Kaplan psychology ch 1
1/41
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Gall
Founder of phrenology, pseudoscience that talked about skull size.
Flourens
ablations/extripation. different parts of brain had different functions
James
functionalism, psychology of how brain adapts to environment
dewey
believed psych is a study of the whole person, advocated for functionalism
Broca
brocas region, lesions in specific parts of brain lead to different maladies
helmhltz
measured the speed of a nerve impulse
sherrington
discovered synapses
afferent/sensory neurons
relays sensory information to cns
efferent/motor neurons
relays motor information from cns to muscles
interneurons
located mostly in brain and spinal cord linked with reflixive behavior (stepping on nail).
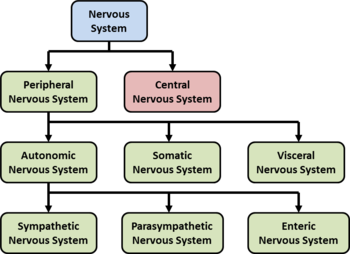
CNS
Brain and spine
PNS
everything else
created a flow chart of all the parts of the nervous system
Parasympathetic nercous system
Conserves energy
constricts bladder, speeds up digestion, lowers heart rate, contricts bronchi, constricts pupils, releases adrenaline and noradrenaline
rest and digest
sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight
raises heart rate, dialates pupils, prevents baldder constriction,
slows digestion, stimulates bile and saliva production
activated by acytlcholine
parts of the hind brain and functions
cerebellum, mudula oblongata, reticular formation
refined motor control
viatl functions
arousal and alertness
parts of the mid brain and functions
inferior and superior colliculi
sensorimotor reflexes
parts and functions of the forebrain
cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, thalmus, hypothalmus, limbic region
advanced cognition, memory and emotion, movement and perception
types of tecniques for neural mapping
fMRI, MRI, CT, PET, rCBF
three meningeies
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
thalmus
relay station for signals within the brain
hypothalums: Lateral Hypothalmus, ventromedial Hypothalmus, Anterior Hypothalmus
LH, hunger center
VMH: satiety center
AH: sexual function
Basal Ganglia
involved in precison motor function
parkinsons disease affects this area
limbic system
emotions and memory
houses the amydgala (fear)
septic nucleii (rewards system)
hippocampus (memory)
cerebral cortex
outer most part of forebrain
gyri and sullci
split into four lobes
frontal lobe
split into prefrontal cortex and motor cortex and brocas area
prefrontal cortex: executive/supervisonary function
motor cortex: volitary movement
brocas area: speech
parietal lobe
somatosensory processing and spatial processing
occipital lobe
contains the visual cortex
involved in vision and motor control
temporal lobe
contains hippocampus and wernickes area, and auditory cortex
language, memory, and hearing
acetylcholine
used in parasympathetic nervous system
adrenaline, noreadrenaline,
catecholamines, regulate emotions
dopamine
catecholamine with important role in movement and posture. Parkinsons is caused by a loss of dopaminergic neurons
Dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia
schizophrenia results from an either too much dopamine or an oversensitivity to dopamine
Serotonin
regulates mood and hunger. Too much equals mania and too little equals depression
GABA, Glycine, and glutamate
GABA and Glycine are inhibitors that act by hyperpolarization, Glutamate is and excititory neurotransmitter
endorphins
peptide neurotransmitters, act as natural pain killers
endorcine glands
pituitary gland acts as a master gland, activating other glands in the body
adrenal glands release epinepherine and norepinepherine,
gonads release sex horomones
types of studies
twin studies
adoption studies
familily studies
neural development
begines with neruolation (groove and folds)
folds in on itself repeatedly and becomes the neural tube (prosencephelon, mesenchephelon, rhombenchephelon)
develops further into telenchephelon, dienchephelon, mesenchephelon, metenchephelon, mytenchephenlon)
moro reflex, babinski reflex, clutching reflex
moro: baby flails its arms out after sudden movement
babinski, baby spreads toes after plantar stimulation
clutcting stimulation, baby clutches items given to it