TERM 2 BIOLOGY- Sem 1 24'
1/203
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
204 Terms
generalised structure of an amino acid
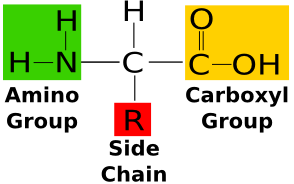
dipeptide
two amino acids
amino acids are joined together by a
type of covalent bond called a ‘peptide bond’
anabolism
synthesis of complex molecules from simpler molecules
polypeptide
many amino acids
condensation reactions remove water to form
a peptide bond
how many different amino acids are there
20
can plants manufacture all 20 amino acids
yes
can animals manufacture all 20 amino acids
no
how many amino acids are essential
9
how many amino acids are non-essential
11
there is an infinite variety of
possible peptide chains
DNA to RNA to
Polypeptide
sequence of amino acids is determined by
DNA
Proteome
set of proteins made by an organism
Denaturation
permanent change to the structure of a protein
how does heat affect polypeptides
breaks bonds between amino acids
how does extreme ph affect polypeptides
higher or lower breaks bonds or causes new interactions
Organelle
structure that is specialised for a specific function within a cell
cell structures that are not organelles
cell wall, cytoskeleton, cytoplasm
no membrane
ribosomes, centrioles, microtubules, proteasomes, nucleoli
single membrane
vesicles and vacuoles, rough er, smooth er, golgi, lysosomes
double membrane
nuclei, mitochondria, chloroplasts, amylopasts, chromoplasts
cell walls are not organelles because
they are extracellular structures
cytoskeletons are not organelles because
they consist of narrow protein filaments and not discrete enough
cytoplasm is not a discrete structure because
many different structures and functions
how many organelles do prokaryotic cells have compared to eukaryotes
fewer
translation can not begin in eukaryotes until
mRNA has passed out of the nucleus via the pores in the nuclear membrane
why does translation wait to begin in eukaryotes for mRNA
allows mRNA to perform post-transcriptional modification
advantages of compartmentalisation in the cytoplasm of cells
enzymes and substrates can be much more concentrated, substances that could cause damage kept inside the membrane, conditions like ph can be maintained, organelles with their contents can be moved around within the cell, larger area of membrane available for processes
adaptations of the mitochondrion for production of a ATP by aerobic cell respiration
outer membrane separates the contents of the mitochondrion from the rest of the cell, cristae projections of the inner membrane that increase surface area, matrix fluid filling the compartment containing all enzymes and substrates for the krebs cycle
adaptations of the chloroplasts for photosynthesis
double membrane, extensive system of internal membranes called thylakoids, small fluid-filled spaces inside the thylakoids, colourless fluid around the thylakoids
what do thylakoid membranes ensure
the chloroplast has a large light-absorbing capacity often arranged in stacks called grana
stroma
a compartment of the plant cell in which the enzymes needed for the calvin cycle
functional benefits of the double membrane
the hydrophobic core is never exposed to water, pores are formed using integral proteins
where are mRNA, tRNA and ribosomes produced
in the nucleus and exported to the cytoplasm
structure and function of free ribosomes and of the rough er
produce proteins used within the cell, on rough er produce proteins for secretions (exported from the cell)
structure and function of the golgi apparatus
processes proteins from the rough ER, packages into the vesicles for secretion
structure and function of vesicles in cells
formed during endocytosis and are made within cells by pinching of a section of membrane to surround a substance used to move things around in cells
DNA is
the genetic material of all living organisms
is dna a nucleic acid
yes
what are the 4 major types of molecules
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
functions of nucleic acids
pass information between generations, code for protein productions
types of nucleic acids
DNA and RNA
DNA function
passes heredity information between generations of cells, codes for making RNA during transcription
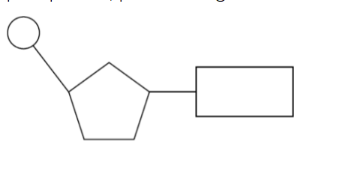
nucleotide structure
sugar-phosphate backbone structure
RNA function
codes for making proteins during translation
what are the 3 types of RNA involved in protein synthesis
mRNA, rRNA , tRNA
some viruses do not have DNA and use
