arch 4521 final exam
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
luminous flux
the time rate of light flow, unit of measure is the lumen
ex: rate of water from sprinkler head
luminous efficiency
-how much energy is being converted into usable light
-a measure of lumens/watt
-the power or rate at which lamps emit light is measure in lumens
-because of large differences in efficiency, lamps of equal wattage can emit very different amounts of light
luminous intensity
-the amount of luminous flux in a given direction measures in lumens per solid angle (candelas or candelpower)
-water per minute sprayed with a cone of a given angle
color reflectance
ratio of reflected flux to incident flux
color absorbance
ratio of absorbed flux to incident flux
color transmittance
ration of transmitted flux to incident flux
illuminance
-the density/amount of luminous flux a given surface
-ex: gallons of water sprayed per minute in a specific area
luminance
-brightness
-the measure of reflected light that is governed by illuminance and reflectance
footcandles
unit for the amount of light reaching an object
lumens
the unit of light output from a light source or luminaire
candlepower distribution curve
-photometric measurements representing the total light intensity pattern produced by a source
specular reflection
-a mirror is a specular reflector
-changes the direction of a beam of light without otherwise appreciably altering the nature of the beam
diffuse reflection
reflection of light from a rough surface in many directions
cosine effect
a beam of sunlight will illuminate a larger area as the sky
opacity
refers to the transparency of a tool or layer
inverse square effect
(be able to calculate
i1/i2=(d2/d1)^2
illuminance from a point light source is inversely proportional to the distance squared
light reflectance
the percentage of light hitting a surface, that is reflected and not absorbed into the surface
light absorption
the percentage of light hitting a surface, that is absorbed and not reflected off of the surface
light transmission
the passing of light or sound waves through a material
colorimetry
hue- range
value- shade
chroma- intensity
sensitivity of the human eye
light enters pupil, focused onto light sensitive retina in back of eye - eye adapts to brightness levels by making the pupil larger using the iris
issues with light trespass
-decreased sleep quality
-glare
-loss of night sky darkness
-spill light affecting neighbors
frit
-painted on exterior of glass to make it semi transparent
-small pieces of glass
color perception
distinguishing the difference between wavelengths of light
characteristics of the field of vision
detail: we only see at high resolution in a small area at the center of our vision
color: we don't see much color outside of the center of our vision
blind spots: we have a blind spot on the left and right side of our vision
factors that affect performance of visual task
-the task: size/proximity (exposure angle) exposure time, brightness, contrast, familiarity
-light condition: illumination level, brightness ratios, glare
-the observers: condition of eyes, adaption, fatigue, health, drunkenness (or sobriety)
light quantity
a space has more than enough lighting horizontally, it may still appear dark if there is a low brightness vertically
light quality
additional illumination vertically will improve the light
contrast ratios
rates of the luminance of the brightest color (white) to that of the darkest color (black) that the system is capable of producing
glare
types
1. direct (discomfort)
2. disability
3. reflected (or veiling)
location of field of vision
all the area a person can see while looking straight ahead
-foveal surround
-foveal vision
-center of vision
how daylight enters a building
-reflection
-direct
what design strategies can optimize daylight penetration
-shading and light shelves
-aperture design
-skylights
-top lighting
-side lighting
-configuring and massing
daylighting rules of thumb
orientation: east/west
room depth: make the depth no more than 2 to 2.5 times the window head height
15/30 rule: sufficient daylight will be delivered at a 15 ft distance from the window wall
daylight capture: varies with aperture slop and orientation
top lighting: for uniform lighting, make the spacing of the skylights 1 to 1.5 times the ceiling height
overcast
illumination of 500-2000 fc (still 10 to 50 times greater than what is needed indoors)
clear skies
illumination of 6,000-10,000 fc (100 to 200 times greater than requirements for good indoor illumination)
daylighting factor
the ratio of daylight indoors as compared to the overall amount available outdoors
daylight opportunities
-micro climate and site
-configuring and massing
-daylight zoning
-room proportion and shape
-aperture quntity and location
-shading and light shelves
-glazing type
-finishes
-furnishings
-light control
-operation
relationship of window head height to daylight penetration
make the depth of the room more than 2 to 2.5 times the window head height
concept of overcast sky
the challenge is quantity of light in the space while quality is good.
ex: a skylight would be a lot bigger/floor area for an overcast sky to let in more light while a skylight would be much smaller/floor area for clear sky to reduce direct glare. The brightness distribution of an overcast sky is typically 3 times greater at the zenith than at the horizon
visible transmittance
amount of light allowed through a window
solar heat gain coefficients
amount of heat allowed through a window
15/30 rule
sufficient daylight will be delivered at a 15ft distance from the window wall
basic lamp types and application
-incandescent
-fluorescent
-HID
-LED
-other/specialty
inverse square law
intensity is inversely proportional to the square of distance from the source
i1/i2=d1^2/d2^2
color temperature
color appearance of light sources can be defined in terms of "degree" kelvin
color rendering index
-measures how faithfully a light source reveals the colors of objects
-ranges from 0-100
-the higher the CRI number, the better color rendering ability of the lamp
basic components of a luminaire and what they do
What is it:
an entire fixture assembly including the instrument, lamp and mounting device
Components:
-source/ballast
-reflector
-shield/diffusor -housing
types:
-direct
-indirect
-semi-direct
-semi-indirect
-general diffuse
how light level varies from a source with distance
the intensity of light is inversely proportional to the square of the distance. This means that as the distance from a light source increase, the intensity of light is equal to the value multiplied by 1/d^2
primary factors that determine coefficient of untilization
-room surface reflection (ceiling, wall, floor)
-room size and proportion (room cavity ratio)
-luminaire characteristics (efficiency and intensity distribution)
light pollution
brightening of the night sky caused by street lights and other man-made sources, which has a disruptive effect on natural cycles and inhibits the observation of stars and planets.
