Psychology Chapter One and Two Notes
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
Psychology
The scientific study of behavior and mental processes.

Five main goals of psychology
To describe, predict, explain, control, change, and influence behavior and mental processes.

Psychiatrists
Are medical doctors and have medical degrees, followed by several years of specialized training in the treatment of mental disorders. They can also hospitalize people, order biomedical therapies, and prescribe medications.

Psychologists
Are not medical doctors and cannot order medical treatments.

Clinical Psychology
Focuses on the causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of psychological disorders.

School Psychology
Applies psychological principles and findings in primary and secondary schools.

Health Psychology
Research psychological factors in the development, prevention, and treatment of illness; stress, and coping; promoting health-enhancing behaviors.

Biological Psychology
Explores relationships between psychological processes and the body’s physical system.

Neuroscience
Refers specifically to the study of the brain and the rest of the nervous system.

Positive Psychology
Focuses on the study of optimal human functioning and aims to discover and promote strengths and virtues that enable individuals and communities to thrive.

Theory
Tentative explanation that tries to integrate and account for the relationships of various findings and observations.

Hypothesis
A tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables; a testable prediction or question.

Random selection
A process in which subjects are selected randomly from a larger group and it is important in the research participant selection process because it allows every group member to have an equal chance of being included in the study.

Meta-analysis
Pooling the effect sizes of several studies into a single analysis.
Case study
An intensive, in-depth investigation of an individual, a family, or some other social unit.

Population
The selected group of participants for the study.

Sample
A segment of the population is used to represent the group that is being studied.
Correlational study
Examine how strongly two variables are related to, or associated with, each other. Can be used to analyze the data gathered by any type of descriptive method and is also used to analyze the results of experiments. Does not indicate causality.
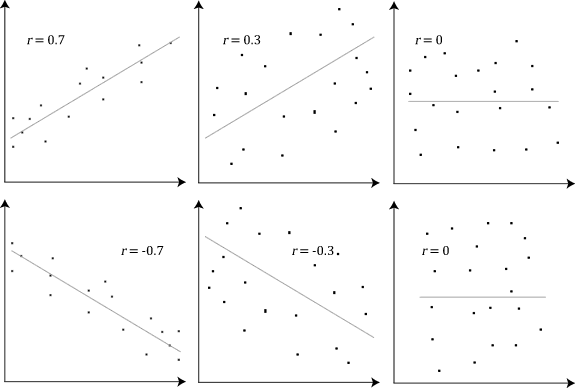
Steps in the scientific method
Formulate a Testable Hypothesis
Design the Study and Collect the Data
Analyze the Data and Draw Conclusions
Report the Findings

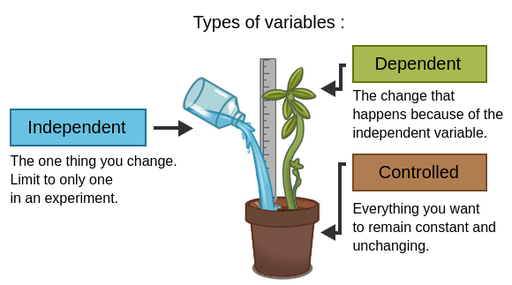
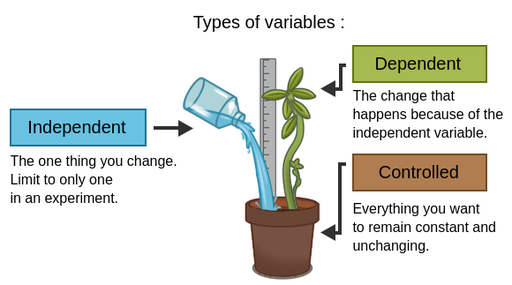
Independent variable
Factor that is purposely manipulated to produce a change in an experiment (predictor/treatment variable).
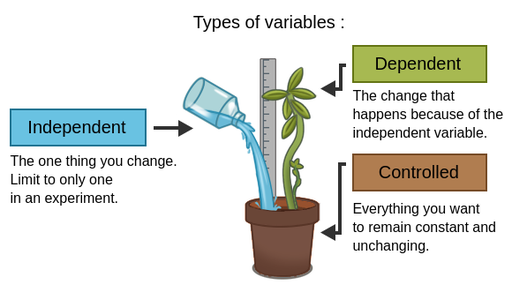
Dependent Variable
Factor that is observed and measured for change in an experiment; thought to be influenced by the independent variable (outcome variable).
Confounding Variable
External variables that are not the focus of the experiment, but could affect the outcome of an experiment (extraneous variable).
Double-blind technique/study
Both the participants and researchers interacting with them are blinded or unaware of the treatment or condition to which the participants have been assigned.

Placebo
A fake substance, treatment, or procedure that has no known direct effects.
Placebo Effect
Any change attributed to the person’s beliefs and expectations rather than to an actual drug, treatment, or procedure (also called the expectancy effect).
The American Psychological Association (APA) provides ethical principles regarding research with human participants. These five key provisions include:
Informed consent and voluntary participation
Students as research participants
The use of deception
Confidentiality of information
Information about the study and debriefing

Biological Perspective
Emphasizes studying the physical bases of human and animal behavior, nervous system, endocrine system, immune system, genetics.
Psychodynamic Perspective
Emphasizes importance of unconscious influences, early childhood life experiences in explaining human behavior.
Behavioral Perspective
Emphasizes how behavior is acquired or modified by environmental causes.

Humanistic Perspective
Focuses on motivation of people to grow, self-concept, free will and choice, self-direction and reaching one's full potential.
Positive Psychology
Focuses on study of optimal human functioning; aims to discover and promote strengths and virtues that enable individuals and communities to thrive.
Cognitive Perspective
Focuses on the important role of mental processes in how we process information: memory, intelligence, language development, perception, problem solving, and learning
Cross-cultural Perspective
Emphasizes how cultural factors influence patterns of behavior.

Evolutionary Perspective
Emphasizes the application of principles of evolution to explain behavior, natural selection.

Collectivistic Cultures
Cultures that emphasize the needs and goals of the group over the needs and goals of the individual.

Individualistic Cultures
Cultures that emphasize the needs and goals of the individual over the needs and goals of the group.

Ethnocentrism
Belief in the superiority of one's nation culture, or ethnic group.

Culture
Enduring behaviors, ideas, attitudes, and traditions shared by a large group of people and transmitted from one generation to the next.

Aristotle (384-322 BC)
Believed sensory experience to be the basis of all knowledge. Was one of the first to write about sleep, memory, the senses, dreams, and learning.

Mary Calkins (1863-1930)
First woman president of the APA (American Psychological Association)

Rene Descartes (1596-1650)
French philosopher that argued for dualism between mind and body. Promoted the belief that the mind and body are two separate entities - interactive dualism.

Sigmund Freud (1856-1939)
Founder of psychoanalysis, a controversial theory about the workings of the unconscious mind.

G. Stanley Hall (1844-1924)
American psychologist who established the first psychology research laboratory in the U.S.; founded the American Psychological Association

William James (1842-1910)
Considered the first American psychologist and theories formed functionalism - mental processes helping individuals adapt to environment.

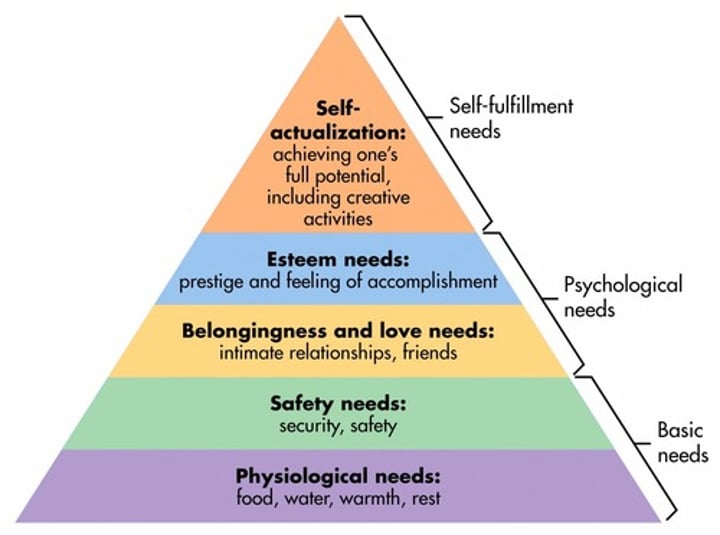
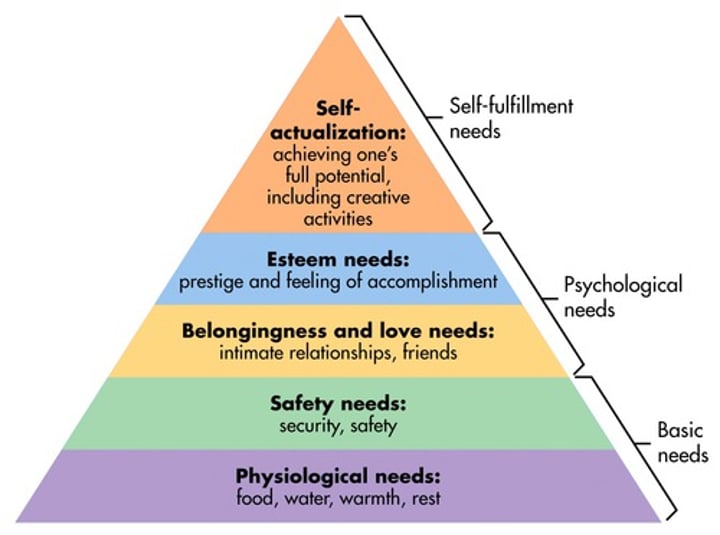
Abraham Maslow
Humanistic psychologist known for his "Hierarchy of Needs" and the concept of "self-actualization"
Ivan Pavlov (1849-1936)
Russian physiologist and learning theorist famous for the discovery of classical conditioning, in which learning occurs through association.
Carl Rogers (1902-1987)
American psychologist who helped to found humanistic psychology. and developed client-centered psychotherapy.

B.F. Skinner (1904-1990)
Behaviorist that developed the theory of operant conditioning by training pigeons and rats. Reinforcement and punishment.
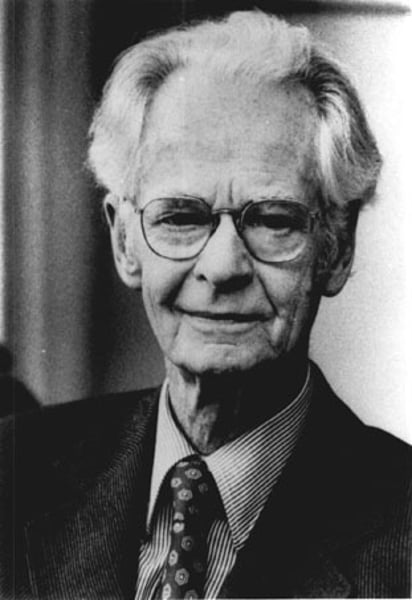

Edward Titchener (1867-1927)
Studied under Wundt; focused on identifying basic elements of the mind. Founded structuralism.

