physics theory
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
scalar
values with only magnitude and no direction
vector
values with magnitude and a direction
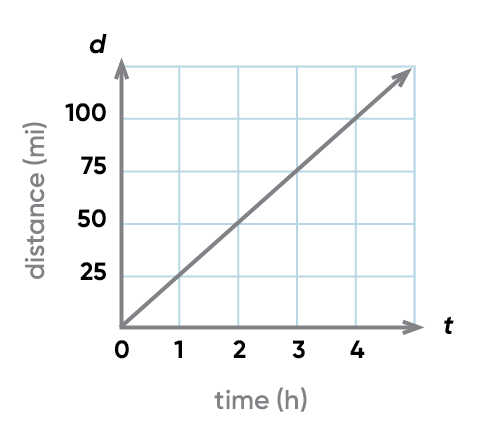
what graph is this? whats the equation and proportion of it?
linear! y=mx and y ∝ x
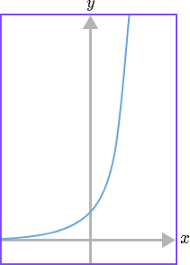
what graph is this? whats the equation and proportion of it?
power! y=kx² and y ∝ x²
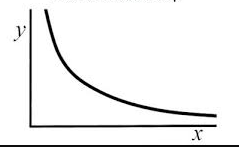
what graph is this? whats the equation and proportion of it?
inverse! y/x and y ∝ 1/x
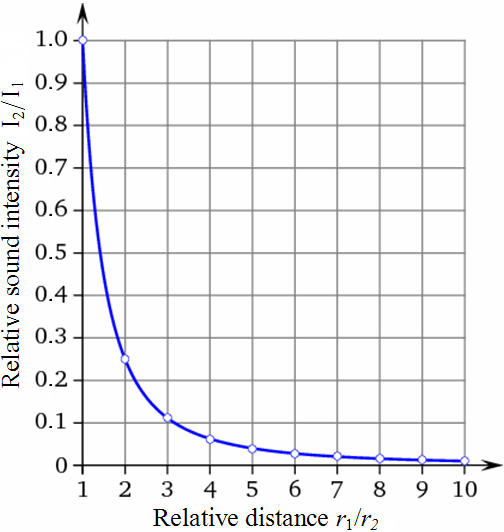
what graph is this? whats the equation and proportion of it?
inverse square! y=k/x² and y ∝ 1/x²
**HINT! it drops faster than inverse
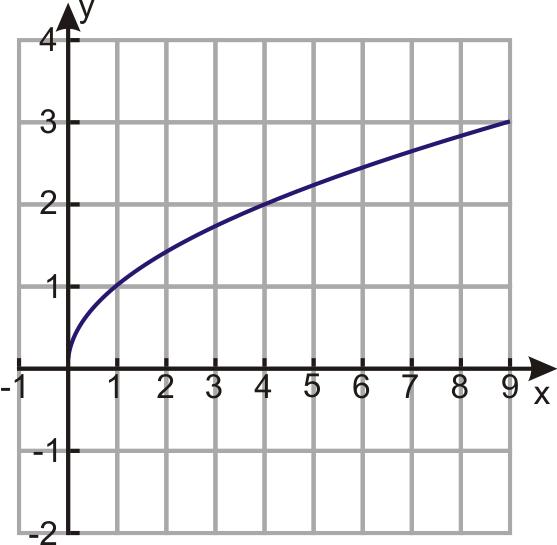
what graph is this? whats the equation and proportion of it?
square root! y=√x and y ∝ √x
position
the location of an object relative to a reference point
displacement
the change of position
velocity
the rate of change of position
acceleration
the rate of change of velocity
direction of acceleration
the direction of displacement and velocity is always the same, but acceleration depends. if speeding up, acceleration is the same as displacement and velocity, if slowing down acceleration is the other way.
free fall rules
if an object is thrown upwards into the air, to find the highest high of the object use: v2= 0m/s
if an object is thrown up into the air and eventually returns to the same position, its initial and final velocity are related: v1=v2
if an object travels upward and changes direction, the overall displacement and distance are different! the equation only requires displacement
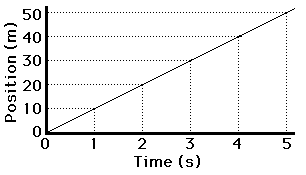
what does the slope of a position vs time graph represent?
