AP Bio Semester 1
1/532
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
533 Terms
Polar covalent bonds in water molecules result in
hydrogen bonding
Water is a ___ molecule
polar
What does polarity alow water to do?
to form hydrogen bonds with each other
4 properties of water
- cohesive behavior
- ability to moderate temp
- expansion upon freezing
- versatility as a solvent
Cohesion
Hydrogen bonds between H2O molecules (sticking to itself)
Hydrogen bonds are ____ bonds
intermolecular
Adhesion
Hydrogen bonds between H2O & other polar moelcules (sticking to other things)
What is cohesion responsible for?
Waters
- high heat of vaporization
- high specific heat
- High surface tension
Transpiration
plants/trees ability to pull H2O molecules up
What does transpiration result from?
- cohesion
- adhesion
- evaporation
surface tension
force exterted by H2O molecules on the surface of a body of H2O
Surface tension creates
a kind of web or net upo the surface
Specific heat
the amount of heat that must be absorbed or lost for 1 gram of that substance to change its temp by 1 C
Specific heat of water
1 cal/ (g*C)
Why does H2O resist changing its temp?
Bc of its high specific heat
Heat of vaporization
the heat a liquid must absorb for 1 g to be converted to gas
Evaporative cooling
Helps stabilize temps in organisms & bodies of H2O
H2O is less dense as a
solid than as a liquid
Solution
liquid that is completely homogenous mixture of substances
Solvent
dissolving agent of a solution
Solute
substance that is dissolved
Why is water a versatile solvent?
bc of its polarity
Hydrophilic
likes H2O
Hydrophobic
hates H2O
Acid
increased H+ concentration
- less than 7 on pH scale
- the more H+ ions the more acidic
Base
decreased H+ concentration
- more than 7 on pH scale
- the less H+ ions (or more OH- ions) the more basic
Strong acids & bases dissociate completely in
water
Dissolved CO2 in seawater forms
carbonic acid
Ocean acidification
carbonic acid formed from dissolved CO2
As seawater acidifies, H+ ions combine with carbonate ions to...
produce bicarbonate ions
Carbon commonly bonds to
- carbon
- hydrogen
- oxygen
- nitrogen
What happens when carbon bonds to other carbons?
Results in carbon skeletons