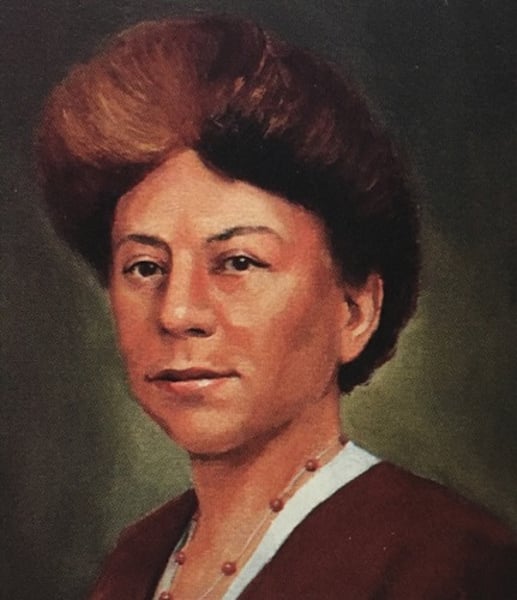
Margaret Floy Washburn (1871-1939)
First woman to earn a PhD in psychology (1894). Known for her experimental work involving animal behavior and sensation/perception processes.

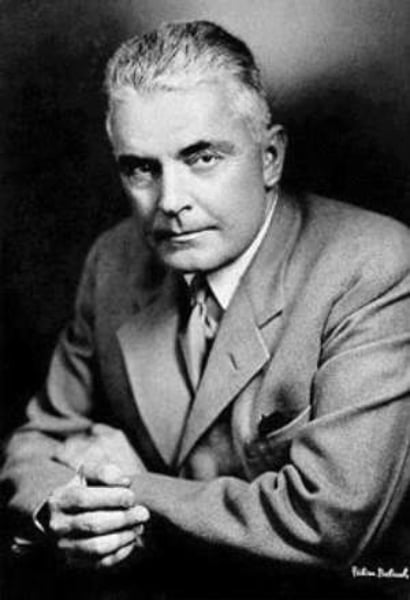
John Watson (1878-1958)
Declared that psychology must limit itself to observable phenomena, not unobservable concepts like the unconscious mind, if it is to be considered a science. Established American Behaviorism.

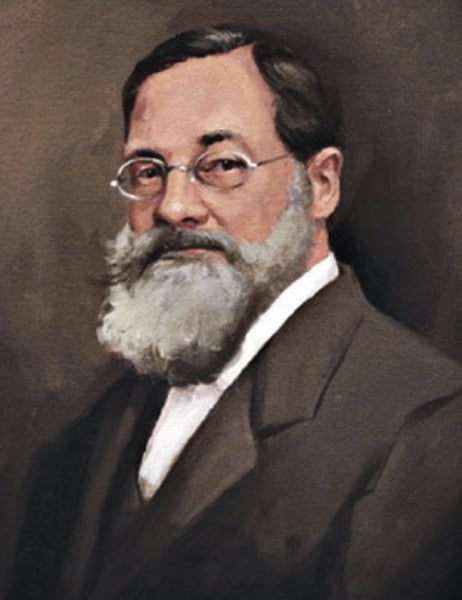
Whilhelm Wundt 1879
Credited as the founder or father of scientific psychology.
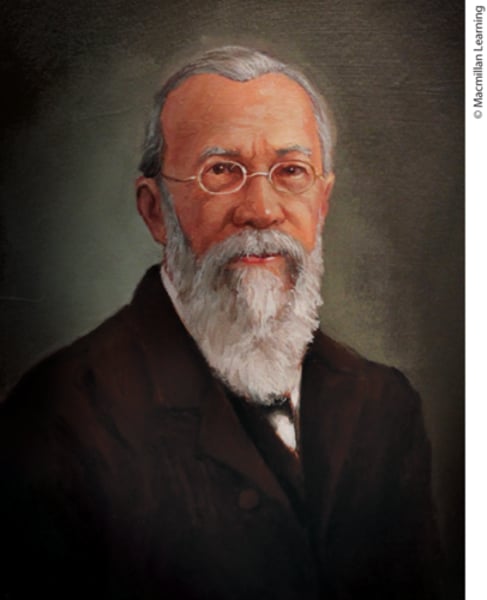

Francis Sumner (1895-1954)
First African American awarded Ph.D. in psychology in 1920.
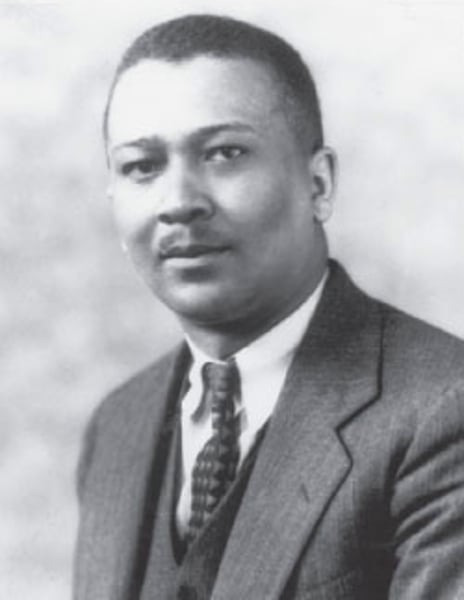

Kenneth and Mamie Clark
Used dolls to study children's attitude towards race. Their findings were used in the 1954 Brown vs. Board.

Pauline Elizabeth Scarborough (1935-2015)
Championed inclusion of women in the story of psychology. Explored ways women's changing social status affected the field of psychology.

