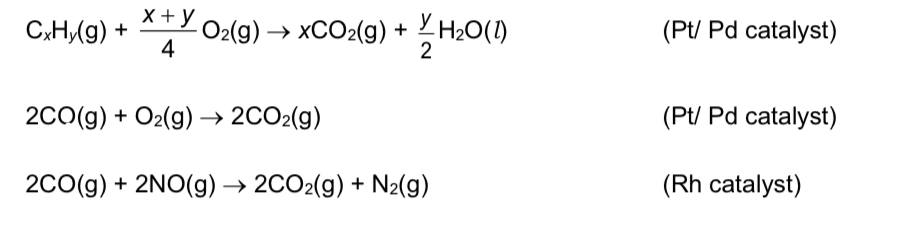ALKANES
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms

Are alkanes saturated or unsaturated and how are they hybridised?
→ saturated (with H)
→ sp³ hybridised, tetrahedral, 109.5°
General formula of alkanes?
→ Straight and branched chain - CnH2n+2
→ Cycloalkanes - CnH2n
Why do alkanes have relatively low boiling point?
→ Alkanes have weak id-id between alkanes molecules
How does melting point/boiling point increase in alkanes?
→ With increasing number of C atoms, there is an increase in size of electrons cloud and hence polarisability of alkane molecules,
→ increasing strength of instantaneous dipole-induced dipole attraction,
→ hence more energy is needed to overcome these forces, leading to increasing mp/bp.
→ Straight chain alkanes have higher boiling point than branched alkanes due to the straight chain molecules having larger surface area of contact between them,
→ thus there are stronger intermolecular instantaneous dipole-induced dipole interactions which need more energy to overcome
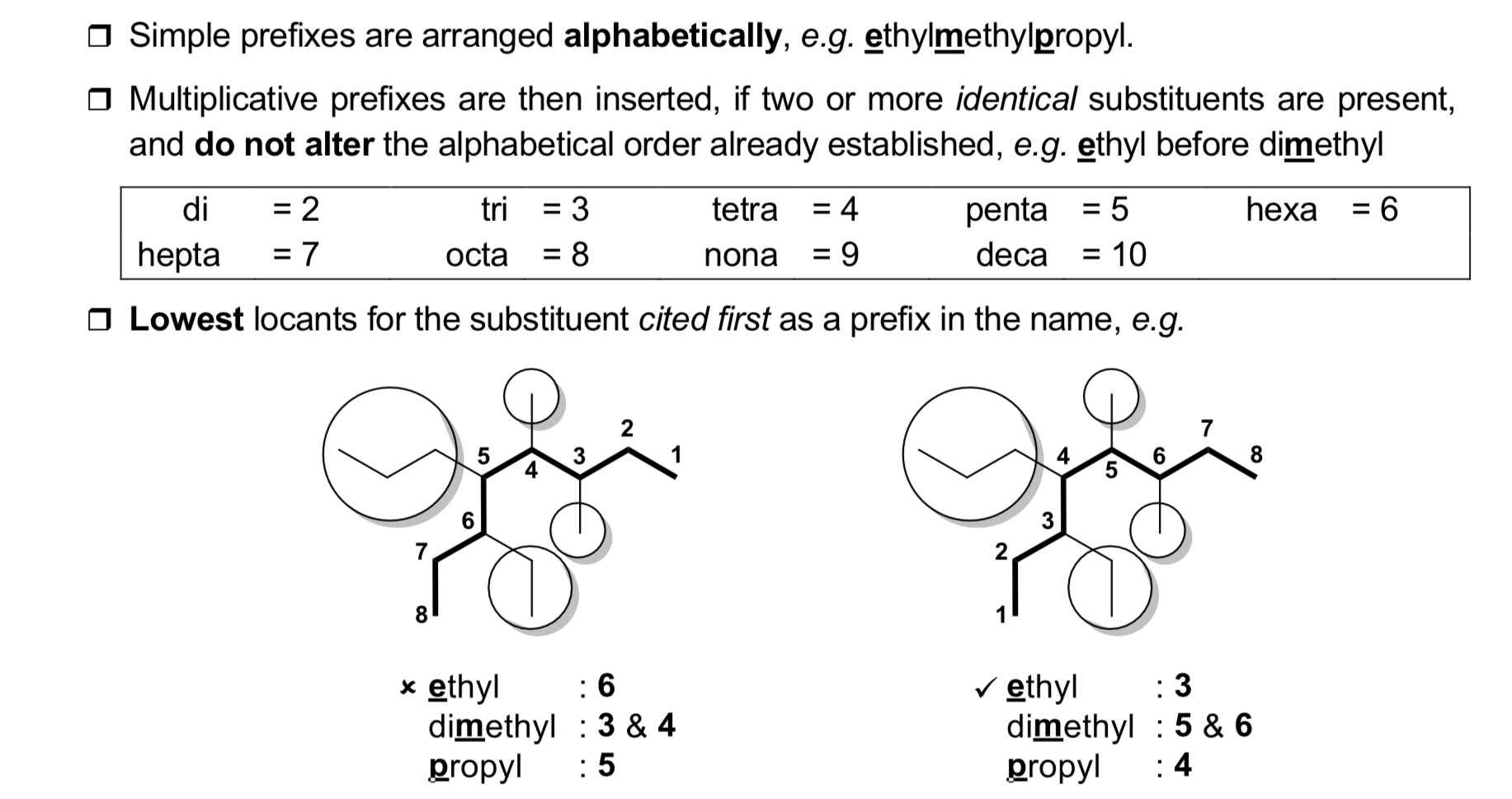
How to name alkanes?