Major elements of life
CHNOPS
Hydrocarbons
organic molecules consisting of only carbon & hydrogen
Hydrogen carbons can undergo reactions that release
a large amount of energy
Isomers
compounds with the same molecular formula but diff structures & properties
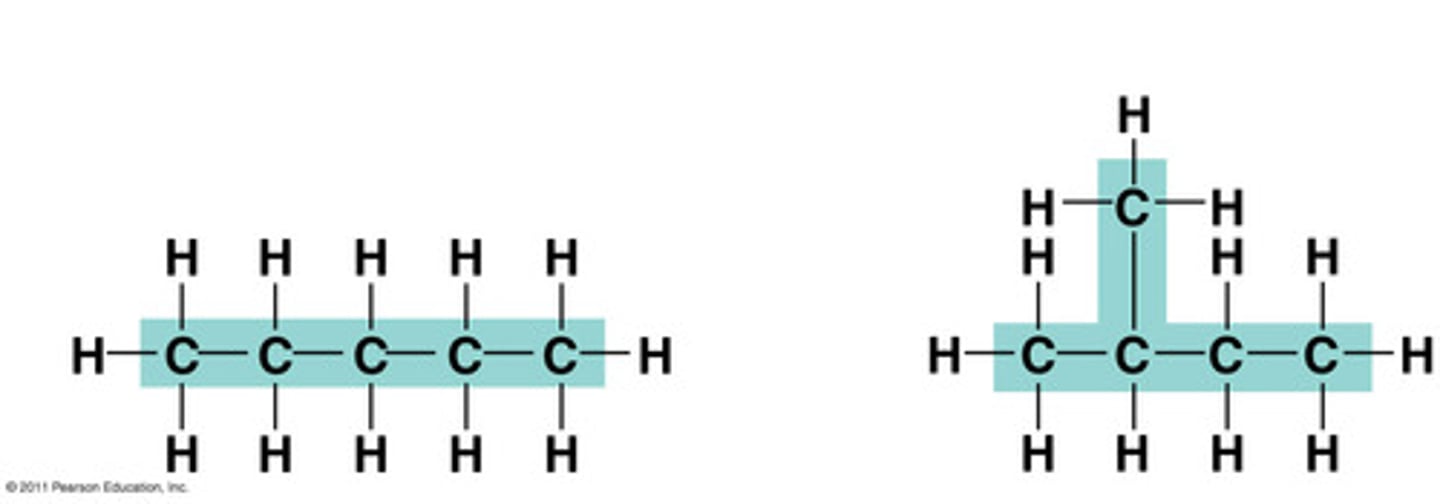
Structural isomers
have diff covalent arrangments of their atoms
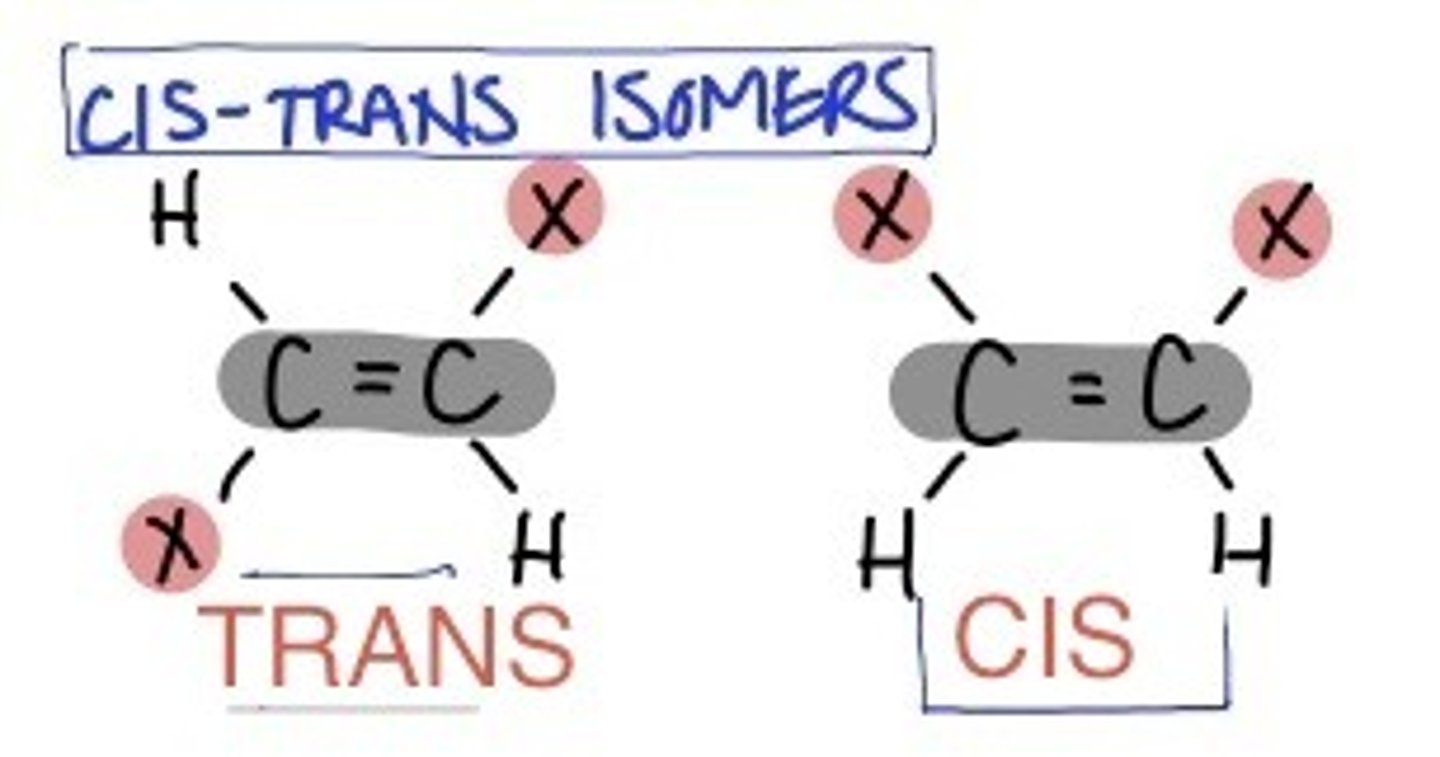
Cis-trans isomers
have the same covalent bonds but differ in their spatial arrangements
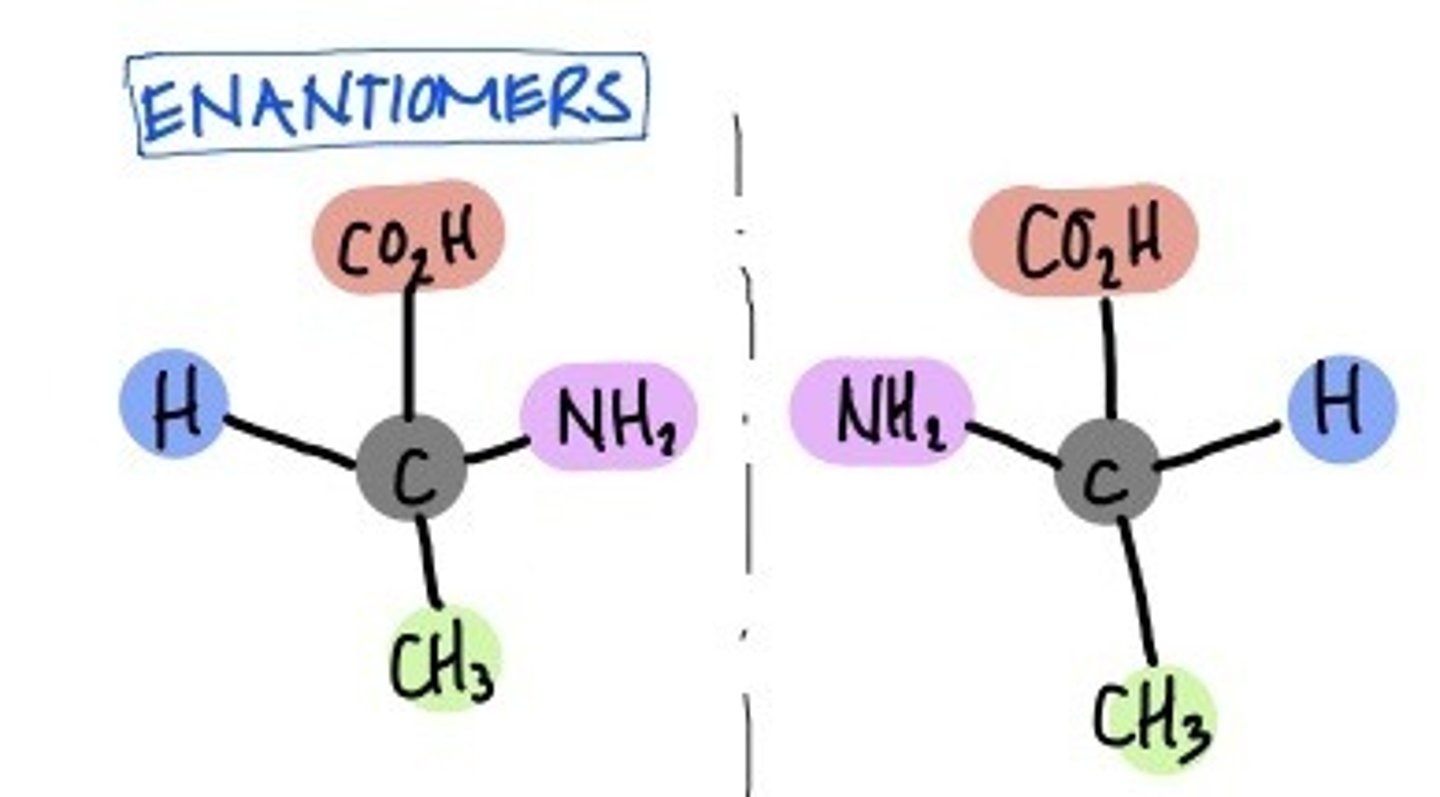
Enantiomers
isomers that are mirror images of each other
Functional groups
Components of organic molecules that are most commonly involved in chemical reactions
7 functions groups that are msot important in chem of life
- hydroxyl group
- carbonyl group
- carboxyl group
- amino group
- sulfhydryl group
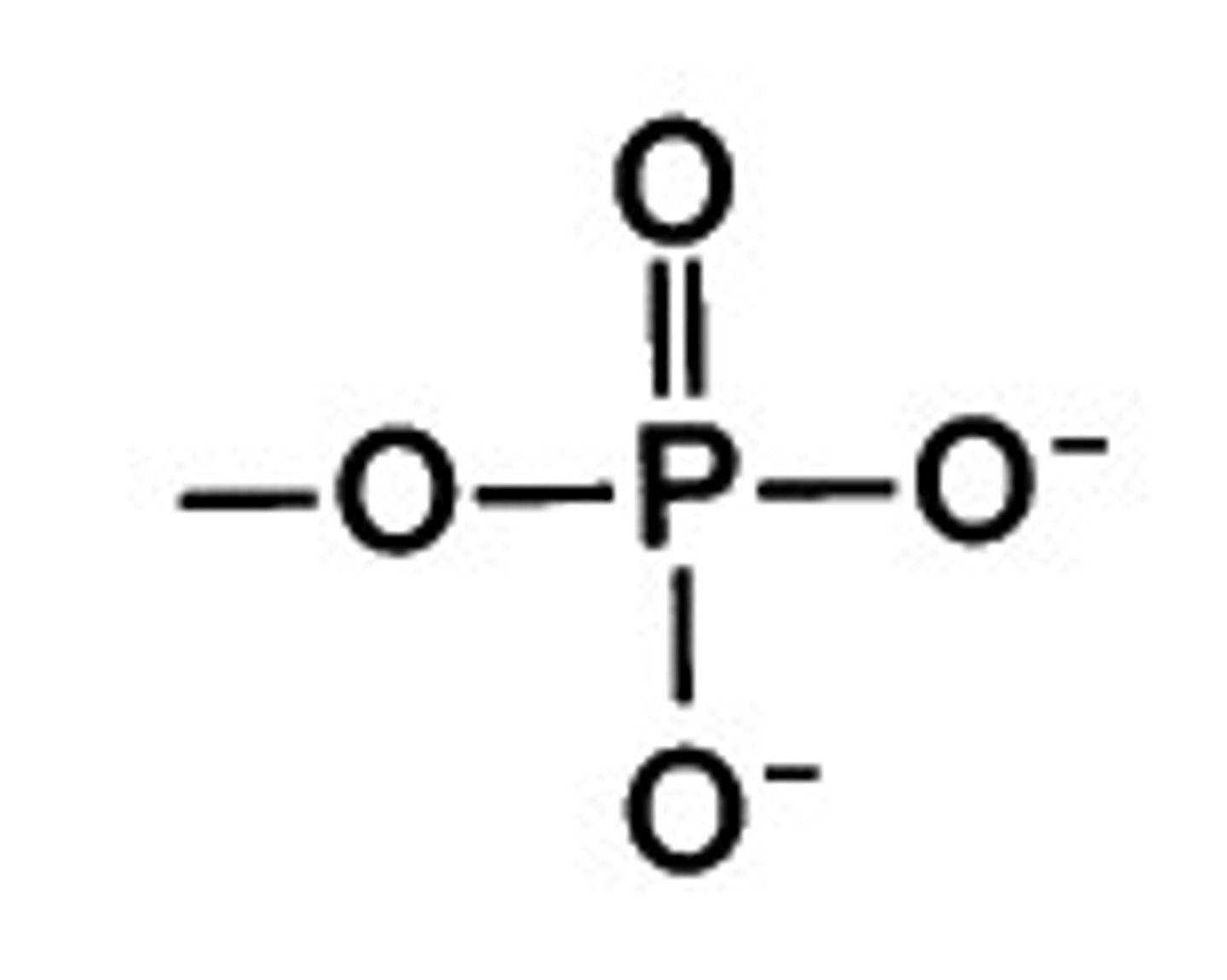
- phosphate group
- methyl group
Important organic phospate
ATP
ATP
adenine triphosphate
- stores the potential to react with water
Phosphate group
key for energy exchange
Methyl group
used to silence DNA (turn off genes)
Polar functional groups
