L36 B cells and antibody
B cells
Lymphocytes that develop in the bone marrow and express unique antigen receptors (BCR or secreted antibody).
Plasma cells
Activated B cells that secrete antibody.
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards about B cells and antibodies
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
B cells
Lymphocytes that develop in the bone marrow and express unique antigen receptors (BCR or secreted antibody).
Plasma cells
Activated B cells that secrete antibody.
Memory B cells
Provide 'memory' for future immune responses. Live long and stimulated quickly during 2ndary response.
Maturing T cell vs B cell
Both originate in red bone marrow, T cells migrate (in blood) to thymus and mature there, B cells stay in bone marrow. Develop immunocompetence and self-tolerance.
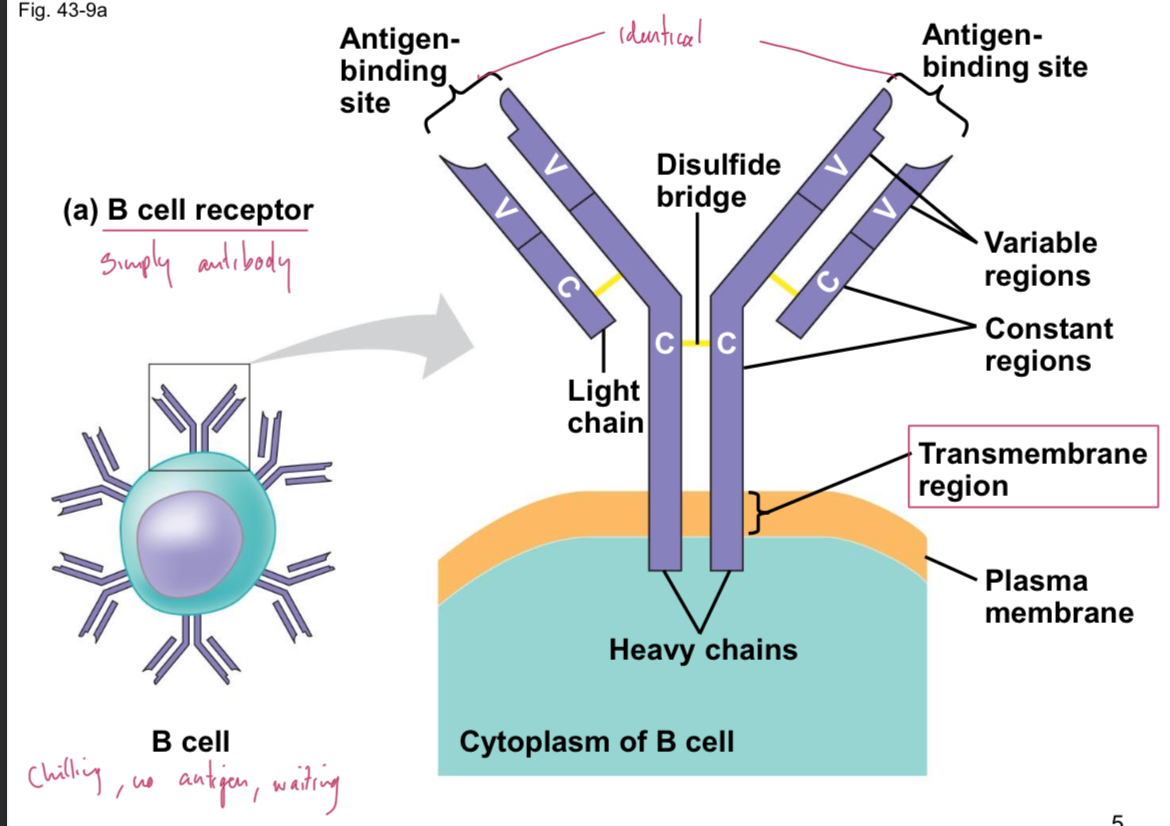
B cell receptor (BCR)
Surface receptor on B cells that binds to antigen and activates B cell; mainly IgM/IgD antibodies. Anchored via transmembrane domain (TM) which secreted antibodies lack.
Functions of antibody
Neutralisation, opsonisation, complement activation.