light trespass
-decreased sleep quality
-glare
-loss of night sky darkness
-spill light affecting neighbors
sound absorption
The process of dissipating sound energy by converting it to heat.
sound transmission
the passing of sound waves through a material
acoustic properties of openings
the properties of a material to absorb or reflect sound acoustically
area effect
acoustical materials spaced apart can have greater absorption than the same amount of material butted together.
The increase in efficiency is due to absorption by soft exposed edges and also diffraction of sound energy around panel perimeters
articulation index
a tool used to predict the amount of speech that is audible to a patient with a specific hearing loss. The AI figure for a given patient can range from zero to one, representing the proportion of the average speech signal that is audible
ceiling attenuation class
indicates the ceiling's ability to prevent airborne sound from traveling between adjacent rooms when the dividing wall does not connect with the structural ceiling
considerations for sound reduction of mechanical equipment
-how high does the barrier have to be
-how close should the barrier be
-how much sound attenuation will we get from the barrier
considerations for sound reductions in doors and windows
-keyhole consideration
-airtight seals
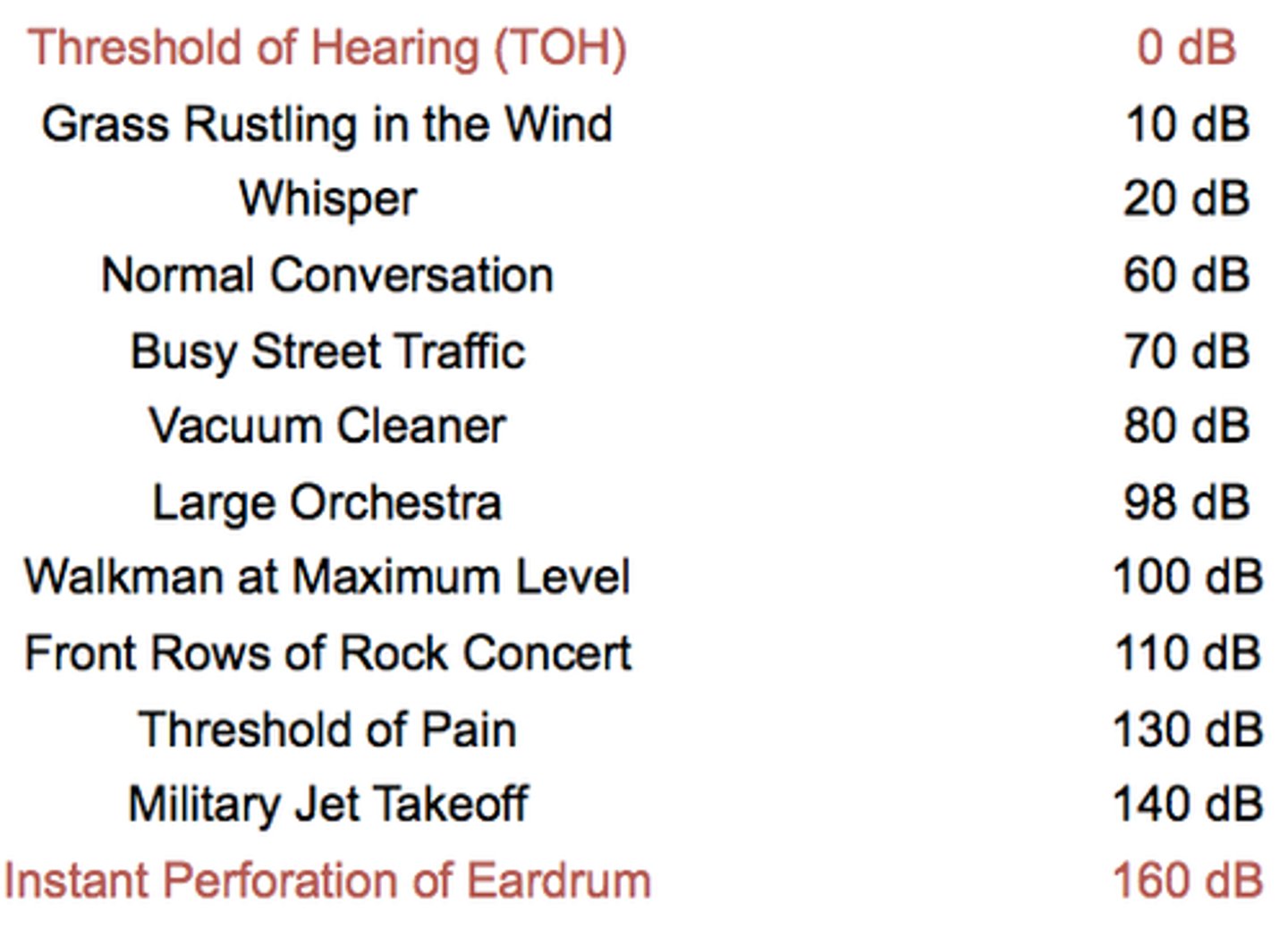
decibel level for human hearing
0-barely audible
20- whisper
130- painful
200- damage
diffuse sound field
an acoustic field where sound waves reach the observer from all directions. The reflected sound is of similar magnitude to the direct sound when it reaches the observer, and as a result, does not appear to have a single source.
