman
an American researcher and founder of Animal Behavior at Rutgers, wrote a chapter critiquing Lorenz’s theory
what was the debate between Lorenz and Lehrman over?
a difference in emphasis
Lorenz: where things go to
Lehrman: where things came from
“binaryness”
if you view everything through a binary lens, but things like development aren’t always binary
development is crucial to understanding sex
brain differences between sexes
parts of frontal cortex and limbic systems larger in women
parts of parietal cortex and amygdala larger in men
greater neuronal density in temporal lobe (language processing and comprehension) in women
macroanatomy between male and female
larger brain volume and weight in males
some cortical areas larger for both
women have more grey matter than men when corrected for brain size
larger grey:white ratio in women
what is an issue with emphasizing sex brain differences?
they are “overhyped” and have no huge differences
men’s brains are bigger in relation to what? more cells, strength, myelin, or something else?
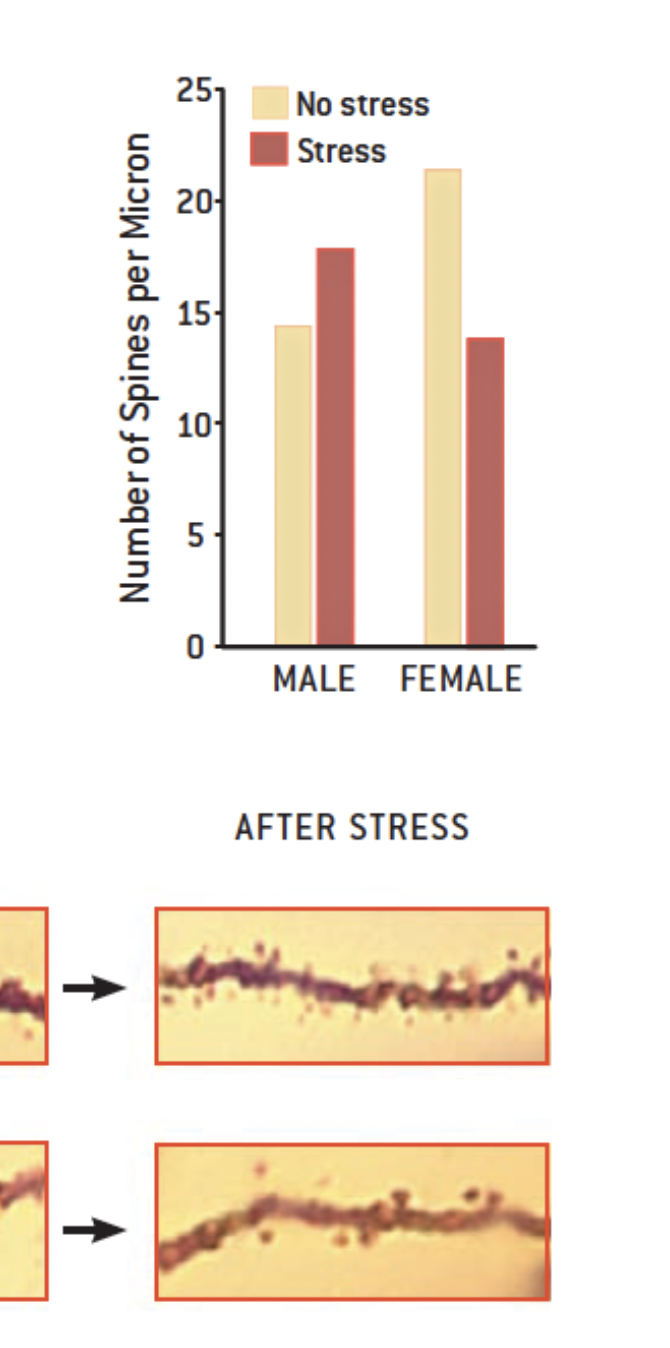
what do dendritic spine graphs tell us about stress?
females respond more dramatically to stress
stress leads to learning in males but a reduction in females
Celia Moore’s framework
studied effects of male hormones on male brains and maternal behavior
mother rats lick male pups 6x more than female pups
why do mother rats lick their male pups more than females?
the male pups became masculinized through testosterone, which affects their urine and the mother’s behavior
mother prefers the testosterone
examples of categorization
naming brain structures
assigning functions to structures
naming and categorizing genes
categorizing sex binary (male and female)
Alice Dreger
wrote about “The Age of Gonads” and the medical invention of sex
histology in 19th century had a quest to find out “true” sex
The Age of Gonads
a time of classifying gonads in order to maximize binary categorizations of sex
ended by Blair-Bell
what was the result of ending “the age of gonads”?
each body was allowed only one “true” sex, which was determined and even created by the medical doctor
Crouch claims that the birth of an infant with ambiguous genitalia is a…
medical and psychosocial emergency
Crouch ideas
earlier doctors concerned with discovery of sex, while modern idea is the creation of sex
intersexed children are invested with negative meaning through naming
John Money and Anke Ehrhardt
describe newborns as “psychosexually neutral”
different types of men and women
Dr. Harry Benjamin
a German medical endocrinologist who performed sex change surgery in the U.S.