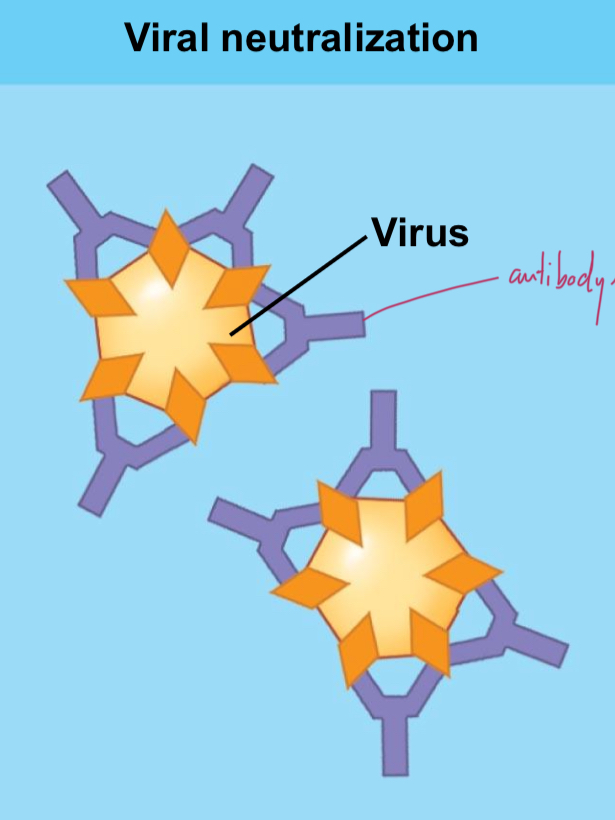
Neutralization
Antibodies bind to virus so it cannot bind to host cell.
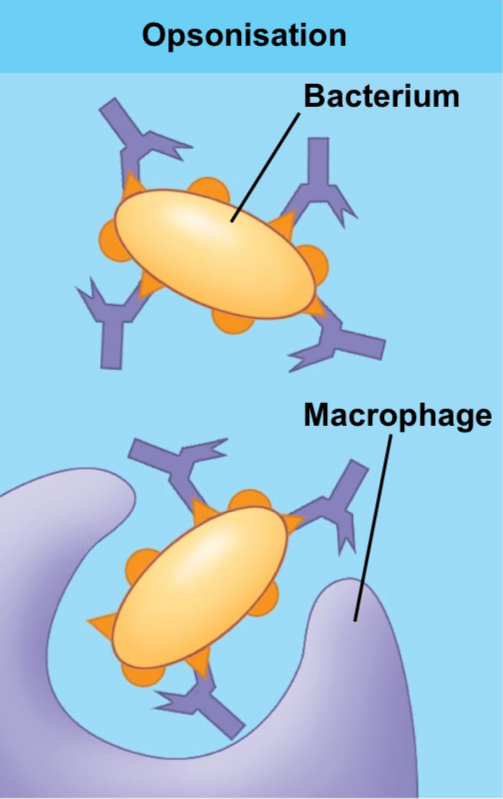
Opsonization
Tags pathogens to make them tasty to phagocytes ('Eat me!').
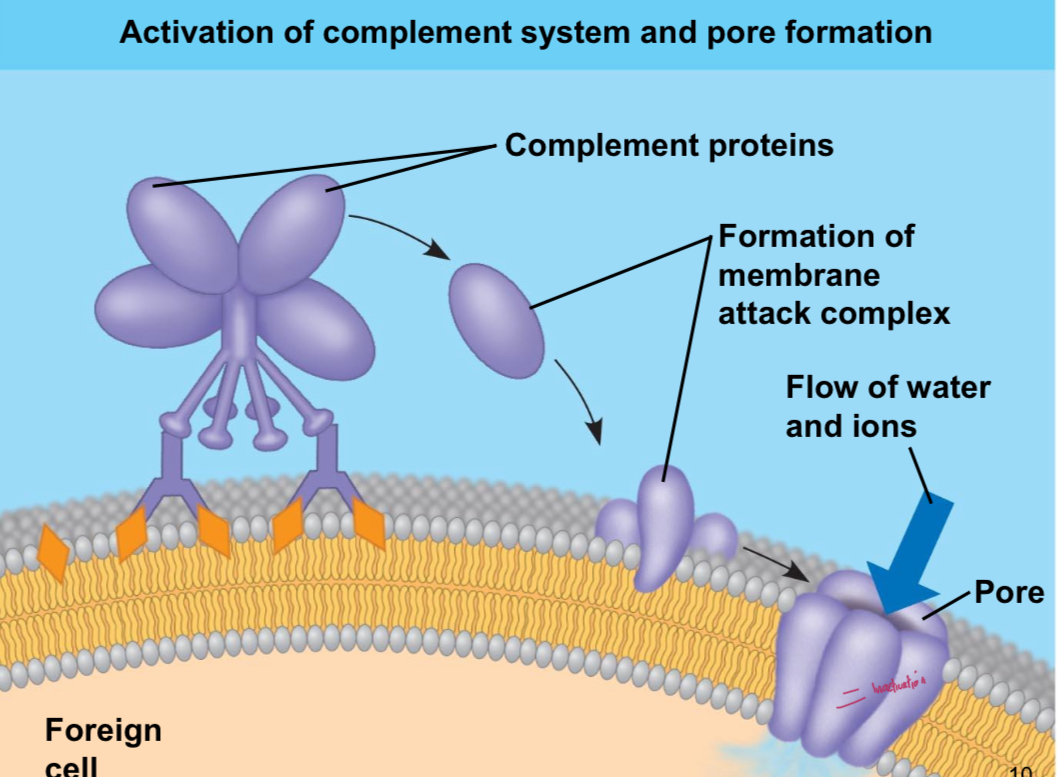
Complement activation
Particularly effective with IgM and via the classical pathway. Complement binds to antibodies and then form MAC.
