AP Psych Berliner Unit 5
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Learned Helplessness
A belief that one has no control over their circumstances, learned through repeated exposure to uncontrollable events, leading to feelings of passivity and lack of effort to change the situation.

Social Learning Theory
theory that emphasizes the importance of observing, imitating, and modeling behaviors, as well as the role of cognitive processes, in learning from others within social contexts.

Modeling
Learning by observing and imitating the behaviors of others.

Observational learning
learning by observing others

Vicarious Conditioning
Learning by observing the consequences of others' actions, without directly experiencing those consequences oneself.

Mirror neurons
brain cells that activate when performing certain actions OR observing someone else perform those actions.
For these neurons, watching someone else do something and doing that thing yourself are indistinguishable.
Found in the motor cortex, somatosensory cortex, Broca's area, temporal lobes, and maybe elsewhere too

Behaviorism
focuses on observable behaviors and the environmental forces that shape those behaviors

Associative Learning
A process of learning in which an individual forms connections between events that occur together.
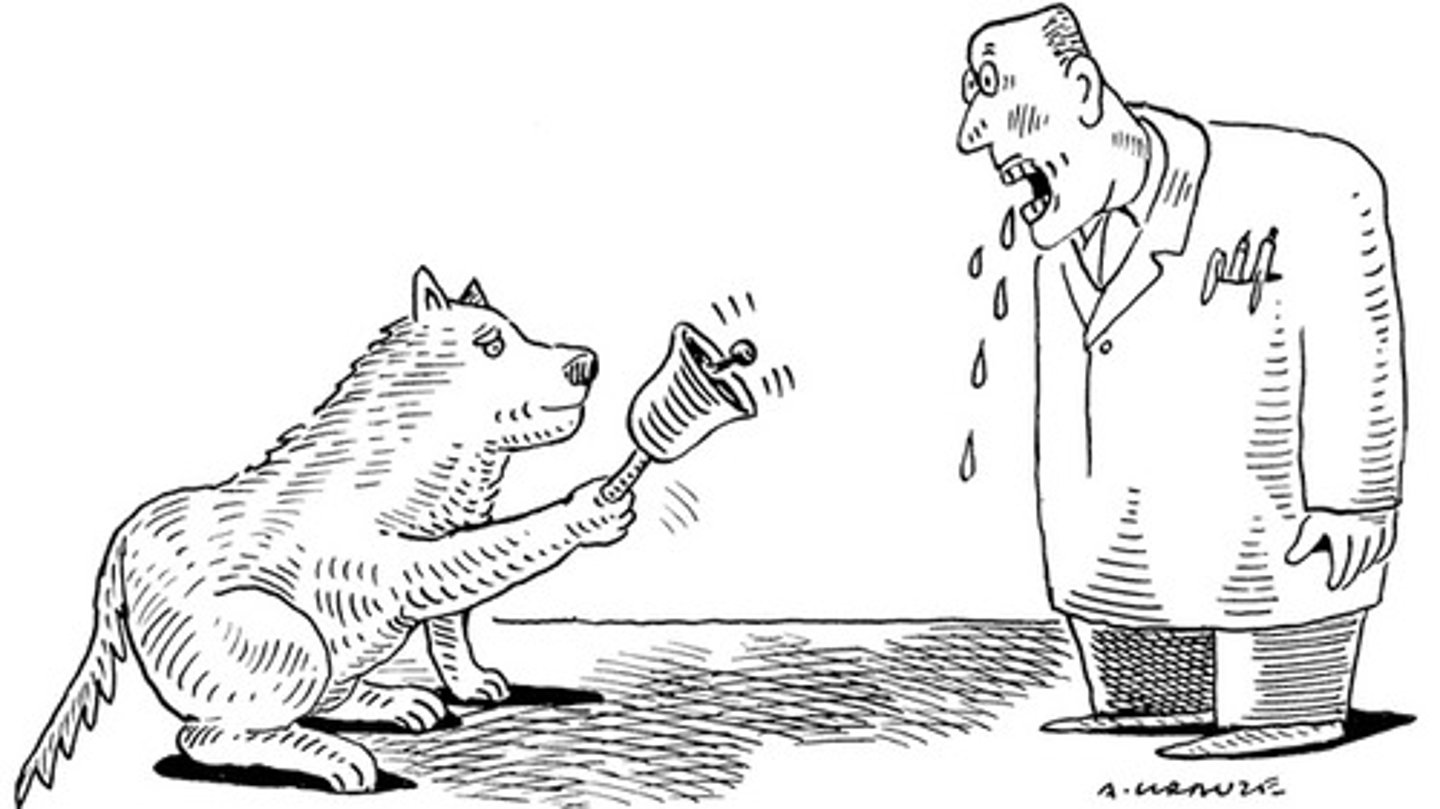

