Structural Levels of Proteins and Denaturation
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
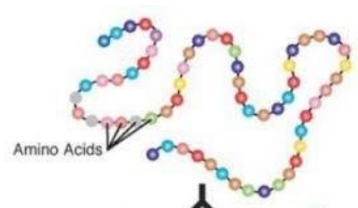
Primary protein
Is a sequence of a chain of amino acids
Secondary protein
Occurs when the sequence of amino acids are linked by hydrogen bonds
The polypeptide chains are folded regularly
Hydrogen bonding causes protein chains to fold and align to produce orderly patterns
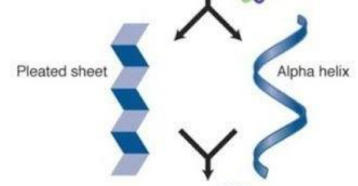
The 2 prominent structure of secondary proteins are
Alpha helix
Beta pleated sheet
Alpha helix
Single protein chain twisted to resemble a coiled helical spring
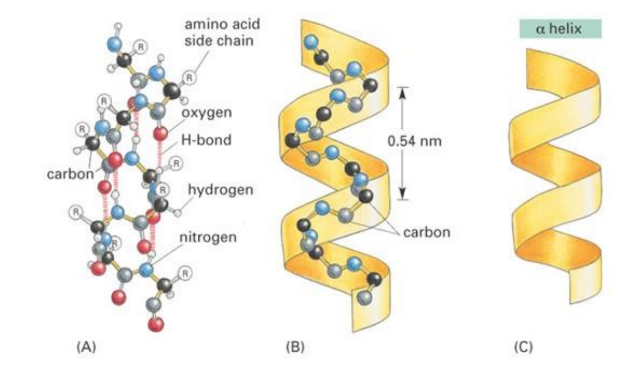
Alpha helix is stabilized by
hydrogen bonds between the electropositive nitrogen atom of a peptide linkage and the electronegative carbonyl atom of the 4th amino acid on the amino terminal side of the peptide bond
Left alpha helix
The n-terminal is on the left side

Right alpha helix
The n-terminal is on the right side

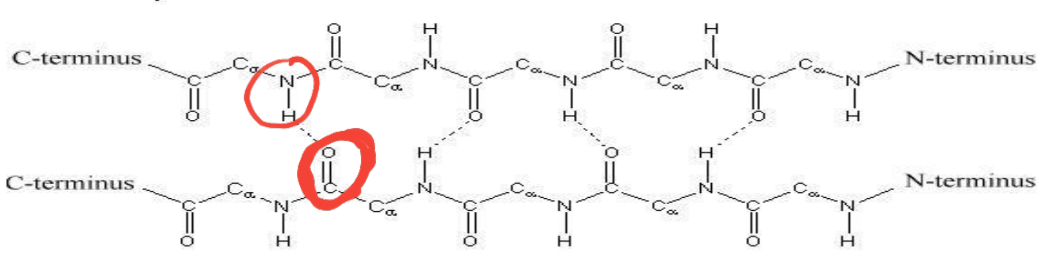
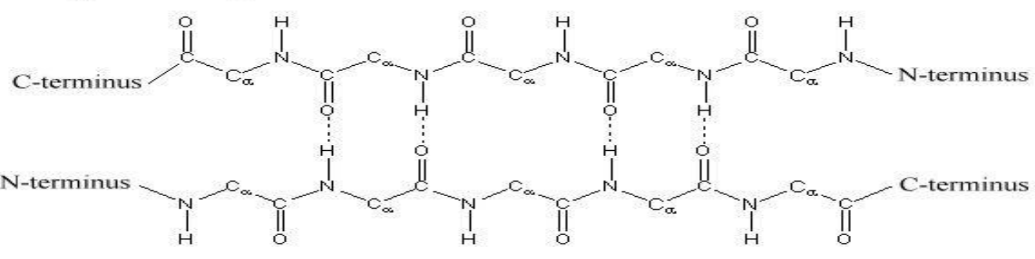
Beta pleated sheet
The polypeptide chain is extended into a zigzag arrangement
Polypeptide chains are arranged side by side in the form of pleats/sheets
The adjacent chains can be parallel or antiparallel
What stabilize the beta pleated sheet
Hydrogen bonds are formed between adjacent segments of polypeptide chains
Parallel beta sheet
Antiparallel beta sheet
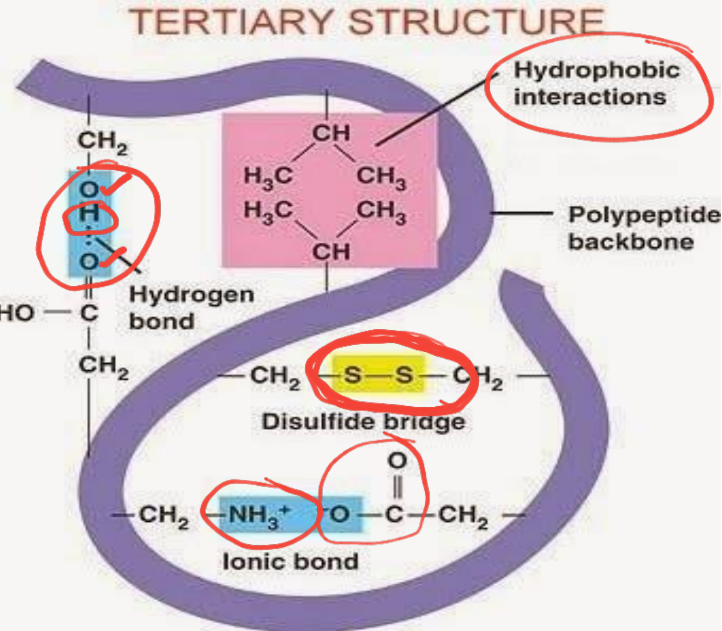
Tertiary protein
Occurs when certain attractions between alpha helices and pleasted sheets
It is the overall three-dimensional arrangement of all atoms in a protein
Forces involve to stabilize the tertiary and quaternary protein structure
Hydrophobic interactions (nonpolar groups cluster inside)
Hydrogen bonds (between polar groups)
Disulfide bridges (-S-S-) (covalent bonds between cysteine residues)
Ionic bonds (between charged side chains)
Quaternary protein
Is a protein consisting of more than one amino acid chain
The arrangement of two or more polypeptide chains (subunits) into a functional protein.