- hydroxyl + carbonyl
- makes a molecule hydrophilic/H2O soluble
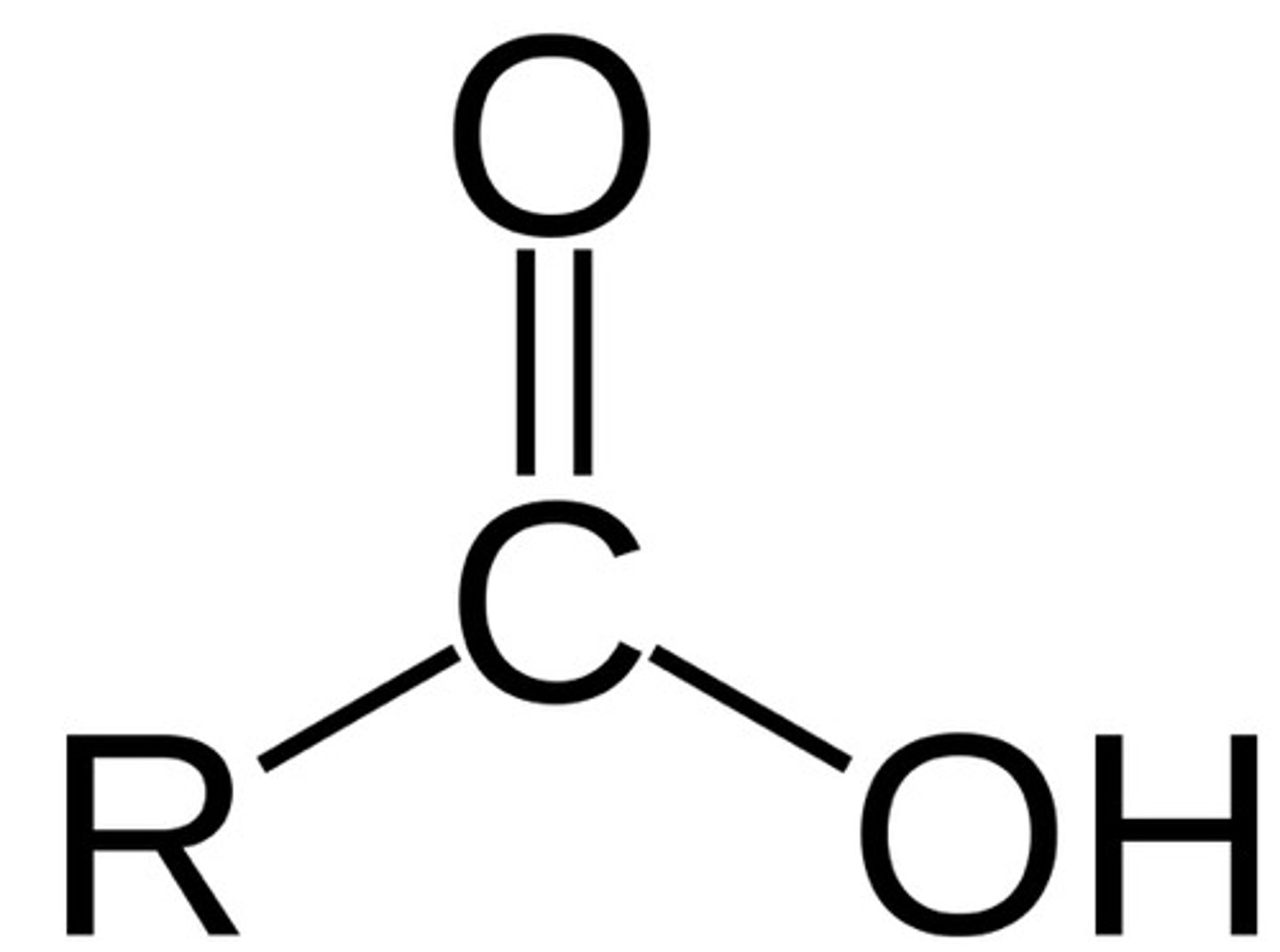
Carboxyl group
essential in amino acids
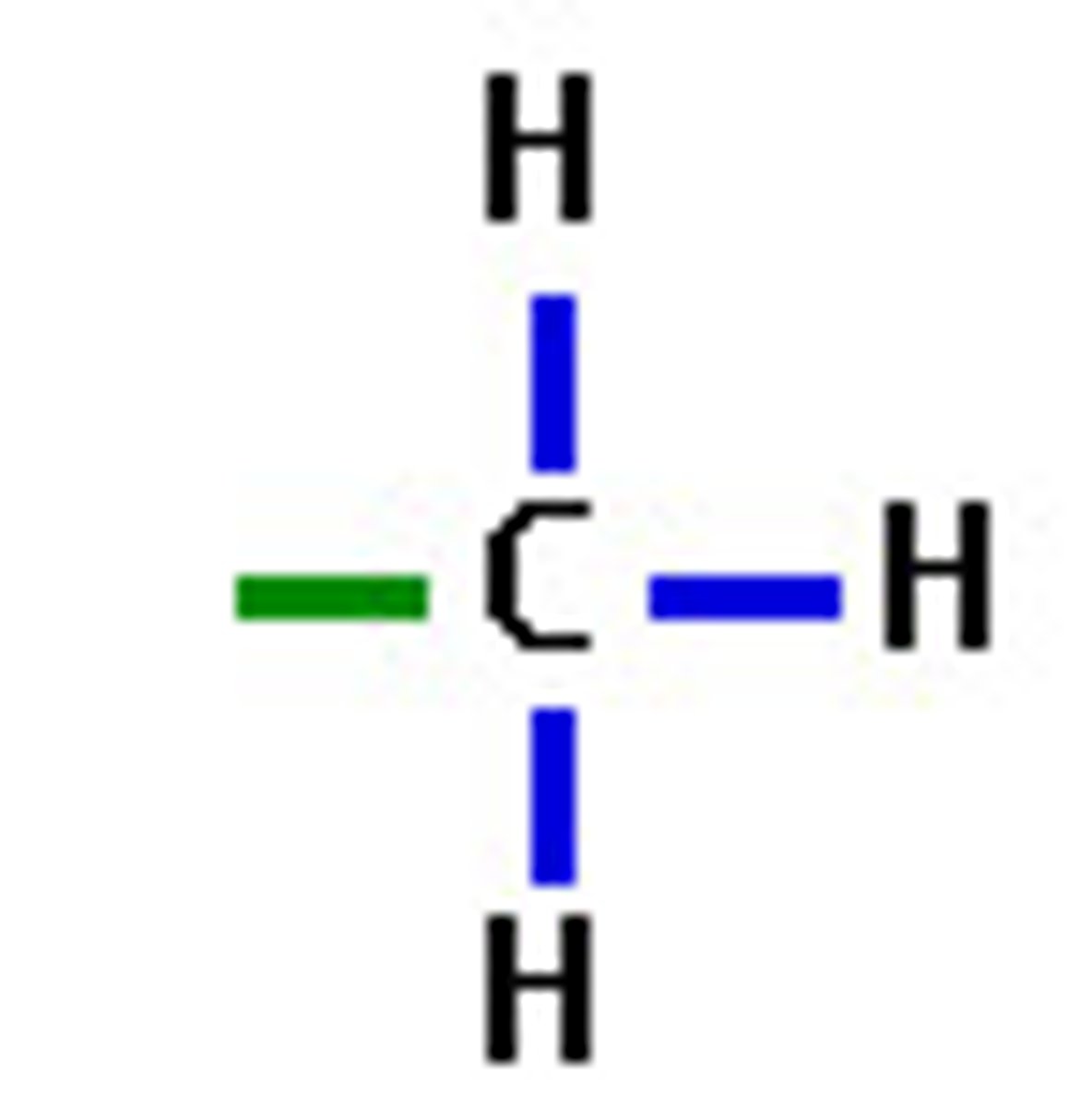
Amino group
essential in amino acids
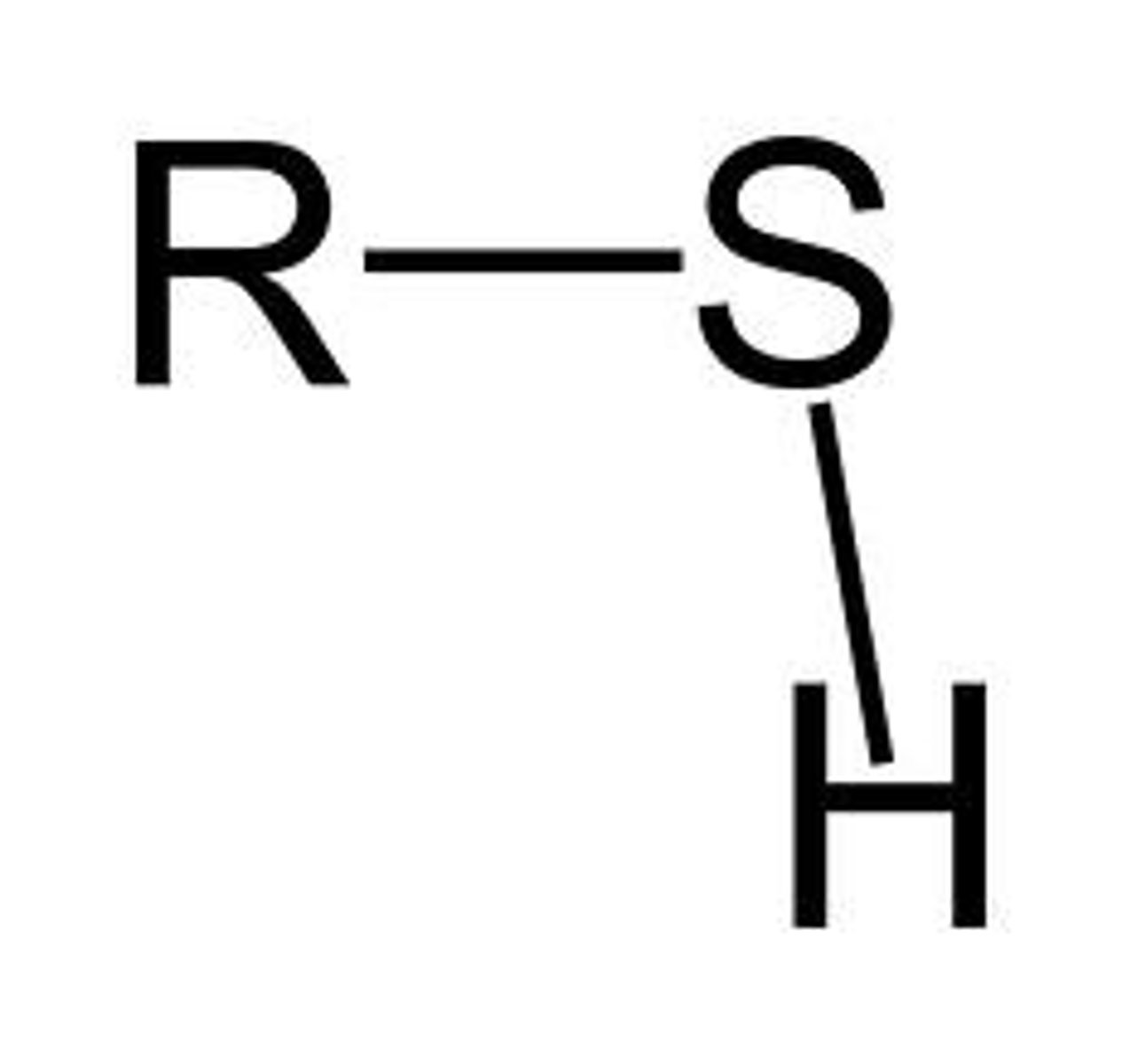
Sulfhydryl group
important in protein structure
Carbohydrates
source of energy & provide sturctrual support
Nucleic acids
store genetic info & function in gene expression
Proteins
wide range of functions
- Catalyzing reactions
- transporting substrates into & out of cells
Lipids
group of diverse molecules that dont mix well with H2O
- make up cell membranes
- provide energy
- act as hormones
Monosaccharides
energy sources + building blocks
disaccharides
energy transfer
polysaccharides
- energy storage
- structures
Macromolecules
large polymers
Polymer
long molecules consisting of many simnilar building blocks
Monomers
repeating units that serve as building blocks
Examples of polymers
- carbohydrates
- proteins
- nucleic acids
Examples of macromolecules
proteins, nucleic acids, polysaccharides
Combine monomers to make
polymers
Dehydration synthesis