velocity, specifically constant velocity! NOTE: IF THE SLOPE IS CURVING UPWARDS IT REPRESENTS SPEEDING UP, IF THE SLOPE IS CURVING DOWNWARDS IT REPRESENTS SLOWING DOWN
gravitational force
the gravitational force is an attractive force that all objects exert on each other and is dependent on the object’s masses.
weak nuclear force
the weak nuclear force between subatomic particles
electromagnetic force
the force that charged particles exert on each other it is responsible for most forces
strong nuclear force
an attractive force that holds protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atom
forces from strongest to weakest
strong, electromagnetic, weak, gravity
newtons first law
an object at rest will remain at rest, an object in motion will remain in motion unless acted on by the unbalanced force. this law is also know as the law of inertia.
inertia
an objects ability to resist change in motion, related to its object’s mass
newtons second law
an object’s acceleration is determined by the net force exerted on it by its environment and by the object’s mass.
direct proportion F ∝ a
if one increases/decreases, the other does the same. if force increases, acceleration increase. if force decreases, acceleration decreases.
inverse proportion m ∝ 1/a
if one increases or decreases, the other does the opposite. if mass increases, acceleration decreases. if mass decreases, acceleration increases.
applied force
push or pull, by hand, foot, etc
tension force
force due to rope and string
friction force
force between two surfaces that are moving or try to move relative to each other
normal force
force due to a surface acting on an object
force of gravity
force of the earth (or planet) pulling an object down towards its centre
newtons third law
force always comes in pairs. every force is an interaction between two objects. ex) when u slap the table the table slaps u
galileo’s law of falling
two objects that r dropped together will fall together regardless of their shapes and amsses
difference between mass and weight
mass is the amount of MATTER an object has
weight is a force measured in N
what does it mean to be an “at a distance” force?
this means that a force exists between two objects even when they are not touching!
what is the difference between “force of gravity” and “acceleration due to gravity”?
acceleration due to gravity is the acceleration all objects experience when falling (-9.8)m/s²
force of gravity is the force that is put upon the object to make it fall at a rate of (-9.8)m/s²
terminal velocity
when an object or person is falling from a great height, the air resistance becomes greater thus making acceleration due to gravity and air resistance equal and balance each other out. Eventually it makes acceleration stop and creates terminal velocity.
static friction
friction that occurs when an object IS NOT moving ex. car parked on a hill, box on a ramp and is not sliding
static friction is stronger than kinetic friction
kinetic friction
frictions that occurs when an object IS moving (sliding), ex. a box sliding across the floor, rubbing ur hands together
kinetic friction is weaker than static friction
coefficient of friction
represents the frictional force resisting the motion of two surfaces
μ = Ff/FN || 0 < μ < 1
gravitational field strength
a space around a mass where a test mass experiences a force
describe when mass appears heavier than normal
moving up fast
moving down, slowing down
a > 0 (acceleration is positive)
describe when mass appears lighter than normal
moving up, slowing down
moving down, speeding up downwards
a < 0 (acceleration is negative)
describe when mass’s actual and apparent weight are equal
not moving
moving up or down WITH constant velocity
a = 0
electric charge
describes whether an object has an excess or deficit of electrons relative to protons
induced charge seperation
the shift in electrons
magnetic dipole
a north/south pair
temporary magnets
a magnet that lose their magnetism over time, especially when dropped, heated or hammered
what r magnets made out of?
IRON, NICKEL, COBALT! materials like this are called ferromagnetic!
magnetic field lines
run from north pole to south pole outside of the magnetic, run from south pole to north
domain theory
ferromagnetic materials consists of dipoles, each dipole is like a little magnet with north and south heh! areas called DOMAINS have dipoles that all point in the same direction, the more aligned the domains are the more magnetized it is.
magnetic declination
the angle between true north and magnetic north
magnetic inclination
aka the magnetic dip, the angle that the magnetic field makes with the surface of the earth
auroras
caused by high-energy particles from the solar wind trapped in the earth’s magnetic fields. when electrons collide with oxygen and nitrogen particles, omitting a light that we see as auroras!!
what is a wave?
