PSYCH - EXAM 4
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Bottom-UP Processing
Detecting basic features of stimulus
Data-driven
Moves from PART to whole

Top-DOWN processing
Observer’s cognitive process
Moves from WHOLE to PART
Conceptually driven processing
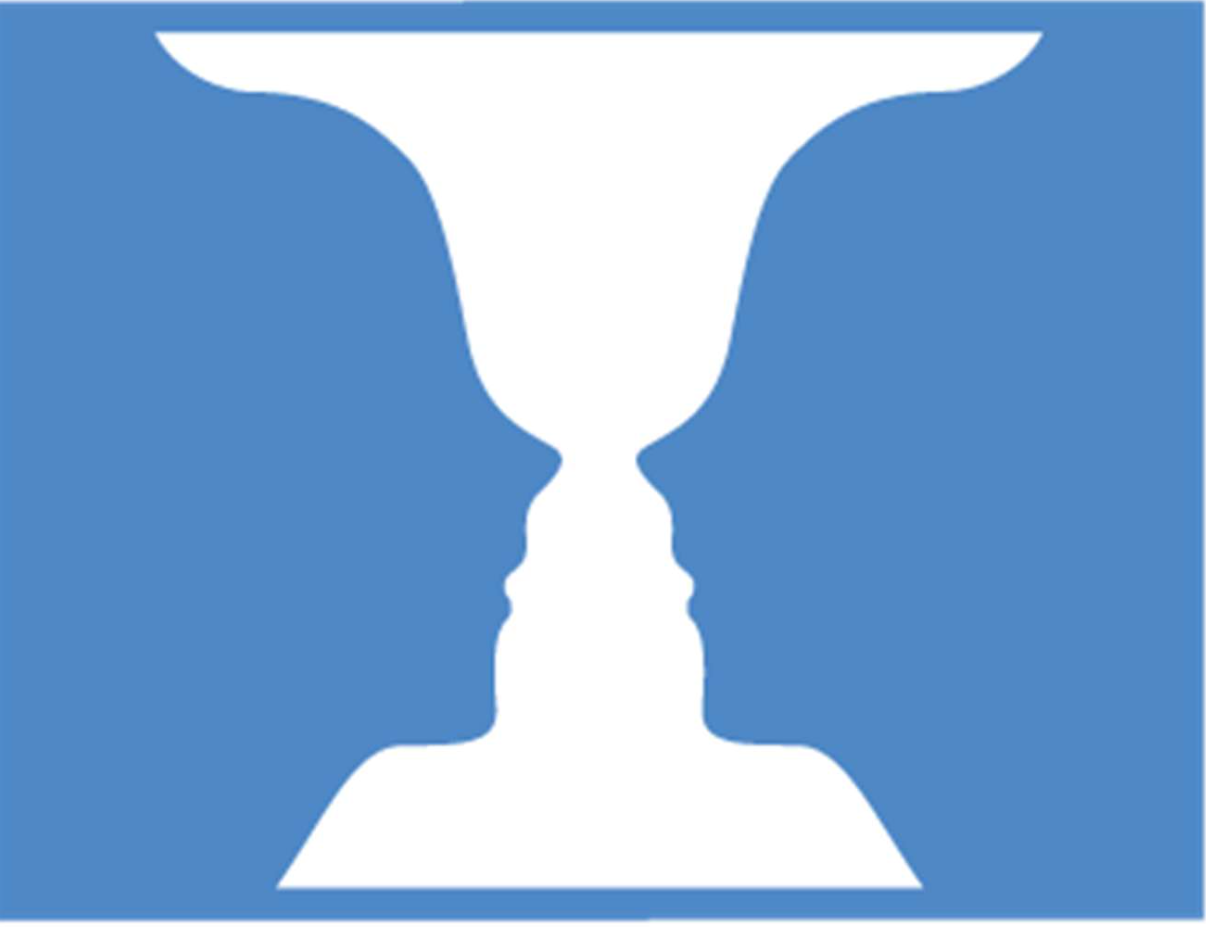