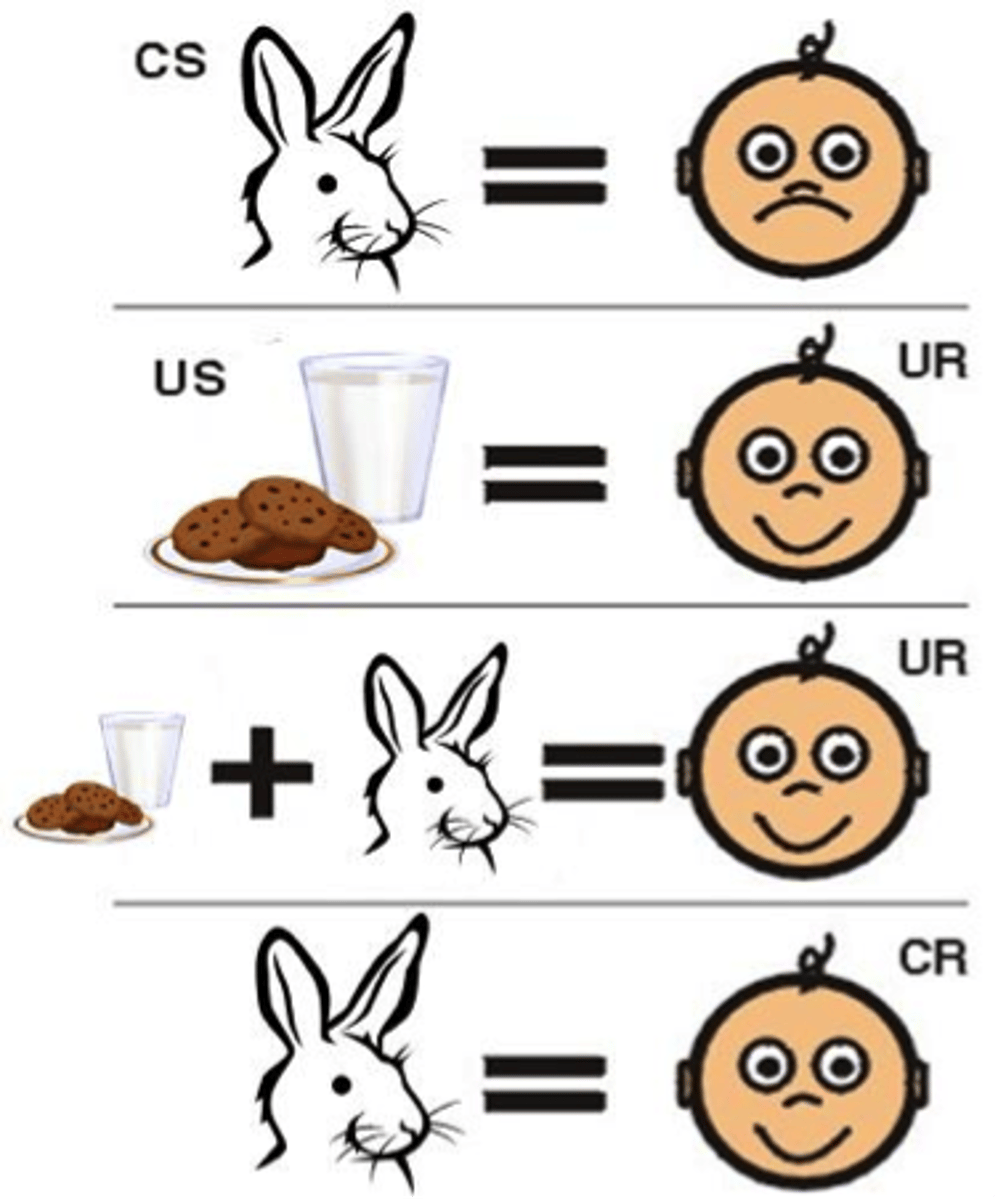
Classical Conditioning
A learning method where we associate two stimuli, enabling us