TEAS A&P
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/225
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
226 Terms
1
New cards
chemical
body structure level that involves interactions among atoms and their combination into molecules
2
New cards
organelle
body structure level that involves a small structure contained within a cell that performs one or more specific functions
3
New cards
cell
body structure level that involves the basic functional units of life; differ in structure and function
4
New cards
tissue
body structure level that involves a group of cells with similar structures and functions
5
New cards
organ
body structure level that involves two or more tissue types that work together to perform one or more common functiono
6
New cards
organ system
body structure level that involves a group of organs classified as a unit because of common functions or set of functions
7
New cards
organism
body structure level that involves any living thing considered as a whole
8
New cards
cavity
a fluid-filled space in that body that holds and protects internal organs
9
New cards
thoracic
the _____ cavity is surrounded by the rib cage and separated from the abdominal cavity by the diaphragm
10
New cards
thoracic
the _____ cavity contains the esophagus, trachea, thymus gland, heart, and both lungs, along with other structures
11
New cards
abdominal
the ____ cavity is bounded by the abdominal muscles below the thoracic cavity
12
New cards
abdominal
the ____ cavity contains the stomach, intestines, liver, spleen, pancreas, and kidneys
13
New cards
pelvic
the ____ cavity is enclosed by the bones of the pelvis
14
New cards
pelvic
the ____ cavity contains the urinary bladder, part of the intestines, and the internal reproductive organs
15
New cards
dorsal
the ____ cavity is the back of the human body, and it is subdivided into two cavities
16
New cards
cranial
the ____ cavity contains the brain
17
New cards
spinal
the ____ cavity contains the spinal cord
18
New cards
inferior
directional term that describes a structure below another
19
New cards
superior
directional term that describes a structure above another
20
New cards
anterior
directional term that describes toward the front of the body
21
New cards
posterior
directional term that describes toward the back of the body
22
New cards
dorsal
directional term that describes toward the back
23
New cards
ventral
directional term that describes toward the front
24
New cards
proximal
directional term that describes closer to the point of attachment to the body than another structure
25
New cards
distal
directional term that describes farther from the point of attachment to the body
26
New cards
lateral
directional term that describes away from the midline of the body
27
New cards
medial
directional term that describes toward the middle or midline of the body
28
New cards
superficial
directional term that describes toward or on the surface
29
New cards
deep
directional term that describes away from the surface
30
New cards
anterosuperior
directional term that describes in front or above
31
New cards
midline
directional term that describes a median line
32
New cards
supine position
directional term that describes lying flat with face and torso facing upward
33
New cards
prone position
directional term that describes lying face down
34
New cards
sagittal plane
plane that runs vertically through the body and separates the body into left and right parts
35
New cards
midsagittal plane
plane that divides the body into two equal halves
36
New cards
transverse plane
plane that runs parallel to the surface of the ground and divides the body into superior and inferior planes
37
New cards
coronal plane
plane that runs vertically from left to right and divides the body into anterior and posterior parts
38
New cards
upper limbs
the arm, forearm, wrist, and hand are considered ____ ____
39
New cards
lower limb
the thigh, leg, ankle, and foot are considered ____ ____
40
New cards
central region
the neck and trunk are considered in the ____ ____
41
New cards
head region
the entire head is in the ____ ___
42
New cards
connective
type of tissue characterized by extracellular material that separates cells from one another
43
New cards
connective
tissue that encloses, separates, and connects tissues to one another; also used for support, moving, storing, cushioning, insulating, transporting, and protecting
44
New cards
immune system cells and blood
connective tissue examples
45
New cards
epithelial
type of tissue classified according to number of cell layers and shapes
46
New cards
epithelial
tissue that protects underlying structures, acts as a barrier, secretes substances, and permits the passage or substances
