Behavioral Neuroscience- Exam 1
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The Neuron, Cranial Nerves, The Brain, Communication, Drugs, and Neurotransmitters (Weeks 1-5)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
In which hemisphere do most people process language?
Left
Which hemisphere controls the left side of the body?
Right
Which hemisphere detects the right visual field?
Left
If your left nostril is plugged and a smell is presented to your right nostril, this olfactory information will go to which hemisphere?
Right (smells are the exception to contralateral processing)
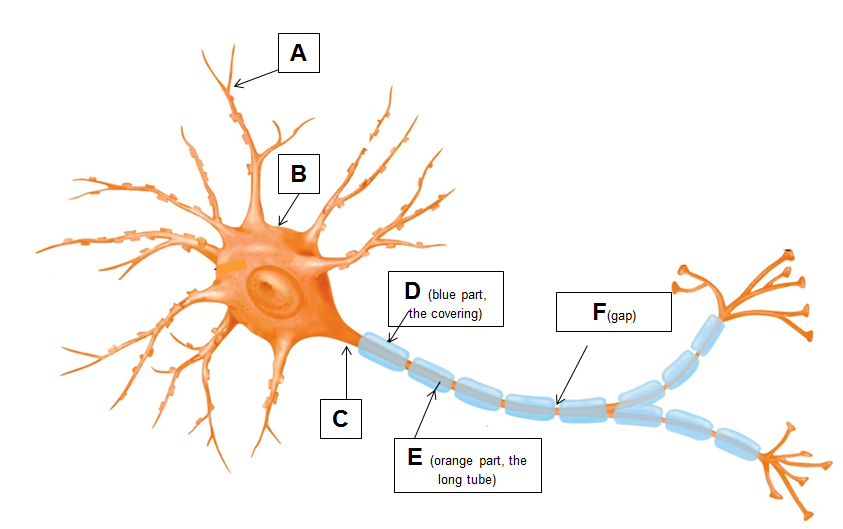
Identify the following parts:
A: dendrite
B: soma
C: axon hillock
D: myelin sheath
E: axon
F: node of Ranvier
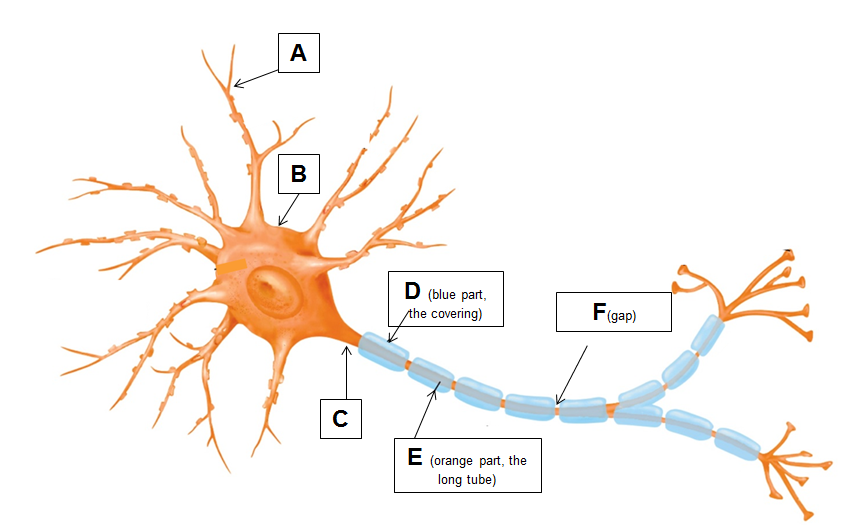
Identify this neuron by structure.
Multipolar
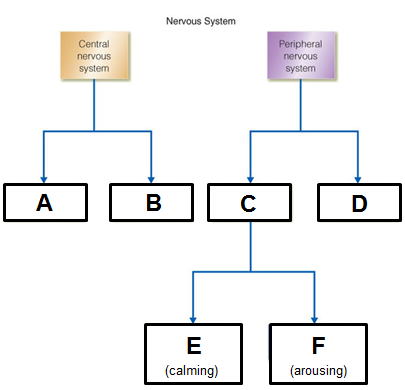
Complete the hierarchical structure of the nervous system.