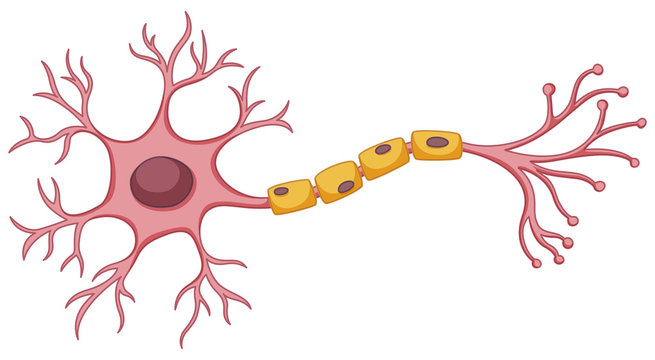
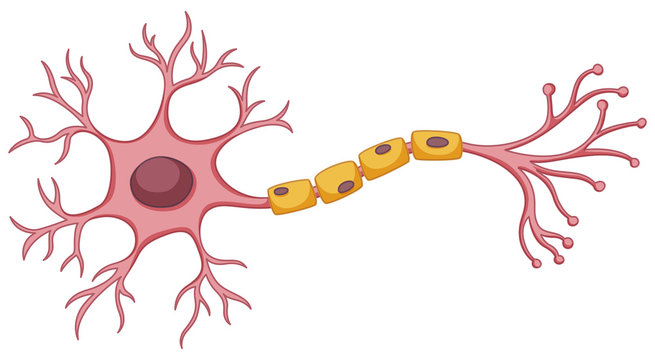
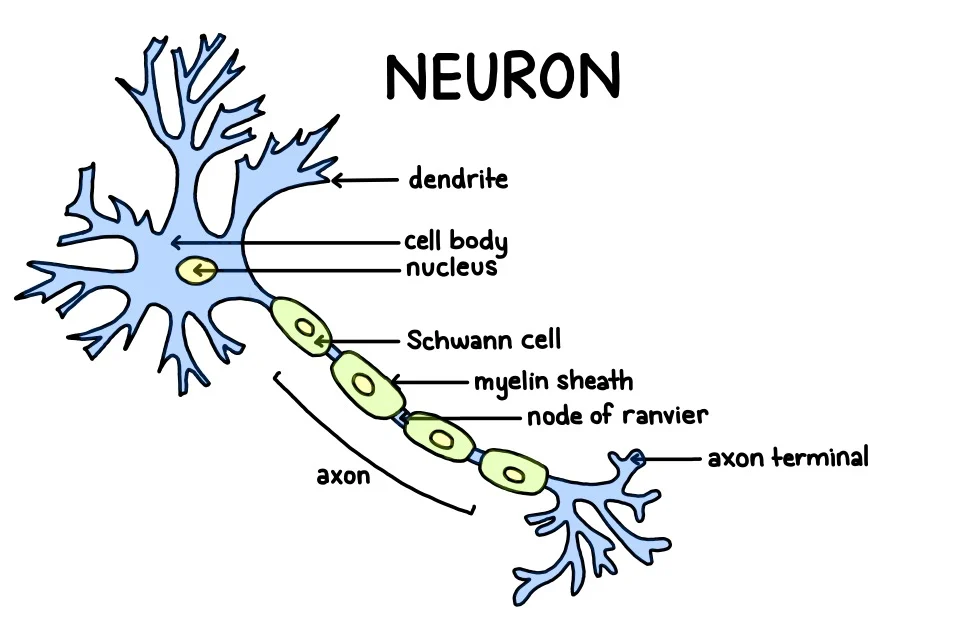
Basic Anatomy of the Neuron
Cell body, dendrites, axon, myelin sheath
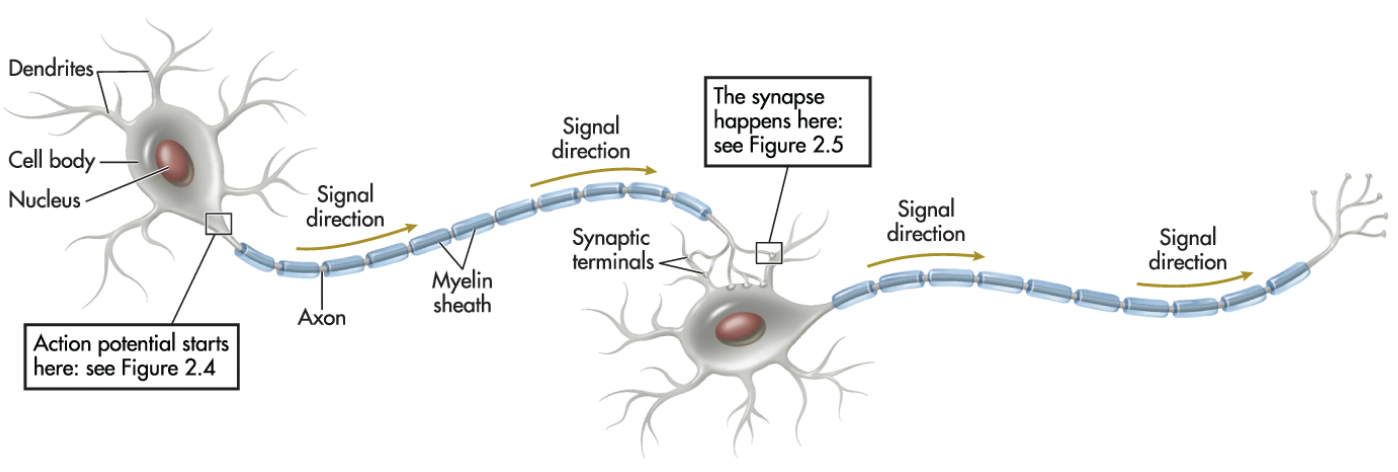
Cell Body
Contains structures that process nutrients, providing the energy the neuron needs to function; also called the soma
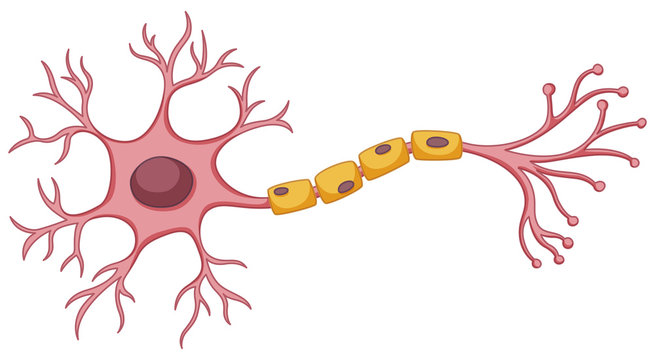
Dendrites
Receives messages from other neurons
Axon
Carries information from the neuron to other cells in the body
Myelin Sheath
White fatty tissue covering that wraps around the axons of some neurons
Reuptake
Leftover neurotransmitters are reabsorbed into the axon terminal
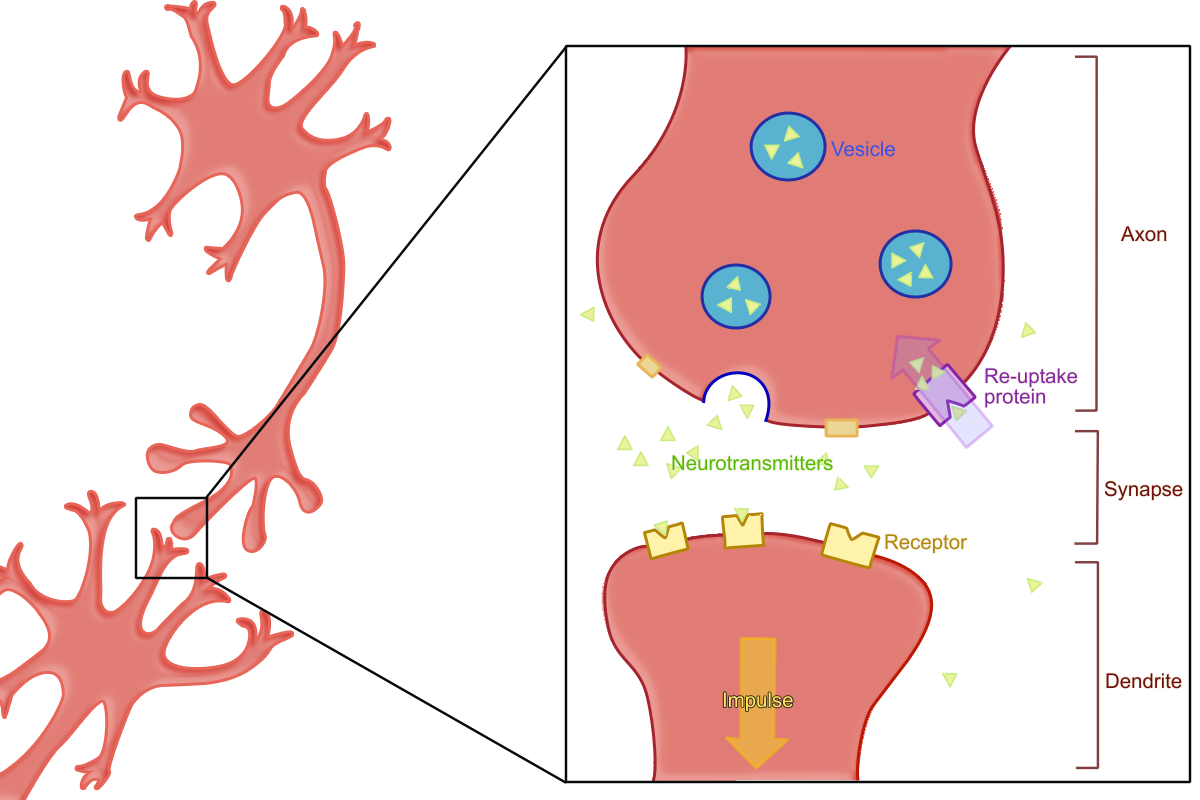
Axon terminals
Located at the end of an axon
Glial Cells
Provide the structural and functional support for neurons throughout the nervous system.
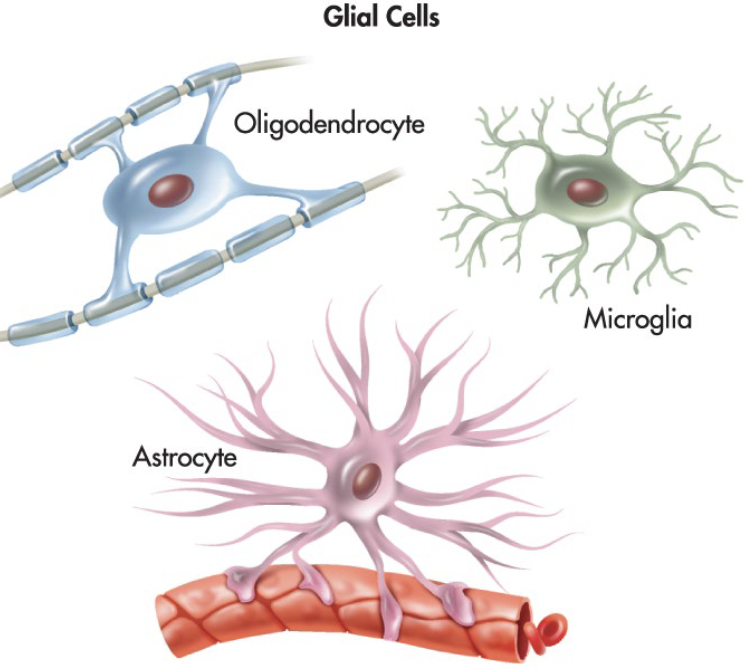
Oligodendrocytes
Form myelin sheath
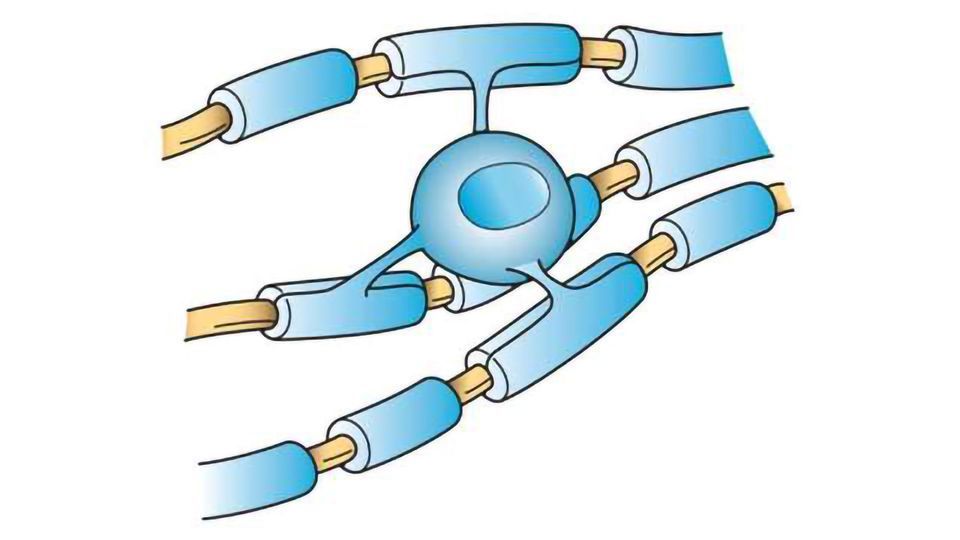
Microglia
Do the brain’s “clean-up” work; part of the immune response
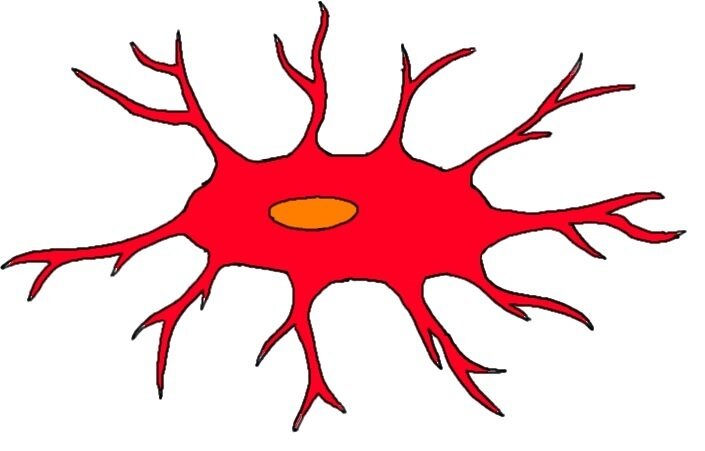
Astrocytes
Are the most common glial cells; structural support; nutrient provision
Neurons
Cells that are highly specialized to receive and transmit information from one part of the body to another.
How many neurons are in your brain?
Around 90 billion
Sensory Neurons
Convey information about the environment to the brain
Motor Neurons
Communicate information to the muscles and glands of the body
Interneurons
Communicate information between neurons
How fast do neurons communicate?
Upward of 270mph
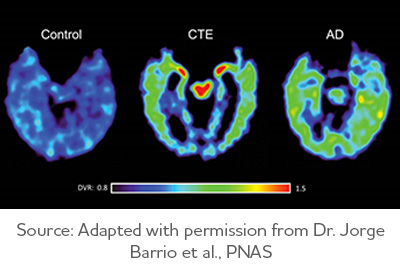
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy.
Caused by repetitive head impacts. Can cause social behavioral problems.
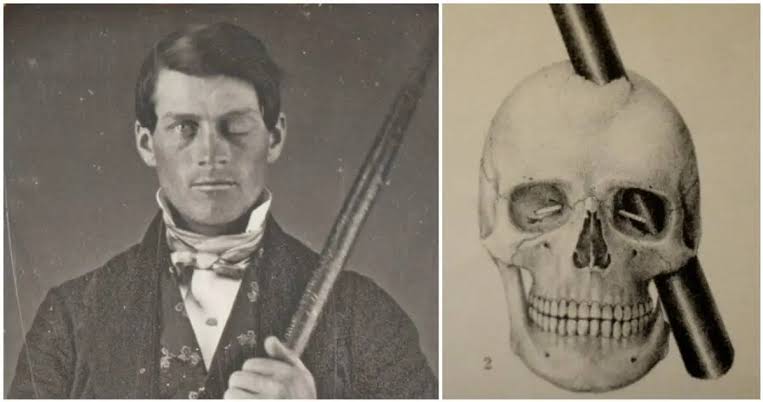
Phineas Gage
A metal rod went through his frontal lobe, affecting his social behavior and planning. The accident helped show psychologists how brain functions are localized.