Example of?
GESTALT
Law of Similarity
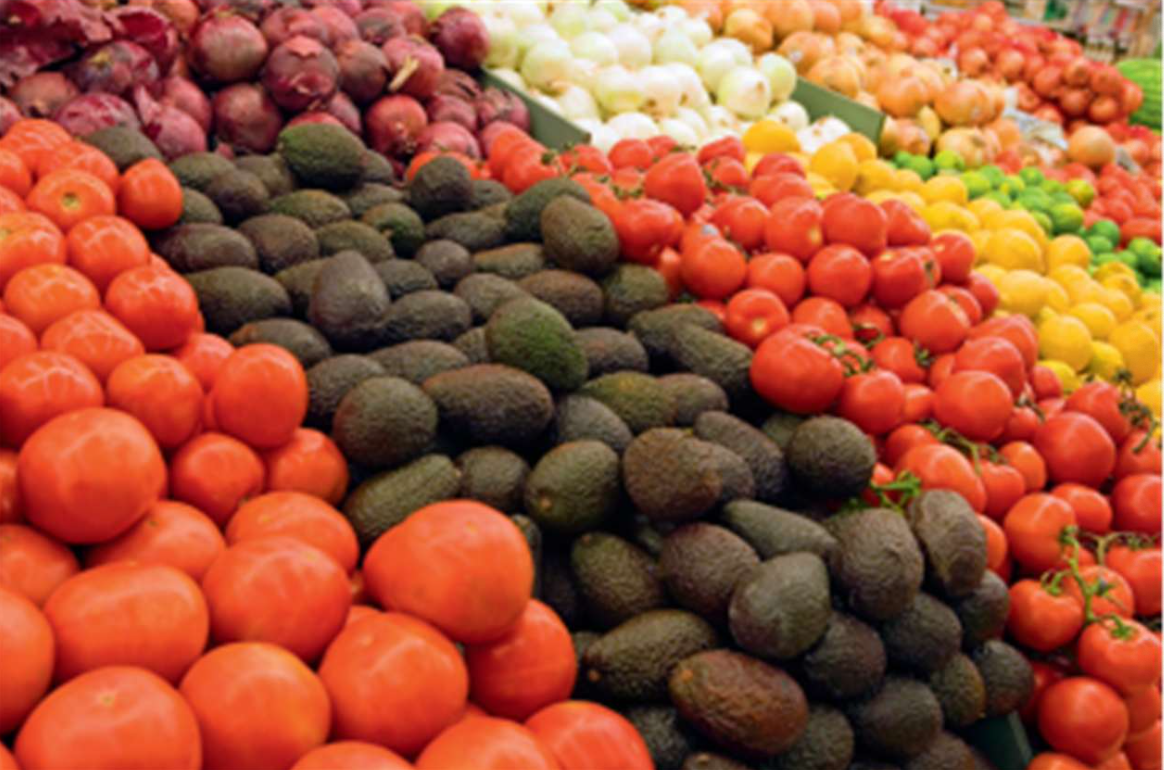

Depth Perception
Distance or 3D features of objects
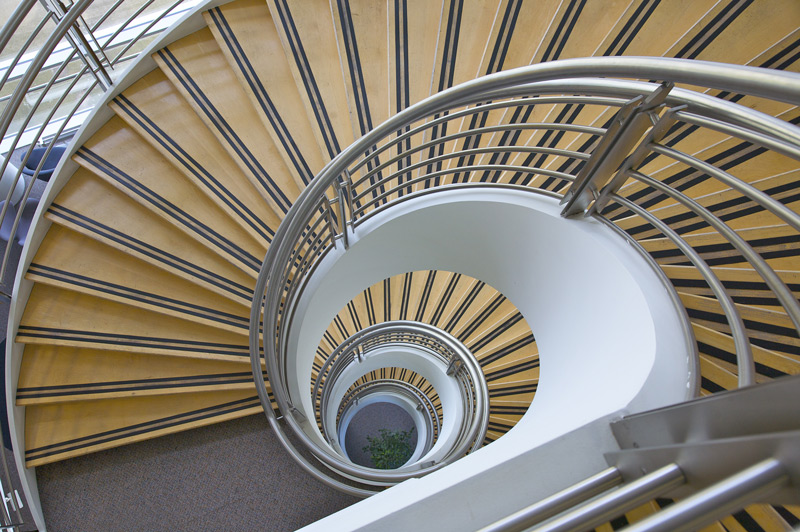

