Immunology and Serology
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
167 Terms
Type of Immunity Associated with immunization
Active
Type of cell that produces antibody
B cells
Immunity Associated with Viral Infections
Cellular
Immunity associated with Bacterial Infections
Humoral
Phagocytosis and NK cells are part of what immunity?
Natural
T cells and B cells are part of ____ immunity
Adaptive
What type of immunity is associated with rubella immunization?
Active
What type of immunity is associated with neonatal syphilitic IgG antibody titers?
Passive
Individual produces antibody
Follows Immunization or Infection
Memory
Active
Antibody Transferred to Individual (gamma gobulin injections, placental transfer)
No memory
Passive
Cellular/Humoral?
T cells/Lymphokines
Cellular
Cellular/Humoral?
Defense against Bacterial infections by phagocytosis
Humoral
Cellular/Humoral?
Hypersensitivity Type IV (delayed)
Cellular
Cellular/Humoral?
Hypersensitivity Type I (immediate)
Humoral
Cellular/Humoral?
Hypersensitivity Type II (ADCC)
Humoral
Cellular/Humoral?
Hypersensitivity III (Immune Complex)
Humoral
%of Total Circulating Lymphoid Cells for: T Cells
80%
%of Total Circulating Lymphoid Cells for: B Cells
5-15%
%of Total Circulating Lymphoid Cells for: NK Cells
5-15%
T/B/NK Cells?
Surface Markers of CD2, CD3, CD4, CD25, CD8
T Cells
T/B/NK Cells?
Surface Markers: CD19, CD20, CD21
B Cells
T/B/NK Cells?
Surface Markers: CD16, CD56
NK Cells
Function of B Cells
Evolve into plasma cells which secrete antibody
Become memory cells
Function of NK cells
Kill virus infected cells and tumor cells
CD4 Function
Release cytokines
Become memory cell
CD8 Function
Become cytotoxic
CD4/CD8 function
Interact with B cells
CD4/CD25 function
suppress immune system
T Helper surface marker
CD4
T Cytotoxic surface marker
CD8
Normal CD4:CD8 ratio
2:1
AIDS CD4:CD8 ratio
1:2
Normal T cell:B cell ratio
8:1
T and B cells can be describe as what kind of WBC?
small lymphocytes
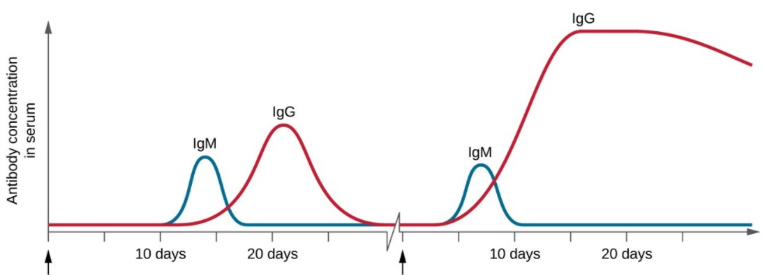
Immune Response Curve Graph
first arrow is showing the ____ dose
Sensitizing

Immune Response Curve Graph
second arrow is showing the ____ dose
Booster
Immunoglobulin Antibody Classes: G.M.A.D.E
Greatest plasma concentration (~75%)
Goes across placenta
IgG
Immunoglobulin Antibody Classes: G.M.A.D.E
Largest immunoglobulin molecule
Activates complement
IgM
Immunoglobulin Antibody Classes: G.M.A.D.E
Body Secretions
IgA
Immunoglobulin Antibody Classes: G.M.A.D.E
Don’t know function
Present with B cells
IgD
Immunoglobulin Antibody Classes: G.M.A.D.E
Allergy reactions
Type I hypersensitivity
IgE
Precipitation Curve: Pros Have Good Bodies
Prozone=____ excess
antibody
Precipitation Curve
Postzone is ____ excess
antigen
Precipitation Curve
Equivalence = Max _____
precipitation
Visible precipitation forms as a
lattice
Double and Single diffusion
Immunoelectrophoresis
Immunofixation
These are all examples of:
Precipitation Testing
Skin tests, RIST, RAST will all test for
Allergies
Hypersensitivity Reaction Types:
Bee sting
Hay fever
Asthma
Type I
Hypersensitivity Reaction Types:
Transfusion reaction
Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA)
Hashimoto Thyroiditis
Goodpasture disease
Type II
Hypersensitivity Reaction Types:
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
Serum Sickness
Type III
Hypersensitivity Reaction Types:
Contact Dermatitis (poison Ivy, Chemicals)
TB
Leprosy
Graft vs Host Disease
Type IV
Mechanism for Type I Hypersensitivity Reaction:
It is _(immunoglobin)__ mediated where the antigen binds to the ____ cells which triggers ____ to release
IgE
Mast
Histamine
Cascade (pathways) require:
magnesium and calcium