Neurogenesis
The ability of our brains to develop new neurons
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers manufactured by the neuron
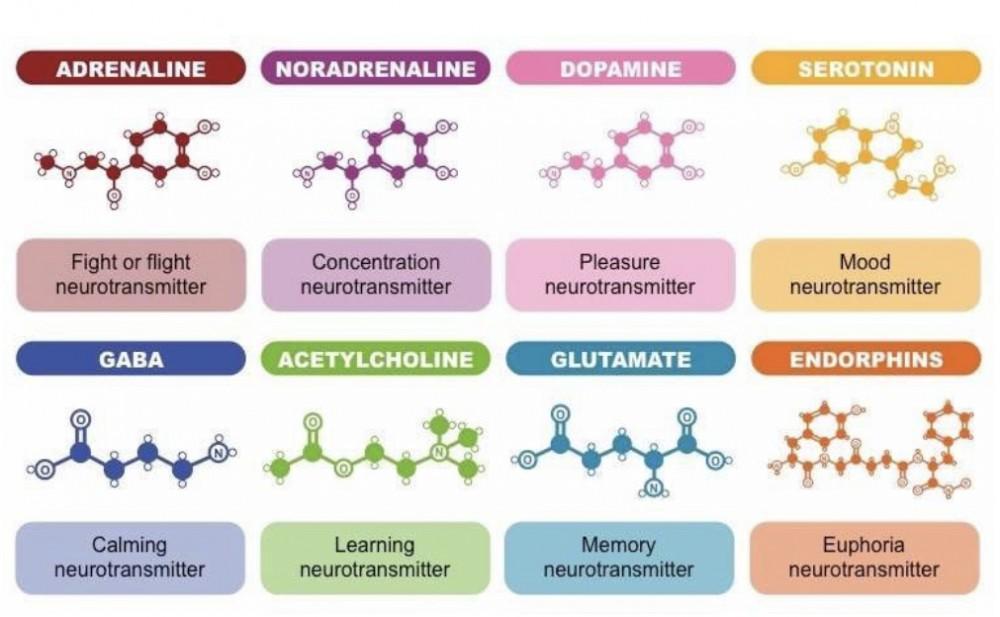
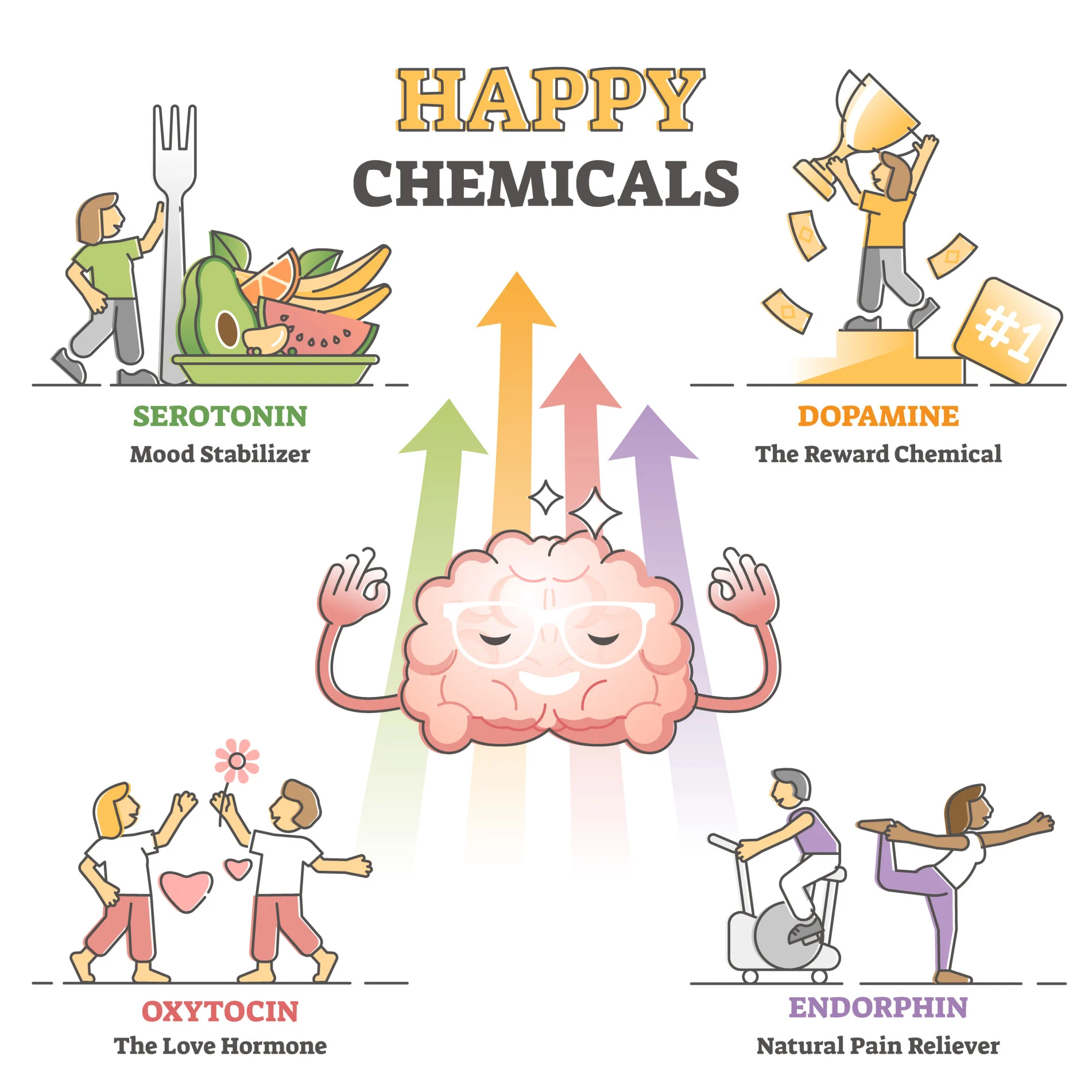
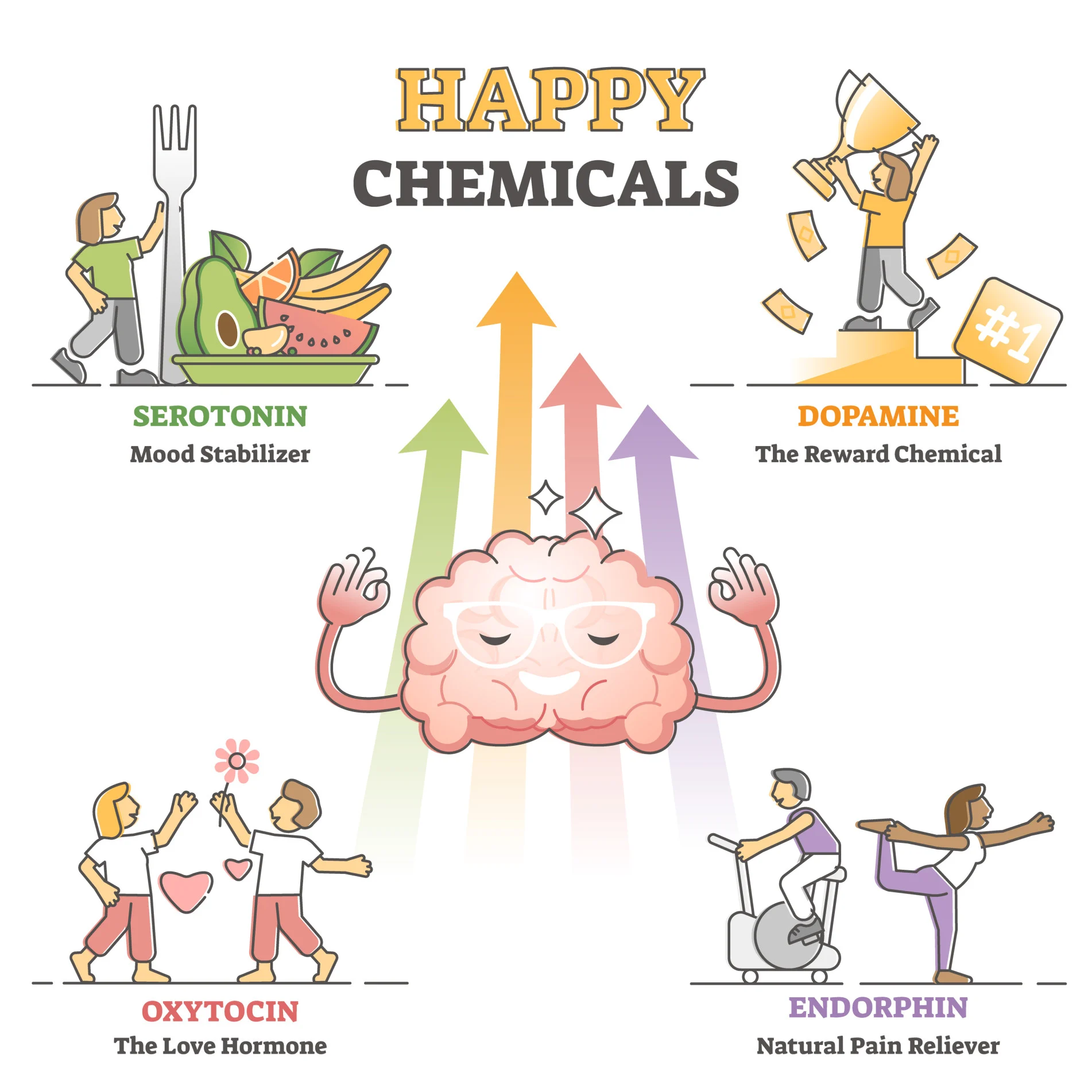
Dopamine
Involved in movement, attention, learning, and pleasurable sensations; Parkison’s disease
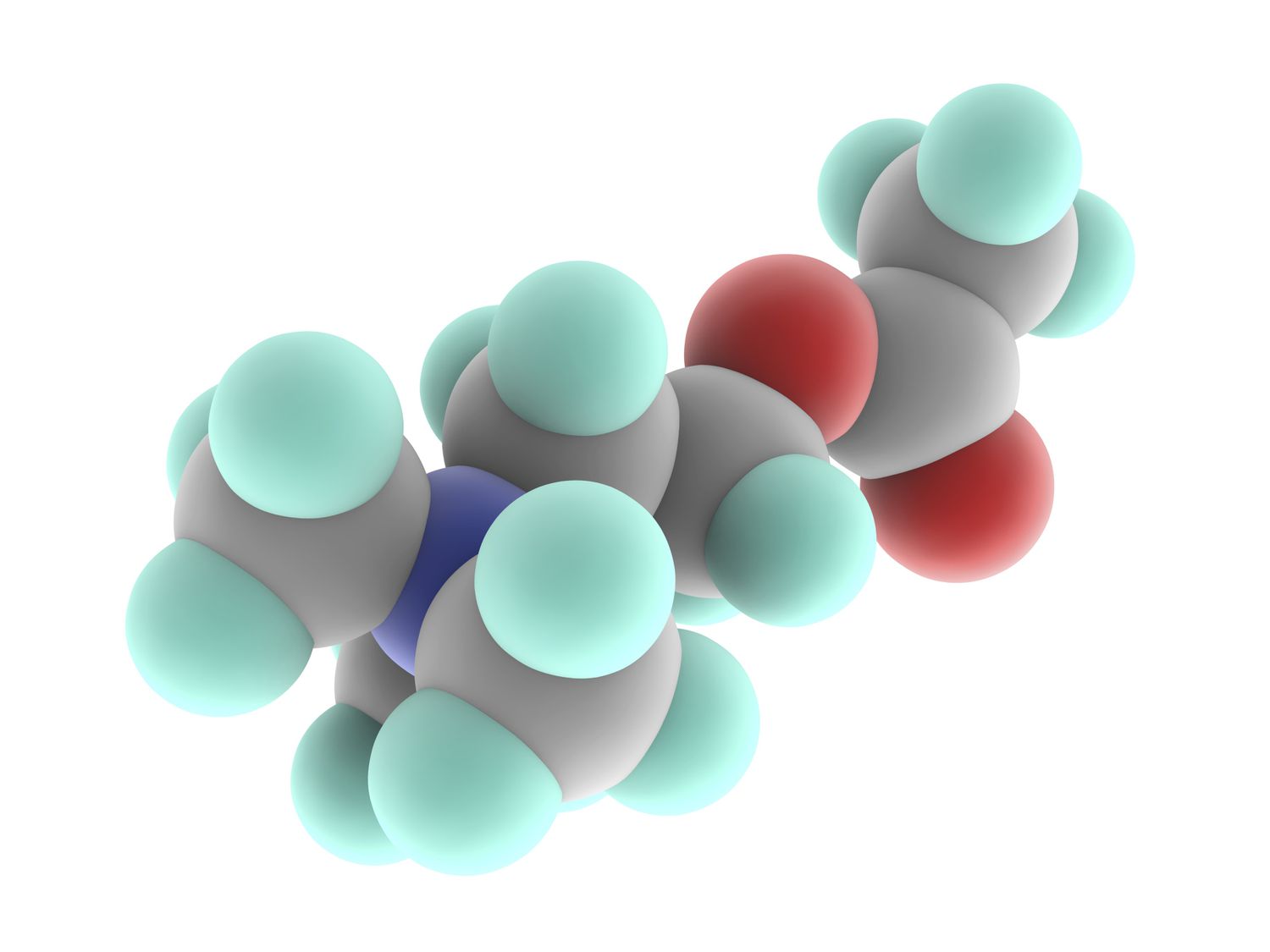
Serotonin
Involved in sleep, appetite, moods, and emotional states
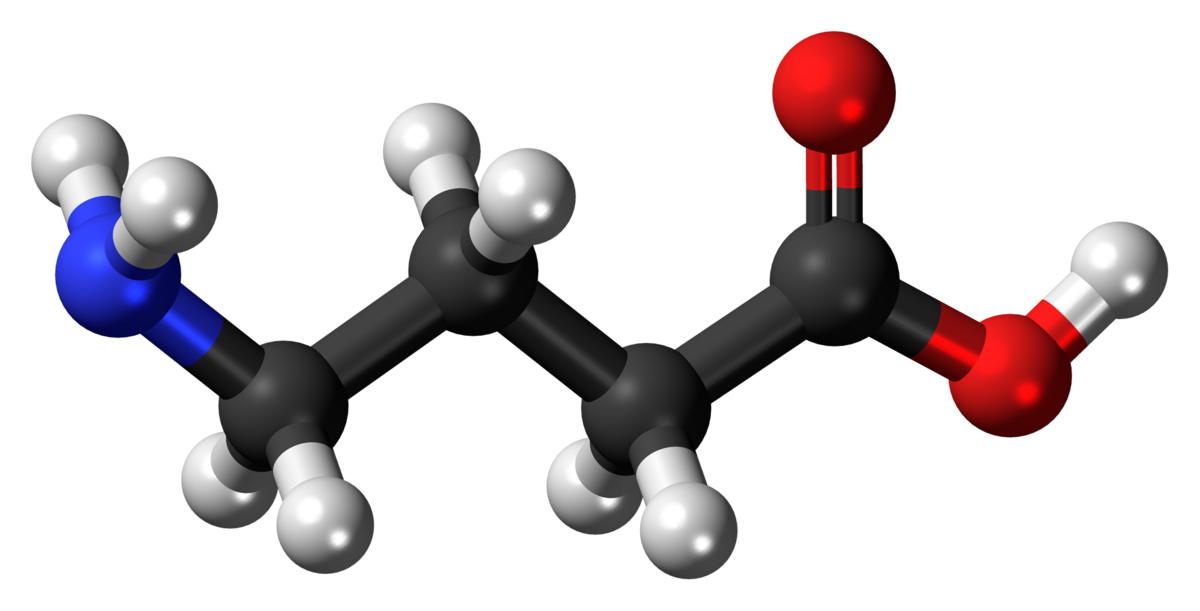
Acetylcholine
Stimulates muscle contraction; involved in memory, learning, and general intellectual functioning; Affects Alzheimer’s disease
GABA
