Chapter 8 Microeconomics
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
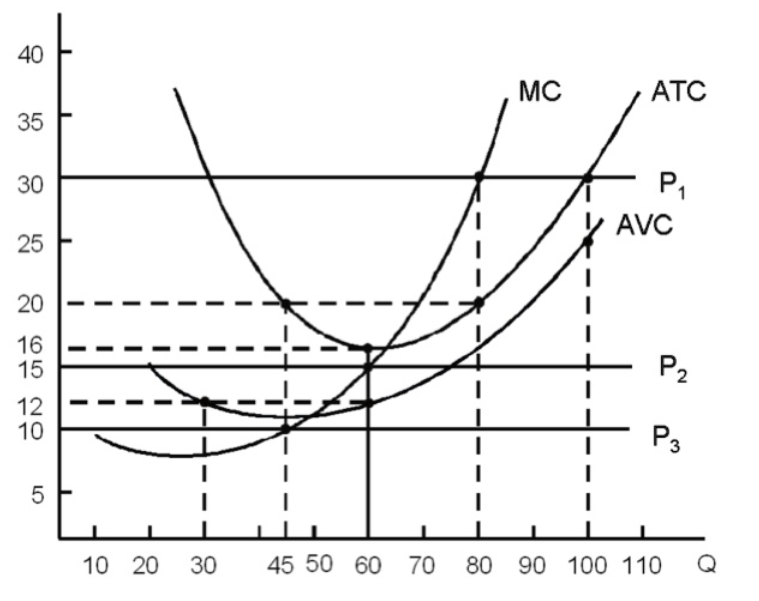
What is the total profit or loss for this perfect competitor if the industry price is equal to $30? Explain your answer and show your calculations.
If the industry price is $30 then the marginal cost is also $30 if this is a perfect competitor. each unit of the quantity of 80 is priced at $30 according to the graph. The Average Total Cost Curve at quantity 80 is equal to $20 for each unit. To find the total profit we must find total revenue and subtract the total cost from it. The total revenue is equal to 80 times $30 which equals $2400. The Total cost is equal to 80 times $20 which is $1600. Next we subtract $1600 from $2400 and get $800 as our profit. Total Revenue= 8030=2400. Total Cost=8020=1600. Profit= Total Revenue-Total Cost= $2400-$1600= $800
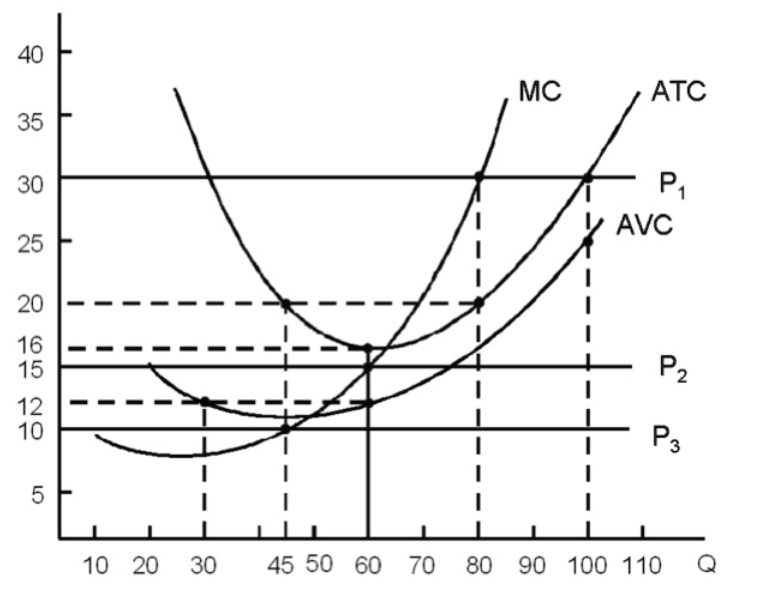
If the industry price falls to $10, what if the level of output for this firm?
0
Explain why the perfectly competitive firm is allocatively efficient.
Competitive firms are allocatively efficient because the firms are price takers. The firms take the market price as the price of their own product. This market price is the value a consumer places on a product. The firm will not overproduce or underproduce the product. By doing this the firms production reflects the preferences of consumers to maximize societal welfare.