A: brain
B: spinal cord
C: autonomic
D: somatic
E: parasympathetic
F: sympathetic
Which motor protein transports materials (such as vesicular organelles) in the retrograde direction in the axon?
cytoplasmic dynein
Imagine that your corpus collosum has been sectioned to minimize your epileptic seizures. Suppose that your left nostril is plugged with cotton and that a fresh rose has been placed near your right nostril. Under these conditions, you would be most likely to:
a. experience a sensory message in your left hemisphere.
b. use your right hand to choose a hidden plastic flower.
c. say that you smell a flower.
d. use your left hand to select a hidden plastic flower.
e. use your right hand to select a pine tree.
d. use your left hand to select a hidden plastic flower

Imagine that your corpus collosum has been sectioned to minimize your epileptic seizures. You are asked to look directly at the dot, as this image is flashed for a moment. Under these conditions, you would be most likely to:
a. Verbally report seeing a fish
b. Verbally report seeing a dog
c. Verbally report seeing nothing
d. Verbally report seeing both a fish and a dog
b. verbally report seeing a dog

Imagine that your corpus collosum has been sectioned to minimize your epileptic seizures. You are asked to look directly at the dot, as this image is flashed for a moment. Under these conditions, you would be most likely to (there are 2 correct answers):
a. Use your right hand to draw a fish
b. Use your right hand to draw a dog
c. Use your left hand to draw a fish
d. Use your left hand to draw a dog
b. Use your right hand to draw a dog
c. Use your left hand to draw a fish
The three types of neurons according to function are:
sensory (afferent), motor (efferent), interneuron
What is NOT a characteristic of axons?
a. used to transmit messages to other neurons or muscles
b. many are coated by a myelin sheath
c. clustered around the cell body like tree branches
d. may be short or very long
e. end with terminal buttons
c. clustered around the cell body like tree branches
Unilateral neglect from damage to the right parietal lobe involves:
the inability to notice objects placed to the left side of a person
Which part of the nervous system plays a dominant role in preparing the body for times of emergency or stress?
sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system
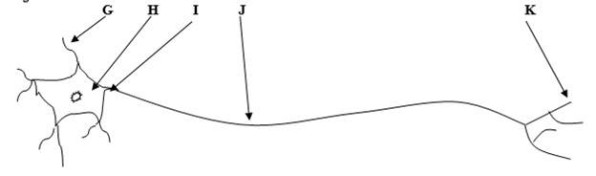
Label each part of this cell indicated by the letters.
G= dendrite
H= soma
I= axon hillock
J= axon
K= terminal buttons