Helps us relieve anxiety naturally, offset excitatory messages and regulate daily sleep-wake cycles
Endorphins
Pain perception and positive emotions
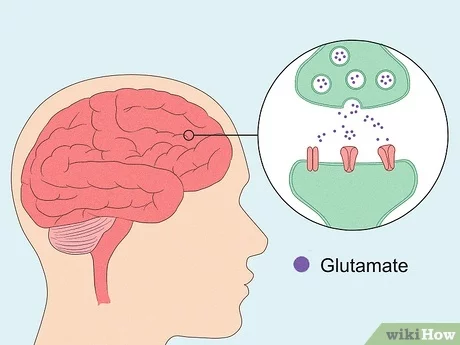
Glutamate
Excitatory messages
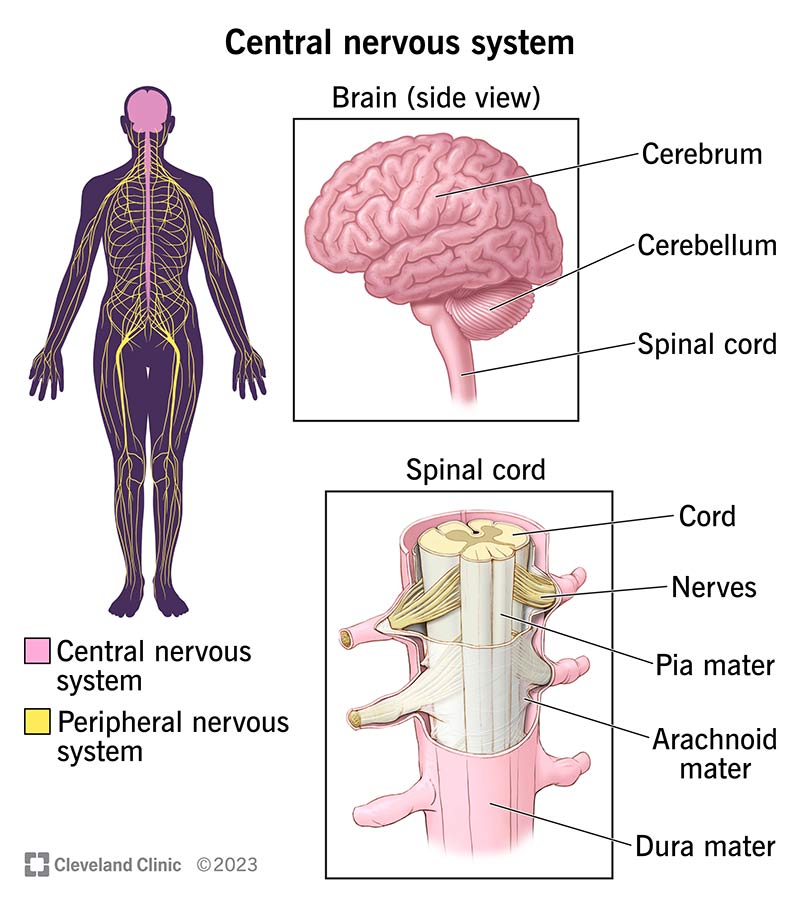
Central Nervous System
The division of the nervous system that is central to all behavior and mental processes; it consists of the brain and spinal cord
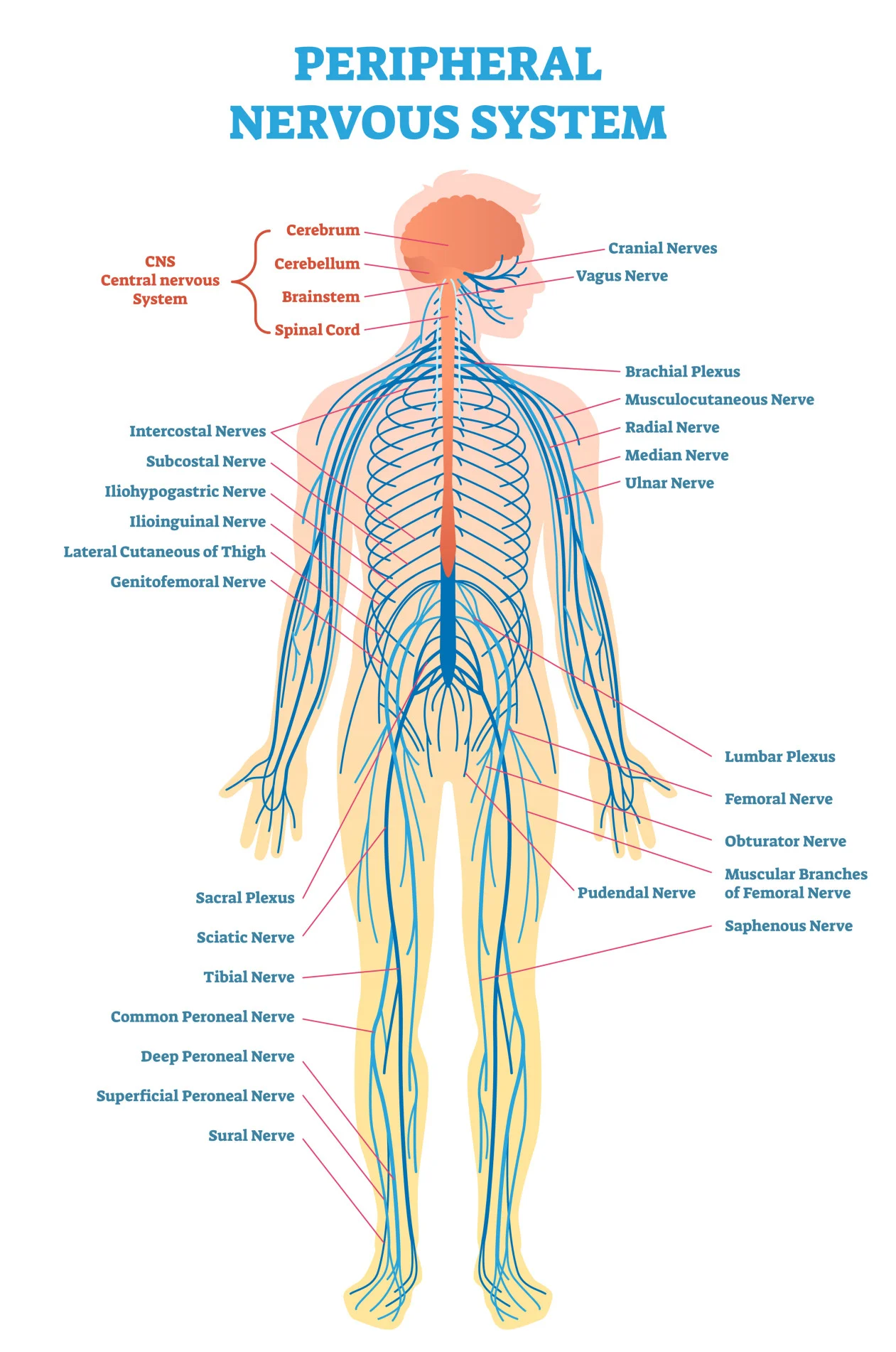
Peripheral Nervous System
The division of the nervous system that includes all the nerves lying outside the central nervous system
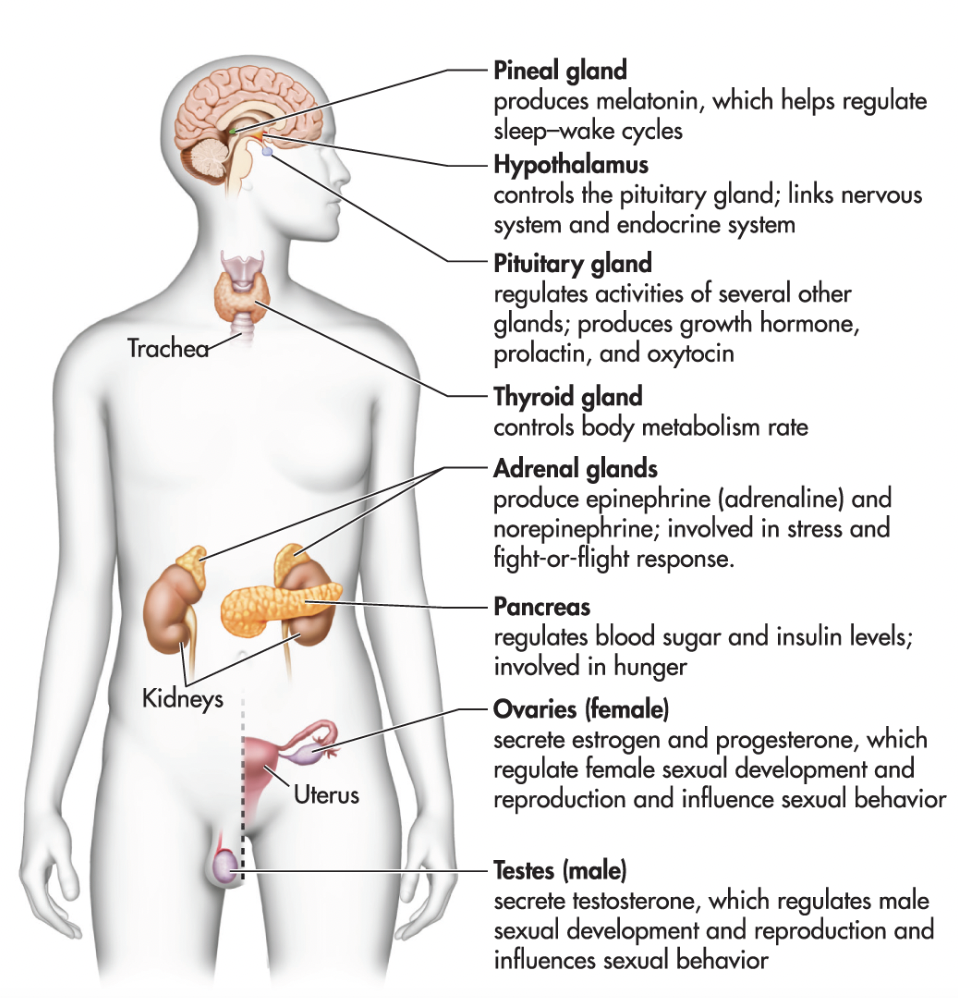
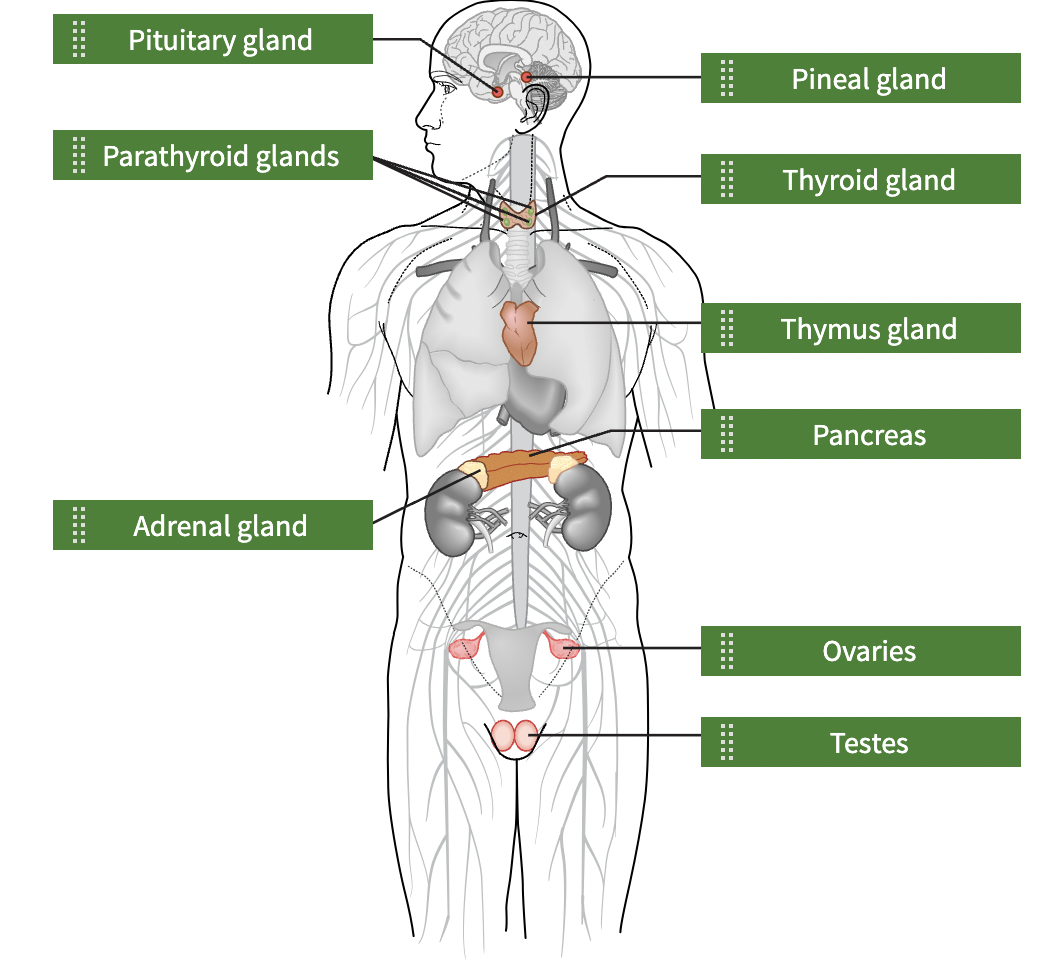
Endocrine System