1) Determine longest continuous carbon chain.
2) Name every substituent.
3) Ensure each carbon atom has smallest number.
4) Write name as single word.
note: if only alkane functional group present, ends in -ane
How are alkanes’ solubility?
→ Insoluble in water - the energy released in forming id-id interactions between alkane molecules and water molecules is insufficient to overcome the id-id interactions between alkane molecules and hydrogen bonds between water molecules
→ Soluble in non-polar solvents such as benzene, hexane - the energy released in forming id-id interactions between alkane molecules and benzene molecules is sufficient to overcome the id-id interactions between the alkane molecules and the id-id interactions between the non-polar benzene molecules
How does alkane density compare to water?
Generally, alkanes are less dense than water
→ density = mass / volume
Why are alkanes generally unreactive?
→ C-C and C-H bonds are strong covalent bonds which are difficult to break under ordinary conditions
→ Alkanes are non-polar with no electrophilic or nucleophilic sites hence they are not susceptible to attack by nucleophiles or electrophiles respectively
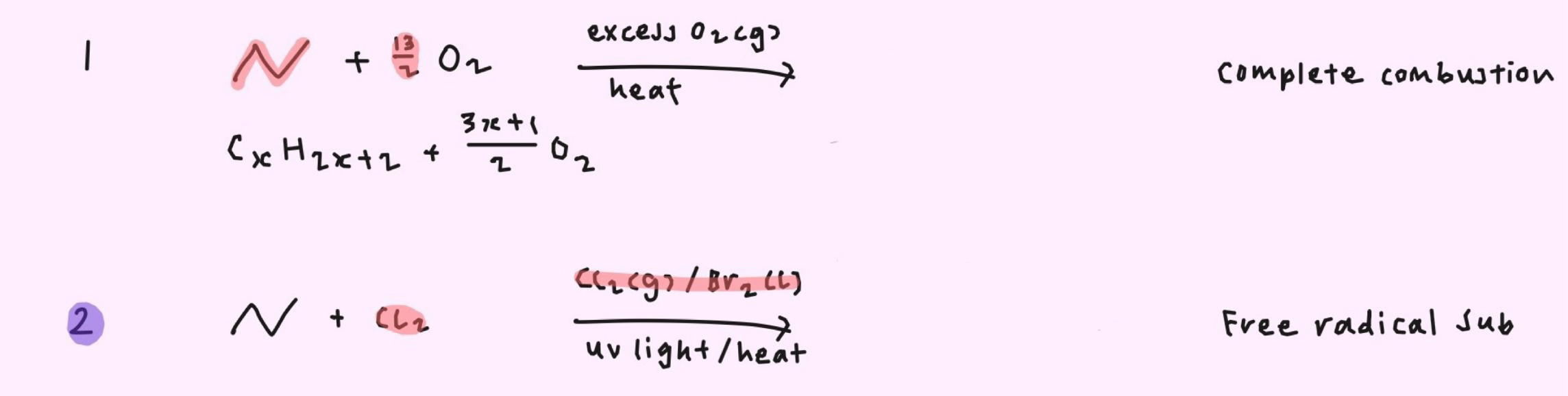
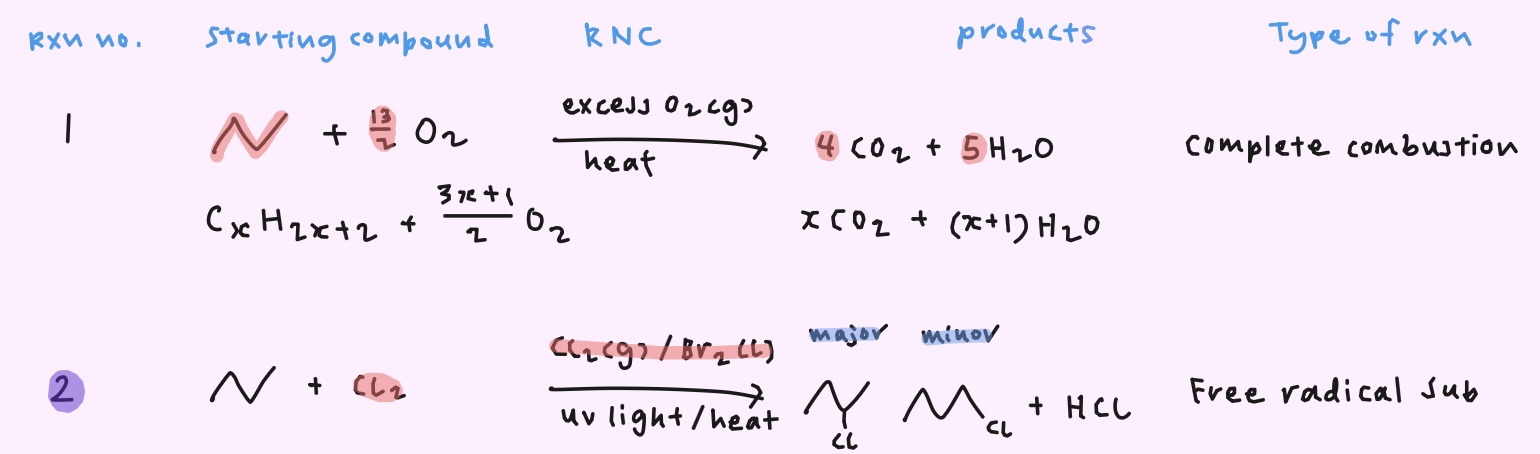
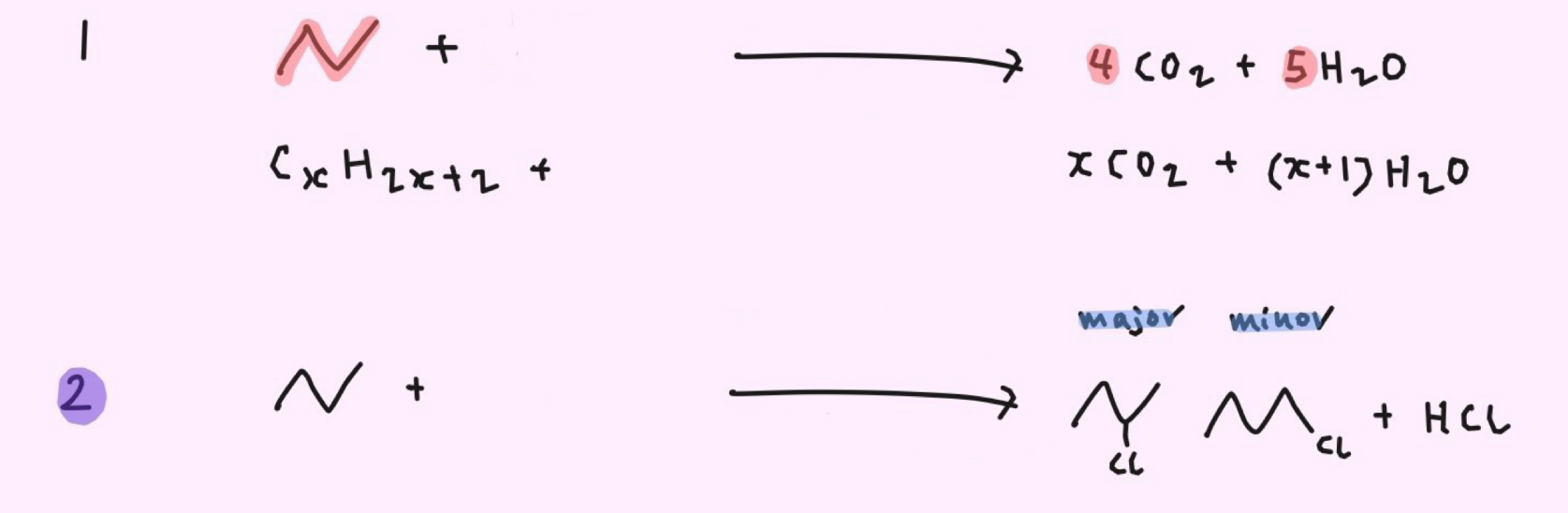
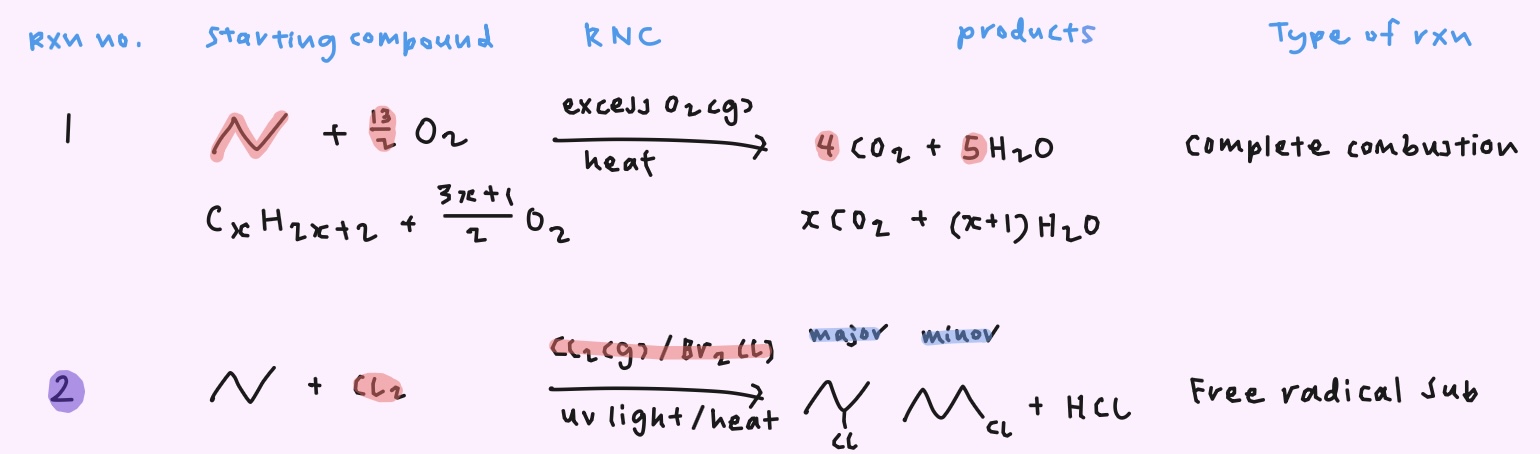
How do you obtain the monosubstituted product as the major product for free radical substitution?
→ Limited amount of halogen
→ Large excess of alkane
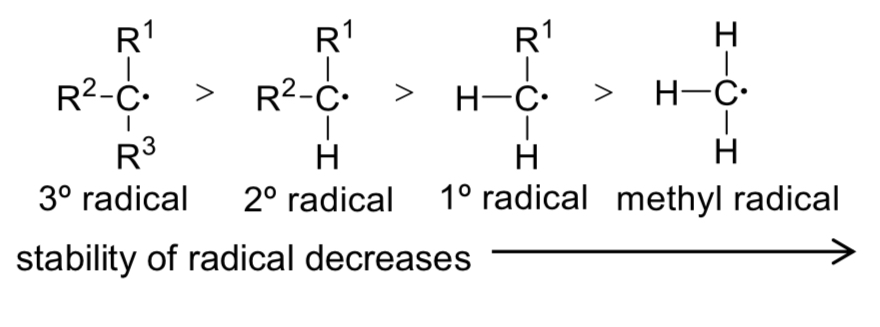
Why are 3° alkyl radicals more stable than 1° alkyl radicals?
→ Alkyl groups are electron-donating, and
→ help increase the electron density in the electron-deficient carbon of alkyl radical,
→ stabilising it.
