Cognitive Development & Aging: Piaget, Vygotsky, and Lifespan Perspectives in Psychology
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
What is cognition?
Mental activities related to thinking.
What is the constructivist perspective on cognition?
Children are active learners who construct knowledge through experiences.
What are the two main perspectives on cognitive development according to Piaget and Vygotsky?
Cognitive Constructivist (Piaget) and Sociocultural Constructivist (Vygotsky).
What is equilibration in cognitive development?
The mental balance between cognitive schemes and information from the environment.
What is disequilibrium in cognitive development?
When a cognitive scheme does not produce satisfying results.
What are the two processes of adaptation in cognitive development?
Assimilation (using existing schemes) and Accommodation (altering existing schemes).
What is the age range for the preoperational stage of cognitive development?
2 to 7 years.
What is symbolic functioning in the preoperational stage?
Using words and images to represent the world.
What is egocentrism in cognitive development?
The inability to see the world from perspectives other than one's own.
What are the characteristics of the concrete operations stage?
Logic about concrete events, understanding conservation, and overcoming egocentrism.
What is the age range for the formal operations stage?
11 to 15 years or into adulthood.
What is adolescent egocentrism?
The belief that one is unique and that everyone is watching them.
What is hypothetico-deductive reasoning?
Combining ideas to form concepts, constructs, and theories.
What is Vygotsky's Sociocultural Theory?
Human activities take place in social settings and cannot be understood apart from these settings.
What role does private speech play in cognitive development?
It serves as a form of self-regulation and guides development.
What is the Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD)?
The difference between what a learner can do without help and what they can do with guidance.
What are some limitations of Vygotsky's perspective?
It may overemphasize social interaction and is not specific about age-related changes.
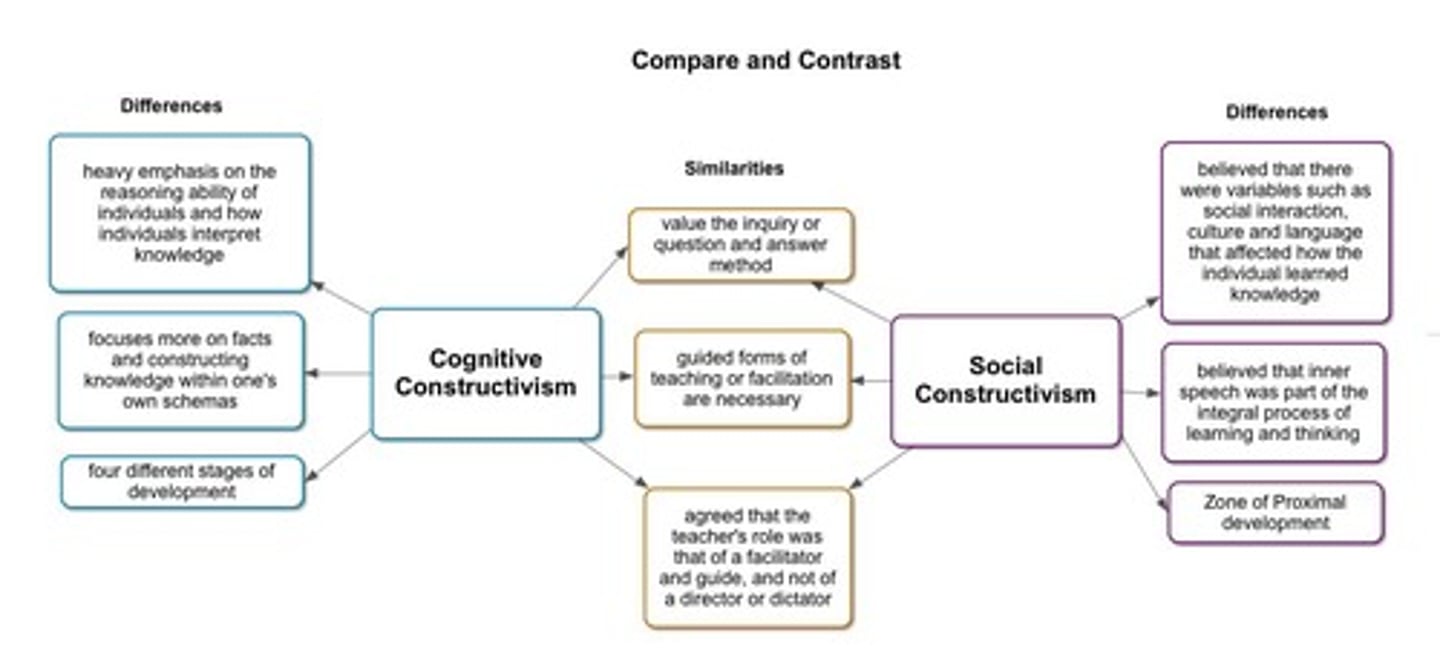
What are the key differences between Piaget and Vygotsky?