supported Christine Jorgensen’s transition
consulted with Kinsey about a transgender kid
Christine Jorgensen
a high profile trans woman from the 1950s
denied a marriage license
entertainer, author, lecturer, leader in sex-alignment surgery in US
endocrine
relating to or denoting glands which secrete hormones or other products directly into the blood
exocrine
relating to or denoting glands that secrete their products through ducts opening onto an epithelium rather than directly into the bloodstream.
hypothalamus
a collection of nuclei at the base of the brain
Cells at the base are specialized neurosecretory cells that function primarily as glands
Terminals release ________ in response to nerve impulses (like transmitters) but the neurohormones are released into ______ of the pituitary, rather than into synaptic space.
neurohormones; portal system
anterior pituitary secretions
TSH, ACTH, LH, FSH, GH, and prolactin (tropic hormones)
posterior pituitary secretions
oxytocin and vasopressin
hypophysis
two glands, fused into one (another name for pituitary gland)
GH (growth hormone) targets…
bones and tissue
prolactin targets…
mammary glands
FSH and LH target…
ovaries, testes
ACTH targets…
adrenal cortex
TSH targets…
thyroid
oxytocin targets…
mammary glands, smooth muscle in uterus
anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) targets…
kidney tubules
magnocellular neurons
oxytocin and vasopressin (posterior pituitary) are manufactured here
oxytocin and vasopressin are…
manufactured in magnocellular bodies and transported down axons
stored in vesicles at cell terminals in the posterior pituitary
released in response to neural impulses, classic NT
adrenal medulla
inner adrenal gland that releases EP, NE, and DA into general circulation
also releases enkephalins
adrenal cortex
outer adrenal gland that three divided hormonal zones that belong to a class of steroid hormones
aldosterone
a steroid hormone that regulates sodium levels in the blood; its secretion is controlled angiotensin II
two functions of the gonads
gamete production
hormone production
gonad function is regulated by…
tropic hormones of the anterior pituitary
seminiferous tubules
site of spermatogenesis
long, convoluted tubules
can identify sperm at various stages of maturation
leydig cells
produce the steroid hormones, primarily androgens, under the influence of the anterior pituitary
ovaries
produce gametes and hormones
cyclic in both functions
fetal ovaries contain ½ million immature follicles
testes vs ovaries function
testes are tonic in gamete production and secretory activities, while ovaries have cyclic changes
5 kinds of sex (male vs female, you filthy pervert)
chromosomal: chromosomes, genes, proteins
gonadal: testes/ovaries
hormonal: testosterone, estrogen, androgen
morphological: form of external body
behavioral: characterizations of “pure” roles
gender role
what we present in society
gender identity
much more personal, how we perceive ourselves
fertilization
two cells interacting, rather than sperm “drilling” into the egg
when a sperm reaches an egg, it “spoons” with it, membranes melt and they merge into one
mutual activation by sperm and egg
before sperm activates egg, female reproductive tract and egg activate the sperm.
once two are together, sperm can activate maturation of egg, enabling it to finish meiotic cell division
capacitation
oviduct cells interact with sperm cell’s membrane
sperm are immature and cannot fertilize the egg, requires capacitation
chromosomal sex determination
said to occur when an ovum is fertilized by a sperm bearing X or Y chromosome (male delivers sex-determining factor)
germinal ridge
thickened ridge of tissue that forms on ventromedial surface of each protokidney
can develop into a testis or an ovary
gonadal sex differentation
bipotential
embryonic gonad is “indifferent” and can become one sex or the other
TDF
testes determining factor; if cells in germinal ridge contain Y → genes will express TDF protein
in the presence of TDF…
the medulla of the ridge develops further into a testis
in the absence of TDF…
outer cortex of ridge develops to form an ovary
two types of developmental pattern
single, bipotential (embryonic gonad becomes either testis or ovary
dual anlagen (presence of TDF or not)
Wolffian duct system
develops into male accessory sex organs, connecting testes to outside
seminal vesicles and vas deferens develop from this
Mullerian duct system