Uses chemical messengers to transmit information from one part of the body to another by secreting hormones into the bloodstream. Regulates vital processes in the body including growth, metabolism, and sexual development. Endocrine glands secrete hormones in the blood, then they travel through the cardiovascular system.
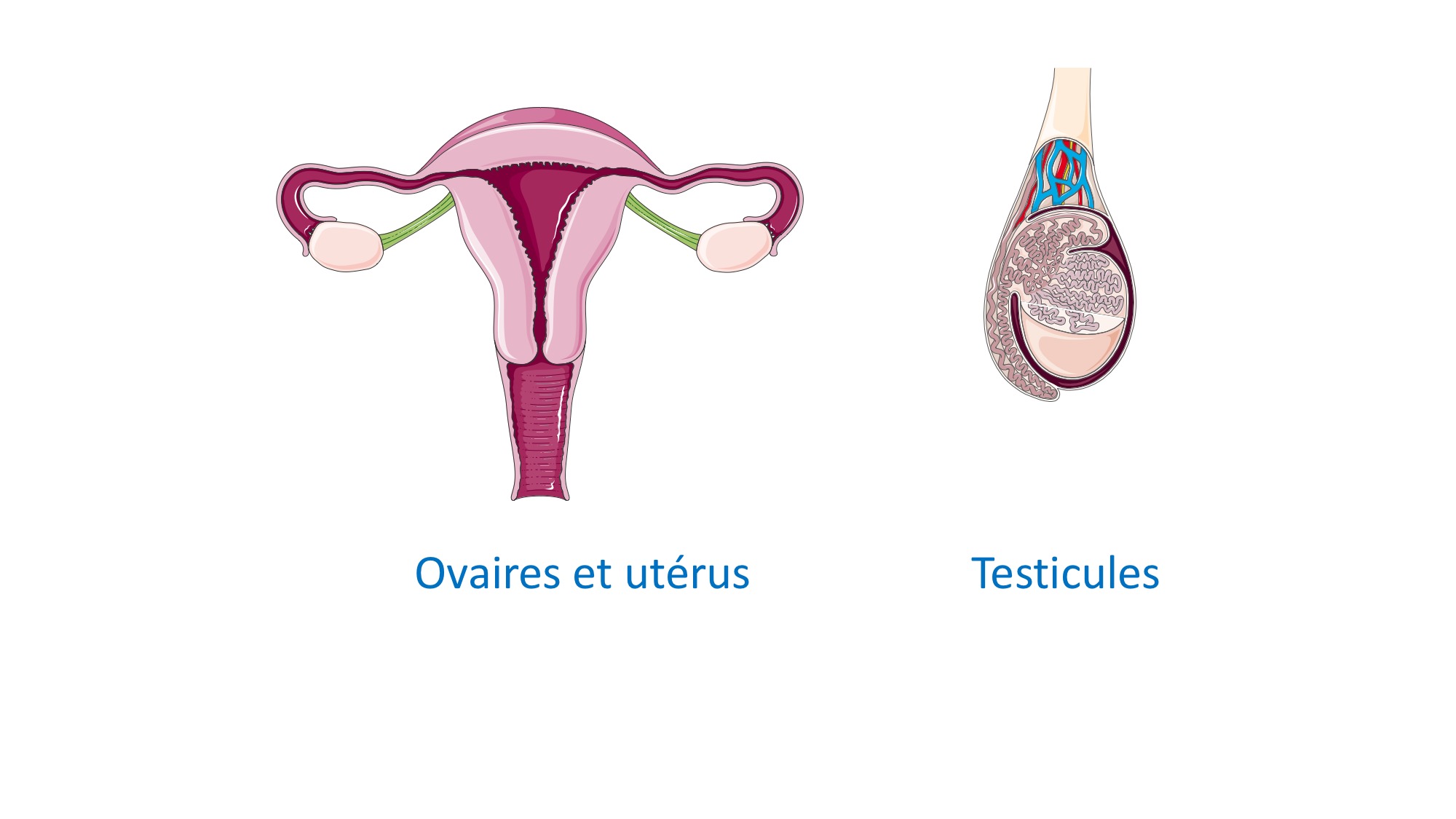
Gonades
Reproductive organs; include ovaries and testes
Hormones
Chemical messengers secreted into the bloodstream. They regulate physical processes and influence behavior and influence emotional and stress response. Closely linked to CNS workings and are (in some cases) chemically identical to neurotransmitters.