Piaget focuses on individual cognitive development; Vygotsky emphasizes social interactions.
What cognitive changes occur in older adulthood?
Slight decrease in processing speed and memory decline that does not interfere with daily functioning.
What factors promote successful cognitive aging?
Education, social engagement, mental activity, minimizing stress, optimizing sleep, moderation in food and alcohol, and physical exercise.
What is stereotype threat in the context of memory tests for older adults?
The phenomenon where older adults perform worse on memory tests due to negative stereotypes.
What is the significance of schemas in cognitive development?
Schemas are mental representations or concepts that help organize knowledge.
What is the role of language in Vygotsky's theory?
Language is central to the transmission of information and co-constructed knowledge.
What is the main implication of Piaget's theory for education?
Children need support to explore their world and discover knowledge.
What is the focus of cognitive development from infancy through late adulthood?
The evolution of thinking, memory, and problem-solving and its importance in patient care.
How is cognition related to other domains of development?
Cognition is intertwined with biological and socioemotional domains, influenced by bodies, relationships, stress, culture, and context.
What does biology provide in the context of cognitive development?
Biology provides the hardware, including prenatal development, physical growth, and aging.
What does cognition represent in the development framework?
Cognition represents the software, encompassing knowledge, problem-solving, language, and memory.
What is the Biblical worldview regarding cognition?
Humans are seen as embodied and meaning-seeking, emphasizing the dignity of cognition in every patient.
What are the three objectives of the cognitive development session?
1) Name and use Piaget's stages; 2) Apply Vygotsky's sociocultural theory; 3) Distinguish typical cognitive aging from neurocognitive disorder.
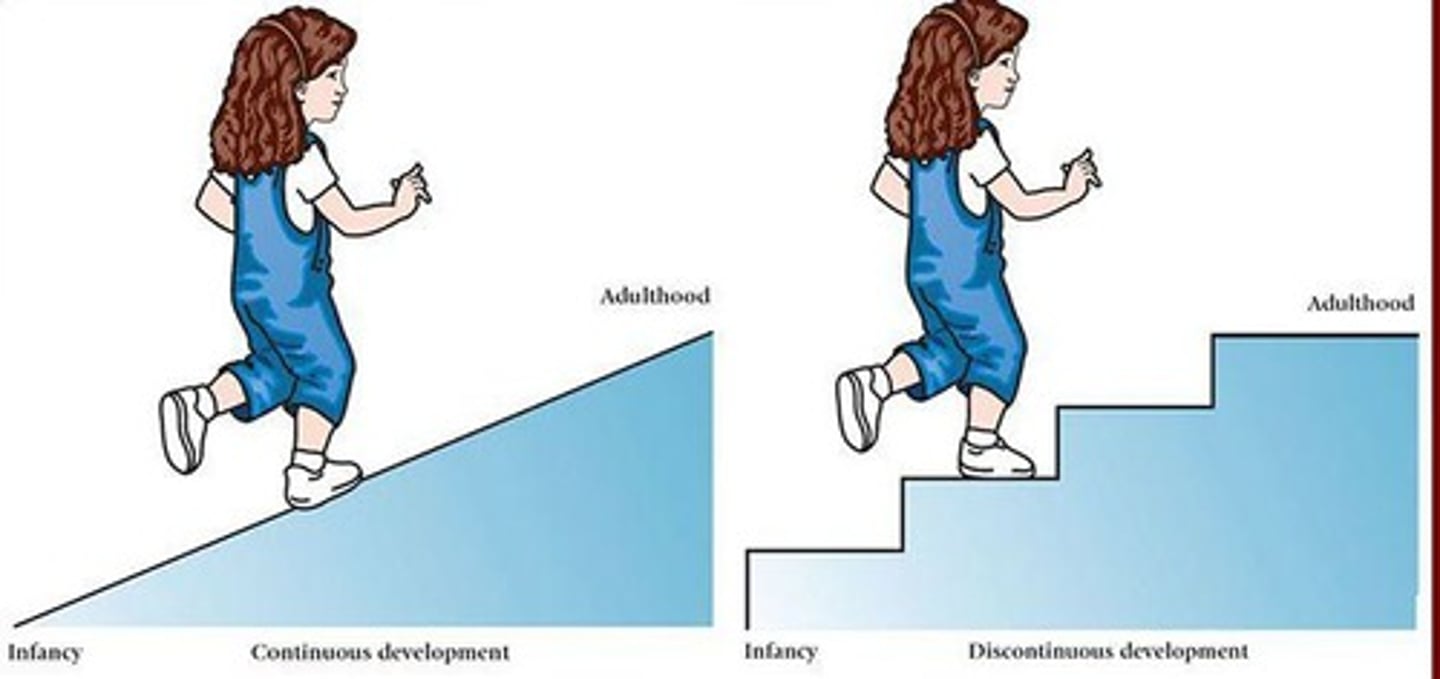
What are the two perspectives on cognitive development's nature?