Example:
Hemoglobin (contains 4 subunits)
Collagen (triple-helix structure)
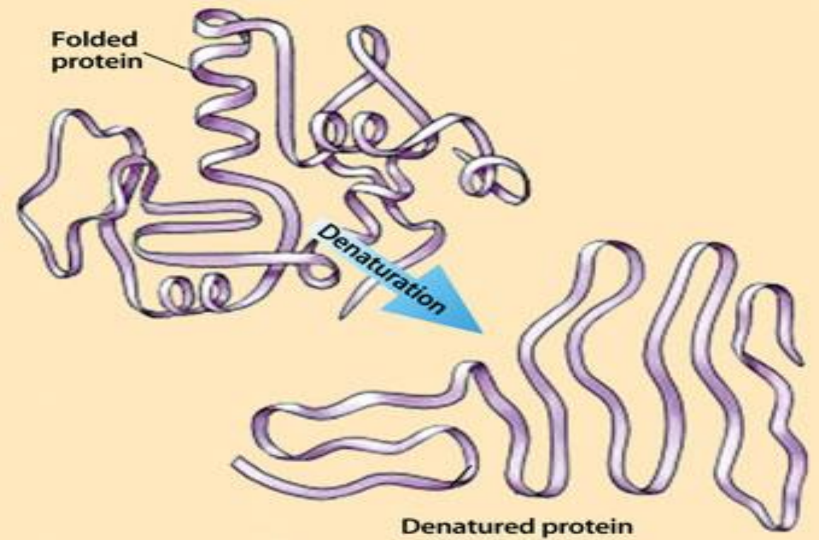
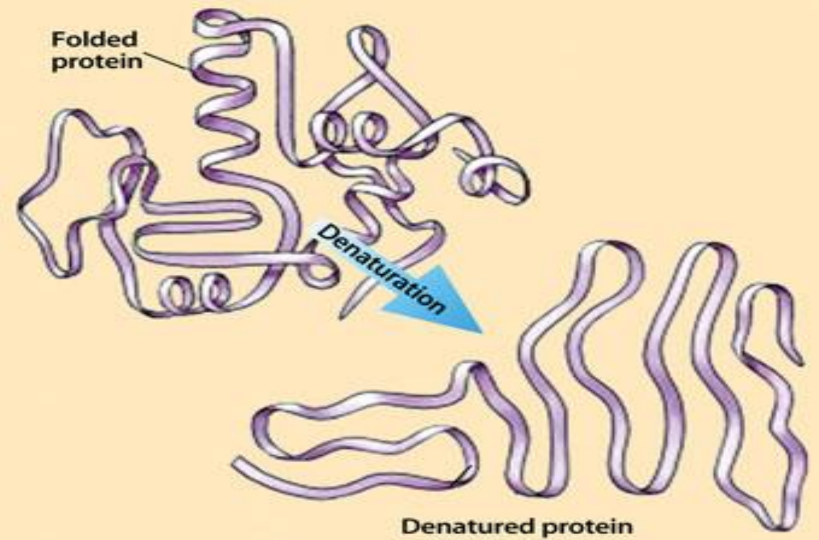
Denaturation
Is the structural changes in proteins that can cause loss of function due to:
heat
extreme pH
organic solvents
solutes
Hemoglobin
Transport protein that carries oxygen in the blood
Collagen
Fibrous protein in connective tissue
Found in tendons, bone, cartilage, and blood vessels
Ferritin
Protein that stores iron in the liver
Actin and Myosin
Proteins that control muscle contraction
Keratin
fibrous protein in hair, skin, and nail
Myoglobin
Protein that stores oxygen in tissues
Insulin
Protein hormone synthesized in the pancreas
Controls blood glucose levels
Types of Denaturation
Flocculation
Coagulation
Flocculation
clumping together of the dispersed chain of the denatured protein
this denaturation is reversible
Coagulation
Occurs when the flocculated protein is heated further. The clumped chains become insoluble not only at its isoelectric pH but also over the entire pH range
this denaturation is irreversible