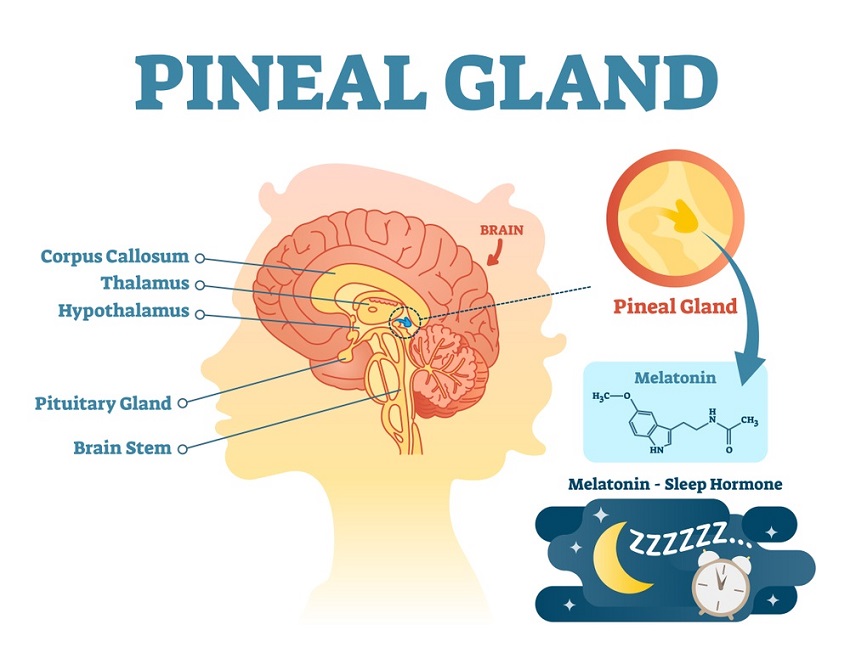
Pineal Gland
Produces melatonin, which helps regulate sleep-wake cycles
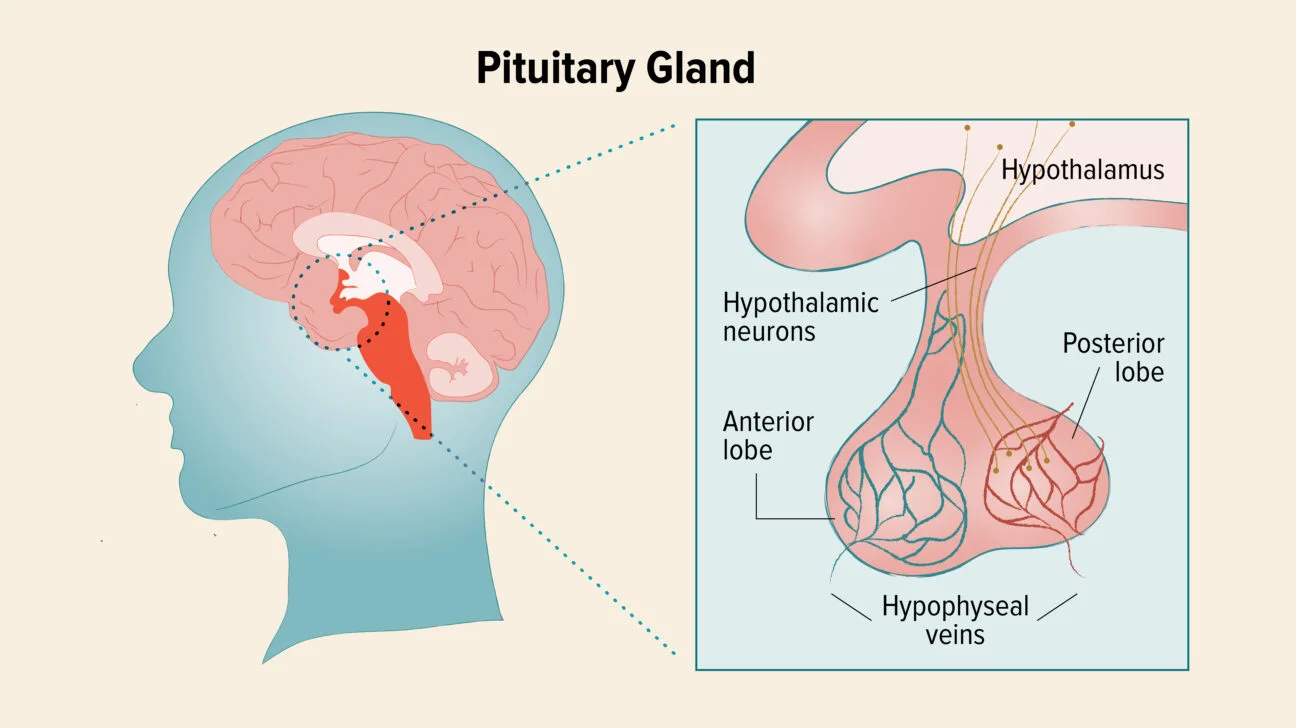
Pituitary Gland
The master gland, regulates the activities of several other glands. Secrets growth hormone
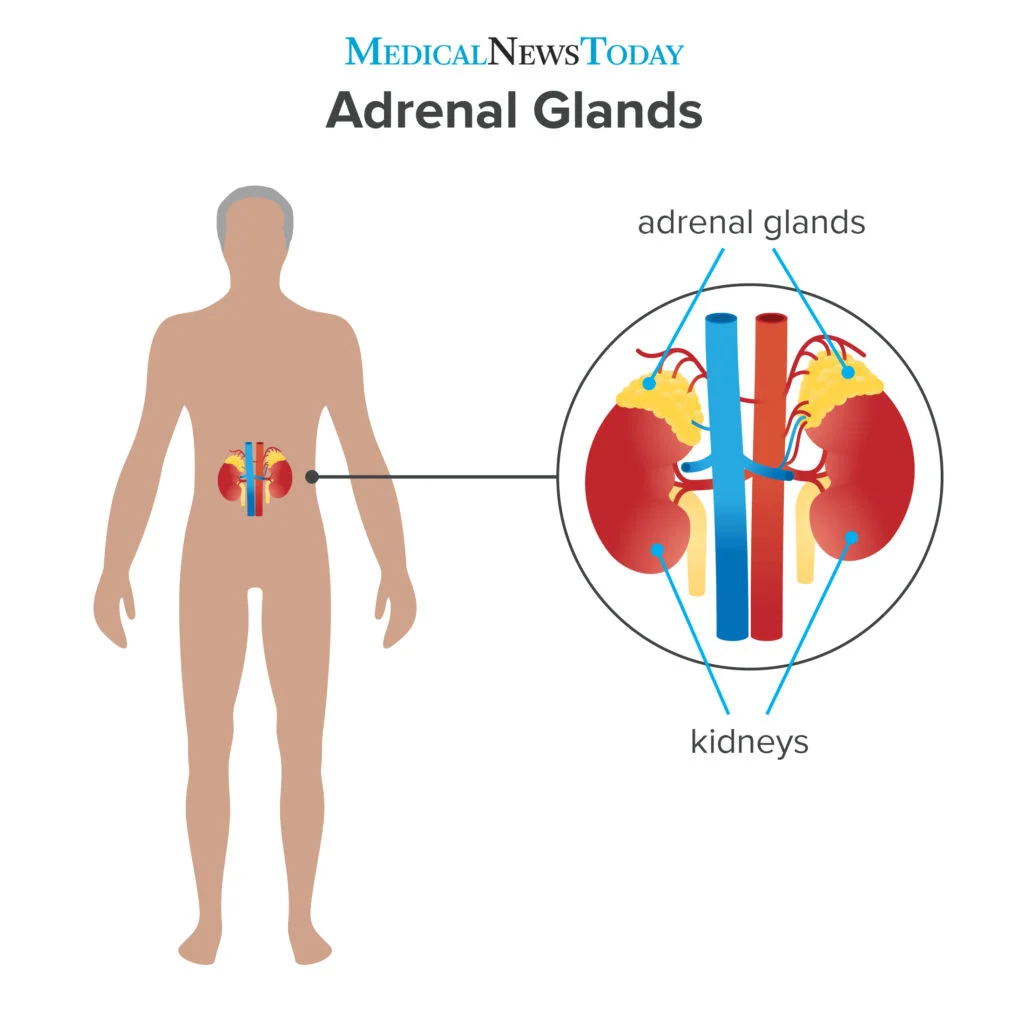
Adrenal Gland
Produce epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine; involved in stress and fight-or-flight response
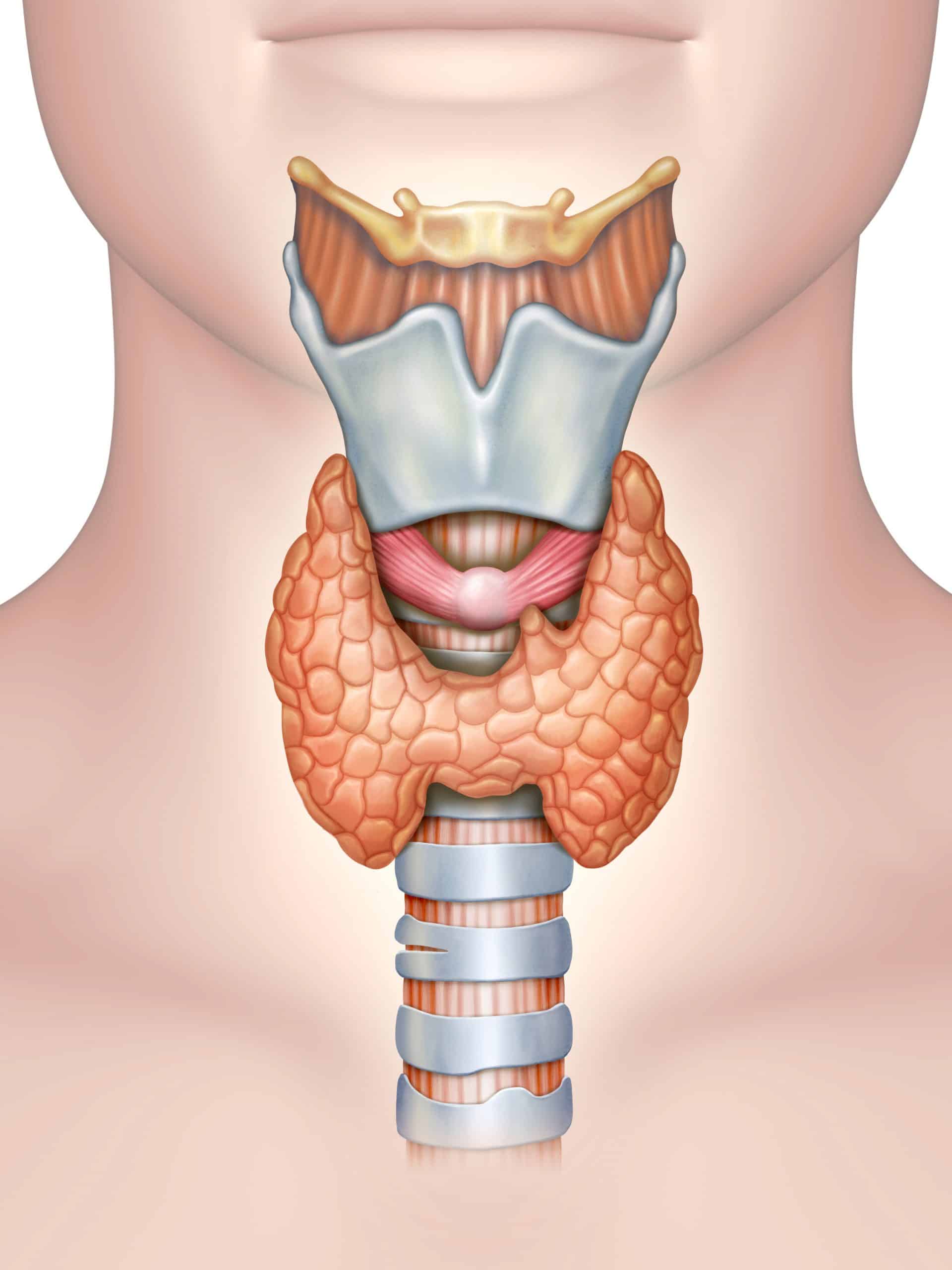
Thyroid Gland
Controls body metabolism rate
Pancreas
Regulates blood sugar and insulin levels; involved in hunger
Oxytocin
“The love hormone” produced in the hypothalamus and released by the pituitary gland. It functions to facilitate childbirth by increasing uterine contractions and the production of milk. It also fosters the bond between the mom and baby