enzymes pull hydroxyl group off of 1 monomer & pulls hydrogen off the other
- The H & Oh combine to form H2O
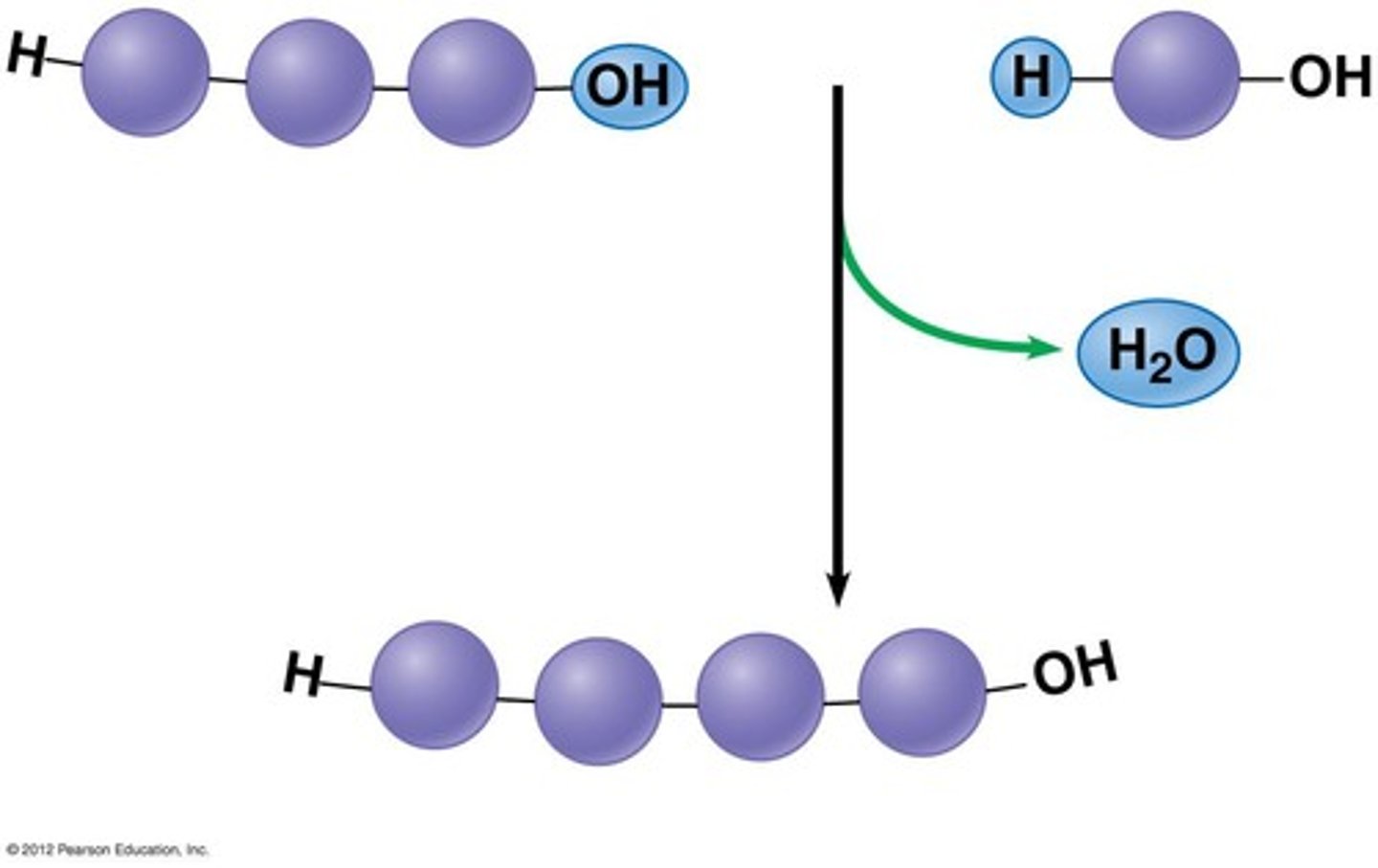
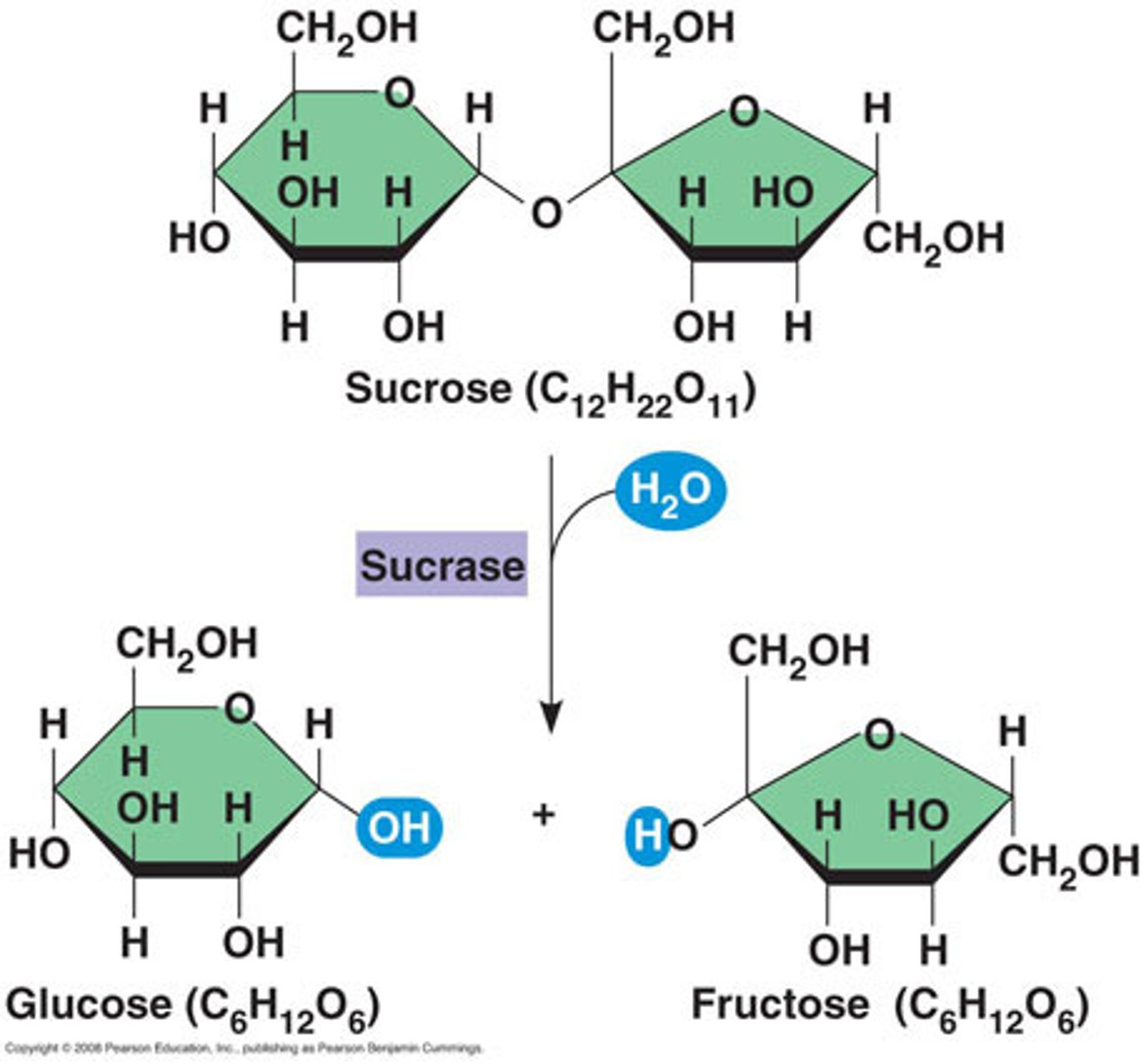
Hydrolysis
Enzymes insert a H2O molecule between the monomers making up the polymer
Enzymes
Specialized macromolecules that speed up chemical reactions such as those to make or break down polymers
The covalent bond between 2 monosaccharides
glycosidic linkage
Starch
a storage polysaccharide of plabts, consists of glucose monomers
Glycogen
storage polysaccharide in animals (readily available glucose for the body)
Cellulose
polymer of glucose
- major component of tough wall of plant cells
Chitin
structural polysaccharide
- found in exoskeleton of arthropods
Fats
constructured from glycerol + fatty acids
Glycerol
3-Carbon alcohol with a hydroxyl group attached to each carbon
Fatty acid
consists of a carboxyl group attached to a long carbon skeleton
Saturated fatty acids
max number of hydrogen atoms possible & no double bonds
- solid at room temp
Unsaturated fatty acids
have 1 or more double bonds
- liquid at room temp
