Left Turning Tendencies & Axis
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Name 4 Left Turning Tendencies
Natural forces that make the plane yaw/roll to the left (on takeoff and climb).
-Torque
-Gyroscopic Precession
-Asymmetrical Thrust (P-Factor)
-Spiraling Slipstream
Describe A-Symmetrical Thrust (P-Factor)
Similar to Torque
Pulls the plane left when flying @ high angle of attack.
When the descending propeller blade has more thrust than the ascending blade.
Describe Torque
When the engine and propeller spin to the right.
Airplane tends to roll/yaw to the left.
Newton’s 3rd Law (action/reaction).
Describe Spiraling Slipstream
The propeller creates a spiral slipstream around the plane.
Hits the left side of the tail —> pushes the tail right —> yaws the nose to the left.
Describe Gyroscopic Precession
When the nose of the plane is pitched up quickly, the spinning propeller acts like a gyroscope.
The force applied appears 90 degrees ahead (in the direction of the rotation around vertical axis).
What are the 3-axis of flight?
Longitudinal Axis
Lateral Axis
Vertical Axis
Describe Vertical Axis
Imaginary line running through the center of the plane.
Rudders/Yaw control this.
Describe Lateral Axis
Imaginary line from one wingtip to the other.
Elevator/Pitch controls this.
Describe Longitudinal Axis
Imaginary line from the front tip of the plane to the back.
Ailerons/Roll controls this.
Position (navigation) lights on an aircraft are:
Red on Left
Green on Right
White on Tail
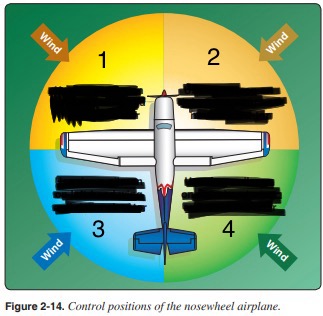
How should the flight controls be held while taxiing a tricycle wheeled airplane?
Aileron Up on L, elevator neutral
Aileron Up on R, elevator neutral
Aileron Down on L, elevator down
Aileron Down on R, elevator down