This part of the neuron is responsible for releasing neurotransmitters.
Terminal buttons
The central nervous system is comprised of the:
Brain and spinal cord
What roman numerals belong to the following cranial nerves:
Olfactory
Facial (taste, tears, saliva, and facial expressions)
Trigeminal (facial muscles and sensations)
Optic (sight)
Vestibulocochlear (auditory)
Vagus (control of PNS e.g. smooth muscles of GI tract)
Olfactory- I
Facial- VII
Trigeminal- V
Optic- II
Vestibulocochlear- VIII
Vagus- X
Which cranial nerve is responsible for vision?
optic
The trigeminal nerve is primarily responsible for:
facial sensation and chewing
Which cranial nerve controls the muscles of facial expressions?
VII- Facial
The vestibulocochlear nerve is associated with which sense?
hearing and balance
The vagus nerve is known for:
hear rate, digestion
Which of the cranial nerves are both sensory and motor?
trigeminal, facial, vagus, and glossopharyngeal
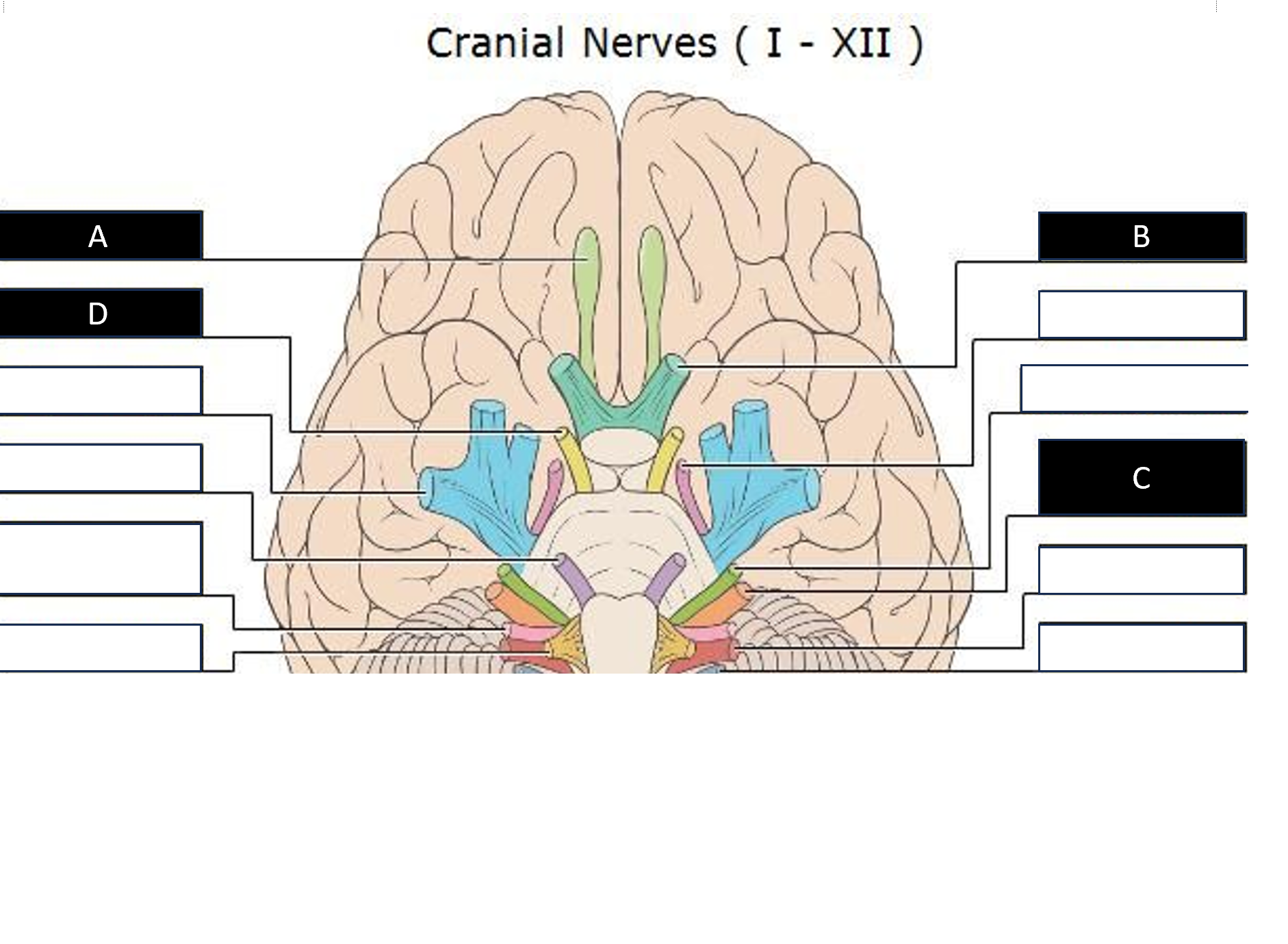
Label the lettered cranial nerves.
A: Olfactory
B: Optic
C: Vestibulocochlear
D: Oculomtor
What are the three major ways to section the human brain (planes, not hind brain, mid brain, fore brain)
Frontal/coronal
Horizontal (axial)
Sagittal
The nose is _________, whereas the back of the head is _________.
rostral; caudal
The term “neuraxis” refers to
an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain
Which term means “above” when referring to the human brain?
superior
Assume that electrical stimulation of the right motor cortex elicits limb movements on the left side of the body. In this instance, we would describe this as a(n) ______ organization of motor cortex and the muscles of the body.
contralateral
The order of the meningeal layers from the surface of the brain outward (so inside to outside layers) are
pia, arachnoid, dura.
The _______ is the soft and spongy layer of the brain meninges.
arachnoid membrane
The four hollow and interconnected spaces within the brain form the
ventricles.
A _______ is a large groove found in the surface of the human cortex.
fissure
What would be expected following damage to the cortex just in front of the central sulcus?
difficulty in controlling the muscles of the body
Which plane is shown here?
coronal
Which plane is shown here?
sagittal
Which substructure of the hind brain is responsible for arousal and sleep?
reticular formation
Which substructure of the forebrain acts like a sensory relay?
thalamus
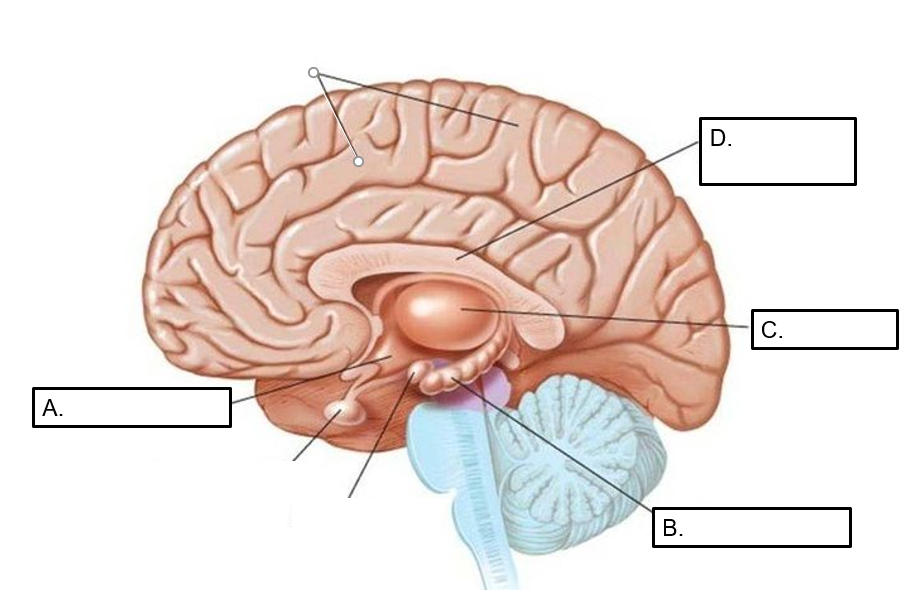
Identify the lettered parts.
