Blood glucose concentration
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What is the set point for blood glucose concentration
80-120mg/100cm³
What is hypoglycaemia
When blood glucose concentration falls below about 72mg/100cm³
What can hypoglycaemia lead to
Fainting, may lead to convulsions and coma
What is hyperglycaemia
When blood glucose concentration is abnormally high (approx 126mg/100cm³
What does hyperglycaemia lead to
decrease in blood water potential causing water to be drawn by osmosis out of the cells, tissue and tissue fluid
Causes blood volume to increase so kidney increases urine output to compensate
Person deprived of fluid, dehydration occurs and blood pressure decreases
How is glucose absorbed into the liver
Glucose absorbed across the epithelial cells of the villi and carried straight to the liver via the hepatic portal vein
How does the liver store glucose absorbed from the blood
As glycogen
Why are there spikes in blood glucose concentration
Not all the glucose can be removed immediately so there is an increase in blood glucose concentration after a carbohydrate meal has been eaten.
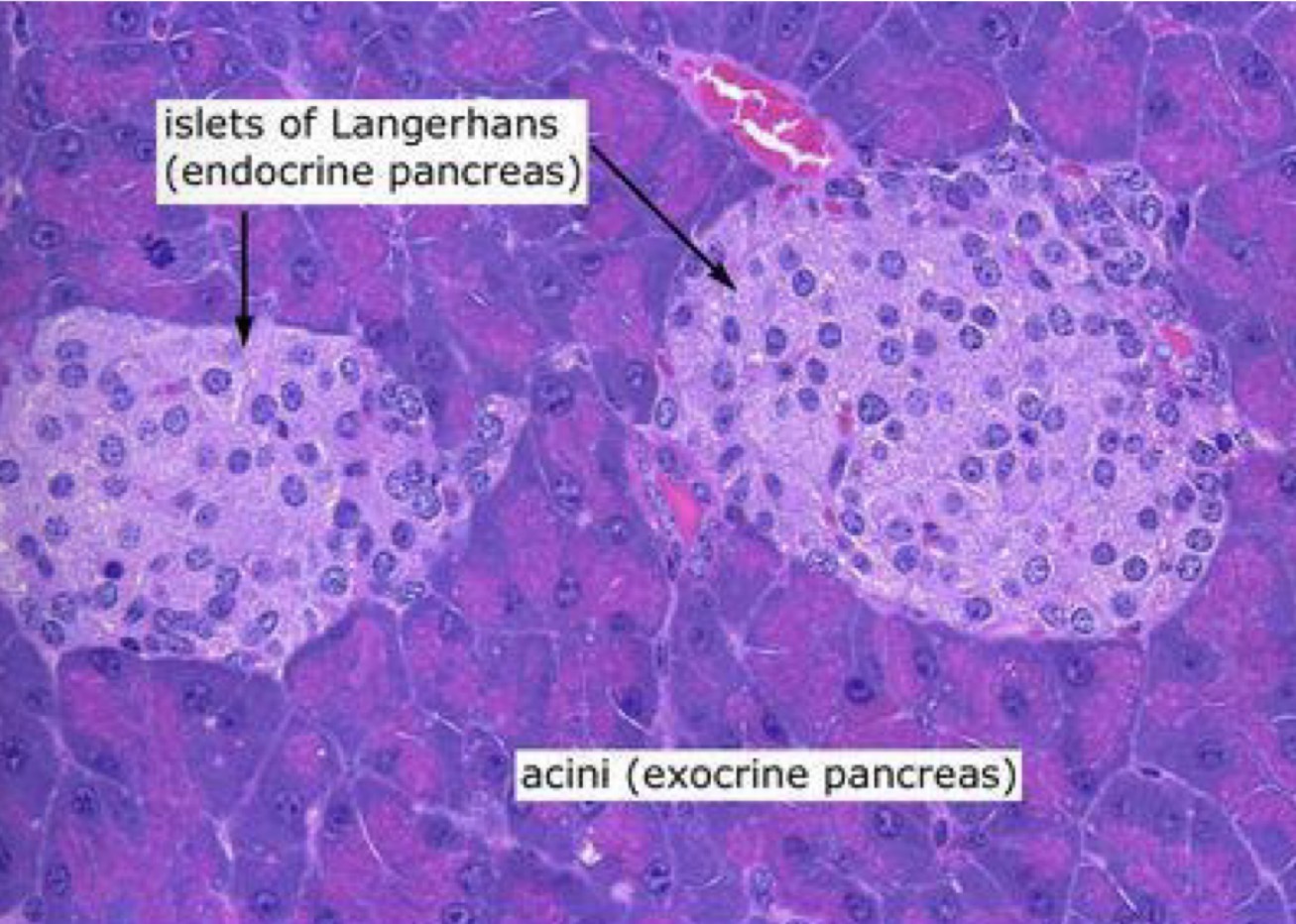
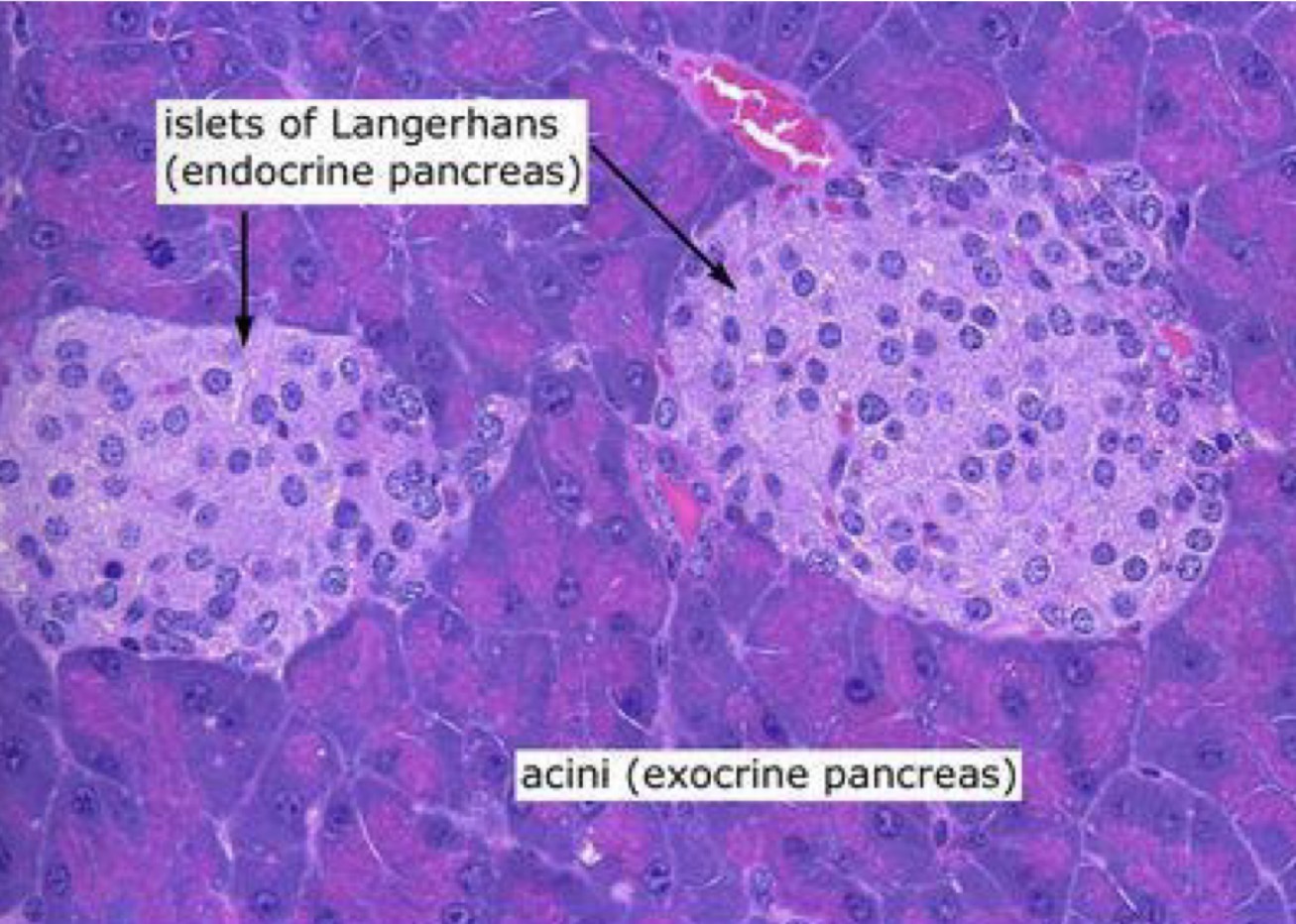
What are the Islets of Langerhans
Patches of cells found within the pancreas
Endocrine glands
Made up of two types of cells - alpha (α) and beta (β) cells
What happens when blood glucose concentration increases
Detected by the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans
Secrete hormone insulin into the blood
Which receptor cell is responsible for detecting falls in blood glucose concentration
Beta cells in the islets of langerhams in the pancreas
What are endocrine glands
Hormone secreting cells
How are the Islets of Langerhans adapted to their function
They have a rich capillary supply to carry their secretions away
What are insulins main target organs (where are insulin receptors)
Liver and skeletal muscle, also in adipose tissue
What does insulin cause
increase uptake of glucose
Increased glycogenesis
Increases glucose to fatty acids and lipids in liver cells
Increases lipid deposits around the body
What is the name for the conversion of glucose to glycogen
Glycogenesis
What receptors cells are responsible for detecting falls in blood glucose concentration
Alpha cells in islets of Langerhans of pancreas
What happens when the apha cells detect a decrease in blood glucose concentration
Alpha cells stimulated to secrete a hormone called glucagon
Beta cells stop secreting insulin
Glucose isn’t taken up as fast by cells
Where are glucagon receptors located
Different receptors in the cell surface membrane of liver cells
What does glucagon do
Stimulated the hydrolysis of glycogen into glucose which can be released into the blood
What is the name for the break down of glycogen into glucose
Glycogenolysis
What is the name for the making of new glucose from amino acids and lipids
Gluconeogenesis