CH4- Tissue Level
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
tissues
group cell in body work together for common functions
histology
study of tissues
tissues categories
epithelial tissue
connective tissue
muscle tissue
nervous tissue
epithelial tissue
cover surface, line passageways
makeup certain glans
GI tract, skin surface
connective tissue
bind things together
fat and soft padding (tissue, bone,tendon)
muscle tissue
responds to stimulus to contract and provide movement
cardiac, smooth, skeletal
nervous tissue
allow propagation of electrochemical signals for communication
brain, spinal cord, nerves
tissue membrane
thin sheet of cell create lining
epithelial tissue is a
large sheet of cell
top polarity
apical surface
bottom polarity
basal surface
cell junctions
cell-to-cell junctions
tight, gap, anchoring junctions
body systems must cross ___
epithelium
squamous epithelial
flat
cuboidal epithelial
equal height x width
columnar epithelial
tall
rectangular
simple
one layer
stratified
multiple layer
pseudostratified
messy arrangment
transitional
urinary organs to expand, stretch
bladder, ureters
simple squamous epithelium
pass through diffusion and filtration
air sac, blood vessels
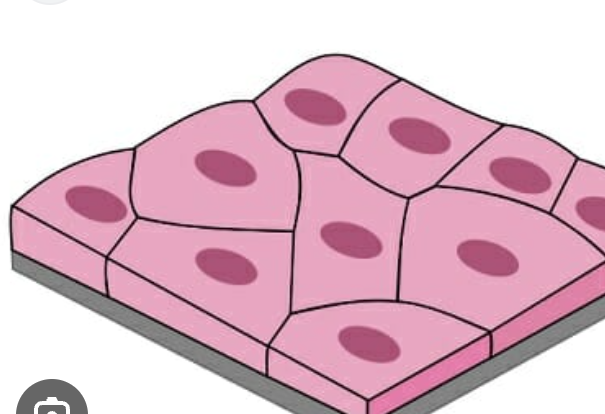
simple cuboidal
secrete and absorbs
small gland and kidney tubules

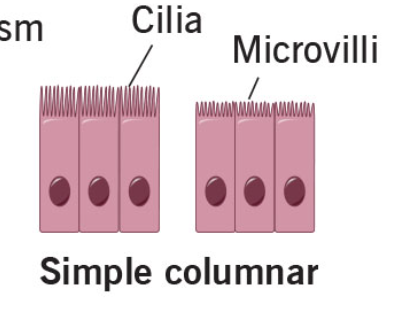
simple columnar
absorb and secreted mucous and enzymes
digestive tract
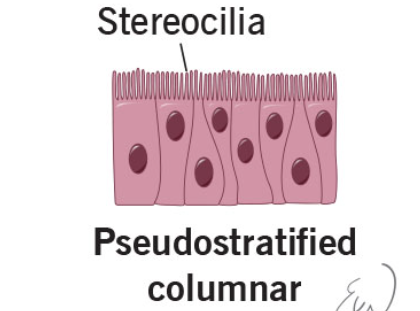
pseudostratified columnar
secrete mucous
ciliated tissue
bronchi trachea
upper respiratory tract
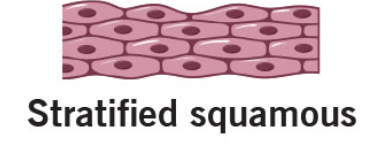
stratified squamous
protect against abrasion
esophagus
vagina
stratified cuboidal
protective tissue
mammary gland
sweat/salivary gland
stratified columnar
secrete and protect
female/male urethrae
glandular epithelia
modified epithelial cell whose main purp is to synthesize and secrete substances
endocrine glands
release substances into blood stream or interstitial fluid
inside
exocrine glands
release substances into ducts that lead surfaces
outside
connective tissue
serve support and connect other tissues and lay down structures
matrix
protein fiber
ground substance
protein fibers
collagen, elastic fibers, reticular fiber
ground substances
fluid, gel
cyte
cell
blast
build, makes
clast
renovates
reticular tissue
fiber provide supportive framework
loose connective tissue
aerolar, adipose, reticular
adipose tissue
consist fat cell with extracellular matrix
store fat for energy and insulation
connective tissue
fixed cell fibrocytes, adipocyte, mesenchymal
fiber types
reticular: same protein subunit as collagen
elastic: protein with lesser amount of other protein
collagen: protein link form straight fiber
dense irregular
tissue consists of collagenous fiber into mesh-like
cartilage
hyaline
fibrocartilage
elastic
hyaline
support with some flexibility
fibrocartilage
provide compressibility and absorb pressure
elastic
firm
type of bones
compact, cancellous
cells: osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts
fluid connective tissue
blood, lymph
blood
erythrocyte and leukocyte (lymphocyte)
membrane
physical barriers line of cover portion of body
type of membranes
mucous
serous (pleura, pericardium, peritoneum)
cutaneous
synovial
mucosae found in
found in digestive, respiratory, urinary, reproductive tract
epithelial surface
moist to reduce friction and facilitate absorption and excretion
lamina propria
areolar connective tissue
serous membrane
double wall; parietal, visceral
(pleura, pericardium, peritoneum)
cutaneous membrane
skin, exterior of body
synovial membrane
line joint cavities
produce synovial fluid
muscle tissue
movement of and within body
skeletal muscle is
voluntary
smooth muscle is
involuntary
muscle tissue types
skeletal
cardiac
smooth
skeletal muscle tissue
voluntary movement
produce heat/protect organs
cardiac muscle tissue
contract to pump blood
smooth muscle tissue
involuntary movement
Involuntarily control respiration
regulate flow of blood
nervous tissue
exchange information around body using electrochemical signs
tissue healing; wound repair
collagen fiber lay down by fibroblasts
nervous tissue is made of
neurons
neuroglia
neuron
cell propagates information
neuroglia
cell support neuron
astrocyte
blood-brain barrier for protection
microglia
immune
Schwann cell and oligodendrocyte
create myelin
ependymal cell
cerebrospinal fluid