Monocular Cues
Distance or depth processed by either eye alone
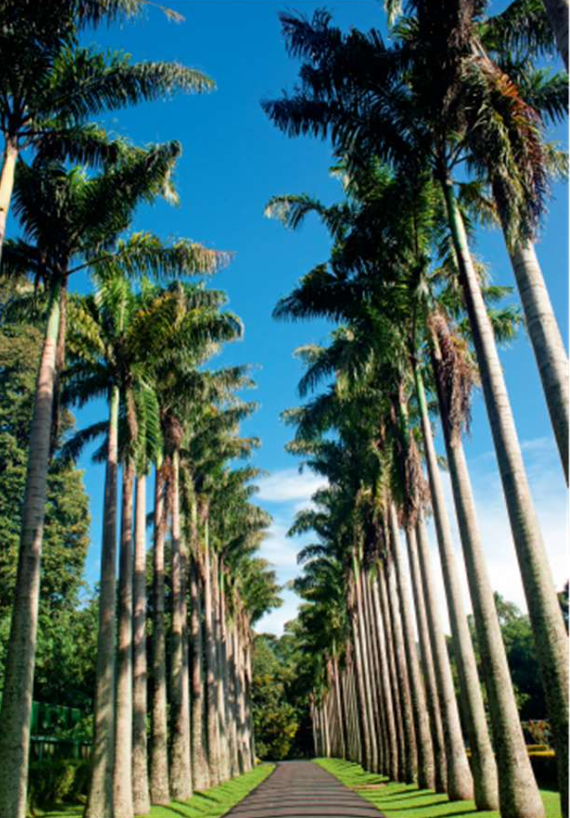