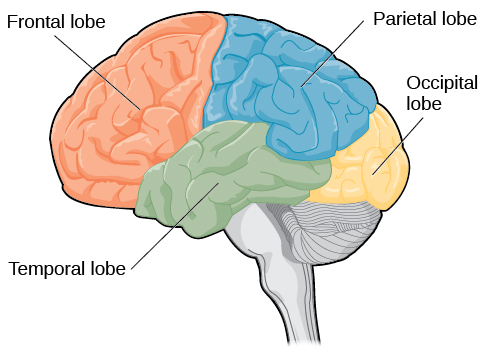
How many lobes does the brain have?
Four: frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital
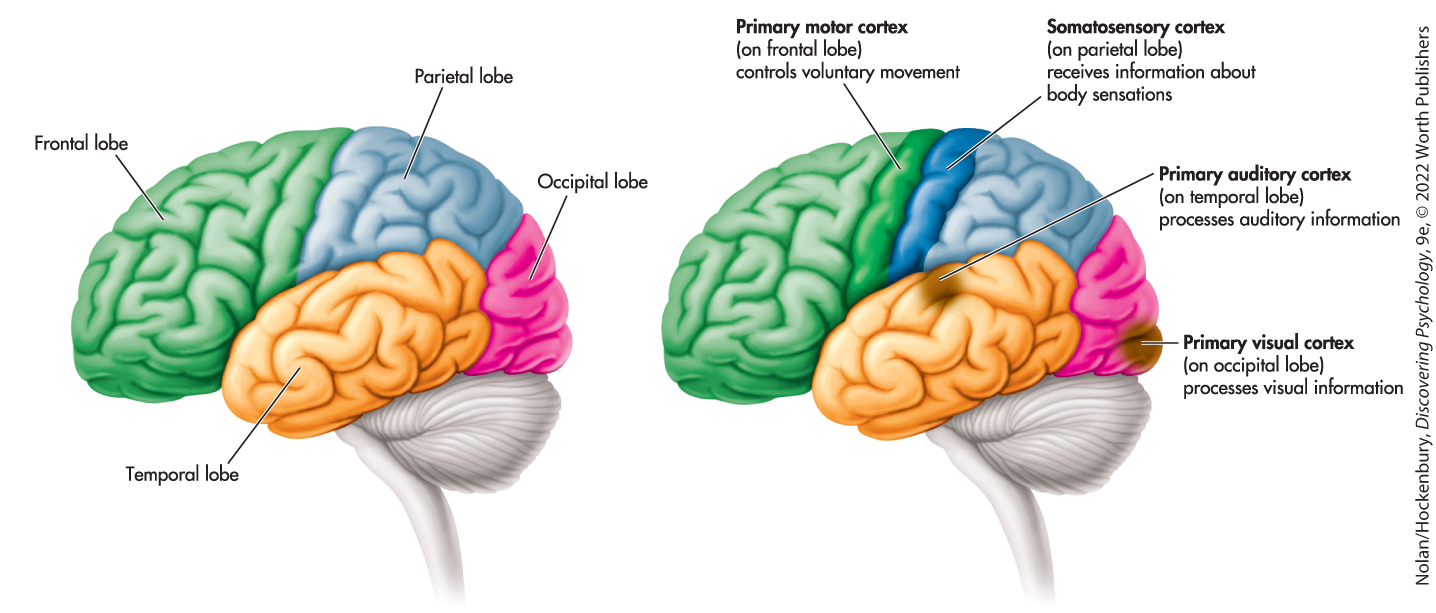
Frontal Lobe
Controls voluntary movement: planning, and emotional control
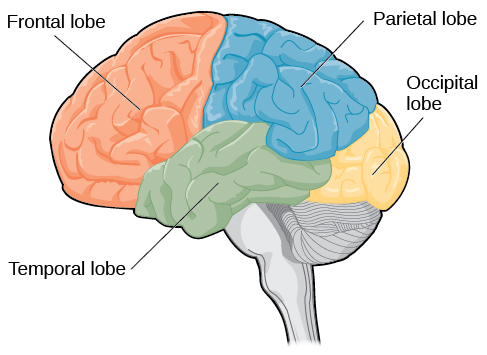
Temporal Lobe
Processes auditory information
Occipital Lobe
Processes visual information
Parietal Lobe
Receives information about body sensations
Karl Wernicke
German neurologist who discovered another area in the left hemisphere that, when damaged, produced a different type of language disturbance.

Neuroplasticity
The ability within the brain to constantly change both the structure and function of many cells in response to experience or trauma.