Lecture 8- Prokaryotes
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What is meant by a prokaryotic cell?
Bacteria and Archaea cells
What are the key differences and similarities between Eukaryotic cells and Prokaryotic
Eukaryotic cells contain membrane bound organelles and a nucleus
Prokaryotic cells DO NOT contain membrane bound organelles and it packages its DNA in a nucleoid
What is the theory of the endosymbiotic origin of the eukaryotic cell
That Eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotic cells, when a larger host cell engulfed prokaryotic cells which survived became mitochondria and chloroplasts.
What are the key features of a bacterial cell.
Cell wall- containing peptidoglycan (important in Gram staining)
Contains no internal membrane bound organelles
Contains circular genomes and usually containing singular chromosome
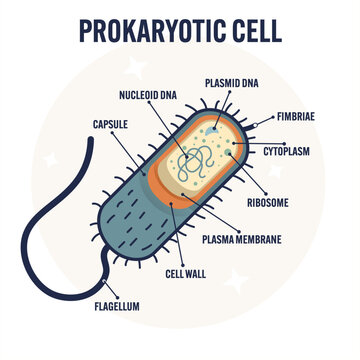
Describe the structure of a typical bacterial cell.
Cell wall (containing peptidoglycan)
Some bacteria contains a flagella
DNA is NOT in a membrane bound organelle called the nucleoid
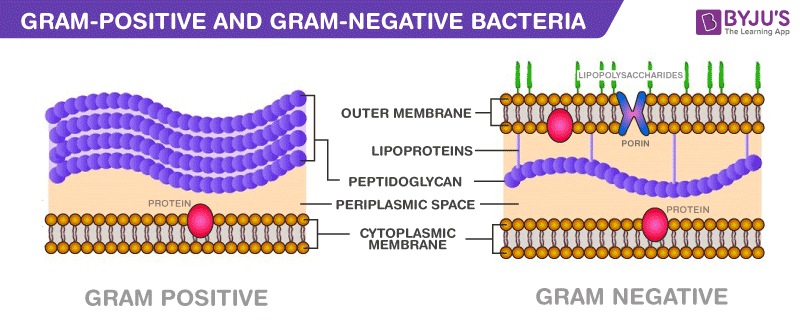
Explain the difference between the gram positive and gram negative cell wall
Differs primarily in cell wall structure:
Gram Positive- Peptiglycodan layer is sitting outside of the outer membrane, which causes it to retain crystal violet
Gram Negative- Peptiglycodan layer is in between outer membranes so it doesn't retain crystal violet
How do bacteria move?
Flagellum- powered by Proton Motive Force
Why are bacteria useful model organisms?
They are less complex compared to Eukaryotes and they have rapid reproduction rates.
What can we learn from a very simple bacterial growth experiment?
To understand possible growth curve and distinct phases
What good and bad things do bacteria do in relation to human health
Good
Aids in gut digestion
Produces essential vitamins
Fighting off harmful bacteria
Bad
Causes infection and illness
Produce toxins
Contribute to chronic diseases