to anticipate events.
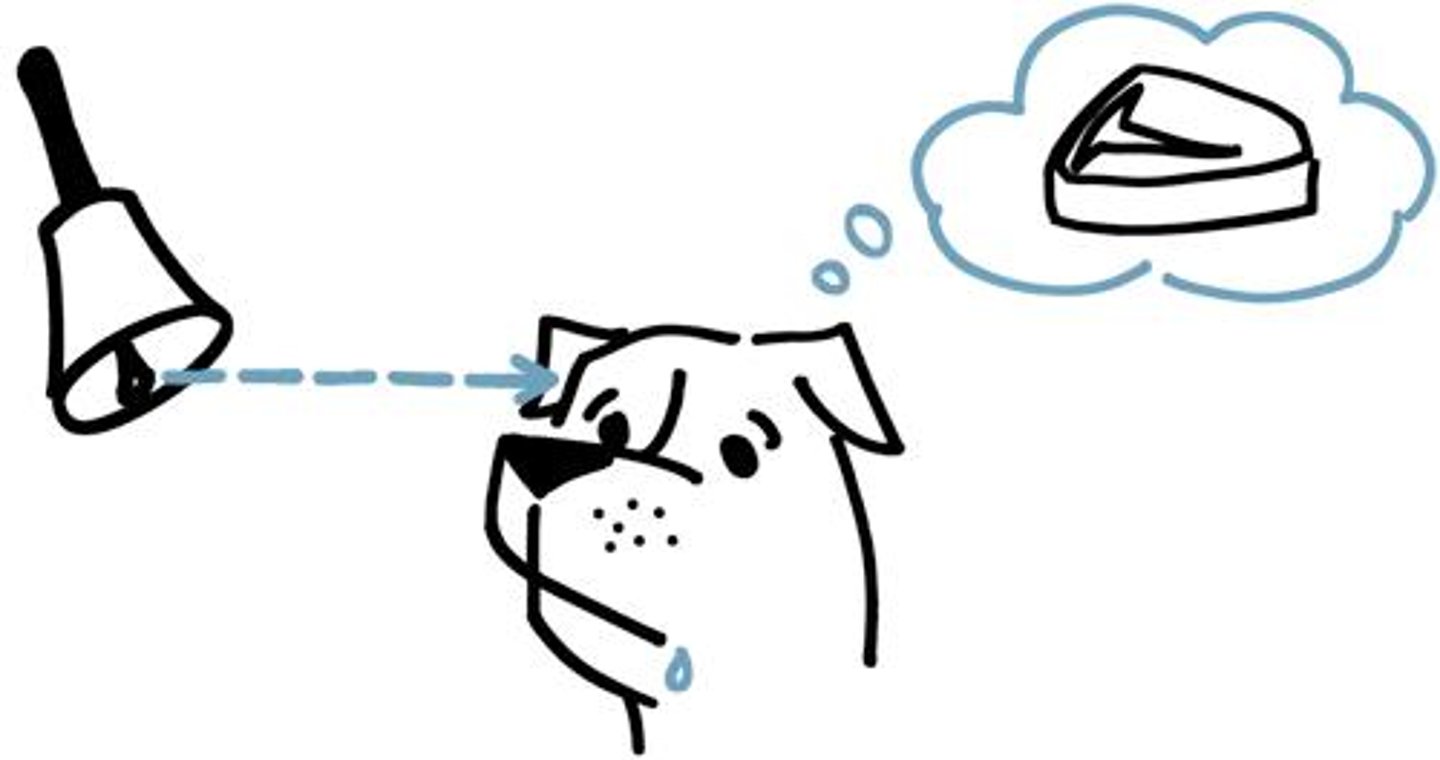
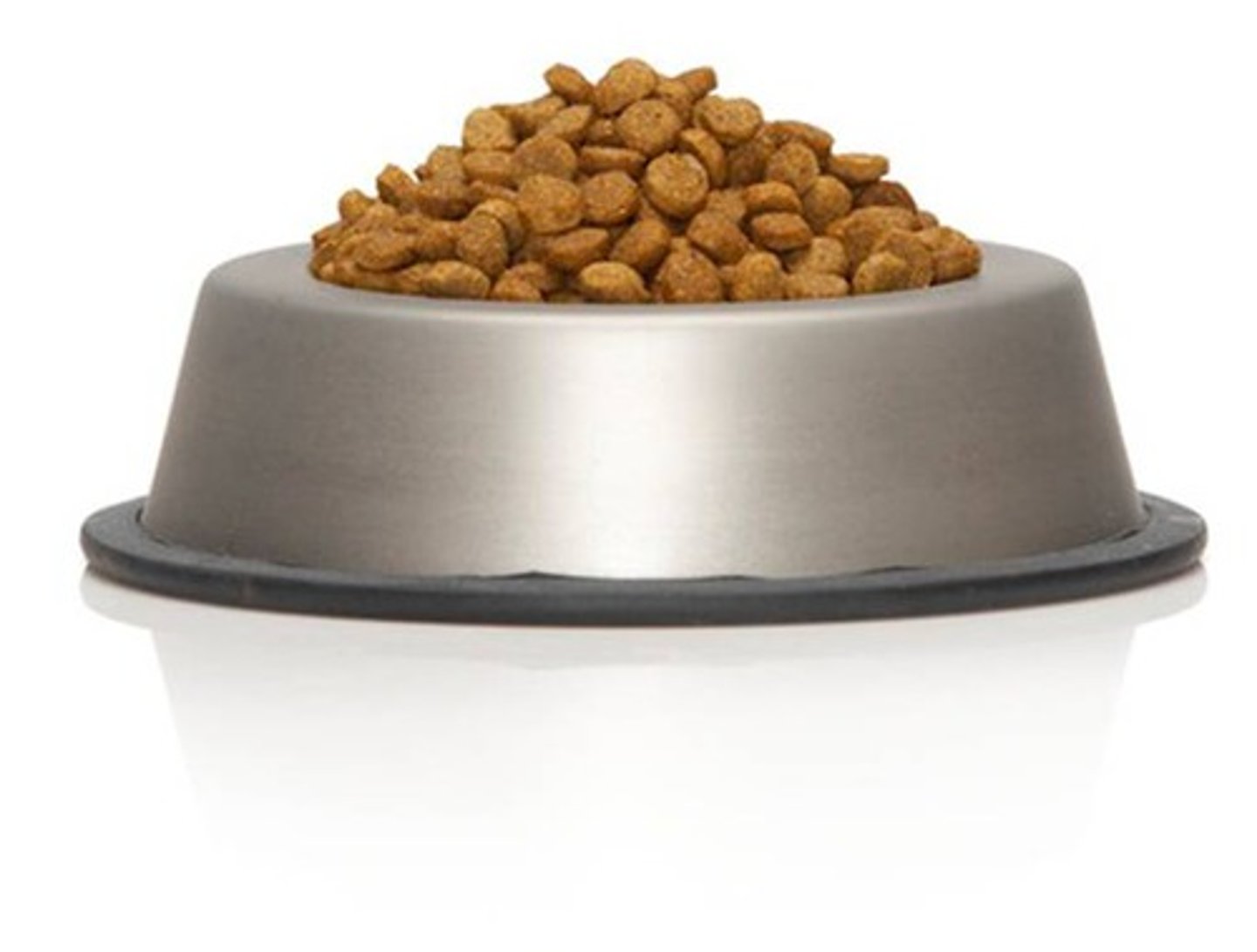
Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS)
A stimulus that naturally and automatically triggers a response without any learning needed.