A= hypothalamus
B= hippocampus
C= thalamus
D= Corpus Callosum
A cation would be attracted to
an anion.
What is true of ion distribution across the axon membrane?
Sodium ions are more concentrated outside the axon membrane
As a consequence of the activity of the sodium-potassium pumps,
intracellular sodium concentrations are kept low
What kind of electrical event is the action potential?
It is an all-or-none electrical event
What event repolarizes the membrane potential from the peak of the action potential (e.g., returns the membrane potential to resting level
Potassium ions move out of the cell
The nervous system codes for variation in the intensity of incoming sensory stimuli by variations in the ________ of a neuron
firing rate
Influx (entry) of ______ ions result in depolarization.
Na+
The electrical charge of the membrane potential is the result of a balance between two passive forces. The first is ________ which is the process by which molecules evenly distribute in a medium (from regions of high concentration to regions of low concentration). The second is ________ which is the process exerted by the attraction of cations and anions.
There is a third, active force that helps maintain the concentration of sodium ions outside of the cell. It is called the ________ pump.
1) diffusion
2) electrostatic force
3) sodium-potassium
Explain how the presence of myelin on an axon speeds up conduction velocity.
The myelin, a fatty membrane, insulates the axon from extracellular fluid. The signal can then jump from one node of Ranvier to the next.
Drugs like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) prevent the reuptake of serotonin. They are:
agonists
Administering a molecule that is a precursor for the synthesis of a synaptic neurotransmitter would be expected to
increase the rate of synthesis and release of that neurotransmitter.
A drug that binds with a postsynaptic receptor, but does not open ion channels, would be termed a(n)
direct antagonist
PCP binds to an alternate binding site for the NMDA glutamate receptor, causing less neurotransmitter action. This binding action makes PCP a(n)
indirect antagonist
Inactivation of a transporter in the presynaptic membrane would be expected to
increase the levels of the transmitter in the synapse
Muscle contractions often need to happen quickly, so they are controlled via _______ receptors.
ionotropic
What do antagonists do?
They reduce postsynaptic effects.
Valium has a therapeutic index of over 100. Barbiturates have an index of around 2-3. Which drug is safer?
Valium
John has been prescribed a pain medication for chronic back pain. Over time, he notices that the same dose of the medication no longer provides the same level of pain relief, and he needs to take a higher dose to achieve the same effect. What is John experiencing?
tolerance
What are the four steps of pharmacokinetics?
Absorption
Distribution
Metabolism
Excretion
What are some routes of drug administration?
Oral Administration
Intravenous (IV) Injection
Intramuscular (IM) Injection
Sublingual Administration
Inhalation Administration
Topical Administration
Subcutaneous (SC) Injection
Intrarectal Administration
Intraperitoneal (IP) Injection
Intracerebral Administration
Intracerebroventricular Administration
What is blindsight?
unconscious vision
What are the amino acids?
glutamate, GABA, and glycine
What are the catecholamines?
dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine
What are the peptides?
opioids
What are the things associated with dopamine?
drive
psychosis
Parkinson’s
attention
motor control
inhibition of prolactin
narcotics
extrapyramidal functioning
Which amino acids are inhibitory?
GABA and Glycine
What is associated with acetylcholine?
Botox and muscarinic receptors
Where is dopamine produced?
ventral tegmental area and substantia nigra
Where is serotonin produced?
raphe nuclei
Which neurotransmitter is usually released through axonal varicosities?
norepinephrine
What things are associated with opioids?
analgesia, respiration depression, miosis, euphoria, drowsiness, and constipation
What is an example of a soluble gas?
nitric oxide
Which neurotransmitter does caffeine affect?
adenosine
Which neurotransmitter does Sildenafil (Viagra) affect?
nitric oxide
Which receptor does marijuana affect?
cannabinoid receptor
Which neurotransmitter does nicotine affect?
acetylcholine
What is the reward pathway of the brain?
mesolimbic system