Classical pathway is activated by the:
Immune complexes (IgG/IgM)
Complement Binding order for Classical Pathways (C1, C2, etc)
C1, C4, C2, C4
Classical Pathway: “a” fragments go into _____ while “b” fragments attach to _____
plasma
cell
Alternative pathways are activated by:
lipopolysaccharides
polysaccharides
Alternative Pathway involves mainly this complement:
C3
Alternative pathway involves Factors ___ and ___, and Control Factors ___ and ____
B and D
H and I
Membrane Attack Complex (MAC) last Complement (goes in order):
C5b6789
In Hypersensitivity Type I, Eosinophils are in the late/early stage of the reaction and can lead to ___ ____
late
tissue damage
ELISA type for total IgE
Sandwich (EIA)
IgE specific antigens
Allergens
Most sensitive test in all stages of Syphilis?
FTA-ABS and ELISA
Clinical Sensitivity
Ability of test to give positive results if patient has the disease
Clinical Specificity
Ability of test to give negative results if patient does not have disease
How to determine diagnosis of Viral and Bacterial disease using titers
Must see 4-fold or 2 tube rise in titer to be clinically significant
These tests are MORE/LESS sensitive:
Immunoassays
Nephelometry
MORE
These tests are MORE/LESS sensitive:
Agglutination
Precipitation
Complement Fixation
Immunodiffusions
Electrophoresis
LESS
Lattice tests are MORE/LESS sensitive while Nonlattice tests are MORE/LESS sensitive
LESS
MORE
Best marker for inflammation
CRP
Analytical Specificity
Ability of test to detect substances without interference from cross-reacting substances
False negatives yield lower _____; False positives yield lower _____
sensitivity
specificity
VDRL
Heat inactivation required for this Non-Treponemal test
RPR
This Non-Treponemal test will have charcoal clumps form as its reaction
False positives for VDRL and RPR
malaria , SLE, RE, hepatitis, pneumonia, aging, and infectious mononucleosis
Antibody used in Non-Treponemal tests
Reagin
EBV Specific Serology Methods
Indirect Immunofluorescence, ELISA, or CLIA
Recent or Current EBV infection methods
IgM Anti-VCA, Anti-EA, IgG Anti-VCA without Anti-EBNA
Past EBV Infection Methods
Anti-EBNA, IgG Anti-VCA without IgM Anti-VCA
Most specific test for Strep Group A?
anti DNase B
HIV screening method
ELISA for HIV-1 antibody
HIV confirming test (CDC recommended)
Nucleic Acid testing
HIV confirming methods
Western blot
nucleic acid
Western Blot method: HIV positive if what bands are present?
p24, gp41, gp120, gp160
Disease Associated with Oligoclonal IgG Bands in Spinal Fluid
Multiple Sclerosis
The best method for screening cerebrospinal fluid for syphilis
VDRL
Processing: What should you NOT do to specimens testing for Cold Agglutinin Assay?
refrigerate them
This disease results in hyperthyroidism
Graves Disease
This disease results in hyporthyroidism
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
Chronic Granulomatous Disease dysfunction
Ineffective Phagocytosis
Chediak-Higashi Syndrome dysfunction
Impaired Neutrophil Function
DiGeorge’s Syndrome dysfunction
T cell Deficiency
HIV dysfunction
Decreased: T-Helpers, Th/Ts Ratio, T Cell Proliferation
Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome dysfunction
Partial Combined Immunodeficiency
Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Disease (SCID)
Complete or Marked Deficiency of T and B Lymphocytes
This is positive in all celiac patients
HLA-DG2 and HLA-DQ8
Best antibodies to test for in celiac patients
tTG-IgA and tTG-IgG
Antibodies in Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis and TSH are all INCREASED/DECREASED
increased
Antibodies in Graves disease are INCREASED/DECREASED while TSH is INCREASED/DECREASED
increased
decreased