VMT 216 Quiz #1 (LECTURE)
1/231
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chap. 1-4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
232 Terms
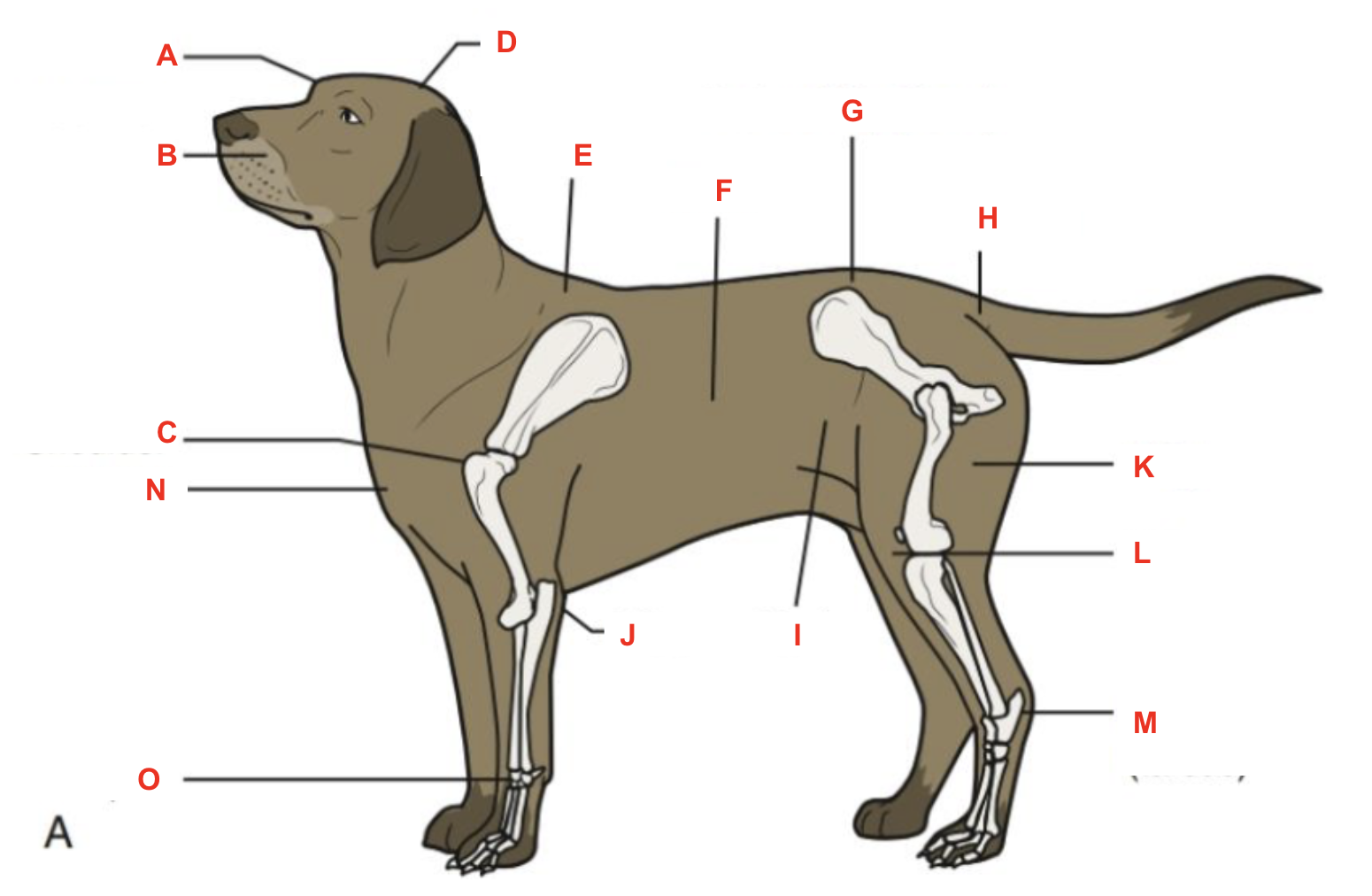
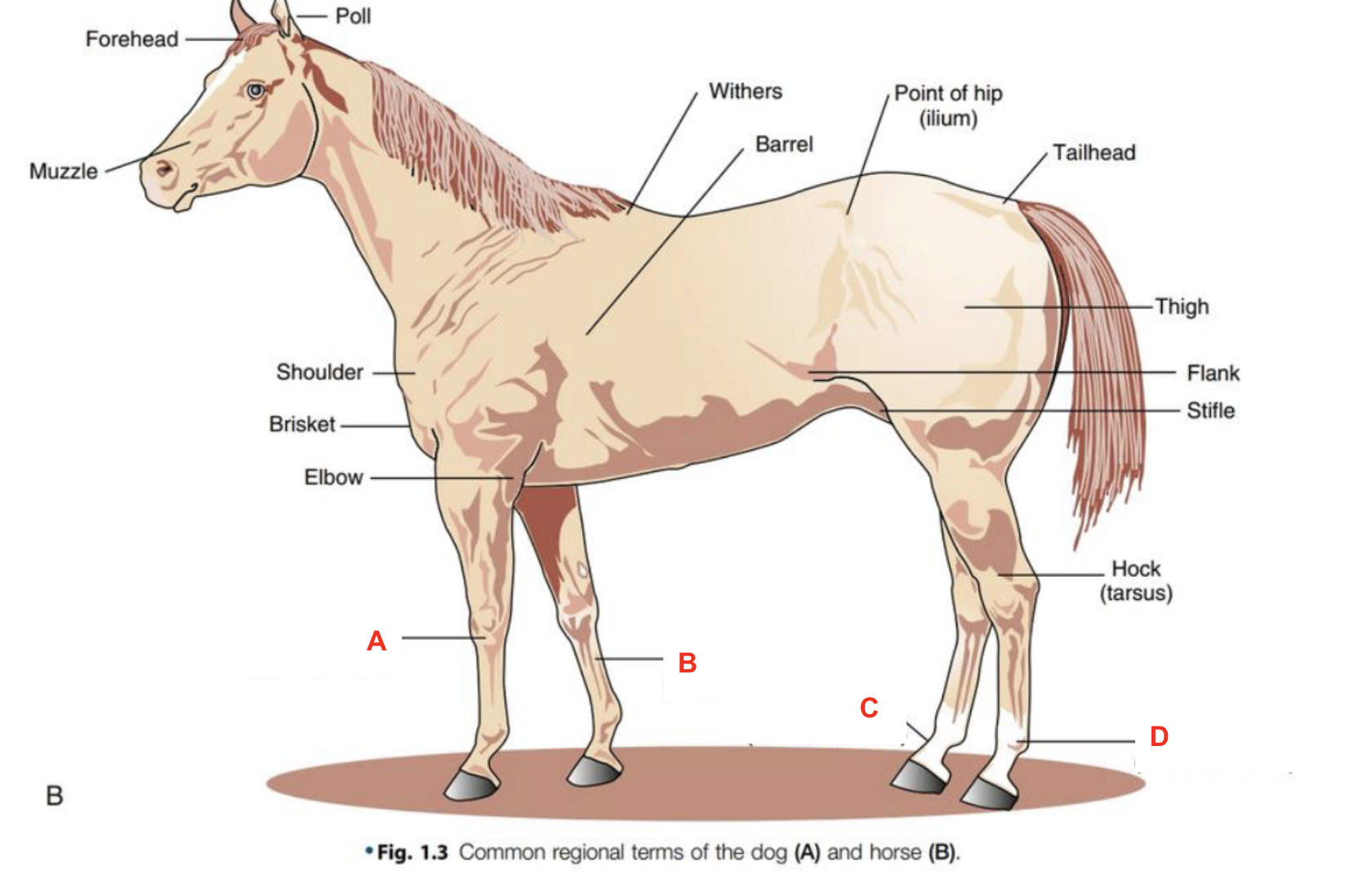
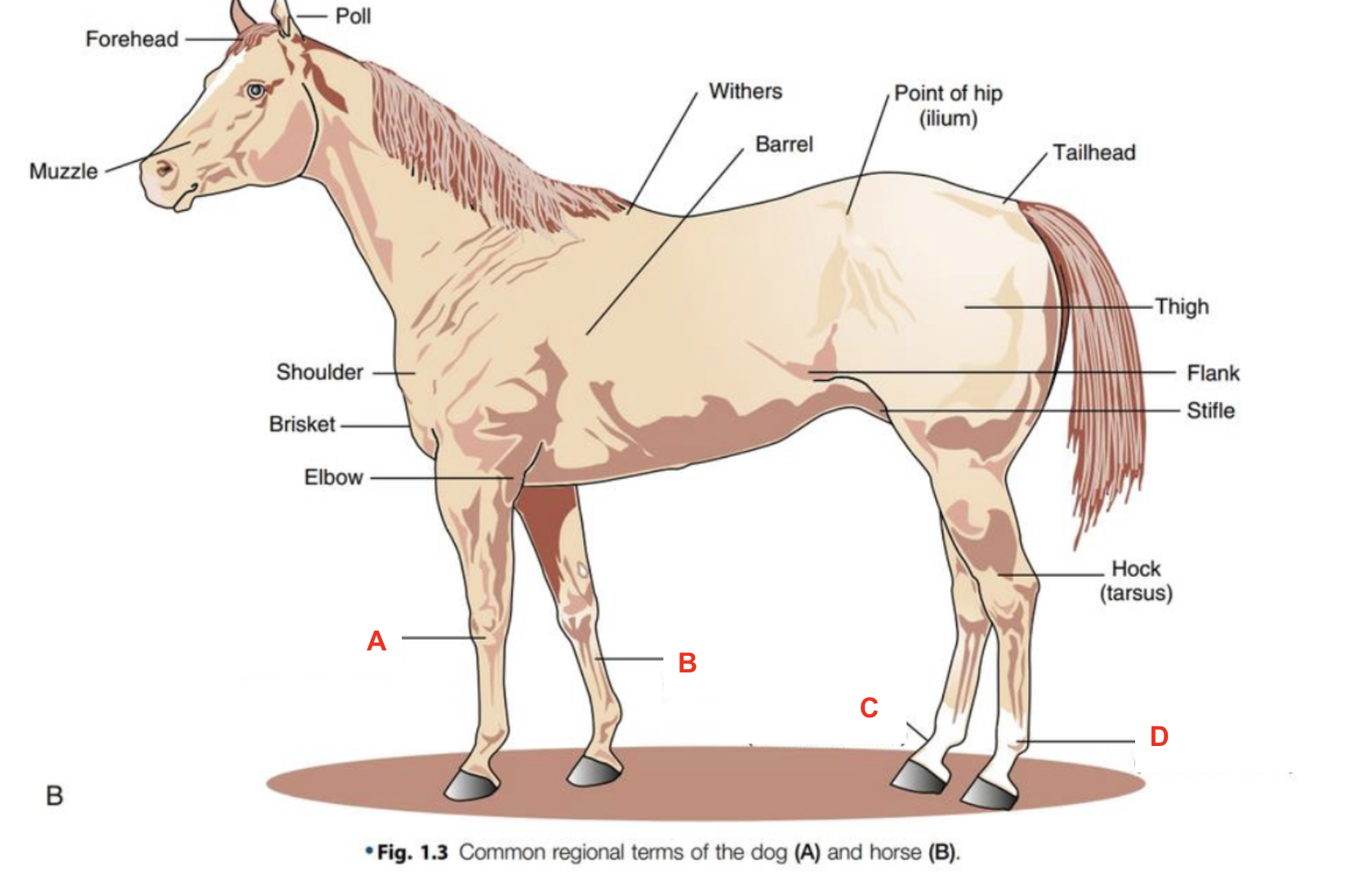
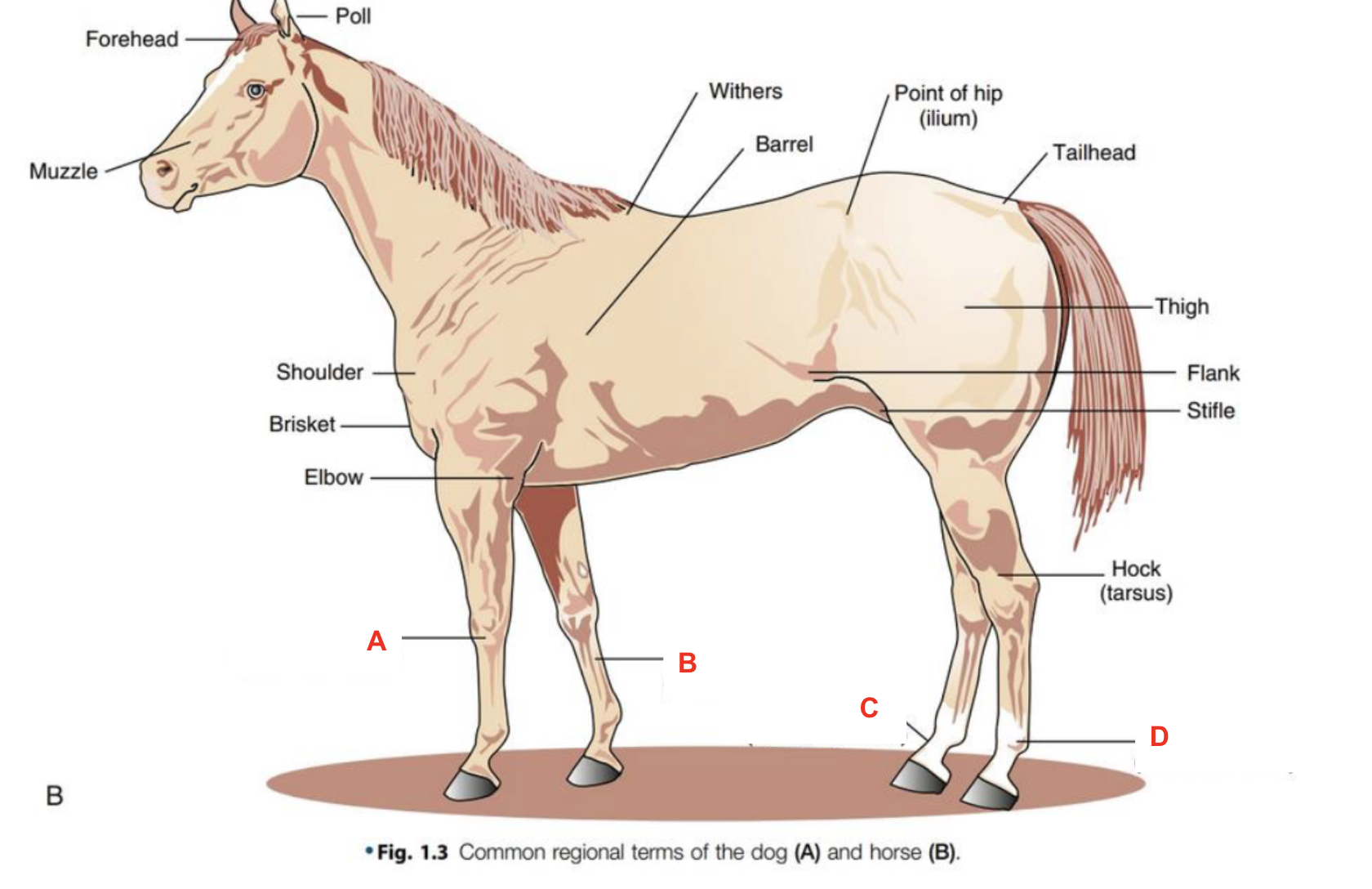
Identify what part of the body is labelled “A”
forehead
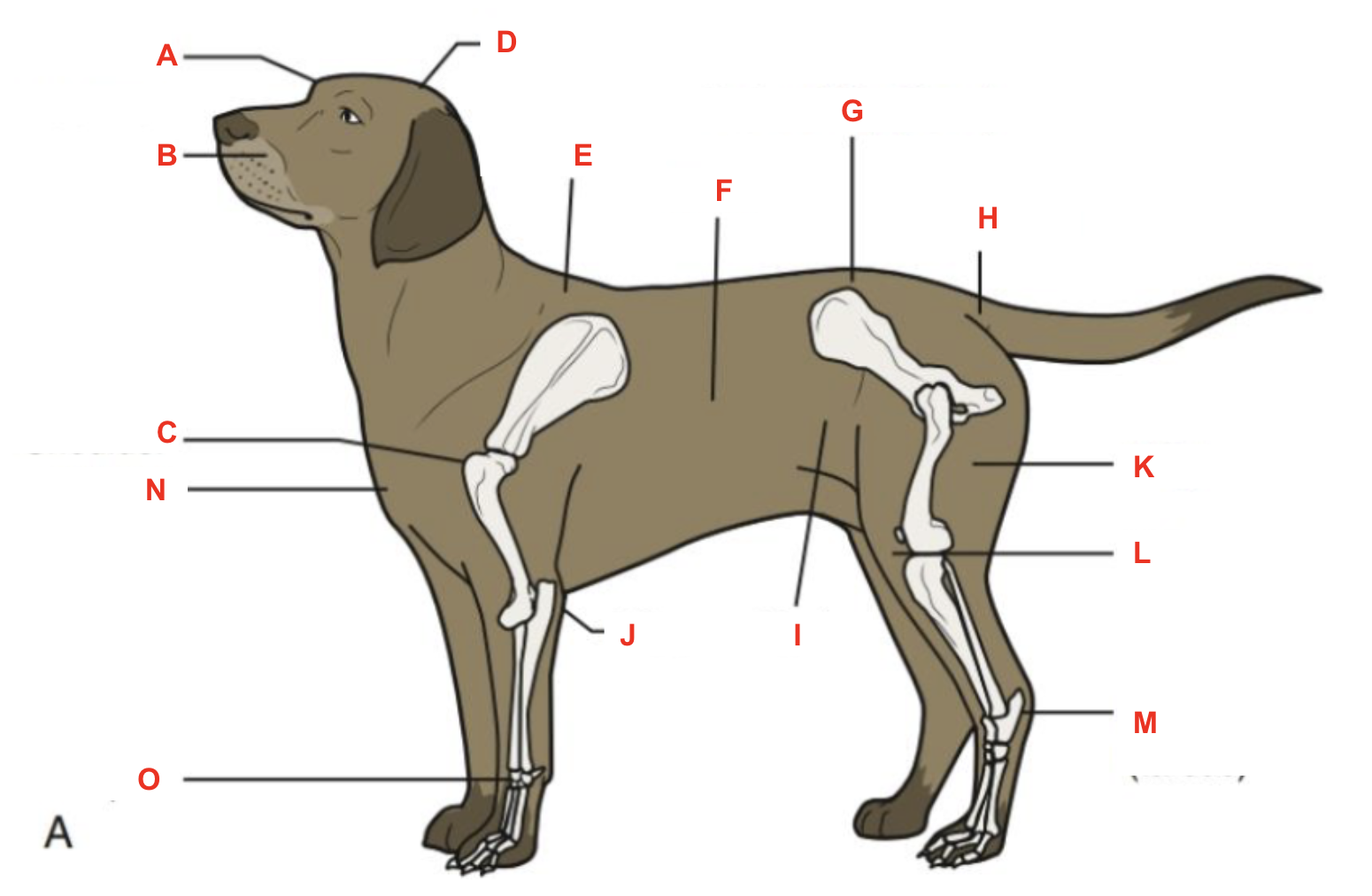
Identify what part of the body is labelled “B”
muzzle
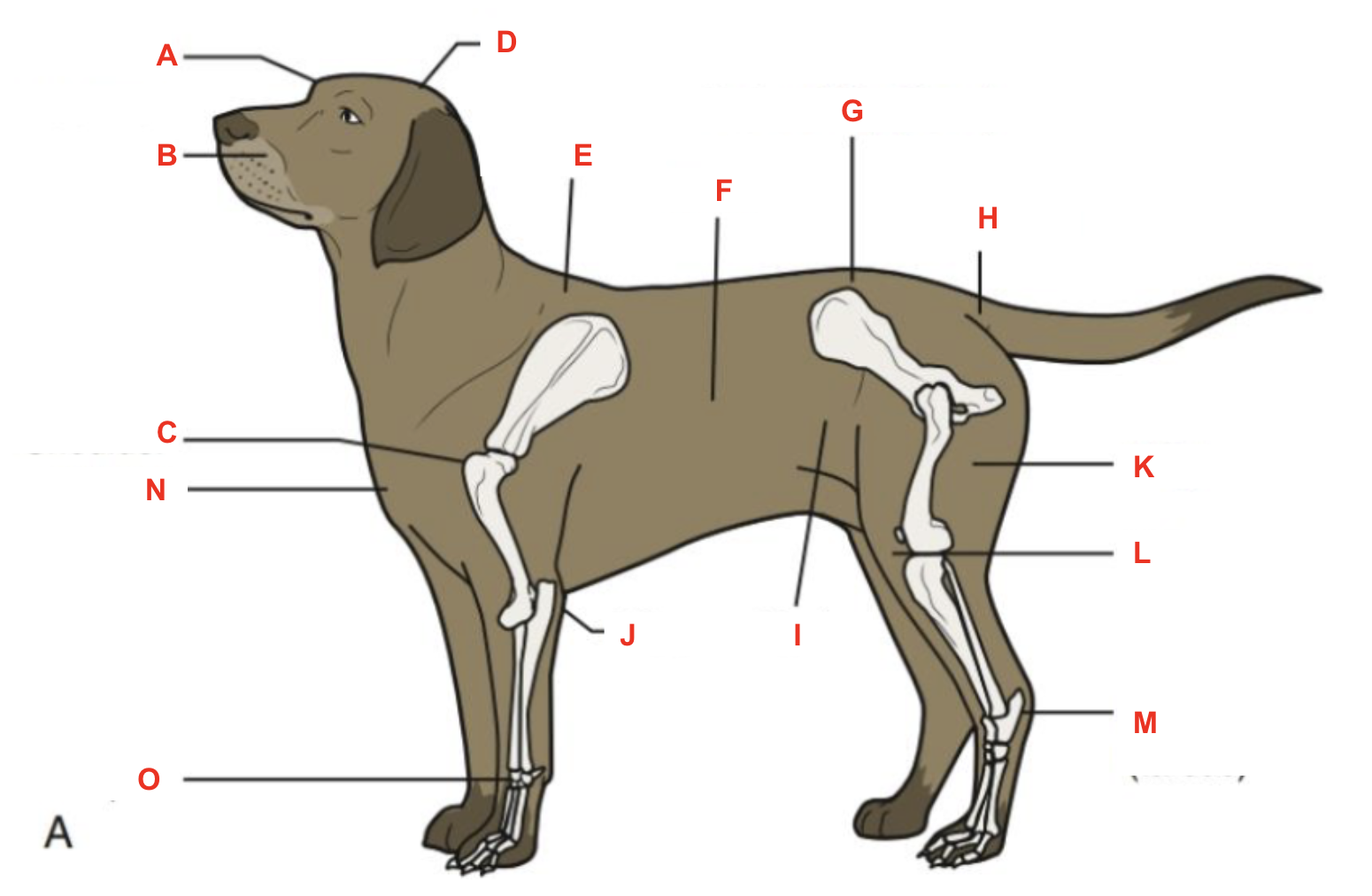
Identify what part of the body is labelled “C”
shoulder
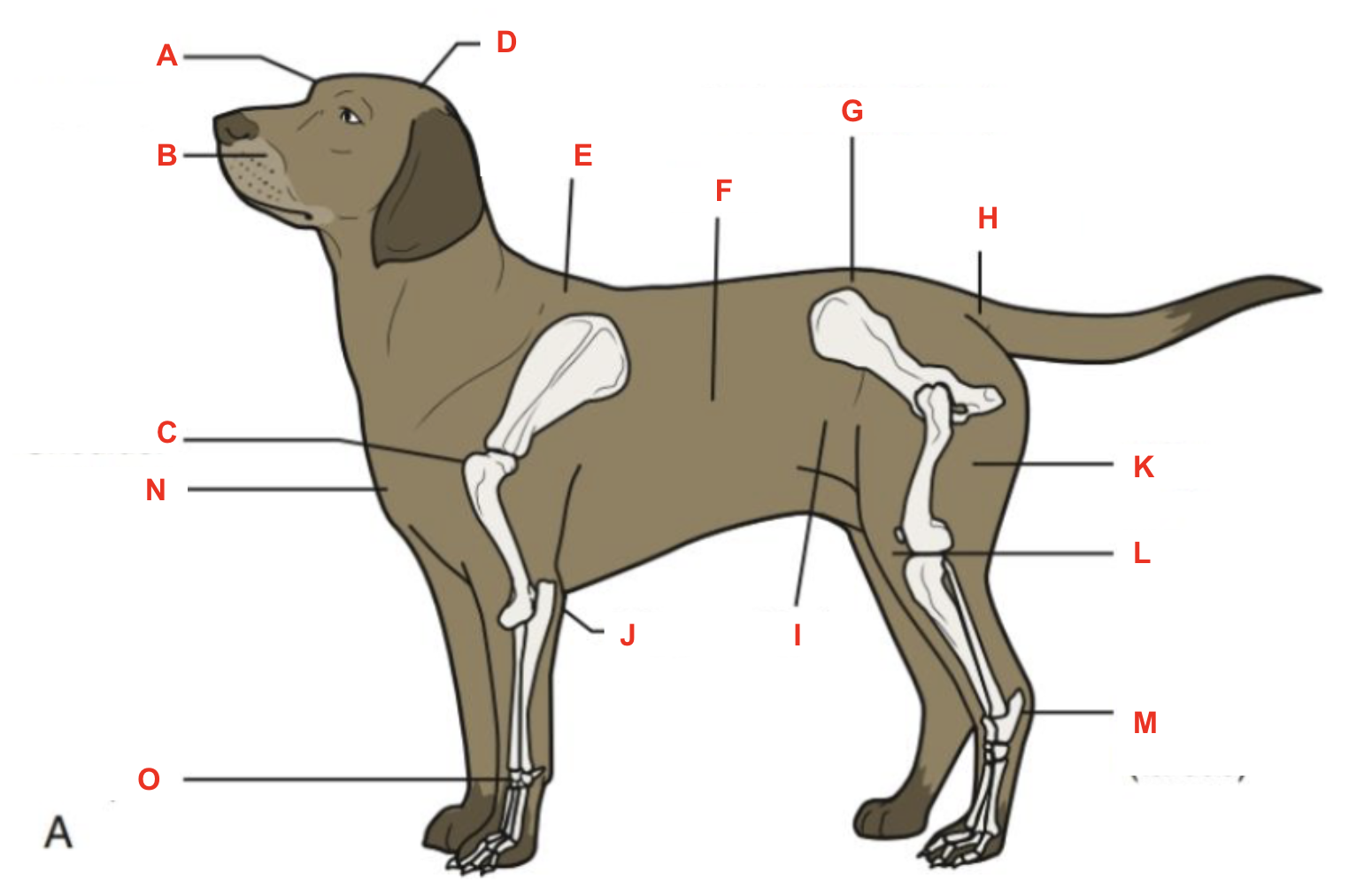
Identify what part of the body is labelled “D”
poll
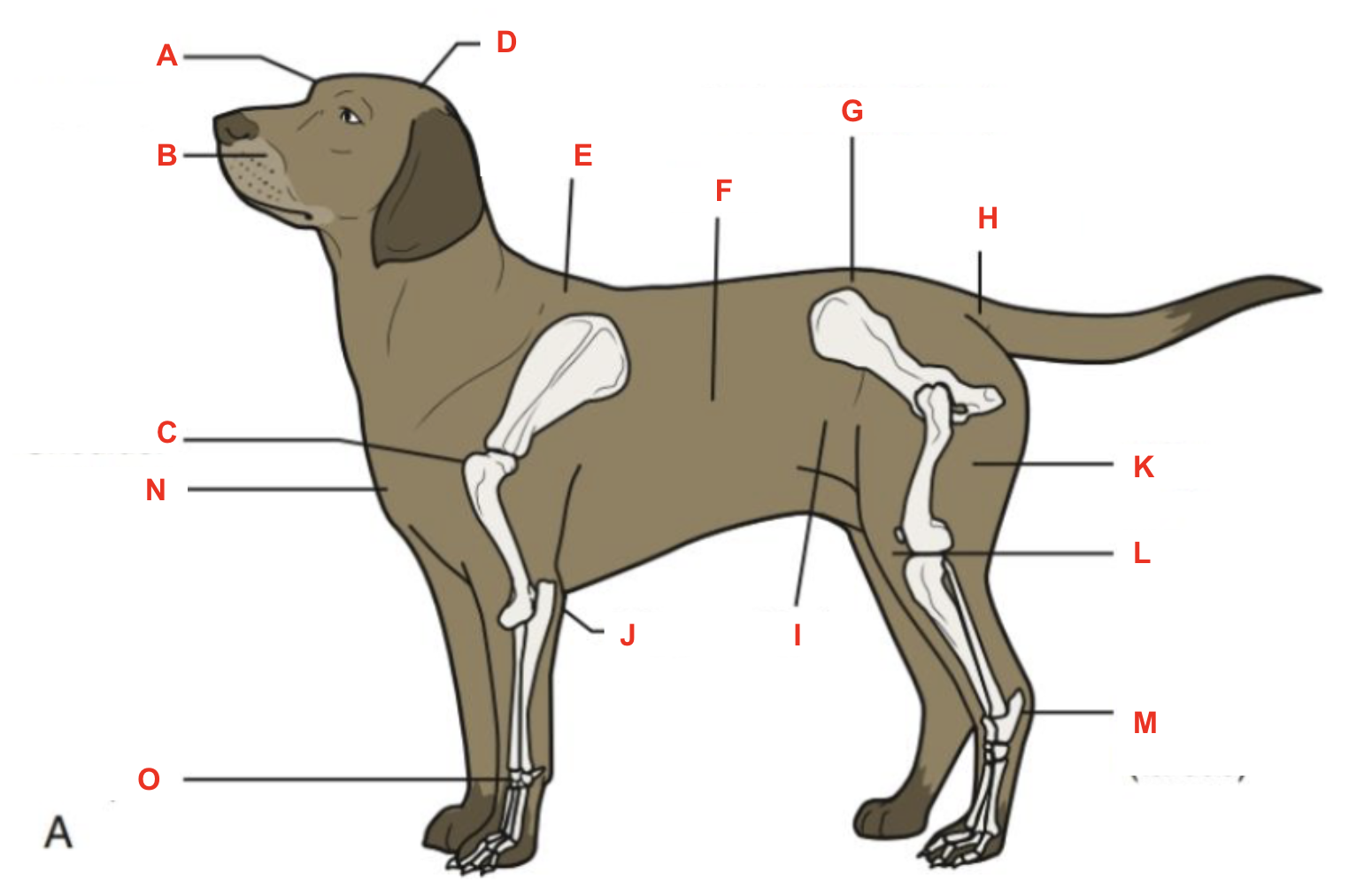
Identify what part of the body is labelled “E”
withers
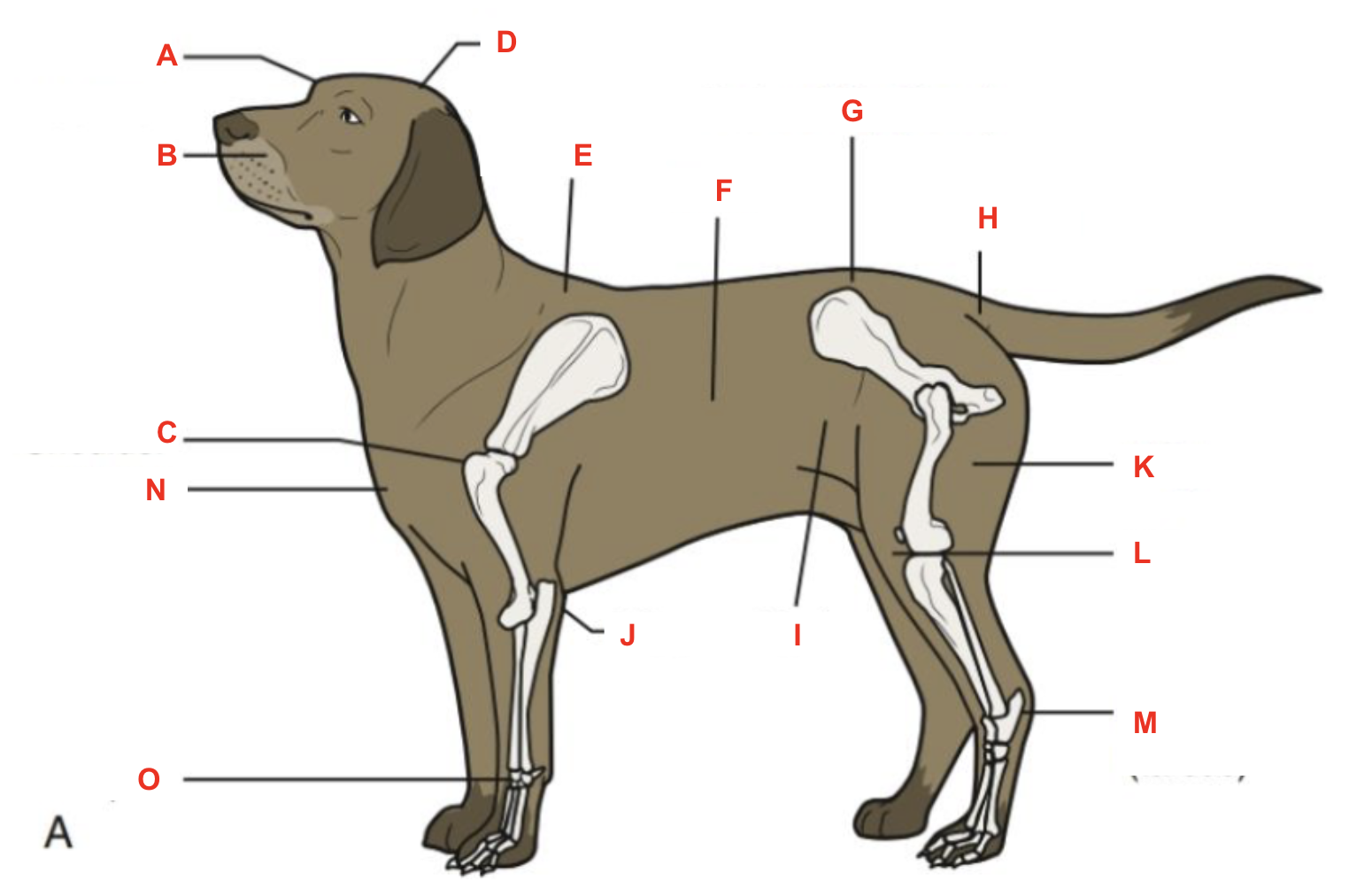
Identify what part of the body is labelled “F”
barrel
Identify what part of the body is labelled “G”
point of hip