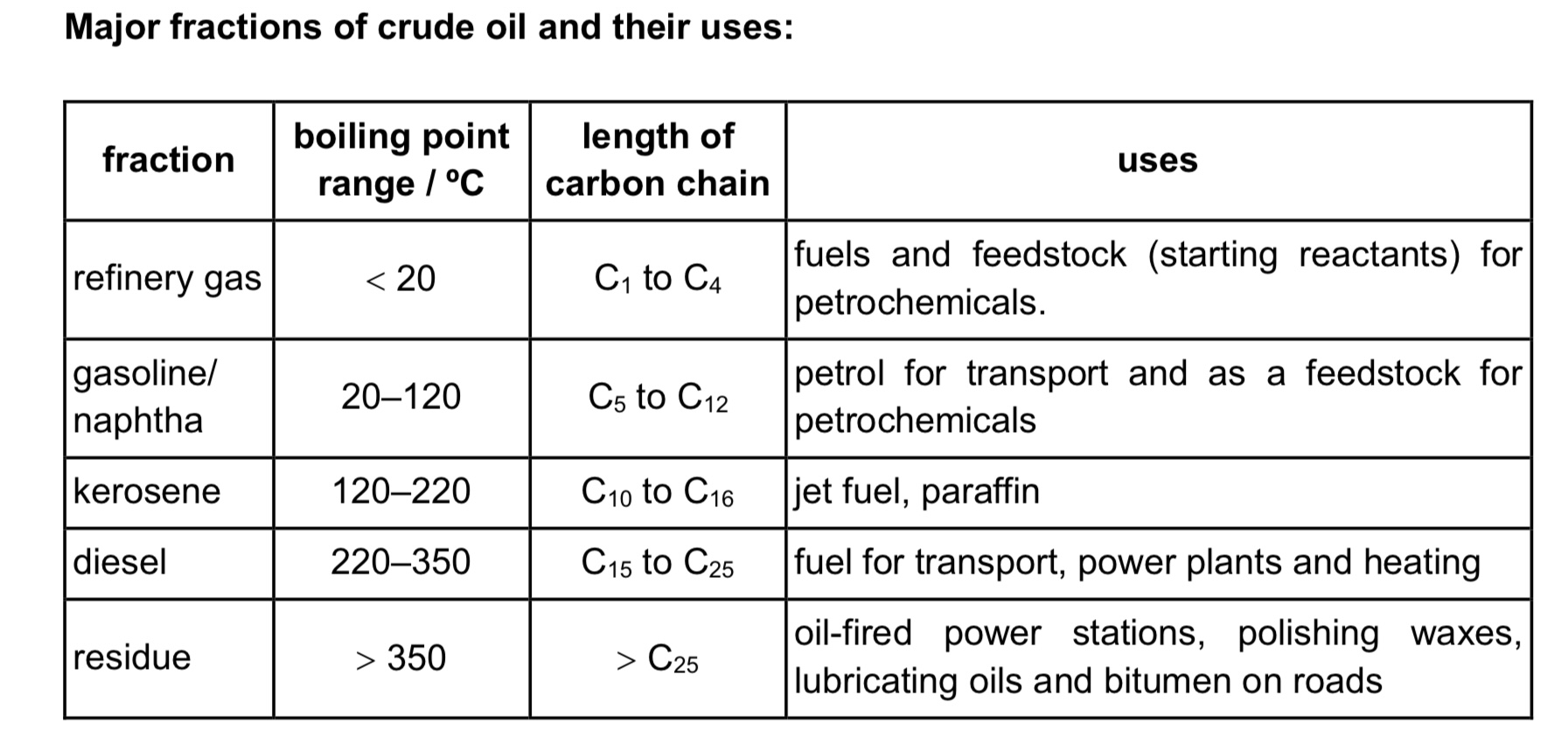
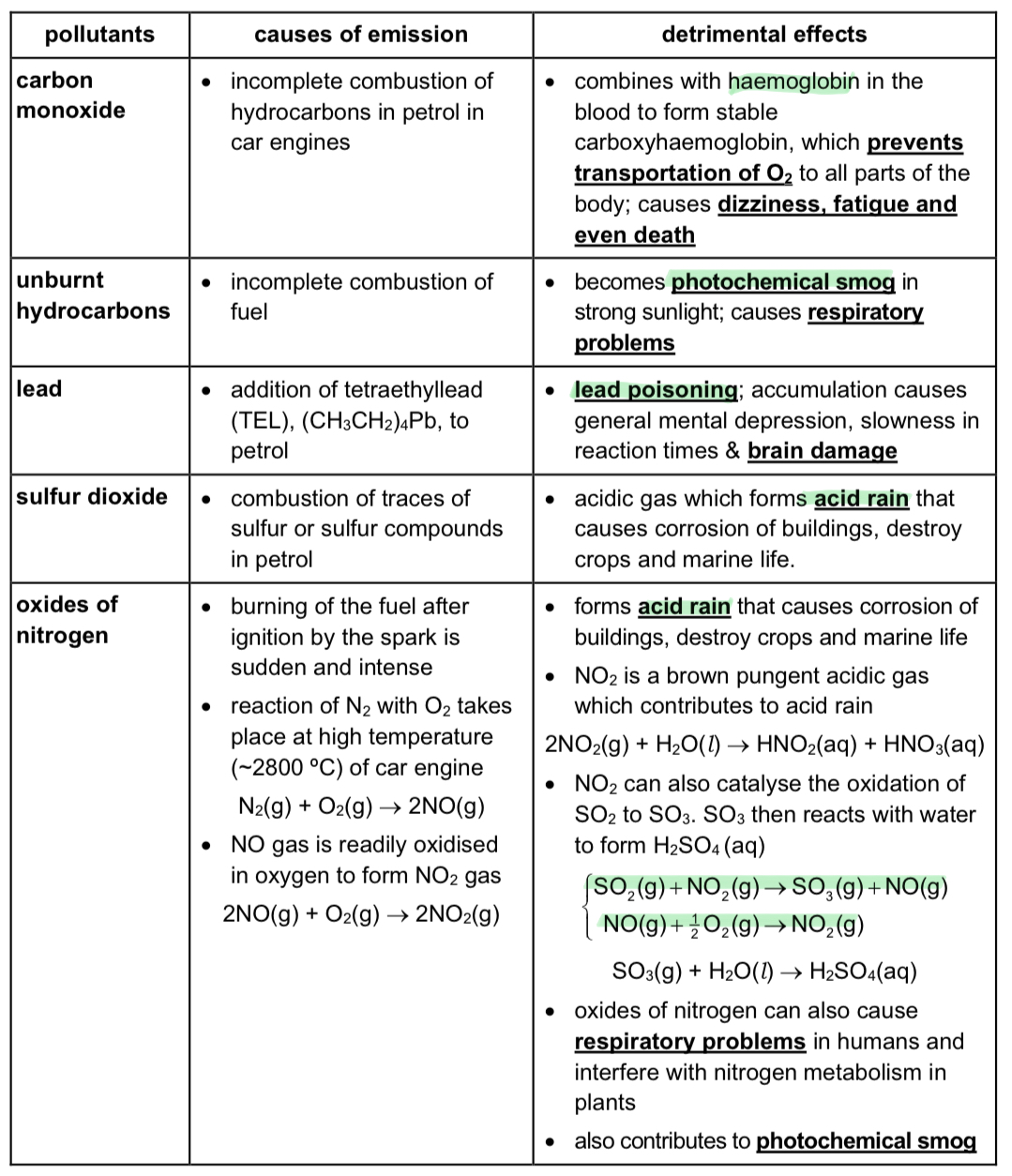
What are some pollutants from internal combustion engines, their sources, and detrimental effects?
Name 4 greenhouse gases and their detrimental effects.
→ Carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), water vapour (H2O)