Explain why and how the perfect competitor will always break even in the long run.
When a firm breaks even in the long run it means it earns an economic profit of zero. Zero economic profit means that the firm covers all implicit and explicit costs. This is different from Accounting profit where it doesn't take into account implicit costs or in other words opportunity cost, meaning the firm makes a accounting profit when economic costs is zero. A perfect competitor will also produces at the quantity where p=mc so that it doesn't suffer any losses. The last reason why perfect competitors break even in the long run is that they can freely exit the industry in other words they don't experience any extra costs leaving the industry.

Given the data provided in the table below, what will the fixed costs equal for production at quantity (Q) level 4?
$9.00

Given the data provided in the table below, what will the marginal revenue equal for production at quantity (Q) level 4?
$5.00
If the quality differences of similar products are mostly imperceptible to the average consumer's eyes, which of the following will most likely play a major role in influencing the decisions of purchasers?
price of competing products
Firms operating in a market situation that creates _____ , sell their product in a market with other firms who produce identical or extremely similar products.
perfect competition
If a competitive firm experiences a shift in costs of production that decreases marginal costs at all levels of output,
expanding output levels at any given price will be profitable.
Under perfect competition, any profit-maximizing producer faces a market price equal to its
marginal costs
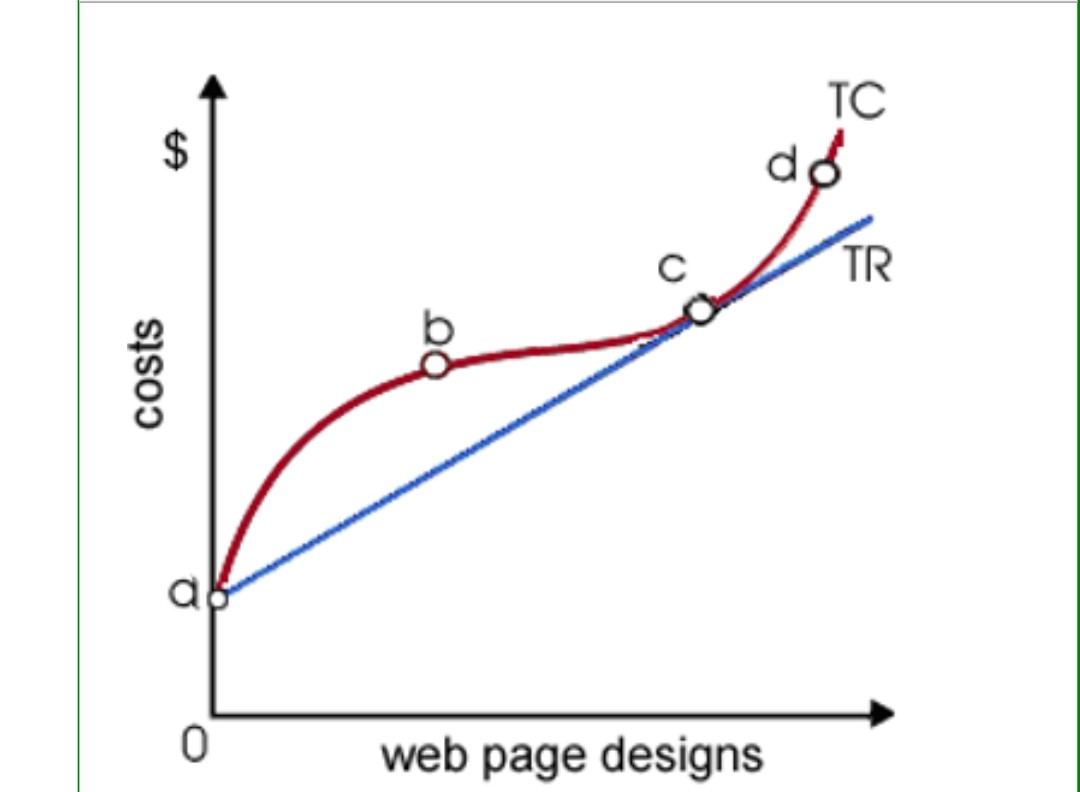
Refer to the diagram above. Which of the following explains the slope of the total revenue curve illustrated in this graph?
total revenue shown as a straight line sloping up indicates a perfectly competitive firm. And. The slope of the total revenue curve is determined by the price of the goods

Given the data provided in the table below, what will the marginal cost equal for production at quantity (Q) level 4?