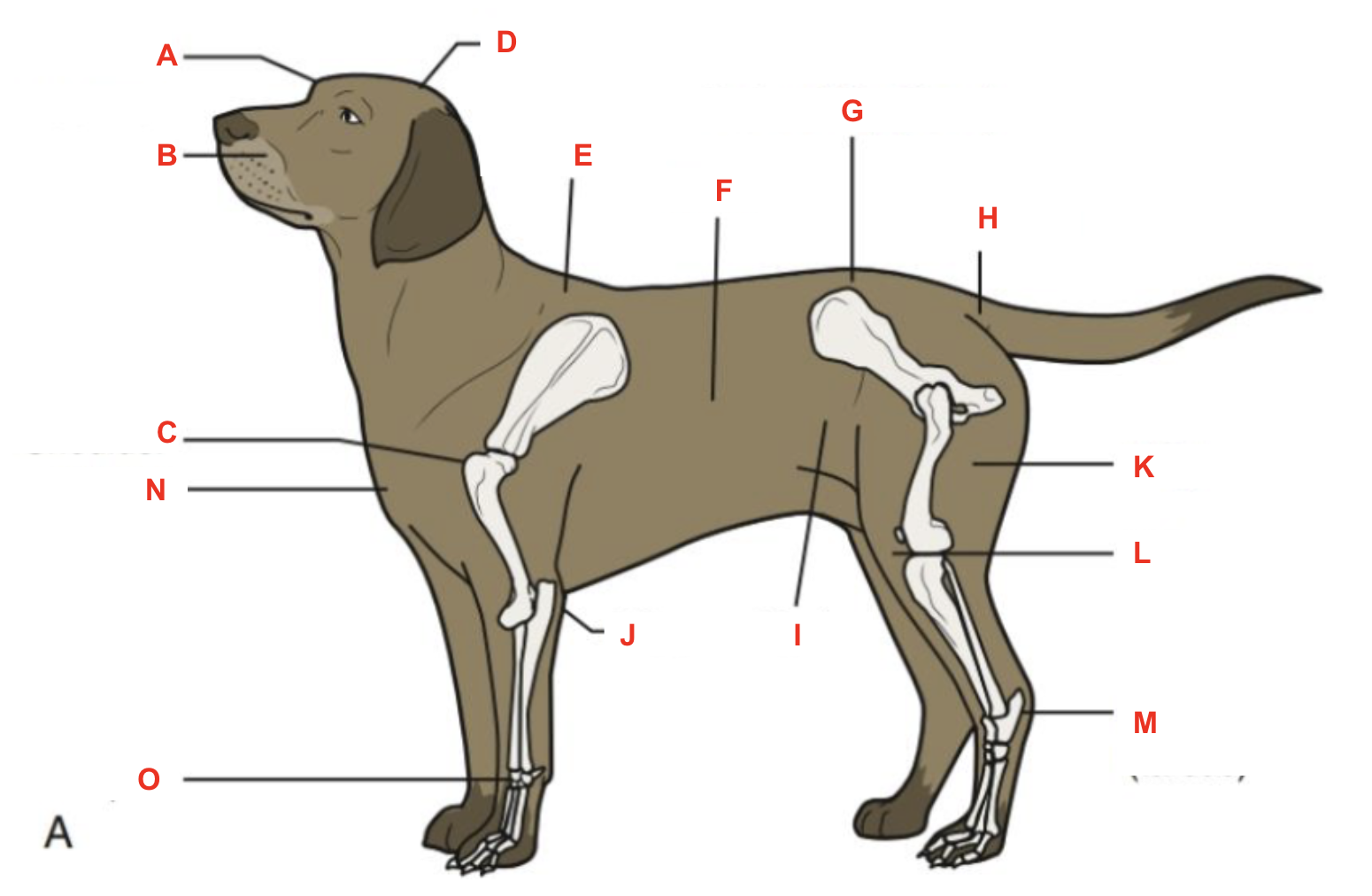
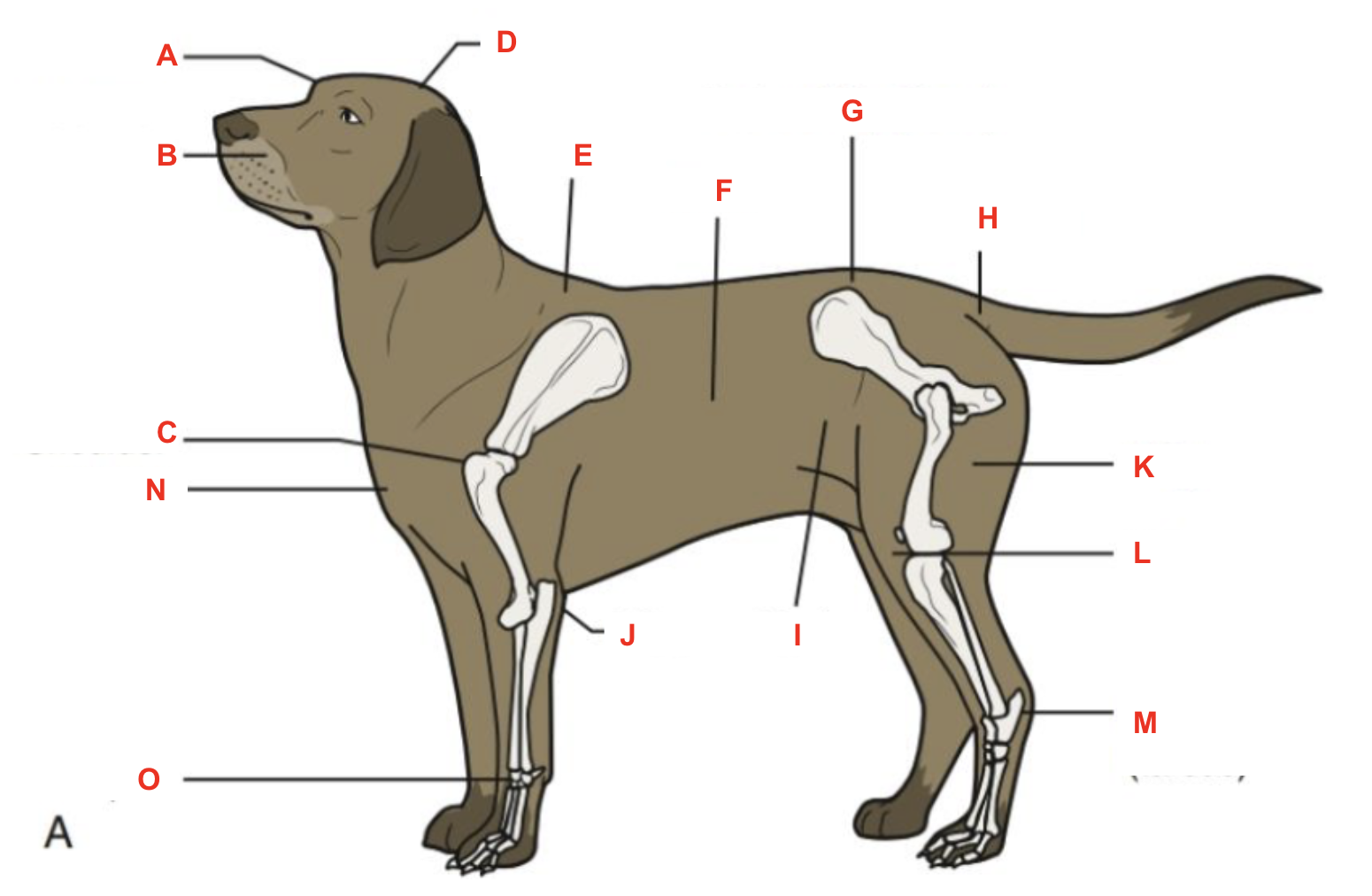
Identify what part of the body is labelled “H”
tailhead
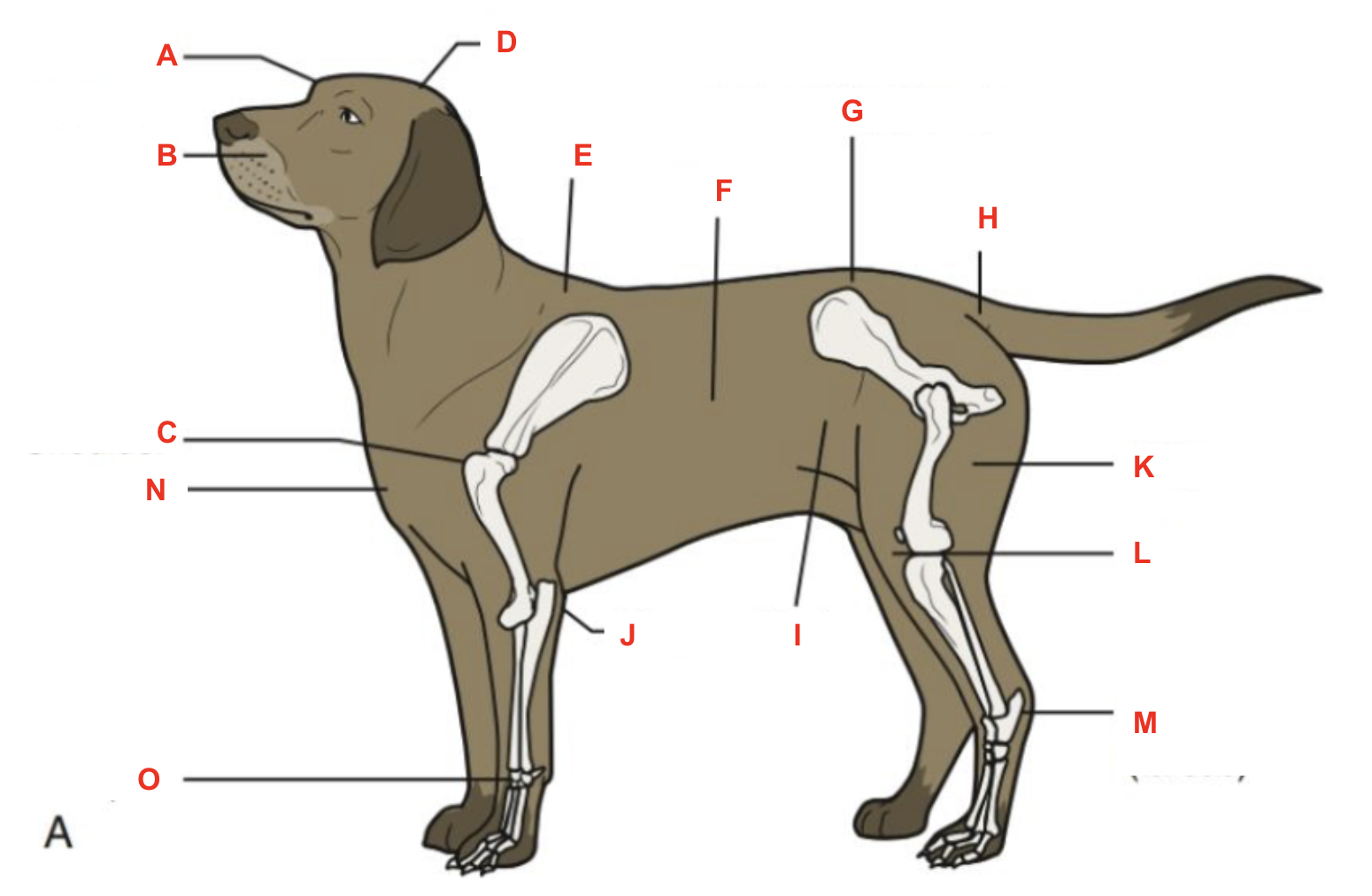
Identify what part of the body is labelled “I”
flank
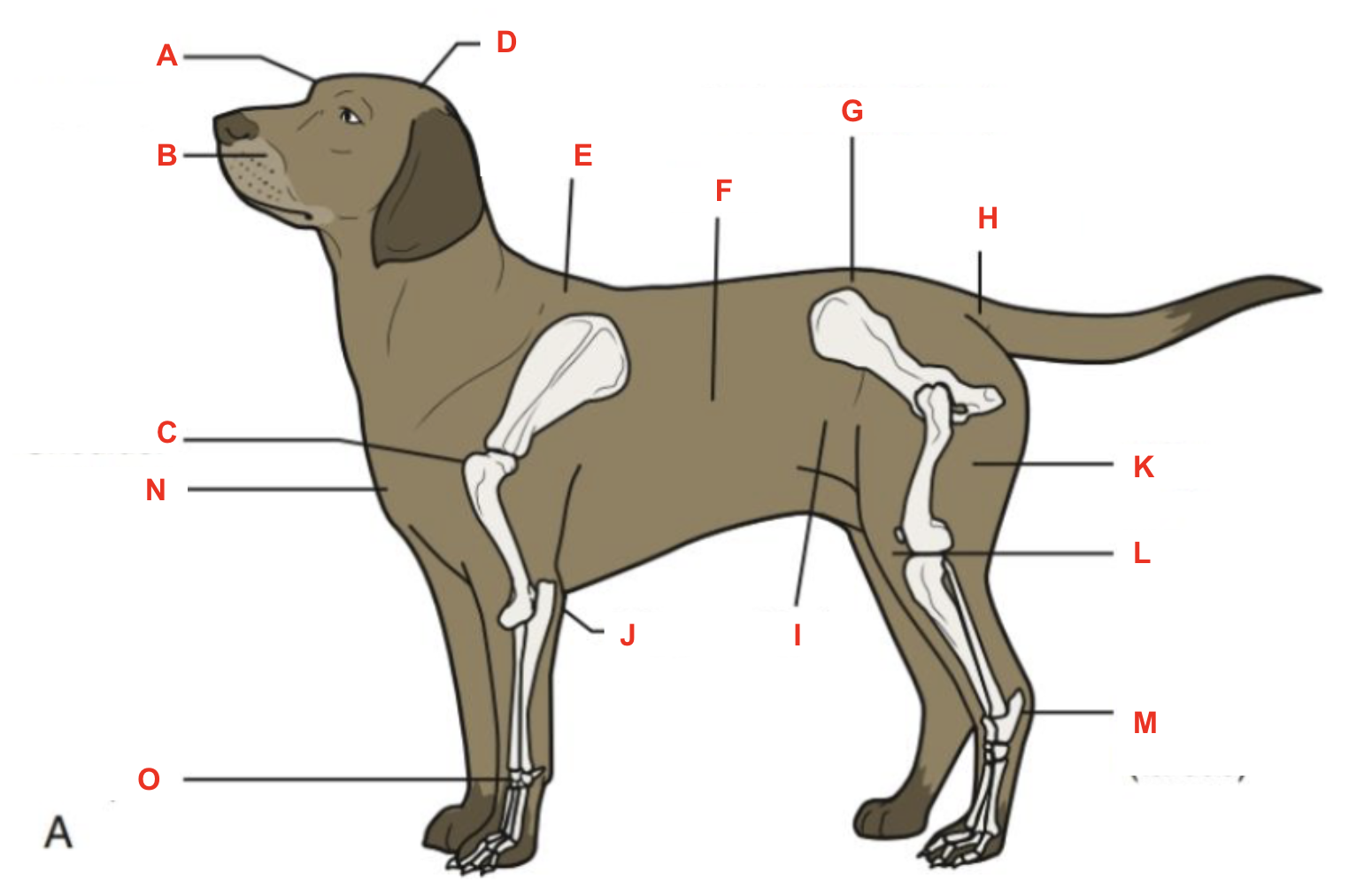
Identify what part of the body is labelled “J”
elbow
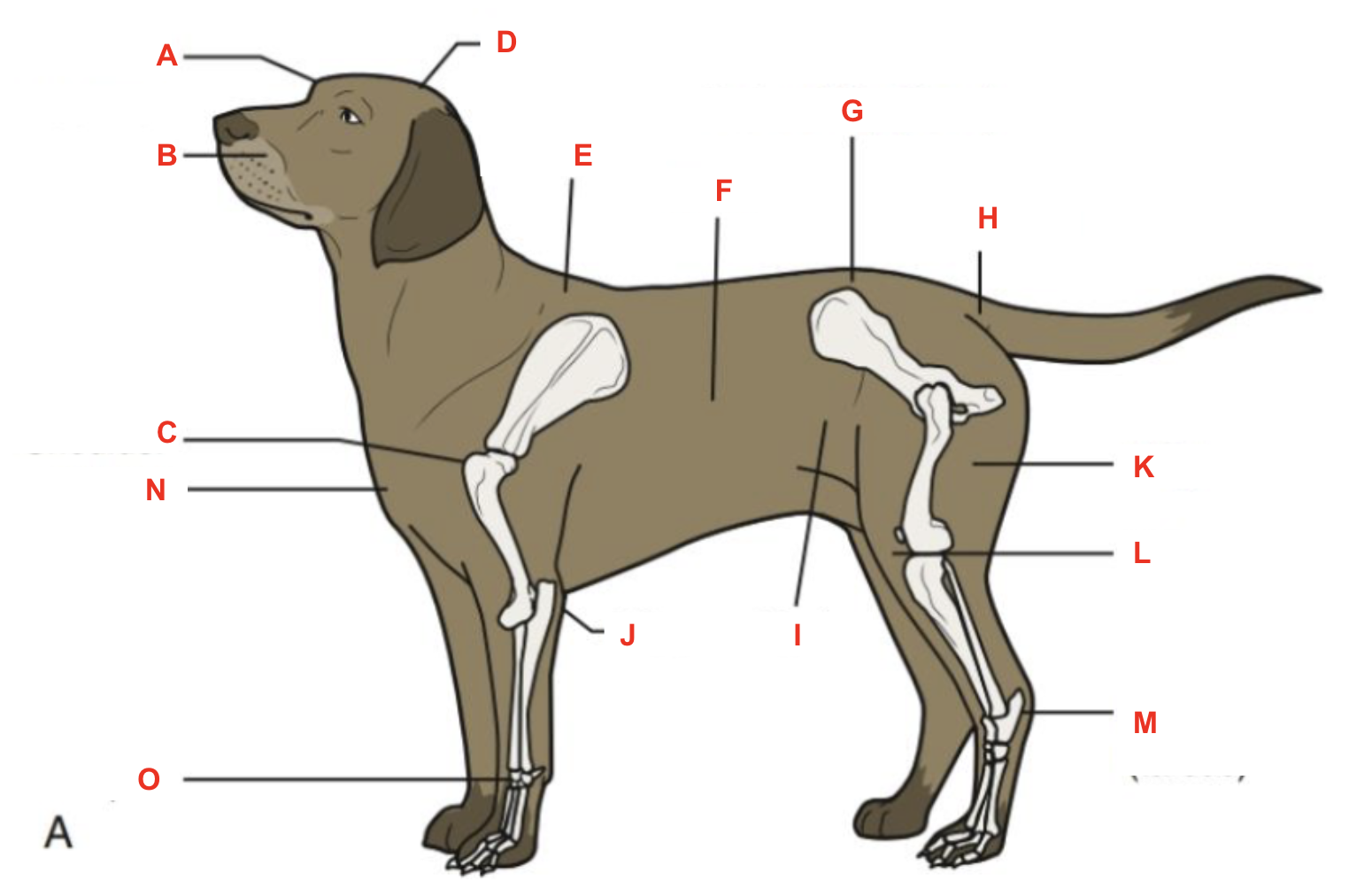
Identify what part of the body is labelled “K”
thigh
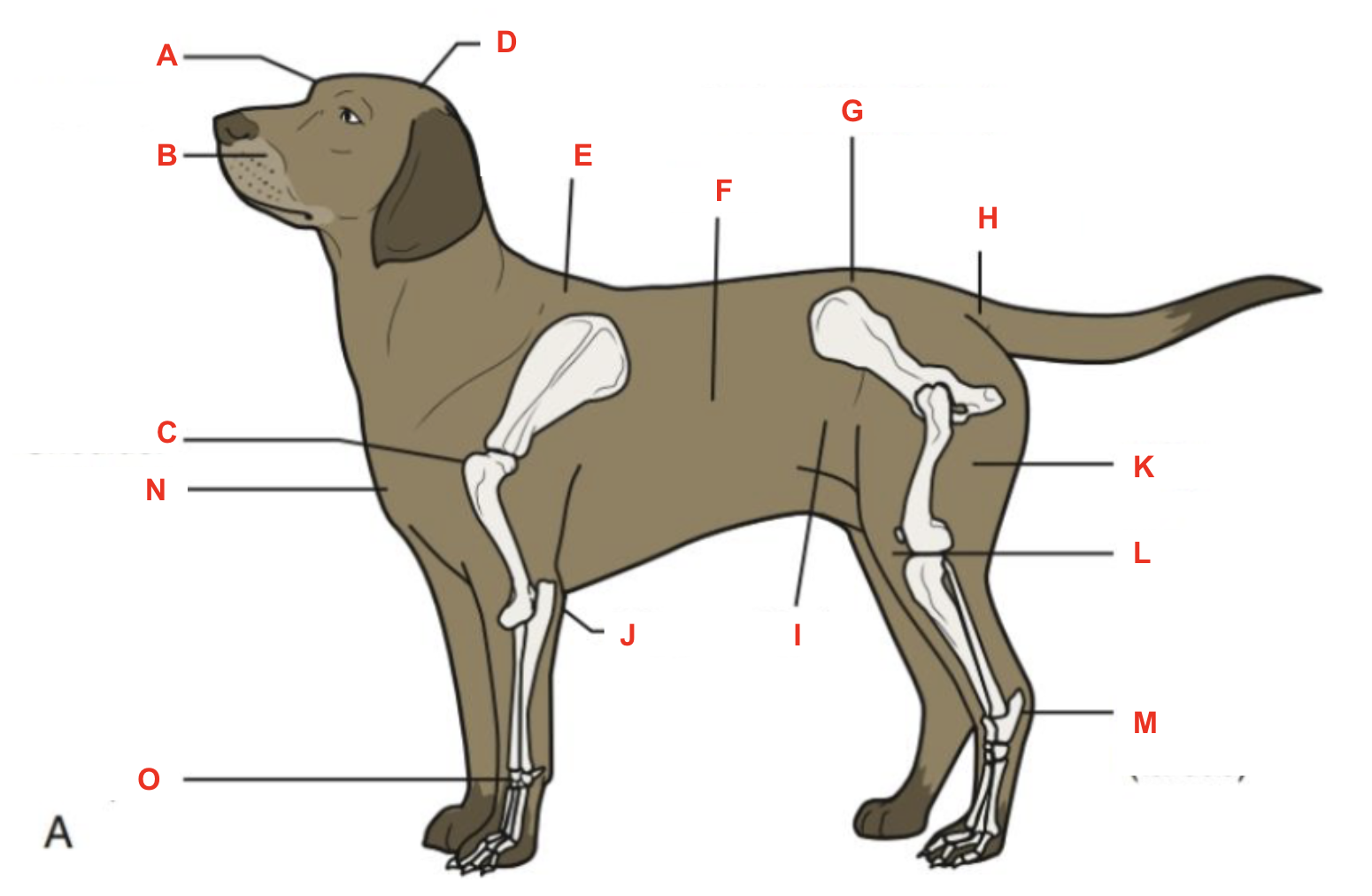
Identify what part of the body is labelled “L”
stifle
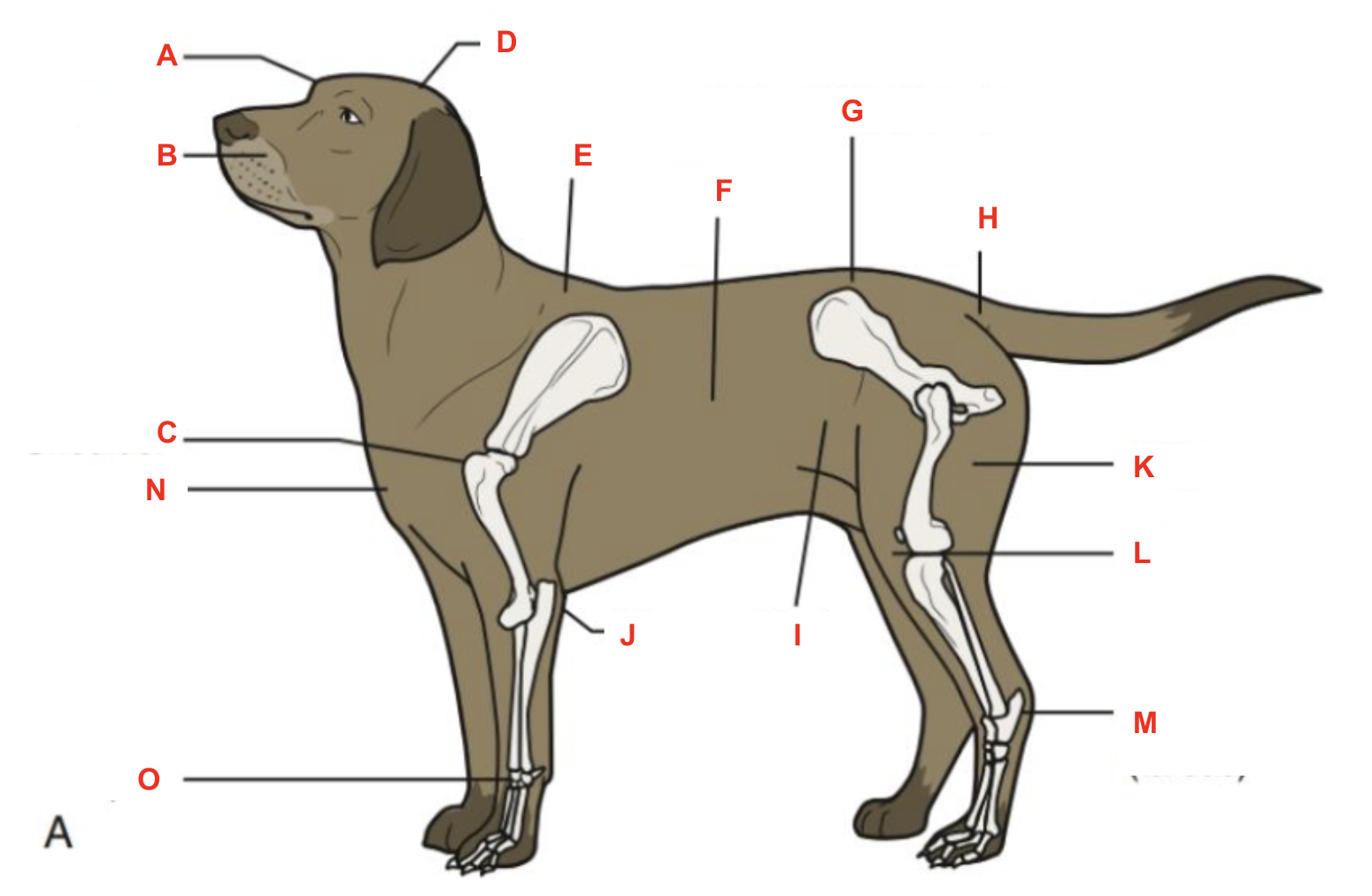
Identify what part of the body is labelled “M”
hock (tarsus)
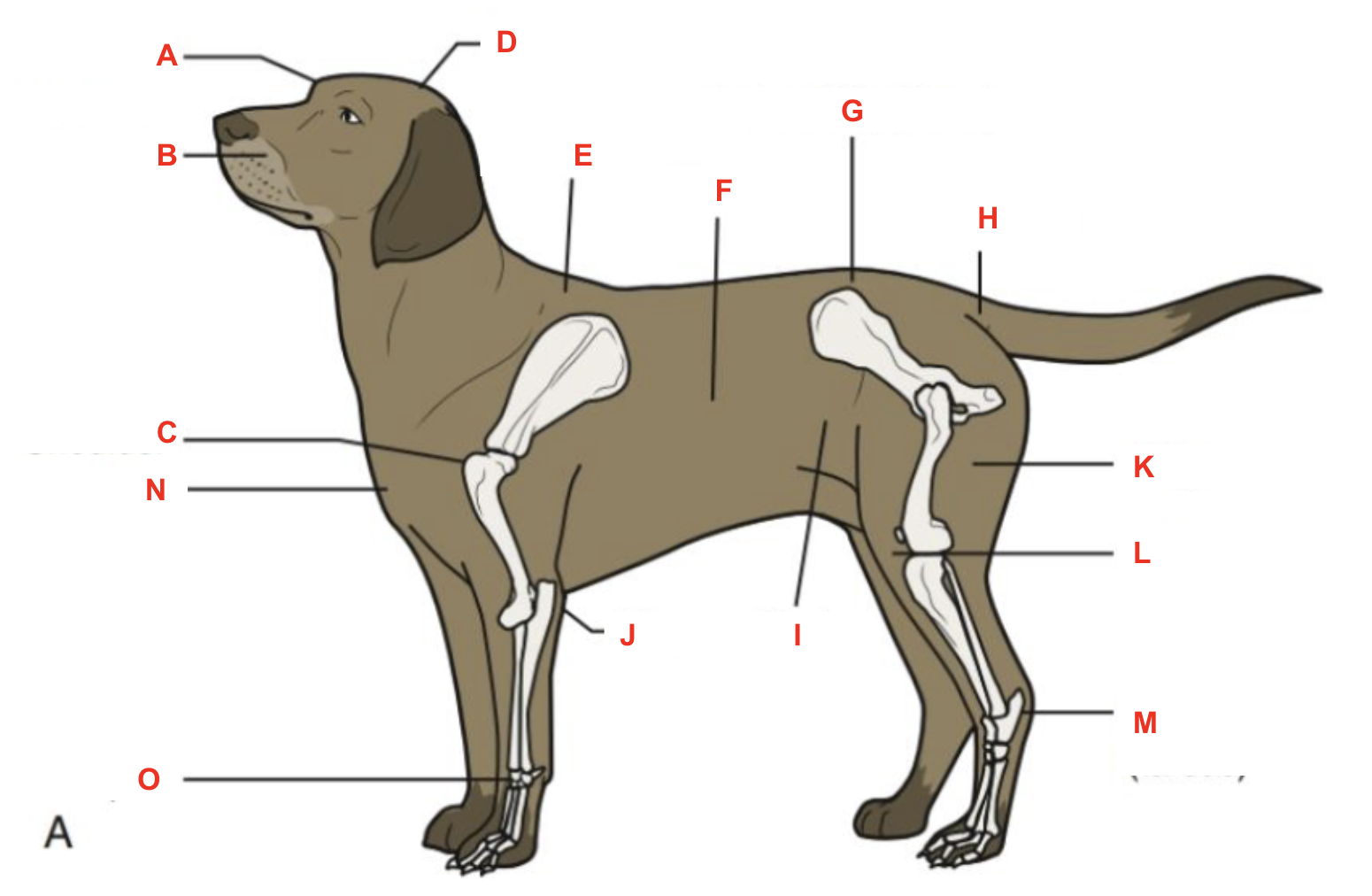
Identify what part of the body is labelled “N”
brisket
Identify what part of the body is labelled “O”
carpus
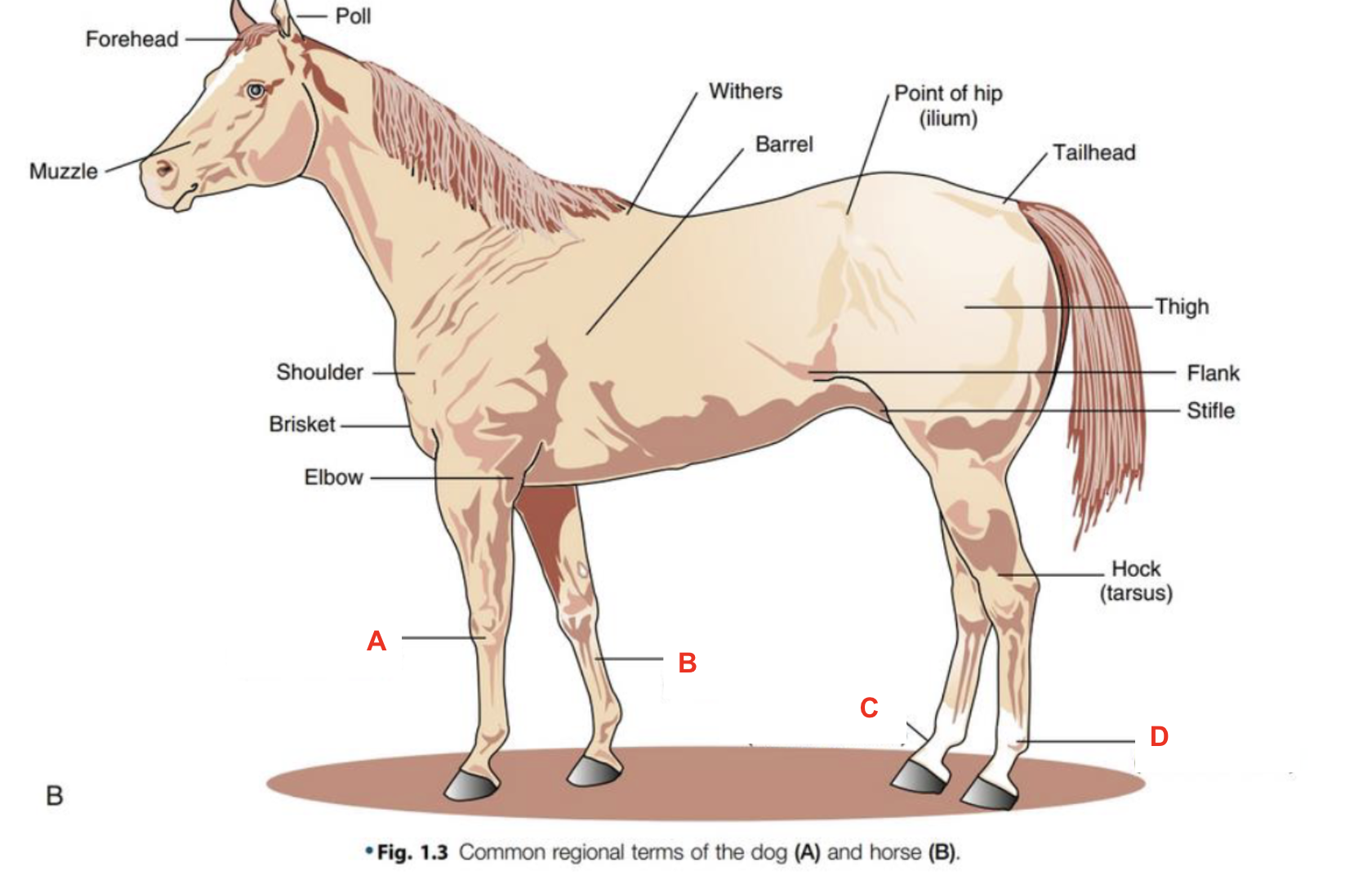
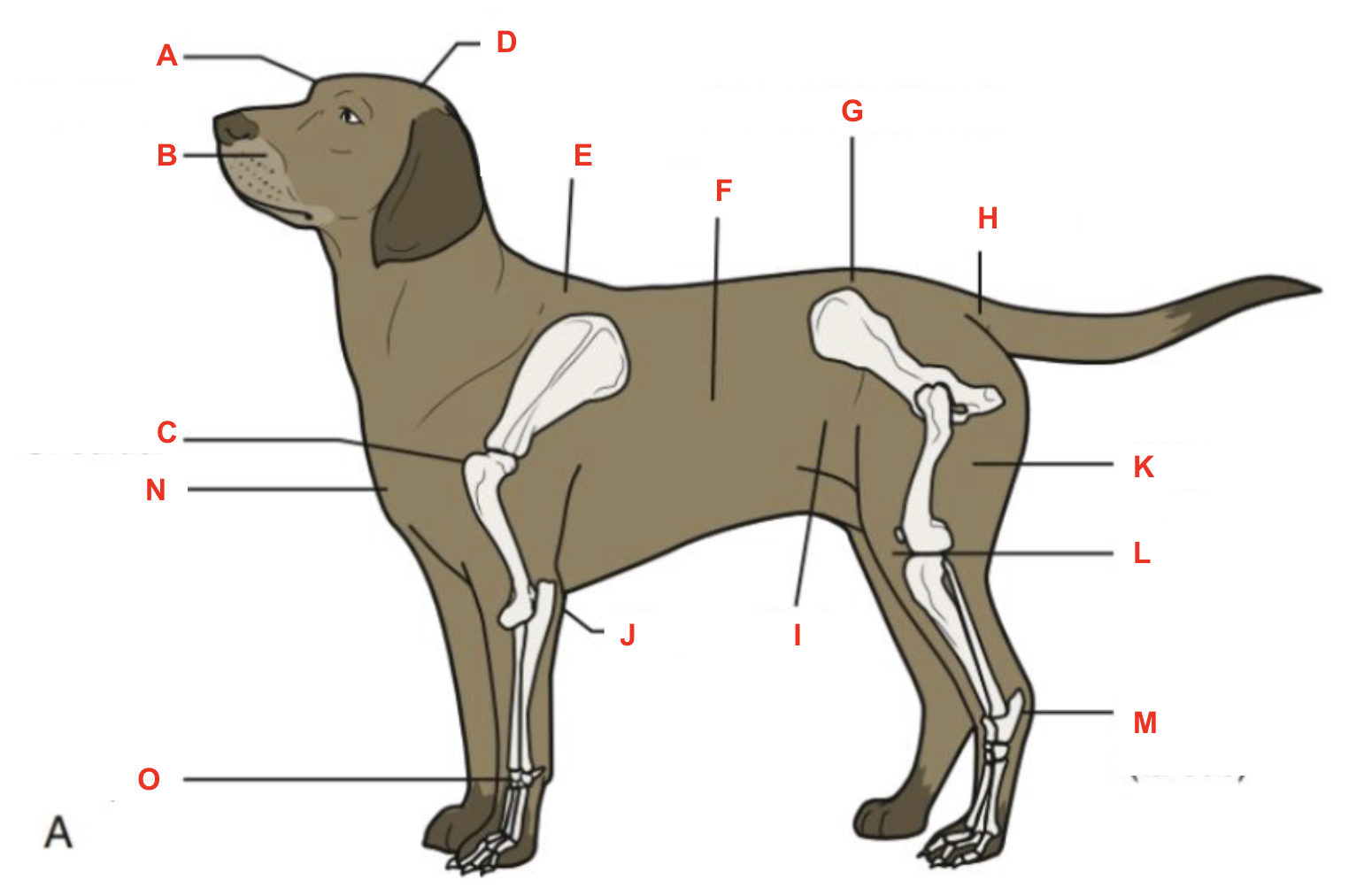
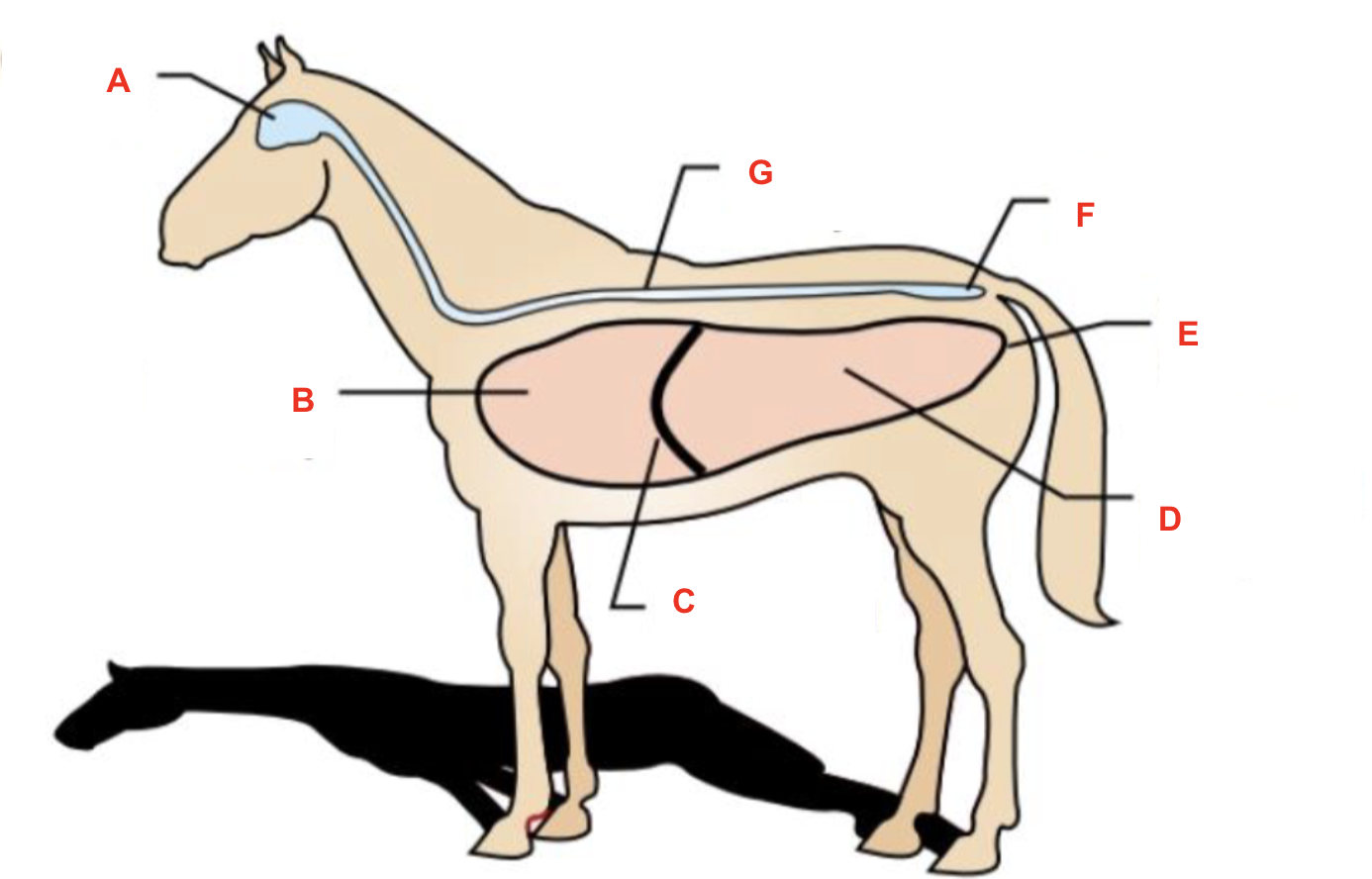
Identify what part of the body is labelled “A”
knee (carpus)