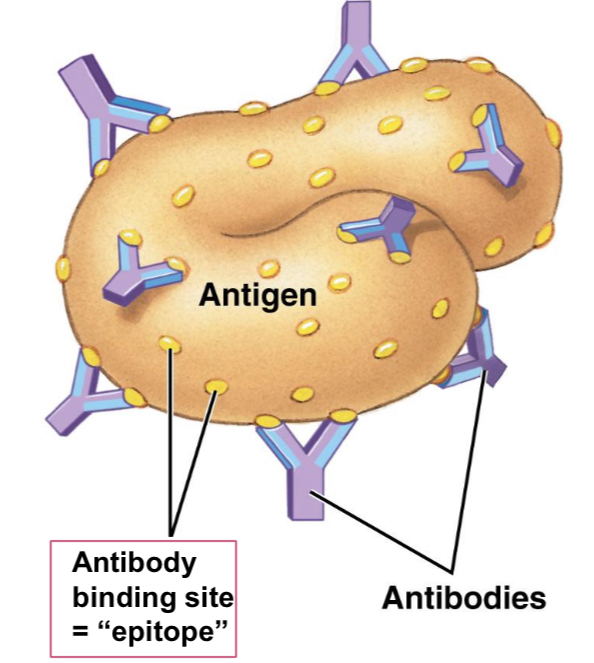
Native antigen
An antigen that does not need to be processed into a peptide to be recognized by antibodies (or in context of MHC)
Epitope
The antibody-binding site on an antigen.
Different classes of immunoglobulin (antibody)
IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE, IgD.
IgG (monomer) all rounder
Most abundant Ig class in blood; opsonizes/neutralizes, only ig class that crosses placenta for passive immunity, and targets viruses/bacteria.

IgA (dimer)
Present in secretions (tears, saliva, mucus, breast milk). Monomeric form in blood. Defends mucous membranes esp gut. Providing passive immunity to nursing infants, targets viruses/bacteria.
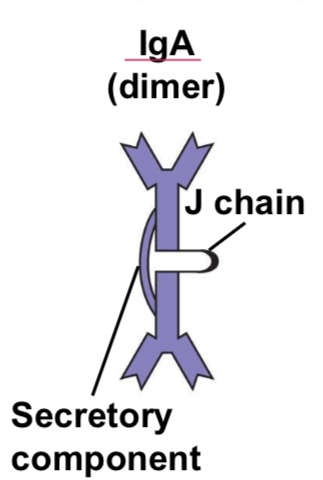
Passive immunity
Not active, doesn’t have to encounter organism. Transferred to infant through breast milk (IgA) and they recieve protection for a couple of days.