$4.00
When a firm makes plans for investments in physical capital, it compares the _ on these investments with ____.
projected rates of return; the cost of financial capital to the firm
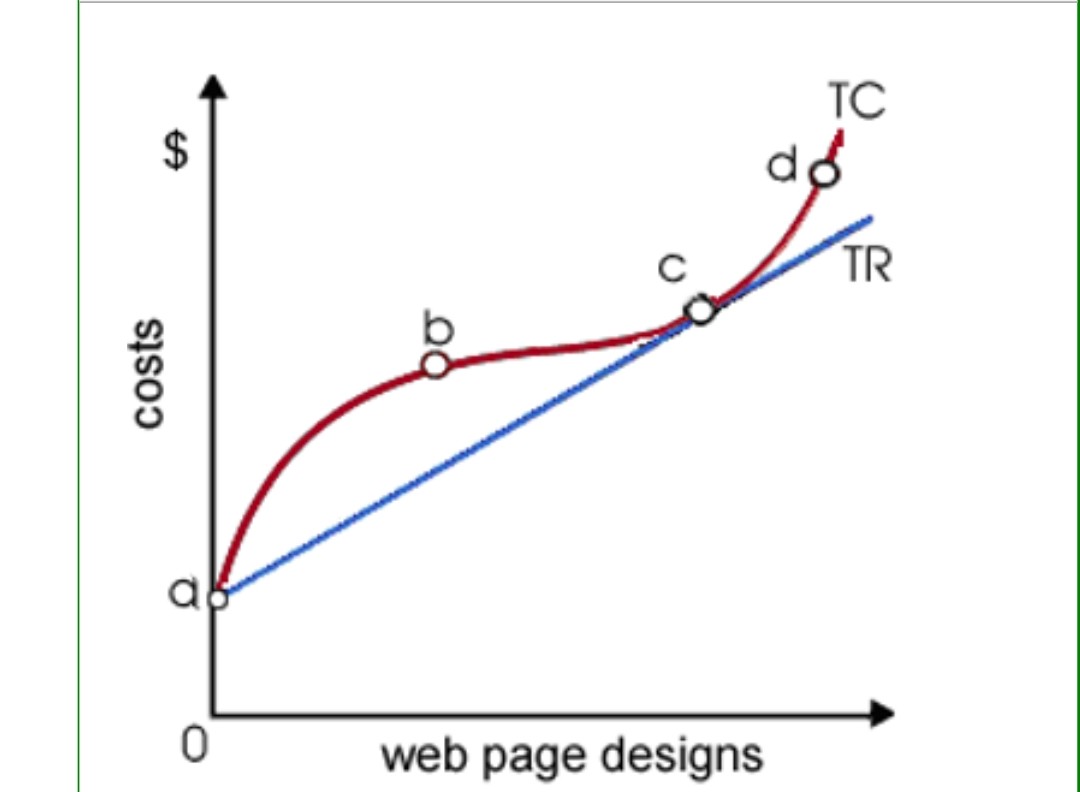
Refer to the diagram above. In this instance, the range of production possibilities at point d,
is a steeper slope reflecting a return to losses due to diminishing returns.
A perfectly competitive industry is a
hypothetical extreme.