Identify what part of the body is labelled “B”
cannon
Identify what part of the body is labelled “C”
pastern
Identify what part of the body is labelled “D”
fetlock
Identify what cavity is labelled “A”
cranial cavity
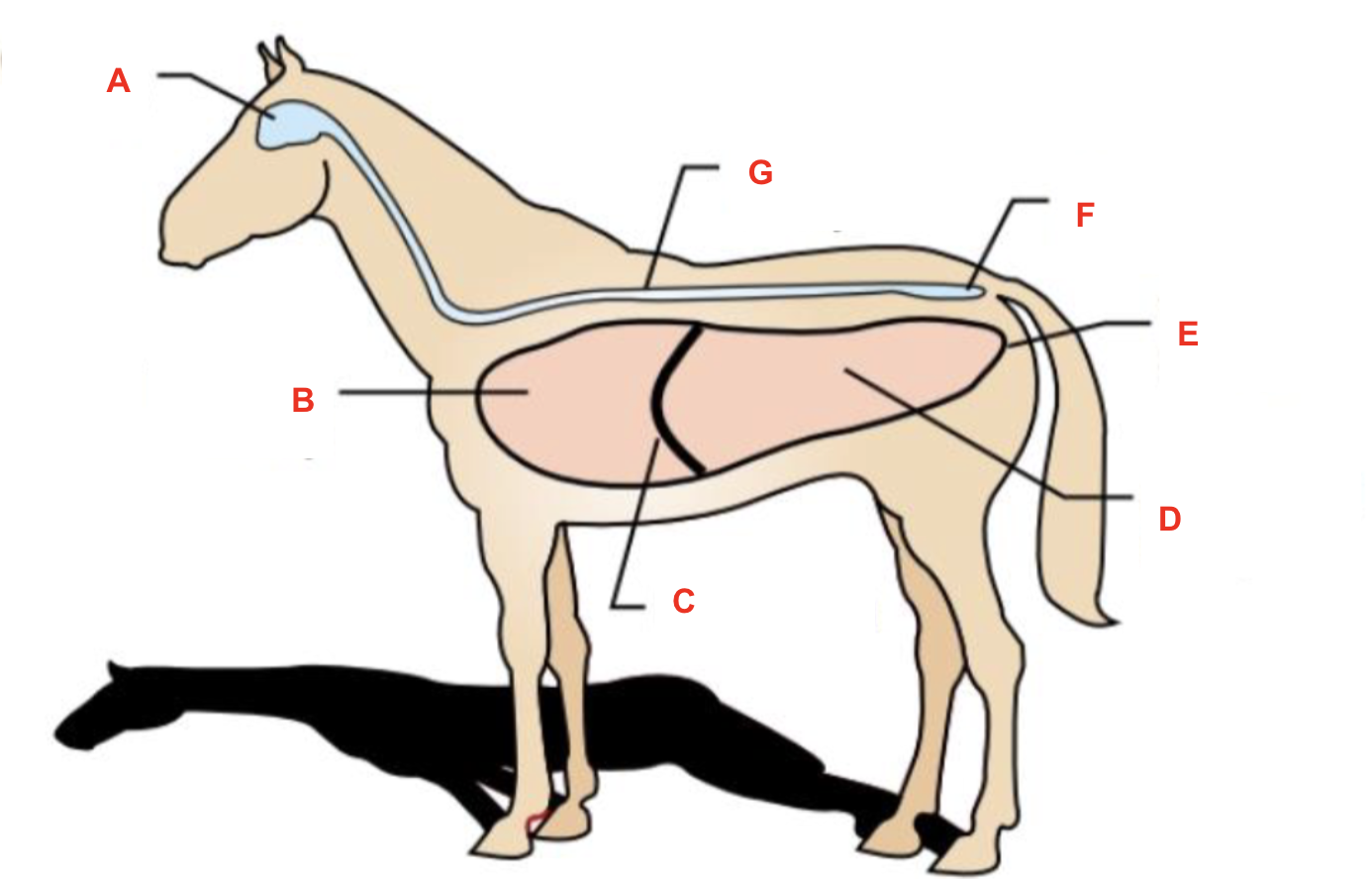
Identify what cavity is labelled “B”
thoracic cavity
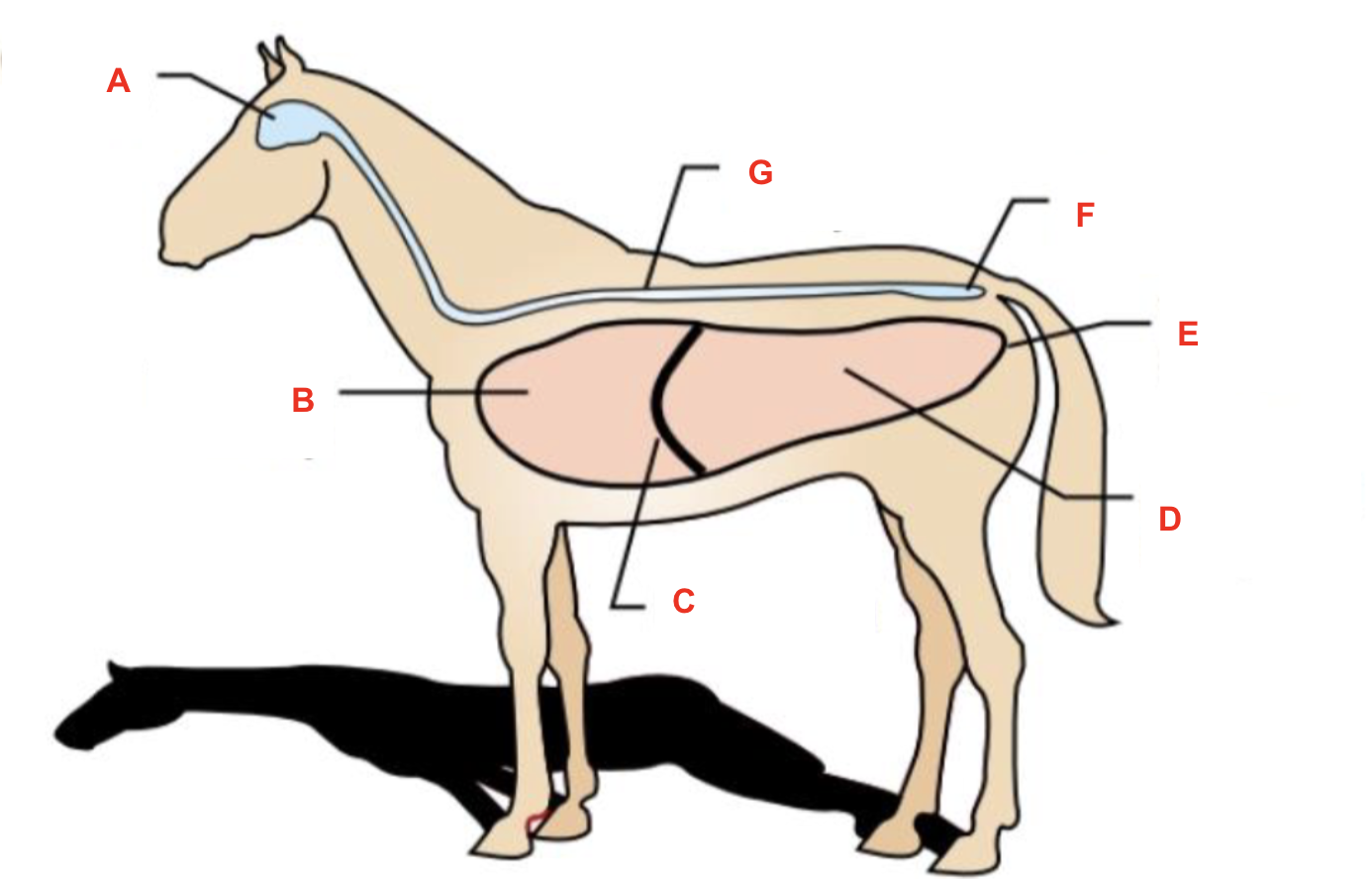
Identify what cavity is labelled “C”
diaphragm
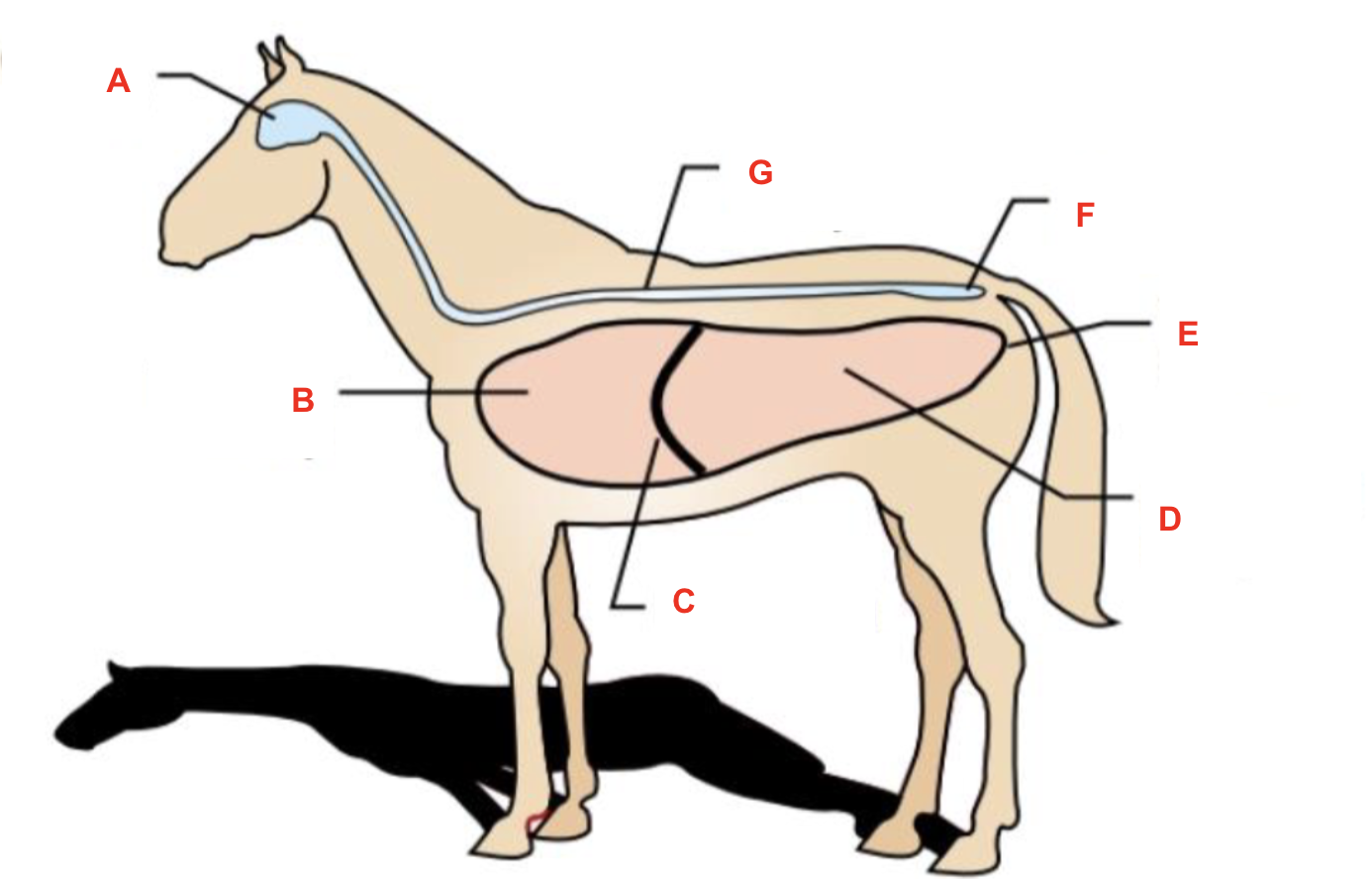
Identify what cavity is labelled “D”
abdominal cavity
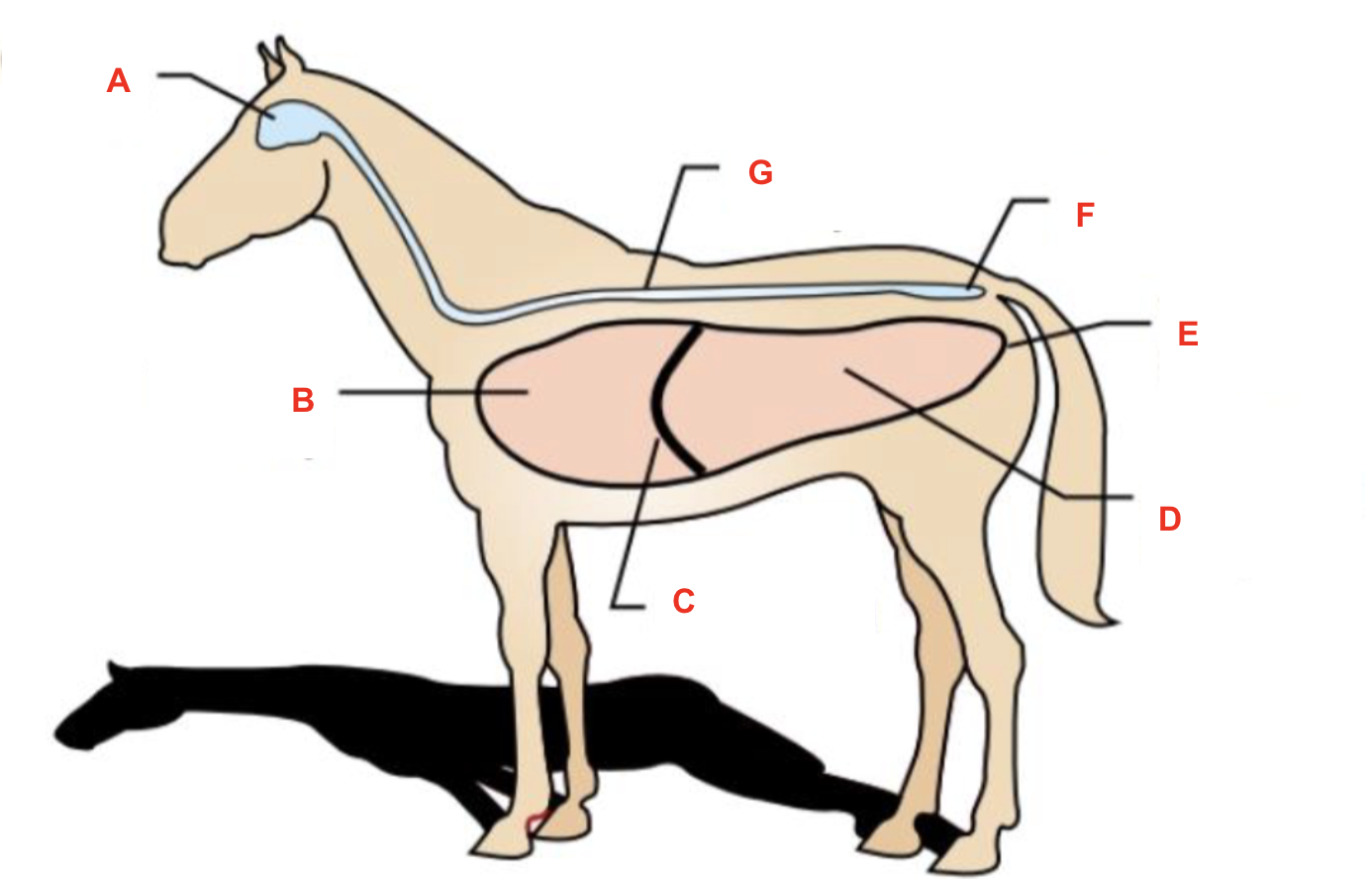
Identify what cavity is labelled “E”
ventral cavity
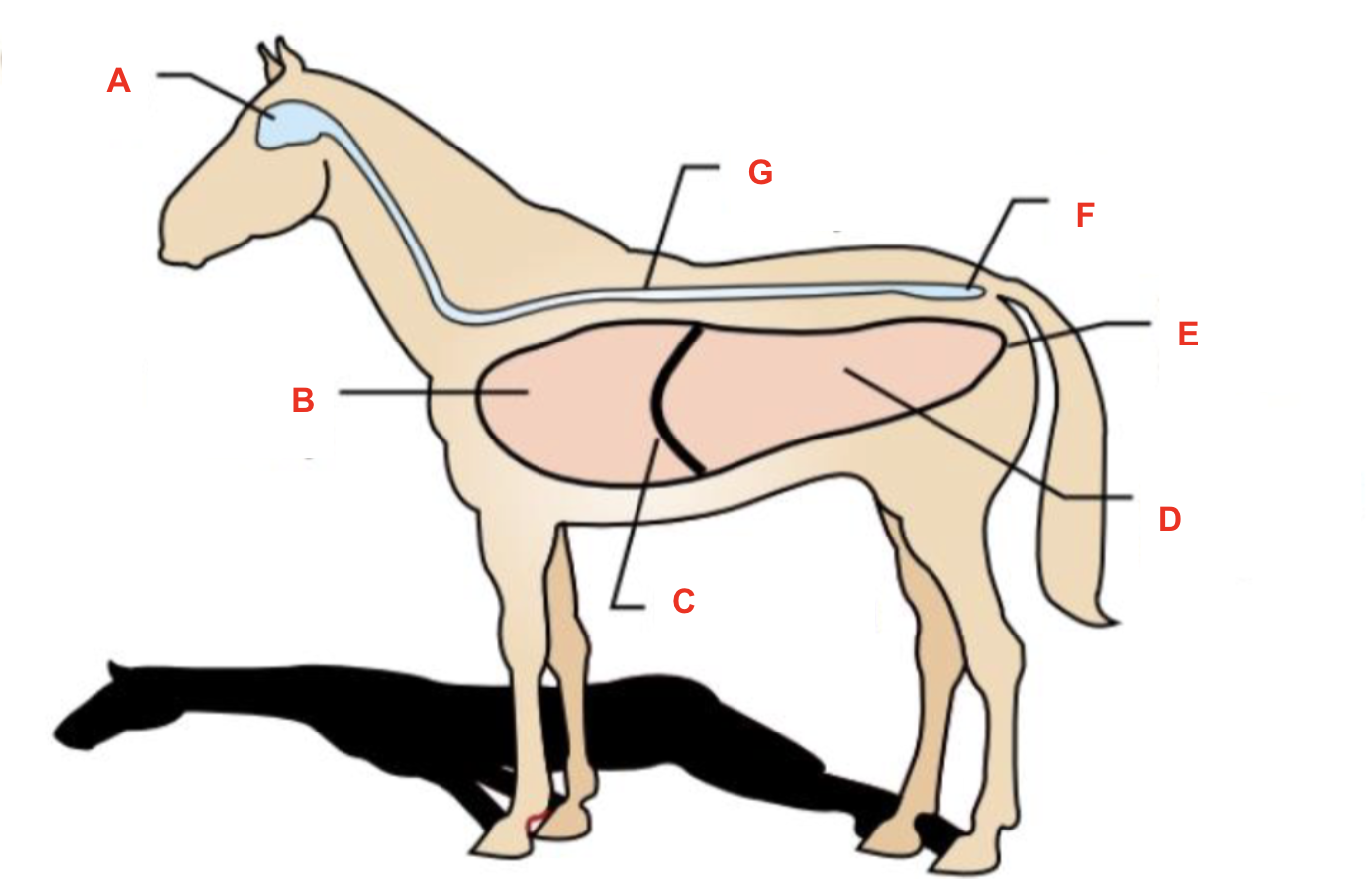
Identify what cavity is labelled “F”
dorsal cavity
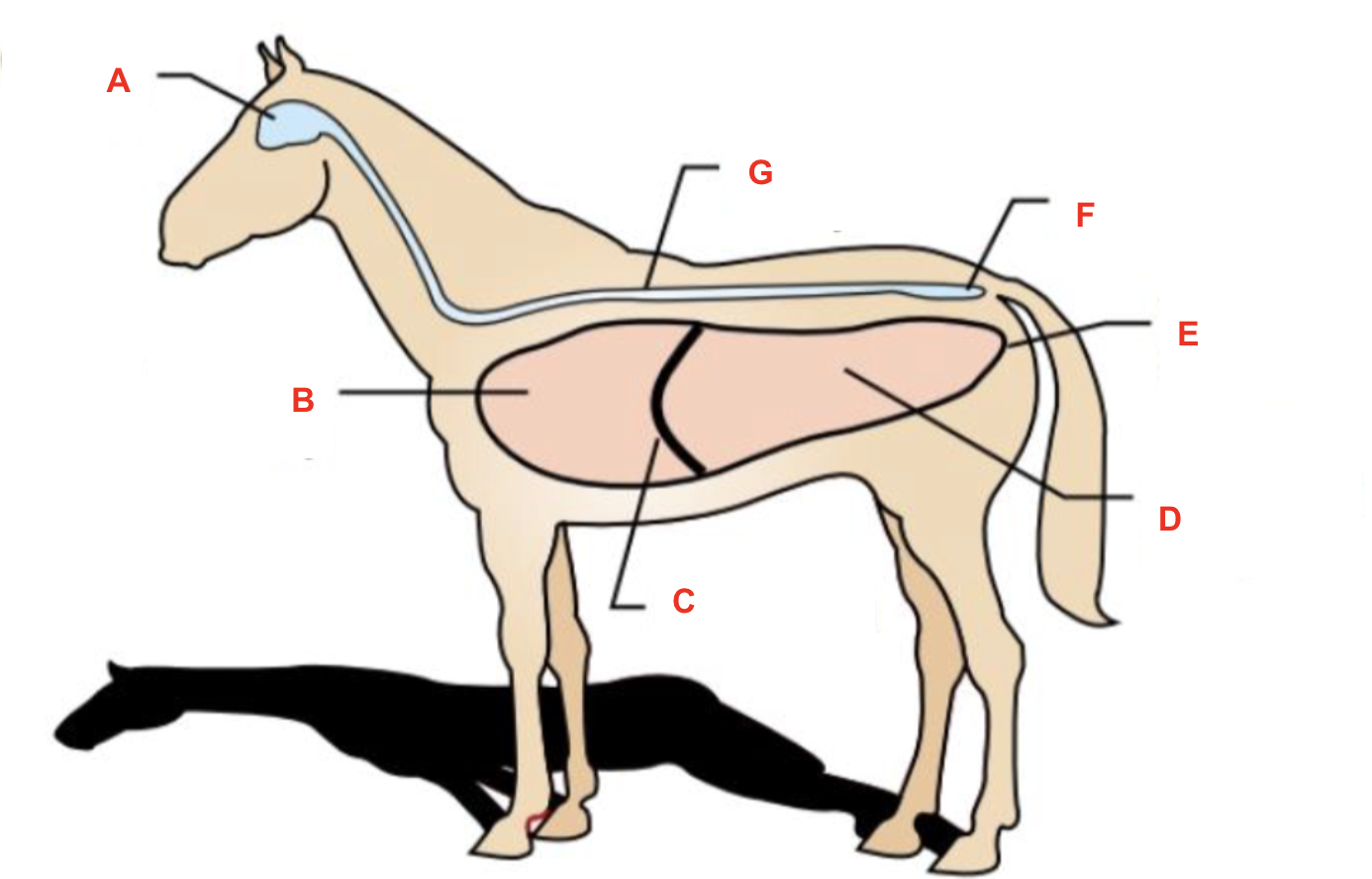
Identify what cavity is labelled “G”
spinal cavity
The sagittal plane splits the body into…
two unequal left and right halves
The median plane splits the body into…
two equal left and right halves