direct sound
any sound recorded directly from the event
early sound
Sound that reaches the listener within a short time (50 to 80 ms) after the direct sound
reverberation field
a component of the response associated with reflections from boundaries of the subsystem and blocked connections and is statistical
directivity of sound and variation with frequency
-high frequencies are very directional
-low frequencies are effectively non directional
echo
a sound or series of sounds caused by the reflection of sound waves from a surface back to the listener
factors that influence environmental noise
-day/night average sound levels as a function of population density
-warm/cool air
-site/site specific qualities
flutter echo
an energy that's trapped between two surfaces and the angle that the sound enters between the two surfaces
free sound field
there are no reflections; sound waves reach an observer directly from a sound emitting object. The sound waves passes the observer exactly once, and never returns
noise reduction
the difference between the intensity levels of two rooms separated by a barrier of a given transmission loss
noise criterion curves
-a set of curves that weight the dB scale to reflect human hearing
-low frequencies are more tolerable than high frequencies
-they are intended to quantify the differing perception of loudness across different frequencies
dB scale
Scale used to measure sound intensity. 0dB is the faintest noise we can detect. 120dB is the threshold of pain.
impact insulation class
an integer-number rating of how well a building floor attenuates impact sounds, such as footsteps
what happens whens doubling the distance in open field
6 dB reduction for a doubling distance in free field conditions from point source, 1/4 of the old intensity
how to add and subtract sources of various SPL dB amounts
dB are not additive to add two or more noise levels, if the difference between the highest and next highest noise level is
ex: 0-1 dB then add 3 dB to the higher level to give the total noise level
doubling power of sound sources, halving power of sound sources
-every time you double the number of identical sound sources, you can add 3dB
-halving the number of identical sound sources, you can subtract 3dB
multiplying sound power
to determine the SPL dB level of N sound producers add 10log(N)-for example-for 865dB sound sources = 65dB + 10log(8) = 74
methods of noise reduction
source: proper selection and installation of equipment
path: from point to point by proper selection of construction materials and appropriate construction techniques
receiver: location through acoustical treatment of the relevant spaces
noise reduction coefficient
a scalar representation of the amount of sound energy absorbed upon striking a particular surface. An NRC of 0 indicates perfect reflection; an NRC of 1 indicates perfect absorption
octave band
a frequency band where the highest frequency is twice the lowest frequency
phon
a rating system that takes into account the different perceptions of loudness at different frequencies
pinna
the external part of an ear in humans and mammals: the auricle
pitch
the sensation of a frequency is commonly referred to as this of sound
propagation of sound for curved/flat surfaces
sound concentration caused on curved surfaces
properties of "noise"
-frequency
-sound pressure
-sound power
properties of human hearing
-variation in sensitivity with respect to frequency
-phon
-increased annoyance with increased frequency
properties of waves
-frequency
-wavelength
-amplitude
-speed of sound
- wave form (simple vs complex)
pure tones vs. complex sounds
pure: one frequency
complex: multiple frequency components
range of comfortable sound levels
perceptible sound levels
sound reflection
occurs when sound bounces off hard, rigid, and flat surfaces such as concrete, brick, stone, or glass.
sound diffusion
process of random movement toward equilibrium
sound diffraction
waves bend when they encounter an obstacle
general relationship of absorptive to frequency and thickness
the thicker an absorbent material, the better its low frequency absorption characteristics
relationship between change in dB scale and apparent loudness change
change in 1 dB=imperceptible (except for tones)change in 3 dB = just barely perceptible,change in 6 dB=clearly noticeable, change in 10 dB = about twice (or half) as loud, change in 20 dB = about 4 times (or one-fourth) as loud.
resonant panels
-absorbs low frequencies
-they work by vibrating at these low frequencies and turning sound into heat
reverberation time
a collection of time-delayed versions of a sound that have decayed in intensity over time as they arrive at the listener
reverberations
Multiple or continuous reflections of sound that prolong(distort) the existence of the sound within a confined space
sound
A disturbance that travels through a medium as a longitudinal wave
sound directivity
-projection of sound from source
-the voice sounds natural
-mega horn greatly enhances this