Monocular Cues Example (6)
Relative size
Overlap
Aerial perspective
Texture gradient
Linear perspective
Motion parallax
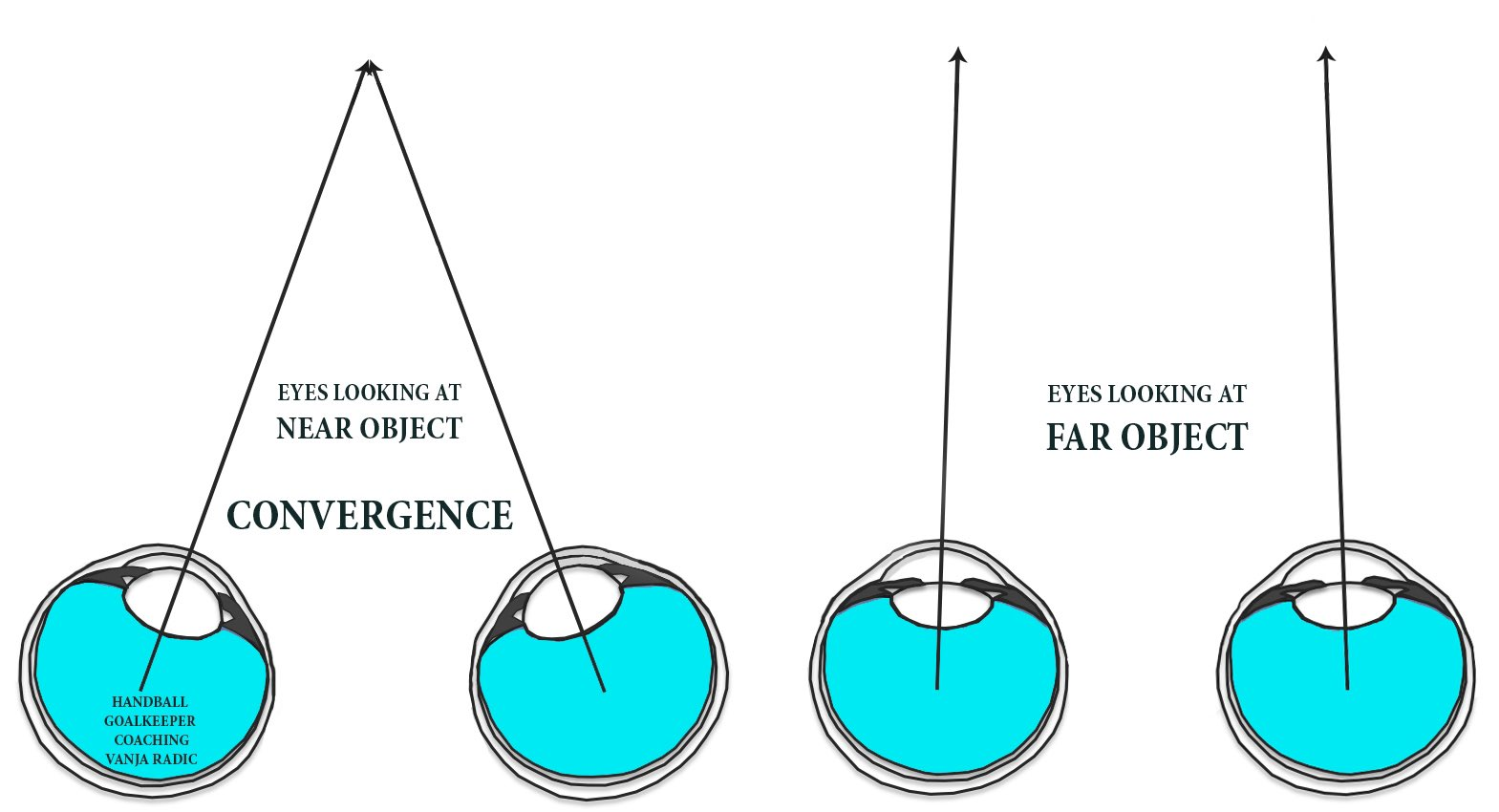
Covergence
Muscles rotate your eyes to focus on an object
More eyes converge → closer the object is
Less eyes converge → farther the object is
Proprioception
Sense of location or position of body parts in relation to one another.

Vestibular Sense
Balance
Responding to GRAVITY, MOTION, and BODY POSITION

Kinesthetic Sense
Sense of LOCATION and BODY position as a result of movement.

Skin
Heaviest and largest sense organ
Contains many SENSORY RECEPTORS
Pacinian corpuscle
Located beneath skin and sends neural message to brain when stimulated
Sensory adaptions occur when pressure is constant
Nociceptors
FOR PAIN
Small sensory fibers in skin, muscles, and internal organs
Fast pain receptors
A-delta fibers
Slow pain receptors
C fibers and substance P
Pain
Unpleasant sensory and emotional experience related to actual or potential tissue damage
Gate-Control Theory of Pain
Pain experience is interpreted by the brain, which SENDS SIGNALS DOWN THE SPINAL CORD


Open pain gateways
Pain experienced or intensified

Closed pain gateways
Pain reduced
Sensitization
Pain pathways become more responsive
Carpentered-world hypothesis
People living in urban environments have are better judges of lines, corners, edges, and other rectangular objects.

How many receptors does a taste bud have?
50 receptors for 5 tastes

What are the four basic tastes?
Sweet
Source
Salty
Bitter
Umami
Umami
Monosodium glutamate