The transverse plane splits the body into…
the cranial and caudal regions
The dorsal plane splits the body into…
the dorsal and ventral regions
The cranial region is…
toward the head
The rostral region is…
toward the tip of the nose
The caudal region is…
toward the tail end
The dorsal region is…
toward the back
The ventral region is…
toward the belly
The medial region is…
toward the median plane
The lateral region is…
away from the median plane
The proximal region is…
toward the body (on an extremity)
The distal region is…
away from the body (on an extremity)
The palmar region is…
the back of the forelimb from the carpus (distally)
The plantar region is…
the back of the hindlimb from the carpus (distally)
If a cut is deep this means…
towards the center (of the body or an extremity)
If a cut is superficial this means…
towards the surface (of the body or an extremity)
The dorsal cavity contains…
the spinal and cranial cavities
The ventral cavity contains…
the thoracic and abdominal cavities
The organs contained in the thoracic cavity are…
heart
lungs
major vessels
lungs
The mesothelium of the thoracic cavity is called…
pluera
Visceral pleura covers…
the organ
Parietal pleura covers…
the wall
The pleural cavity is…
the space between visceral and parietal layers
The organs contained in the abdominal cavity are…
digestive organs
reproductive organs
urinary organs
The mesothelium of the abdominal cavity is called…
peritoneum
Visceral peritoneum covers…
the organs
Parietal peritoneum covers…
the walls
The peritoneal cavity is…
the space between the visceral and parietal peritoneum
The four general tissue types are…
epithelial
connective
muscle
nervous
Epithelial tissue has the following functions…
cover/protect surfaces
secretion
absorption
Epithelial tissue is made up of…
only cells
Connective tissue has the following functions…
bind cells/structures