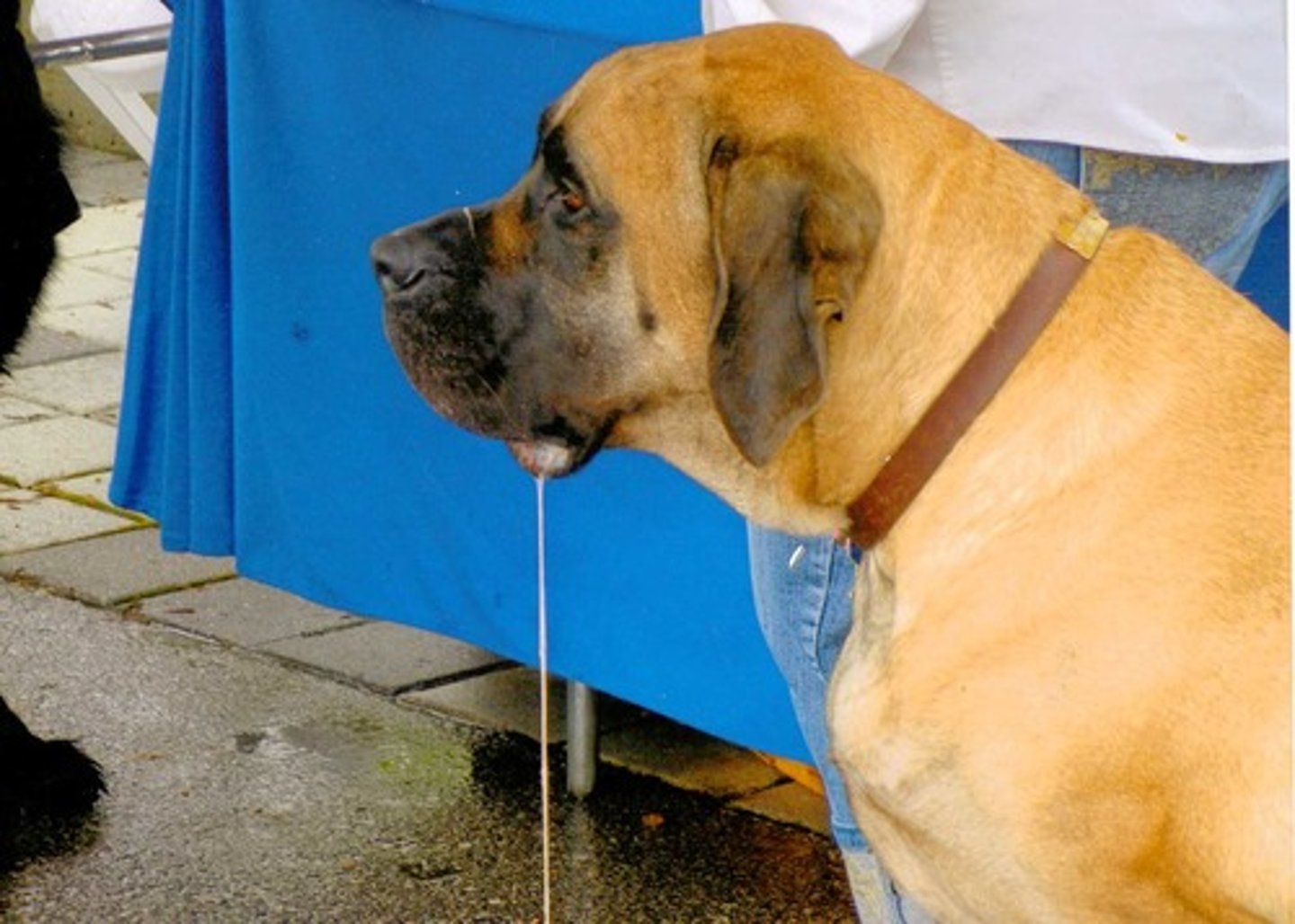
Unconditioned Response (UR)
A natural and automatic reaction to a stimulus that occurs without any prior learning or conditioning.