Phospholipid
2 fatty acids & a phosphate group attached to glycerol
Strucutre of phospholipid
- 3 hydrophobic fatty acid tails
- 1 hydrophilic head
Steroids
lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of 4 fused rings
Cholesterol
type of steroid
- a component in animal cell membranes & a precursor from which other steroids are synthesized
enzymatic proteins
selective acceleration of chemical reactions
defensive proteins
protect against disease
storage proteins
storage of amino acids
transport proteins
transport of substances
hormonal proteins
coordination of an organism's activities
receptor proteins
response of cell to chemical stimuli
contractile & motor
proteins
movement
structural proteins
support
Proteins are constructed from the same set of
20 amino acids
Polypeptides
unbranched polymers built from these amino acids
Peptide bond
bond between amino acids
Protein
Biologically functional molecule that consists of 1 or more polypeptides
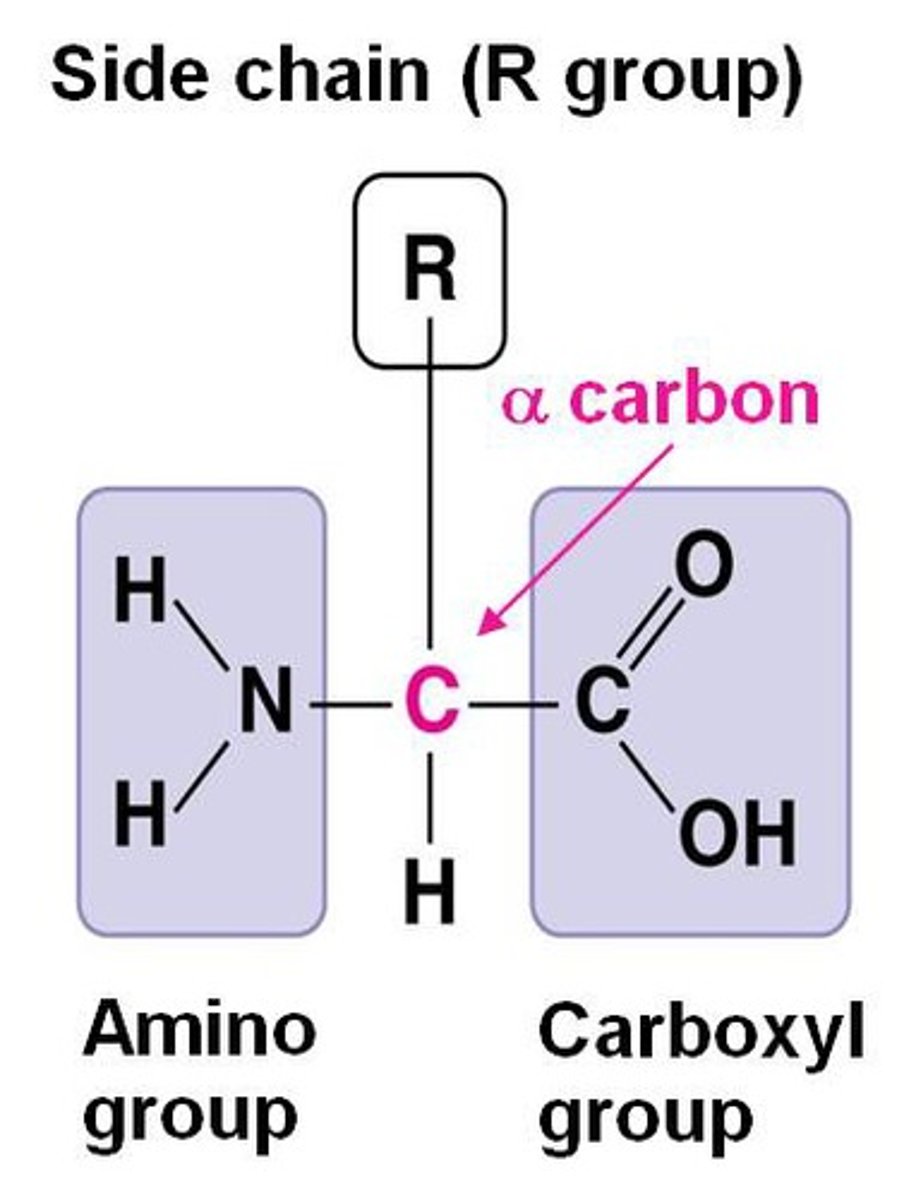
Amino acids
Organic molecules w amino & carboxyl groups
Why do amino acids differ in their properties?