Piaget argued for qualitative stage shifts (staircase), while Vygotsky emphasized continuous growth through guided participation.
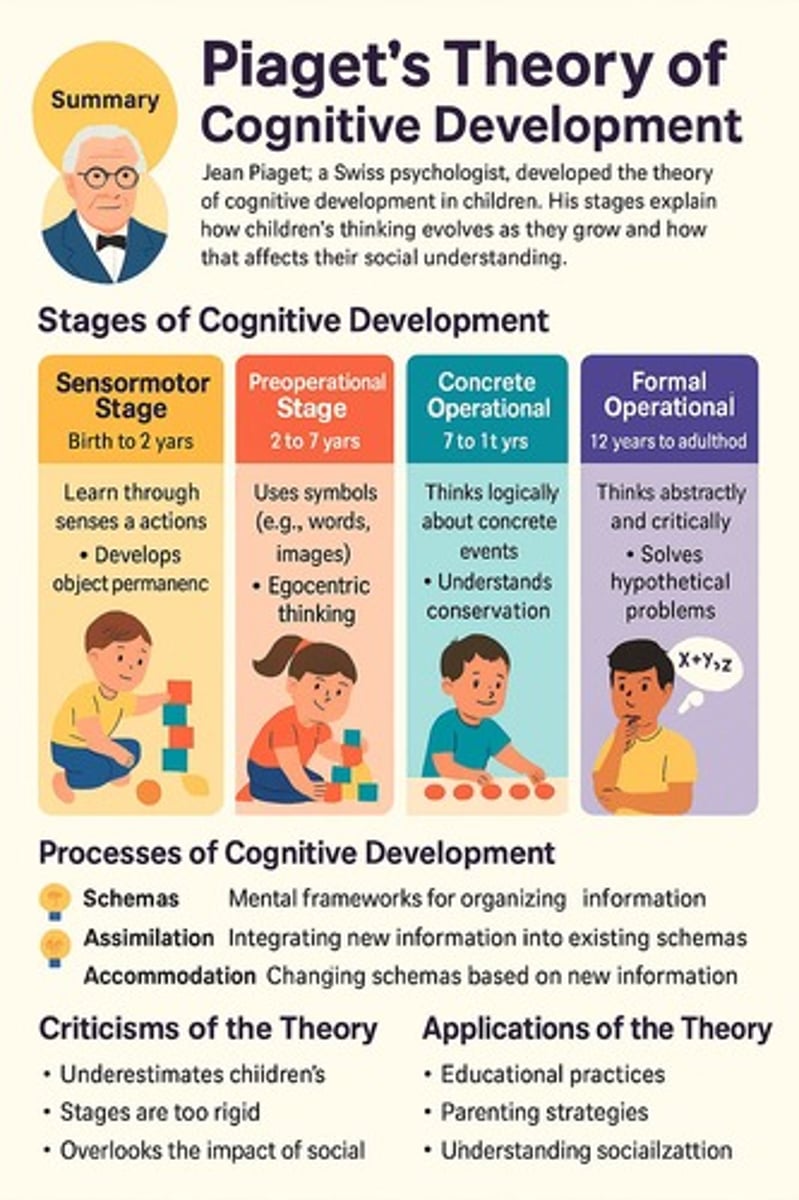
What are the four stages of Piaget's cognitive development theory?
1) Sensorimotor (birth-2), 2) Preoperational (2-7), 3) Concrete Operational (7-11), 4) Formal Operational (11+).
What characterizes the sensorimotor stage of development?
Infants think through perception and action, developing object permanence and intentional actions.
What is object permanence?
The understanding that objects continue to exist even when they cannot be seen, emerging late in the first year.
What is the A-not-B error?
A phenomenon where infants search for an object where they found it previously (A) rather than where they last saw it hidden (B).