47
New cards
skin, lining of internal organs
examples of epithelial tissue
48
New cards
muscle
tissue whose cells resemble long threads and are called fibers
49
New cards
muscle
tissue that provides movement in the body
50
New cards
heart, organs of digestive system
example of muscular tissue
51
New cards
neural
type of tissue whose cells are composed of dendrites, cell bodies, and axons
52
New cards
neural
type of tissue that coordinates and controls many body activities
53
New cards
brain, spinal cord
examples of neural tissue
54
New cards
connective
e
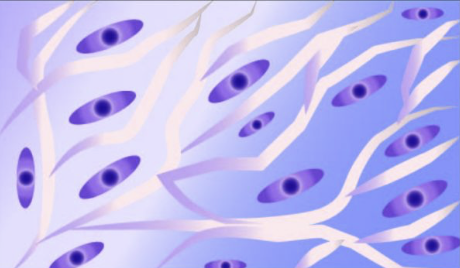
55
New cards
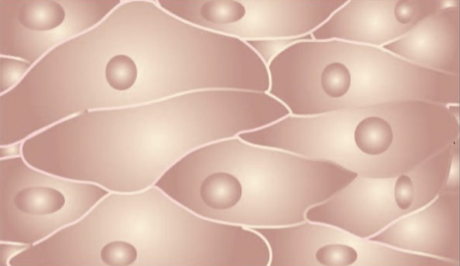
epithelial
type of tissue shown above
56
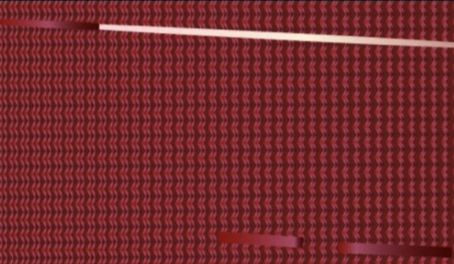
New cards
muscle
type of tissue shown above
57
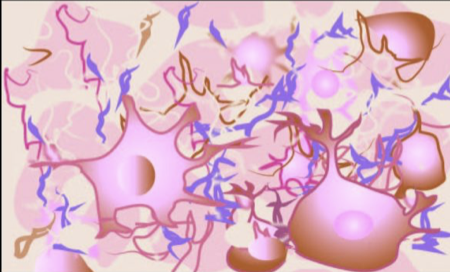
New cards
nervous
type of tissue shown above
58
New cards
homeostasis
the existence and maintenance of a relatively constant environment within the body
59
New cards
negative feedback
mechanism that regulates most systems of the body to maintain homeostasis; any deviation from the set point is made smaller or is resisted
60
New cards
positive feedback
mechanisms that are not homeostatic and rare in healthy individuals; when a deviation from the normal value occurs, response of the system is to make deviation even greater, creating a cycle leading away from homeostasis
61
New cards
positive
inadequate delivery of blood to cardiac muscle is an example of a _____ feedback mechanism
62
New cards
negative
the maintenance of normal blood pressure is an example of a _____ feedback mechanism
63
New cards
blood
type of fluid connective tissue that circulates throughout the body, carrying substances to and say from bodily issues
64
New cards
7.4
pH of blood
65
New cards
plasma
extracellular matrix element of blood
66
New cards
erythrocytes
red blood cells that participate in gas exchange with O2 and CO2
67
New cards
leukocytes
white blood cells that protect the body from foreign substances by eliciting an immune response
68
New cards
thrombocytes
platelets in blood that aid in blood clotting and wound healing
69
New cards
92
plasma is ___% water
70
New cards
5
the average volume of blood in the human body is __L
71
New cards
Buffy coat
72
New cards
plasma
makes up 55% of blood
73
New cards
erythrocytes
makes up 45% of blood
74
New cards
transportation, regulation, protection
3 primary functions of bloodwh
75
New cards
gases, nutrients, wastes, hormones
what does blood transport throughout the body
76
New cards
albumin
main protein in blood, accounting for roughly 60% of plasma proteins
77
New cards
vasodilation
the expansion of blood vessels
78
New cards
vasoconstriction
the contraction of blood vessels
79
New cards
vasodilate
when blood vessels ______, blood flows slowly, causing heat loss
80
New cards
vasoconstrict
when blood vessels ____, blood flow is reduced and less heat is released
81
New cards
platelets
part of blood that repairs broken blood vessels
82
New cards
hemostasis
physiological process that helps maintain blood in its fluid states and stops it from leaking out of a damaged blood vessel through clot formation
83
New cards
antigens
cells found on the surface of a blood cell that differentiates the blood group
84
New cards
antibodies
blood proteins found in plasma that helps differentiate what blood group
85
New cards
A
blood group ___ displays A antigens and B antibodies
86
New cards
B
blood group ___ displays B antigens and A antibodies
87
New cards
O
blood group ___ does not display A or B antigens and both A and B antibodies
88
New cards
AB
blood group ___ displays type A and B antigens but neither in the plasma
89
New cards
O
blood type who is universal blood donor
90
New cards
AB
blood type who is universal acceptor
91
New cards
cardiovascular
the ____ system circulates substances throughout the body using blood as a transporting mechanism
92
New cards
tricuspid
the ____ valve regulates blood flow between the right atrium and right ventricle
93
New cards
pulmonary
the ____ valve regulates blood flow from the right ventricle into the pulmonary artery
94
New cards
mitral
the ____ valve regulates blood flow between the left atrium and left ventricle
95
New cards
aortic
the ____ valve regulates blood flow from the left ventricle to the aorta
96
New cards
aorta
largest artery in body
97
New cards
capillaries
____ have thin walls and a very large surface area
98
New cards
septum
muscular structure that separates the atria from the ventricles
99
New cards
pericardium
outer layer of the heart
100
New cards
myocardium
middle layer of the heart