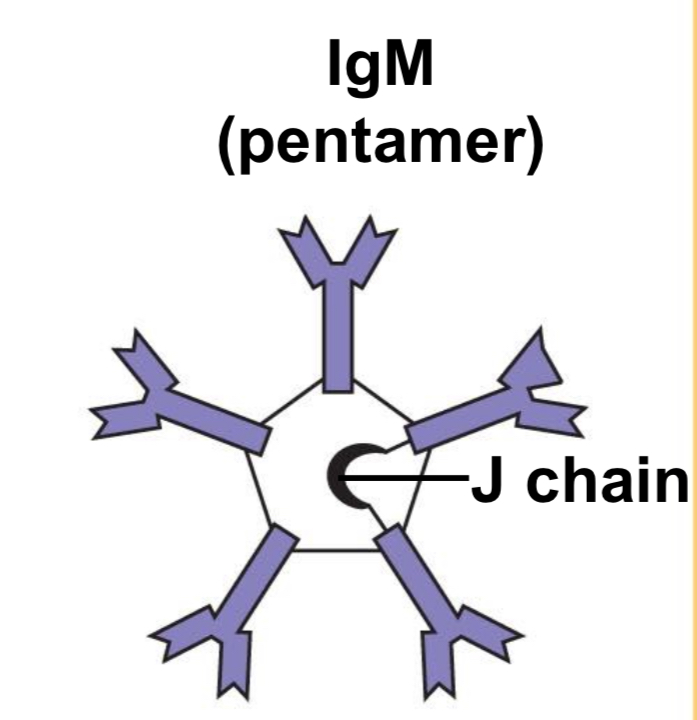
IgM (pentamer)
First Ig class produced after initial antigen exposure, expressed on naive B cells. Very effective in activating complement, targets extracellular bacteria, and acts as antigen receptor (BCR).
IgE (monomer)
Activates mast cells to provide powerful immunity to multicellular parasites and allergic reactions. Present in blood at low concentrations.
IgD (monomer)
Expressed on naïve B cells. Together with IgM acts as an antigen receptor (BCR), specific function unknown.
Memory responses
Stimulation of B cells by antigen + T cell help, leads to formation of plasma cells. A small number of stimulated by cells form a pool of memory cells.
Memory cells (basis for vaccination)
Persist in blood and lymphatic tissue for years. Express antibody as BCR but don’t secrete antibody. Respond rapidly to antigen encounter and become plasma cells.
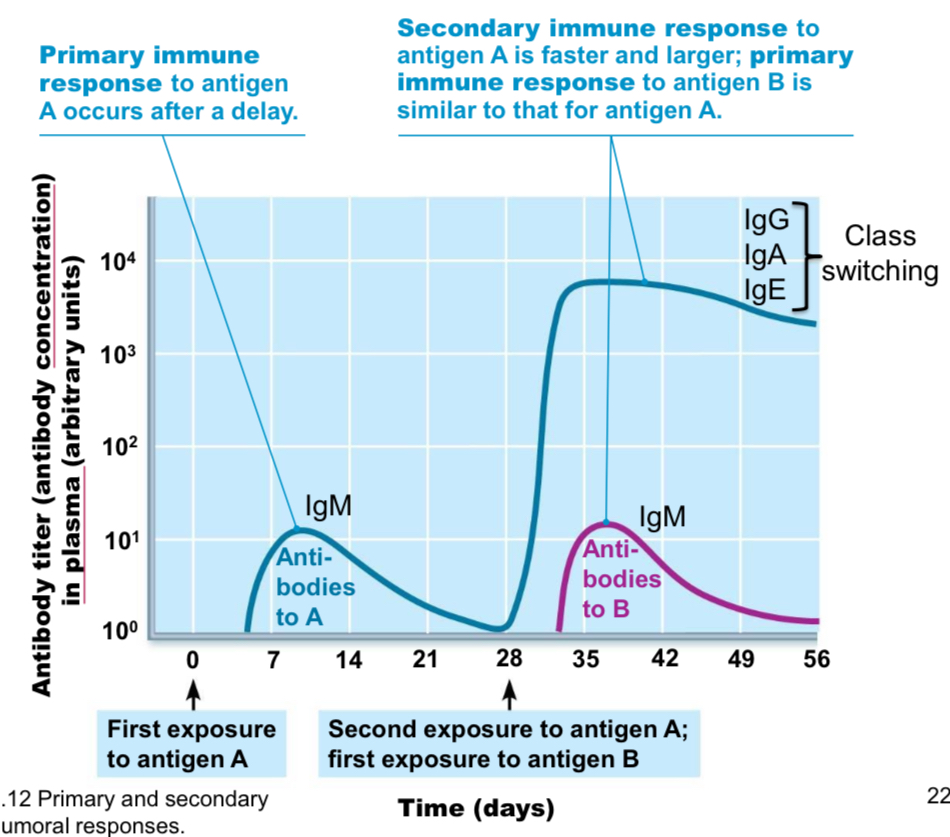
Primary immune response
Takes 7-14 days to produce sufficient antibody to eliminate pathogen, relatively low amount of antibody produced, mainly IgM.
Secondary immune response (basis of success of vaccination)
Fast response (2-3 days), relies on memory B cells. Produces sufficient antibody to eliminate pathogen, mainly IgG with class switching to IgA and IgE (low levels)
Primary vs secondary immune response summary