due to differing side chains, called R groups
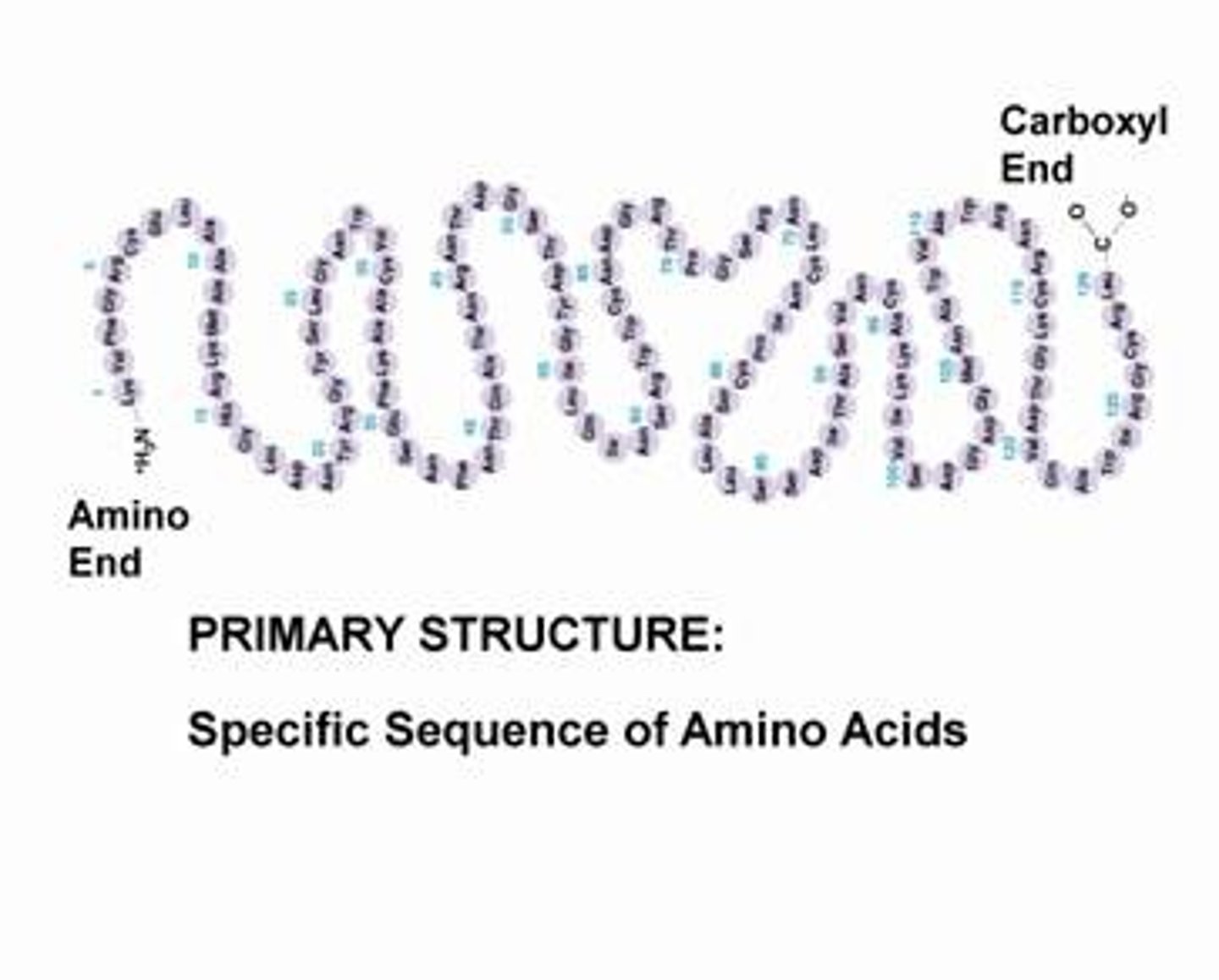
4 levels of protein structure
- primary structure
- secondary structure
- Tertiary structure
- quaternary structure
Primary structure
genetically determined sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
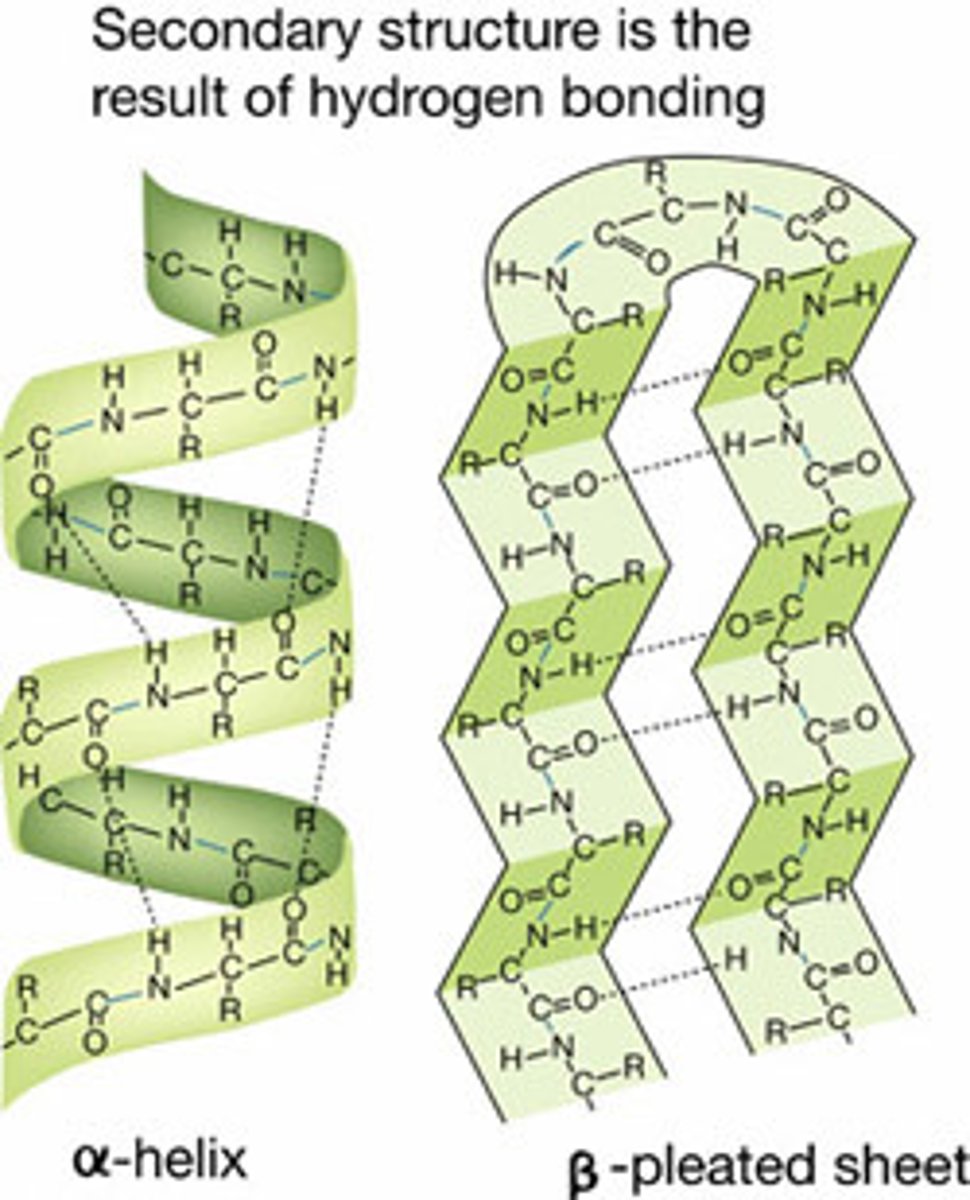
Secondary structure
involves interactions between carbonyl & amino groups in the polypeptide backbone