a wave is a rhythmic disturbance that carries ENERGY through matter or space.
longitudinal waves
the particles in the medium move PARALLEL to the motion of the wave.
transverse waves
the particles in the medium move PERPENDICULAR to the direction of the wave.
mechanical wave
a transfer of energy where A MEDIUM IS REQUIRED! ex. water waves, sound waves
electromagnetic wave
a wave that can transfer energy WITHOUT A MEDIUM! ex. visible light, gamma rays
amplitude
how big the wave is, the maximum displacement. it represents how much energy the wave has.
wavelength
the horizontal distance between corresponding points on the consecutive wave crests.
crest
the highest point of a wave.
trough
the lowest point of a wave.
period
the time it take for ONE WAVELENGTH to pass a given point. hint: TU VELO IS ONE PERSON!! PERIOD!
frequency
the NUMBER OF WAVELENGTHS that pass a given point per second. 1 hertz is 1 wave per second!
the speed of wave is constant if?..
…if the medium it travels through stays constant!
reflection
when waves bounce off of an obstacle
a pulse that reflects from a fixed-end is…
..horizontally and vertically inverted. a CREST becomes a TROUGH and a TROUGH becomes a CREST.
a pulse that reflects from a free end is…
…ONLY horizontally inverted. the crests and troughs remain the SAME.
transmission
when waves move from one medium to another medium.
less dense to a more dense
for the transmitted pulse the orientation stays the same, the amplitude gets smaller, the wavelength gets smaller and it travels slower.
for the reflected pulse the orientation inverts, the amplitude gets smaller, the wavelength remains the same.
more dense to a less dense
for a transmitted pulse the orientation stays the same, the amplitude gets longer, the wavelength gets longer and it travels faster.
for the reflected pulse the orientation stays the same, the aplituder gets smaller, the wavelength stays the same, and its the same speed of the original pulse.
mr wegley attaches a slinky to the wall and begins introducing pulses with different amplitudes and then different wavelengths, why would all the pulses reach the wall at the same time?
regardless of the amplitude, the speed of the pulse is maintained by the properties of the medium.
the wavelengths of a wave doesn’t have any affect on the time.
interference
when two or more waves meet
constructive interference
two waves with the same frequency and phase will merge together and get bigger! (crest + crest ; trough + trough)
destructive interference
two waves with the same frequency and OPPOSITE phase will cancel eachother out. (crest + trough)
standing wave
caused by constructive and destructive interference
nodes
caused by complete destructive interference, they have NO amplitude.
anti-nodes
caused by complete constructive interference, they have MAXIMUM amplitude
wave front
the whole width of the wave crest
wave ray
an arrow drawn perpendicular to the wave front
refraction
when waves bend when they move from one medium to another due to a change in speed
resonance
when a medium vibrates at its natural frequency in response to an external sound wave. ex) singing and breaking a glass.
how does a sound wave move?
its moves by molecules bumping into each other
diffraction
when waves bend around an obstacle
what is the doppler effect?
the apparent change in frequency an observer hears based on the relative motion of the source.
the visible spectrum ranges around?
-400 (violet) to 700 (red) nanometres
what are the two laws of reflection of light
the incident angle is equal to the angle of reflection.
the incident ray, the normal and the reflected ray all lie in the same plane. (they all lie on the same surface)
specular reflection
light that reflects off of a smooth surface
diffuse reflection
light that reflects off of a microscopically rough surface
which way would light bend from a more dense to less medium?
light will move AWAY from the normal.
which way would light bend from a less dense to more dense medium?
light will bend TOWARDS the normal
index of refraction
the property of a material indicating how much speed of light is reduced, it CANNOT be smaller than one. ex) n1 = 1 (air)
dispersion
when white light separates into colours and create a random effect.
stationary sound source
when a person hears the same pitch regardless of the location
what did newton contribute
the laws of newton, object @ rest remain @ rest, EF=ma, action reaction
law of gravity, every particle attracts every other particle in the universe
light dispersion, white light can be separated into different colors
particle theory for light bc light move fast
what did milikan contribute
oil drop experiment to find voltage and size of a singular charge || q=mg/E
what did huygens contribute
wave theory of light bc it can diffract
what did young’s contribute
discovered the interference created during double slit experience