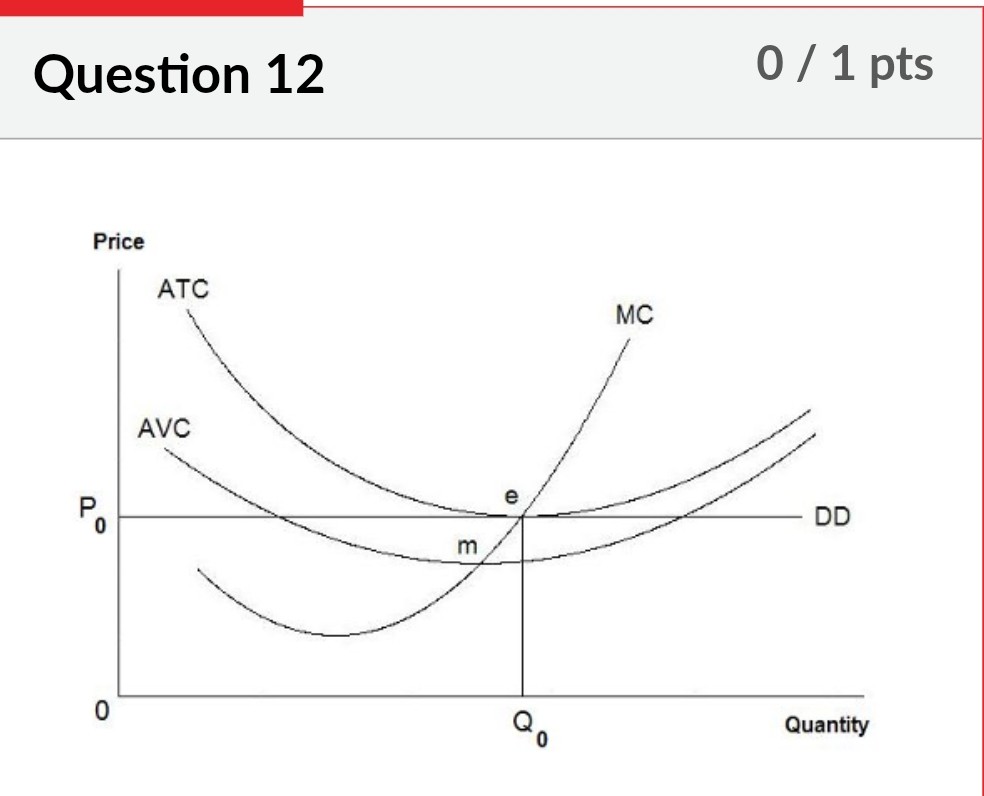
Refer to the diagram above. In this instance, the marginal revenue curve
reflects a perfectly competitive firm. And. is equal to the price of the good. And. is a horizontal straight line
For a perfectly competitive firm, the marginal cost curve is identical to the firm's .
supply curve
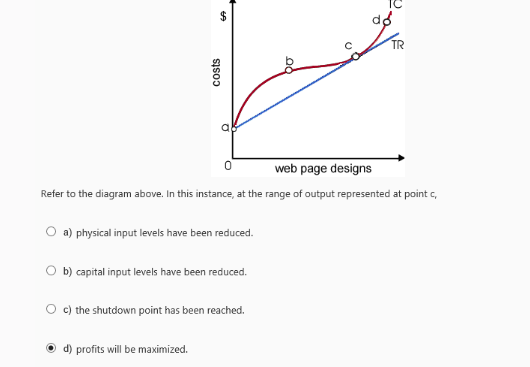
Refer to the diagram above. In this instance, at the range of output represented at point c,
profits will be maximized.
When I'MaGoldMiner chooses what quantity of gold each of its mines will produce over the next 12 months, this quantity, along with the prices prevailing in the market for output and inputs, will
determine the company's total revenue, total costs, and its profits.

Given the data provided in the table below, what will the amount of profit be for production at quantity (Q) level 7?
-$10.00
An _ is calculated by subtracting the firm's costs from its total revenues, _.
accounting profit; excluding opportunity cost
I'maGoldMiner has benefited from a record rise in gold prices in the global commodities market. While the price of its output is highly influenced by market speculation, if it wants to increase production to take advantage of the current profit-maximizing opportunity, the company
must accept market price for its physical capital inputs.
In economic terms, a practical approach to maximizing profits requires an examination of how changes in production affect ____ and ____.
marginal revenue; marginal cost
If a firm is producing so that the point chosen along the production possibility frontier is socially preferred, then that firm is said to have reached
allocative efficiency
When a business adopts a strategy of reducing and/or discontinuing production in response to a sustained pattern of losses, it is
preparing to exit operations.