→ they warm the Earth’s surface and lower atmosphere by trapping heat
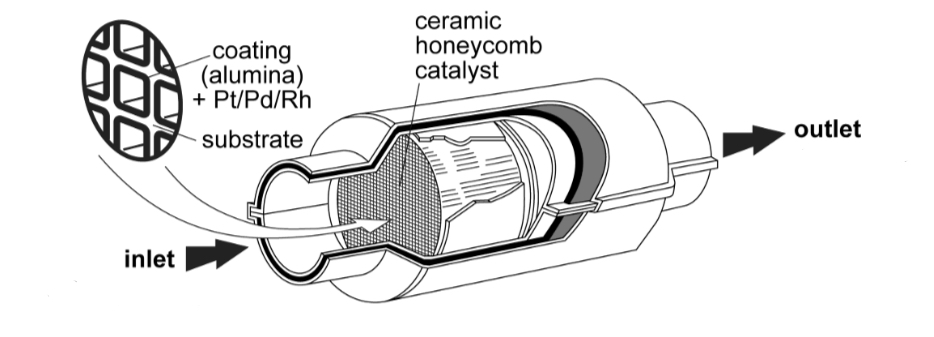
What pollutants do catalytic converters convert, and what are their products?
→ unburnt hydrocarbons oxidised to CO2 and H2O
→ CO oxidised to CO2
→ oxides of nitrogen reduced to N2