What cognitive abilities are developed during the preoperational stage?
Symbolic thought, egocentrism, animism, and a lack of conservation.
What is conservation in cognitive development?
The understanding that quantity does not change even when its shape does, developed during the concrete operational stage.
What reasoning abilities emerge in the concrete operational stage?
Logical reasoning about concrete events, understanding conservation, classification, and seriation.
What characterizes the formal operational stage?
The ability to think abstractly, hypothetically, and systematically solve problems.
What are some critiques of Piaget's theory?
Development is not always strictly stage-like, and social/cultural influences were underplayed.
How can healthcare professionals apply Piaget's theory in practice?
By anticipating patients' reasoning limits at different ages and tailoring teaching methods accordingly.
What is the significance of multisensory cues in infant assessments?
They support engagement and help infants learn through their senses during assessments.
How can healthcare providers address a child's egocentrism during education?
By using perspective-taking strategies and hypothetical reasoning to help them understand health decisions.
What is the role of clinical ties in cognitive development?
To connect developmental principles with practical applications in patient care and education.
What is the importance of teaching for understanding in healthcare?
It emphasizes comprehension over mere compliance, fostering better patient outcomes.
What is the significance of gradual improvement versus sudden leaps in skill acquisition?
Recognizing these patterns helps educators and healthcare providers tailor their teaching strategies.
What is the goal of using medical play with children?
To prepare them for procedures and reduce anxiety through familiarization with medical concepts.
How does the understanding of cognitive development impact interprofessional teamwork?
It enhances collaboration by recognizing the cognitive needs and abilities of patients across the lifespan.
What is Vygotsky's Sociocultural Theory focused on?
Learning with others and continuous growth through culturally organized activities.
What is the purpose of scaffolding in education?
To provide temporary support that is gradually faded as learners gain independence.
What are the three core principles of Vygotsky's theory?
Co-construction with knowledgeable others, culture shapes cognition, and continuous change.
How does private speech contribute to learning according to Vygotsky?
It enhances memory and control when learners verbalize their understanding.
What is the significance of teach-back in patient education?
It allows patients to repeat information in their own words, reinforcing understanding.
What are typical cognitive changes associated with aging?
Slower processing speed and some working memory strain, but stable or improving knowledge and vocabulary.
What distinguishes typical aging from neurocognitive disorders?
Typical aging involves slight memory changes that do not disrupt daily life, while neurocognitive disorders affect daily functioning.
What is a common screening tool for cognitive health?
The clock-drawing test and orientation questions.
What is stereotype threat in the context of cognitive testing for older adults?
Labeling tasks as 'memory tests' can lower performance due to anxiety about age-related stereotypes.
What are some strategies to promote successful cognitive aging?
Education, social engagement, mental activity, stress reduction, sleep optimization, and physical exercise.
What is the role of culture in cognitive development according to Vygotsky?
Culture influences cognitive development by shaping the tools and practices used for learning.
What is the importance of fading support in scaffolding?
It helps learners become more independent by gradually reducing assistance as they gain confidence.
What should a clinician do when assessing cognitive health in older adults?
Differentiate between everyday lapses and functional impairment to guide screening or evaluation.
What is the impact of cognitive pragmatics in older adults?
Older adults often retain stable or improving knowledge and expertise despite some cognitive decline.
What is the significance of co-construction in learning?
It emphasizes collaboration between learners and knowledgeable others to enhance understanding.
How can healthcare providers effectively communicate cognitive health checks?
By framing them as routine checks to reduce anxiety and promote engagement.
What is a practical application of Vygotsky's theory in patient education?
Teaching inside the ZPD by introducing one new step beyond what the patient can do alone.
What is the importance of setting behavioral targets in counseling older adults?
It helps in achieving small wins that contribute to overall brain wellness.
What is the effect of normal aging on memory?
Normal aging leads to subtle memory changes that do not interfere with daily life.
What is the role of language as a cognitive tool in learning?
Language facilitates understanding and memory retention through verbalization.
What should be considered when using prompts in teaching?
Prompts should be designed to guide learners without doing the task for them.
What is the significance of continuous change in Vygotsky's theory?
It highlights that learning and development are ongoing processes throughout life.
What is a key takeaway from Vygotsky's strengths and weaknesses?
It emphasizes social learning and culture but lacks specificity about age-related changes.
What is the impact of collaborative checkups on older adults?
They can reduce anxiety and improve performance by framing tasks positively.
What is the importance of teach-back in clinical settings?
It serves as a method for memory rehearsal and ensures patient understanding.