If marginal cost is rising in a competitive firm's short-run production process and its average variable cost is falling as output is increased, then
marginal cost is below average variable cost.
In a free market economy, firms operating in a perfectly competitive industry are said to have only one major choice to make. Which of the following correctly sets out that choice?
what quantity to produce
In Sam's greenhouse operation, labor is the only short term variable input. After completing a cost analysis, if the marginal product of labor is the same for each unit of labor, this will imply that
the average product of labor is always equal to the marginal product of labor.
In order to produce 100 oatmeal cookies, GoodieCookieCo incurs an average total cost of $0.25 per cookie. The company's marginal cost is constant at $0.10 for all oatmeal cookies produced. The total cost to produce 50 oatmeal cookies is
$20
refers to the additional revenue gained from selling one more unit.
Marginal revenue
When a firm uses retained profits to invest in more energy efficient equipment, an economist would calculate the _ of investing in physical capital.
opportunity cost
What happens in a perfectly competitive industry when economic profit is greater than zero?
existing firms may expand their operations. And. firms may move along their LRAC curves to new outputs. And. there may be pressure on the market price to fall. And. new firms may enter the industry and all of the above
In the ____ , the perfectly competitive firm will seek out ____ .
short run; the quantity of output where profits are highest
In the _, if profits are not possible, the perfectly competitive firm will seek out the quantity of output where
short run; losses are smallest
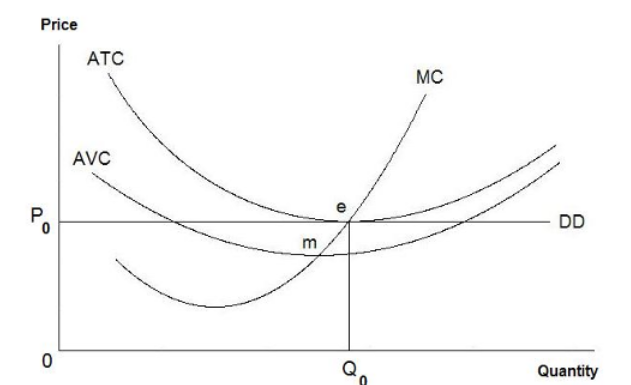
Refer to the diagram above. Based on the information illustrated in this graph, which of the following is an accurate statement?
profits will be reduced by production in the zone where MC exceeds MR
In economics, labor demand is synonymous with
derived demand.
If the price that a firm charges is higher than its _ cost of production for that quantity produced, then the firm will earn profits.
average
If a graph is used to compare total revenue and total cost of a perfectly competitive firm, then the horizontal axis of the graph will represent the __ and the vertical axis will represent _
quantity produced; both total revenue and total costs, measured in dollars.
If accounting profits for a firm are 20% of output, and the opportunity cost of financial capital is 8% of output, then what do the firm's economic profits equal?
12% of output
The term _ refers to a firm operating in a perfectly competitive market that must take the prevailing market price for its product.
price taker
In the , the perfectly competitive firm will react to losses by .
long run; reducing production or shutting down
Economic profit can be derived from calculating total revenues minus all of the firm's costs,
including its opportunity costs.
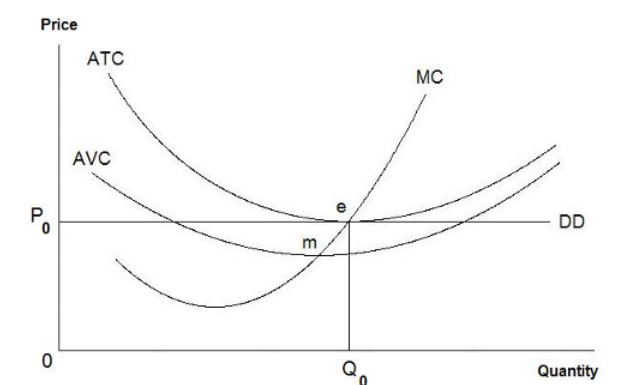
Refer to the diagram above. In this instance, point e shown on the graph indicates
the profit-maximizing point where MR = MC