RNA as their genetic material
what are nucleic acids
chains of nucleotides combined in condensation reactions
what is the nucleotide considered as
the monomer or the nucleic acid polymer
parts of a nucleotide
purine or prymidine nitrogenous base, five-carbon pentose sugar, negatively charged phosphate group
pentose sugars
have 5 carbon atoms, nitrogenous base connects off of carbon 7, carbon 5 branches out of the ring
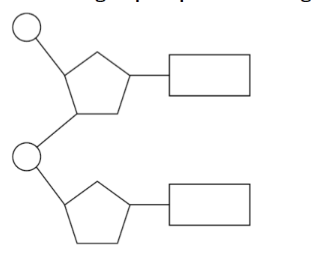
nucleic acid condensation reaction
the backbone is formed when nucleotides combine in a condensation reaction
the molecular DNA double-helix shape is formed by two sugar-phosphate backbones
that run antiparallel to each other and twist together in a helical shape
mRNA
encodes proteins
tRNA
acts as adaptor between mRNA and amino acids
rRNA
forms the ribosome
the sugar-phosphate backbones of nucleic acids provides
structural support
sharing electrons in the covalent bond between sugar and phosphate provides
strength to the structure
five different nitrogenous bases
adenine, thymine, cytosines, guanine, uracil
nitrogenous bases
the bases all have different molecular structures however all five contain nitrogen atoms
Gene
specific sequence of nitrogenous bases in DNA nucleotides that codes for making of a protein
process of decoding a gene consists of two major steps
transcription and translation
RNA as a polymer is formed by
condensation of nucleotide monomers
four nitrogenous bases in RNA
adenine, uracil, cytosine, guanine
DNA as a double helix made of
two antiparallel strands of nucleotides
four nitrogenous bases in DNA
adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine
DNA backbone is formed when nucleotides
combine in a condensation reaction
two strands of the double helix run in
opposite directions
nitrogenous bases join together by
hyrdrogen bons
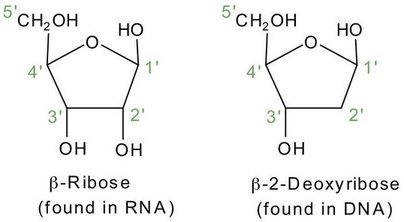
sugar in DNA
deoxyribose
sugar in RNA
ribose
how many backbones in DNA
2
how many backbones in RNA
1
DNA uses thymine
RNA uses uracil
DNA function
passes heredity information between generations, codes for making RNA during transcription
RNA function
codes for making proteins during translation, mRNA, rRNA and tRNA involved in protein synthesis
in the eukaryotic cell DNA
located in the cell nucleus
in the eukaryotic cell RNA
made in the nucleus for transcription but transported to the cytoplasm for translation
in the prokaryotic cell DNA
contained in the nucleoid
in the prokaryotic cell RNA is
found in the cytoplasm
in DNA replication the new strand is built by
by reading the template and adding the complementary DNA nucleotide (semiconservative)
base pairing during transcription
enzyme RNA polymerase builds on RNA strand by reading the DNA template and adding the complementary RNA nucleotide
base pairing during translation
amino acids are brought to the ribosome by tRNA, tRNA forms a temporary bond to the mRNA using complementary base pairing
DNA as an information storage molecule
stores information in the sequence of the nitrogenous bases
What is the capacity of DNA to store information
it is limitless
conservation of the genetic code across all life forms as evidence of universal common ancestry
the sequence of bases forms a code, the genetic code is universal, the universality of the genetic code is due to the LUCA
Pentose sugar
function of codons
code for amino acids
how is a protein made in a cell by the process of translation
RNA is translated using tRNA, this happens in the cytoplasm, mRNA attaches to the ribosomes ribosome forms two subunits, using tRNA the sequence of mRNA is translated in a sequence of amino acids and a polypeptide is formed, once coming to a stop the polypeptide chain is formed and breaks off
Explain the significance of complementary base pairing in DNA
connects two sugar phosphate backbones resulting in stability and the shape of the double helix, ensure one parent strand is present when a new DNA strand is being created, codes for proteins
carbohydrates
carbon, hyrdrogen, oxygen
what are carbohydrates composed of
recurring monomers called monosaccharides
monosaccharides
single sugars
what do monosaccharides form
ring structures as a result of a chemical reaction between functional groups at opposite ends of the molecule
monosaccharide cyclration
hydroxyl group links to a carbonyl group to form a cyclic structure connected by an oxygen atom
how many carbons do most monosaccharides have
5 or 6
carbons
pentose sugars