becomes female accessory sex organs, connecting ovaries to outside
develops into fallopian tubes, uterus and cervix
genital folds
ridges that flank urogenital sinus during embryonic development
genital tubercle
the meeting of genital folds at the front end of the urogenital opening
androgens
responsible for masculinizing the external genitalia, more “variation”
each direction is mutually exclusive
in the absence of androgen…
female morphology develops
female clitoris and labia develop from…
genital tubercle and folds (respectively)
male penis and scrotal sac develop from…
tubercle and fusing of genital folds, respectively
5a-reductase and DHT functions
testosterone is converted to DHT by 5a-reductase, present in both male and female
man with less 5a have incomplete external genitalia
if women have high levels of androgens, she can convert to male external genitalia
congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH)
a group of genetic disorders that affects the adrenal glands, may not produce enough hormones
turner’s syndrome
disorder where you’re missing a second sex chromosome, represented as XO or just X
characteristic features: short, infertility, webbed neck, long arms, irregular elbows
testicular feminization mutation (TFM)
now called androgen insensitivity, occurs when a male has XY but is resistant to hormones (androgens) producing a male appearance
some female physical traits, yet genetic makeup of a man
freemartinism
when cows birthed opposite sexed twins, the female twin was sterile and had masculine traits
masculinized behavior and non-functioning ovaries
Crews’ (1994) ideas
expresses amazement that we don’t know why sex evolved
emphasizes a comparative perspective, and that it is less universal that previously assumed
two roles of sex steroids
organizational: the initial role
activational: exerted later in life
whiptail lizards
parthenogenic whiptail lizards
take turns displaying male sexual behavior, thereby improving ovulation
parthanogenesis
a natural form of asexual reproduction in which the embryo develops directly from an egg without need for fertilization
effects of embryos on each other
prenatal hormone environment has more effect than sex organs
females with males on both sides are exposed to more testosterone
temperature-dependent sex determination
low vs high temperatures can produce a male vs female
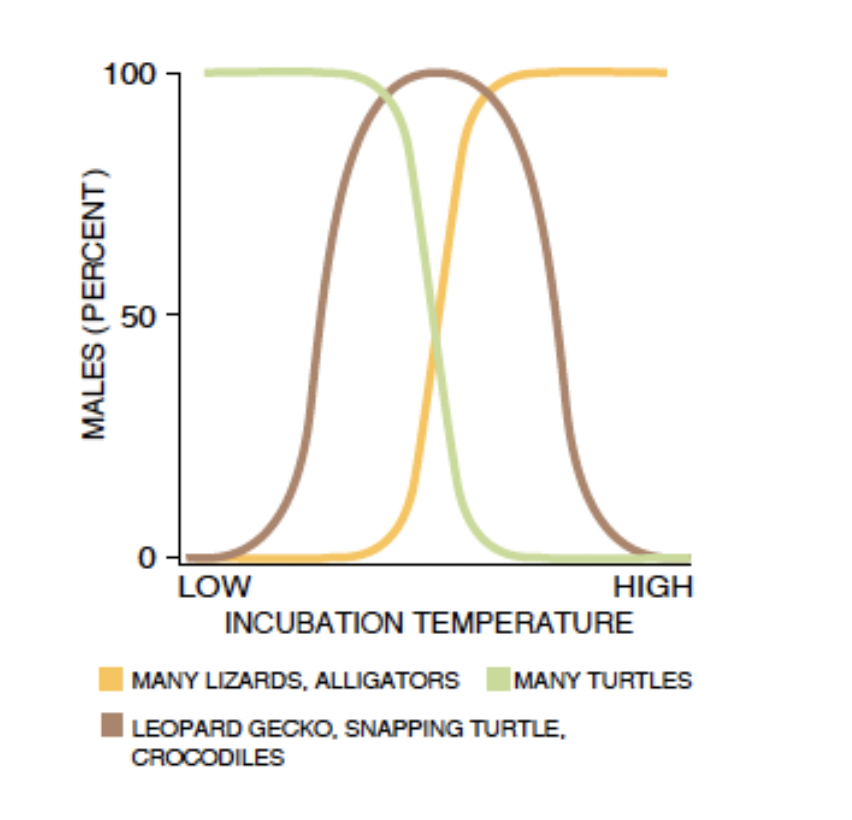
behavioral sex determination
most cases in hermaphroditic species
sex change can be triggered by alterations in social environment
differences in sexual development (DSD)
a group of rare conditions involving genes, hormones and reproductive organs, including genitals
body identity integrity disorder (BIID)
an extremely rare condition whereby an able-bodied and apparently
normal individual describes a long standing desire to have a limb amputated
Carl Elliott’s “The Perfect Voice” takeaways
asks how exactly our voice is identity
Stephen Hawking identified more with American computer voice than a British version, despite being British
tension between natural and artificial (given vs created)
Hawking’s example shows flexibility of identity
primum non nocere
“above all, or first, do no harm”
argument surrounding BIID
however is too vague, as surgeons have to cut a healthy abdominal wall to remove a damaged appendix
Tiers of ethical rules
Particular judgments and actions
Rules
Principles
Ethical theories
moral dilemmas
arise when either of two opposing views can be taken on the basis of moral considerations
happens during moral deliberations
judgment
expresses a decision, verdict or conclusion about a particular action
rules
state the actions of a certain kind ought (or ought not) to be done because they are right (or wrong)
principles
more general and fundamental than moral rules and serve as the foundation or source of justification
theories
bodies of related principles and rules
utilitarianism
gauge the worth of actions by their ends or consequences (focuses on outcomes)
value is said to be nonmoral because such activities
are not fulfilling a moral obligation, but have more
general goals
deontological theories
some features of acts other than their consequences make them right or wrong
principle of autonomy
a guide on how to treat self-determining rights
principle of nonmaleficence
one ought not to inflict evil or harm (what is bad)
principle of beneficence
one ought to prevent and remove evil, and do or promote good