support the body
Connective tissue is made up of…
cells and nonliving intercellular substances
The three types of muscle tissue are…
skeletal
cardiac
smooth
Muscle tissues have the following function…
movement
Skeletal muscle is in charge of…
voluntary movement
Smooth muscle is in charge of…
involuntary movement
Nervous tissue has the following functions…
transmit information
coordinate/control activity
Nervous tissues is made up of…
nerve cells and supporting cells
Organs serve to…
accomplish a specific function
Systems are made up of…
more than one organ
Homeostasis is the…
maintenance of equilibrium within the body
Homeostasis requires…
energy
the whole body
Homeostasis is precise, and manages…
temperature
acid/base balance
fluid balance
hormones
nutrients
oxygen
The four states of matter are…
gas
liquid
solid
plasma
The three types of elements are…
metals
metalloids
non-metals
96% of matter in living organisms is made up of the following four elements…
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
nitrogen
A molecule is made when…
two or more atoms are joined together by a chemical bond
A compound is made when…
atoms of two or more different elements are joined by a chemical bond
The three types of mixtures are…
solutions
colloids
suspensions
Solutions are comprised of…
small solute particles that do not settle out/scatter
Solutions are considered…
homogenous
Colloids are comprised of…
large solute particles that do not settle out but will scatter lightly
Colloids are considered…
heterogenous
Suspensions are comprised of…
very large solute particles that will settle out and scatter lightly
Suspensions are considered…
heterogenous
The three types of chemical reactions are…
synthesis
decomposition
exchange
Synthesis reactions will…
make something
Decomposition reactions will…
break something down
Exchange reactions will…
mix things together
A catalyst is…
a molecule that holds the reactants together to facilitate a reaction
The two types of compounds are…
organic
inorganic
Organic compounds are different than inorganic compounds because they contain…
carbon
The four organic macromolecules are…
carbohydrates
lipids
proteins
nucleic acids
Carbohydrates serve as…
energy source
energy storage
cellular structures
The three types of carbohydrates are…
monosaccharides
disaccharides
polysaccharies
Lipids serve as…
energy source
energy storage
cell membrane structure
The four types of lipids are…
triglycerides
phospholipids
steroids
eicosanoids
Triglycerides are comprised of…
three fatty acids and one glycerol
Phospholipids are comprised of…
one glycerol, one phosphate group, and two fatty acids
Steroids are comprised of…
four carbon rings
Eicosanoids are…
very large lipid molecules
The two types of proteins are…
globular
fibrous