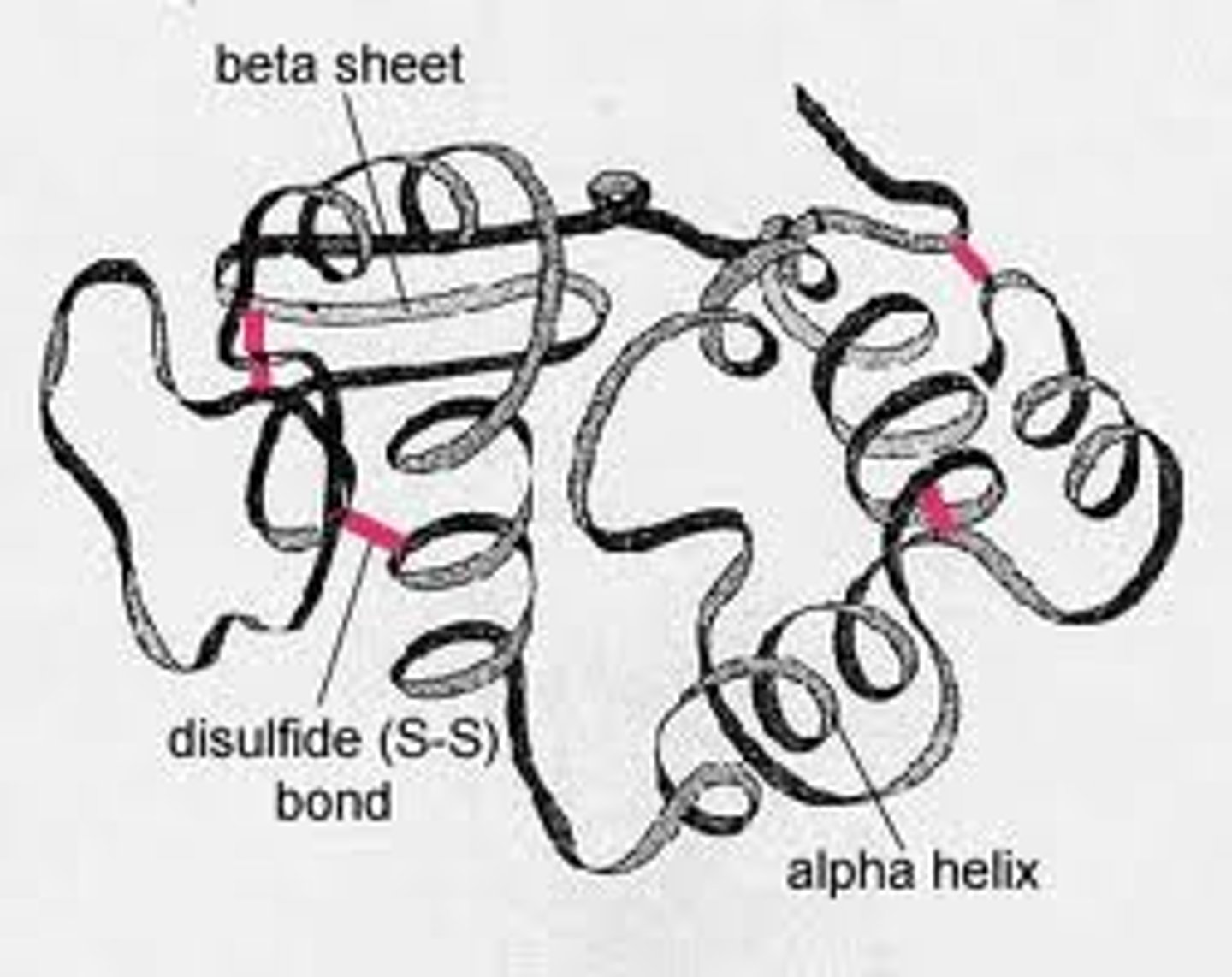
Tertiary structure
Interactions between amino acid side chains (R groups)
Quaternary structure
interactions between multiple folded tertiary polypeptides
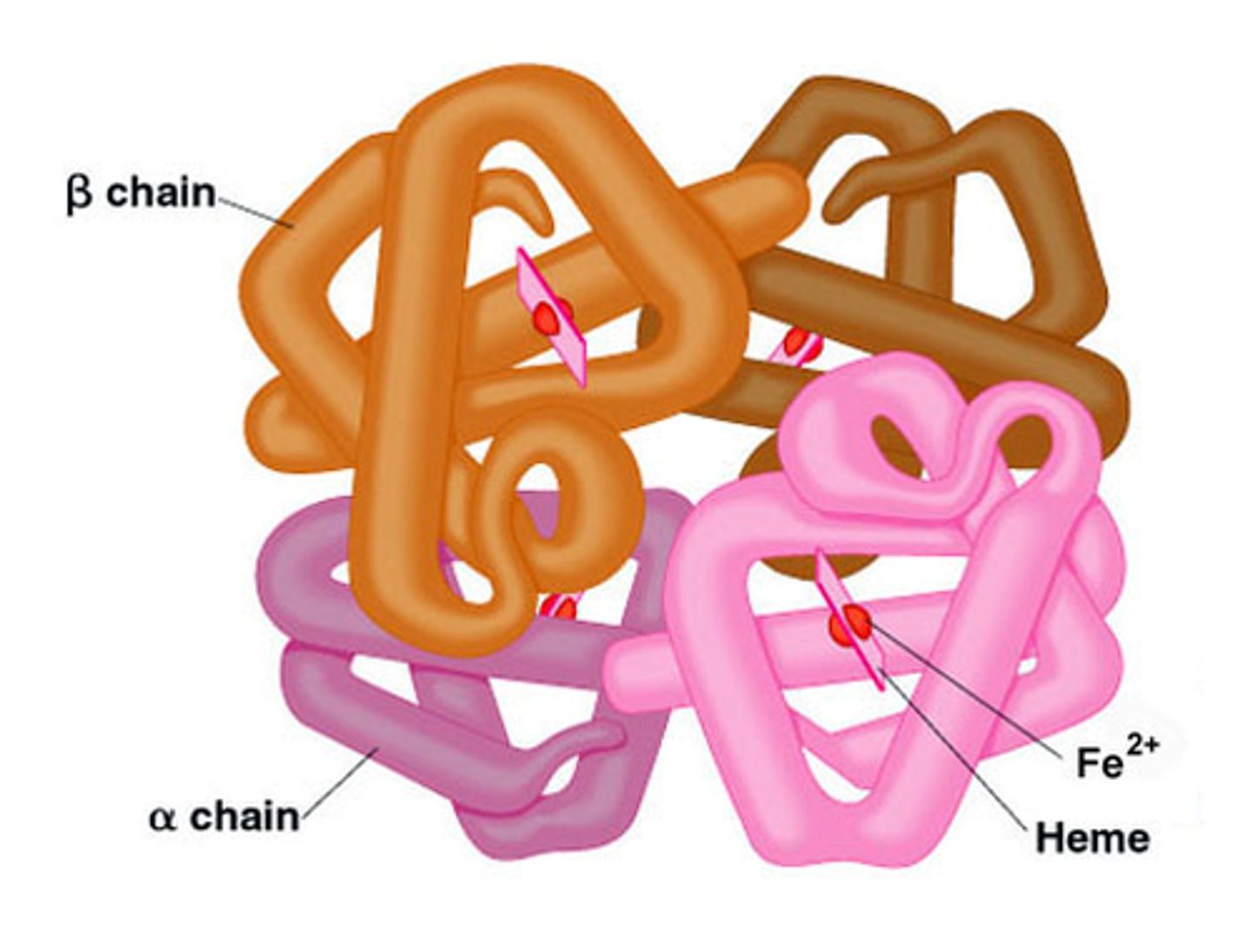
Sickle cell disease
inherited blood disorder, results from a single amino acid substitution in the protein hemoglobin
Denaturation
loss of proteins native structure