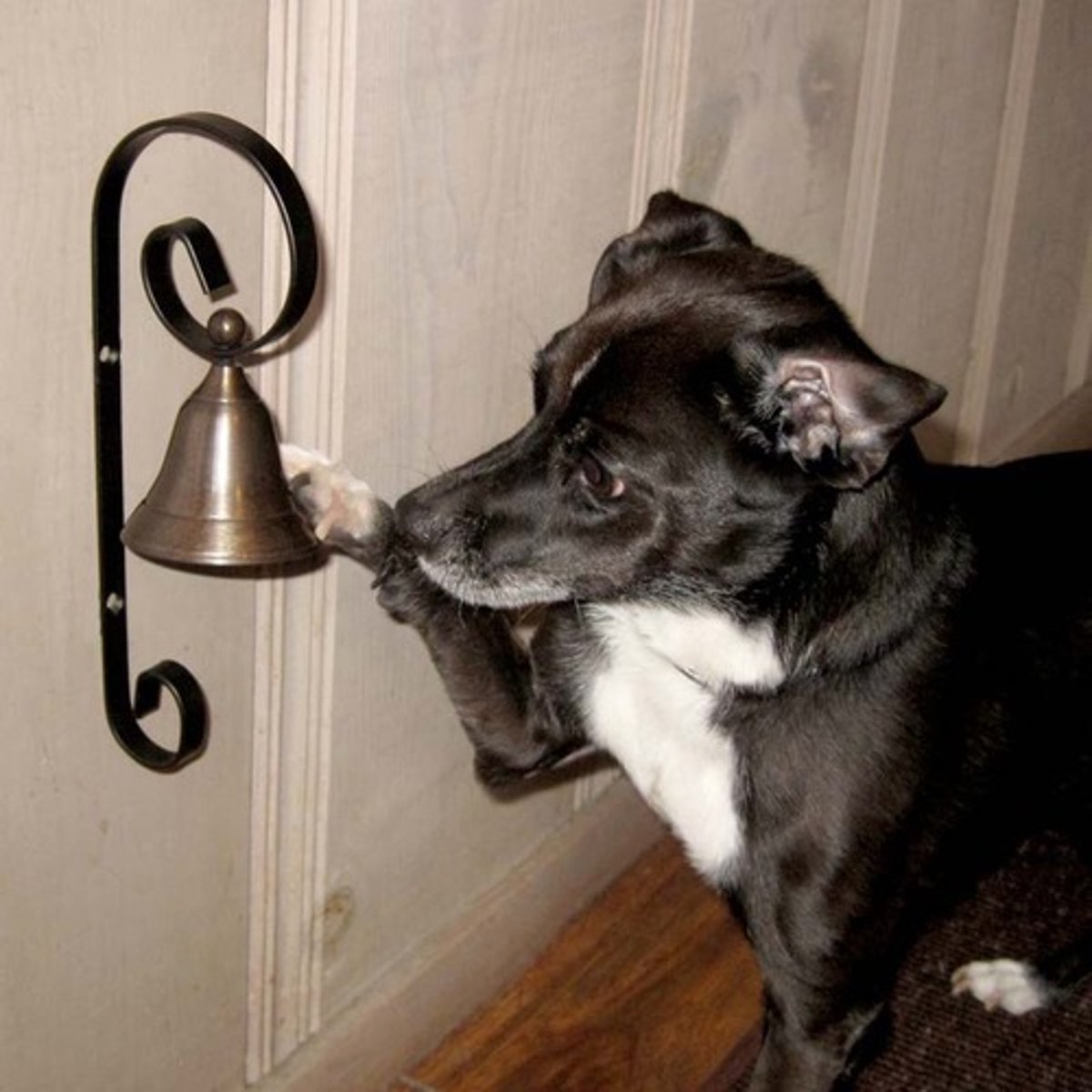
Conditioned Stimulus (CS)
A previously neutral stimulus that, after being repeatedly paired with an unconditioned stimulus, evokes a conditioned response.

Conditioned Response (CR)
A learned response that occurs when a conditioned stimulus is presented, resulting from the association with an unconditioned stimulus.

Acquisition
the initial learning of an association.
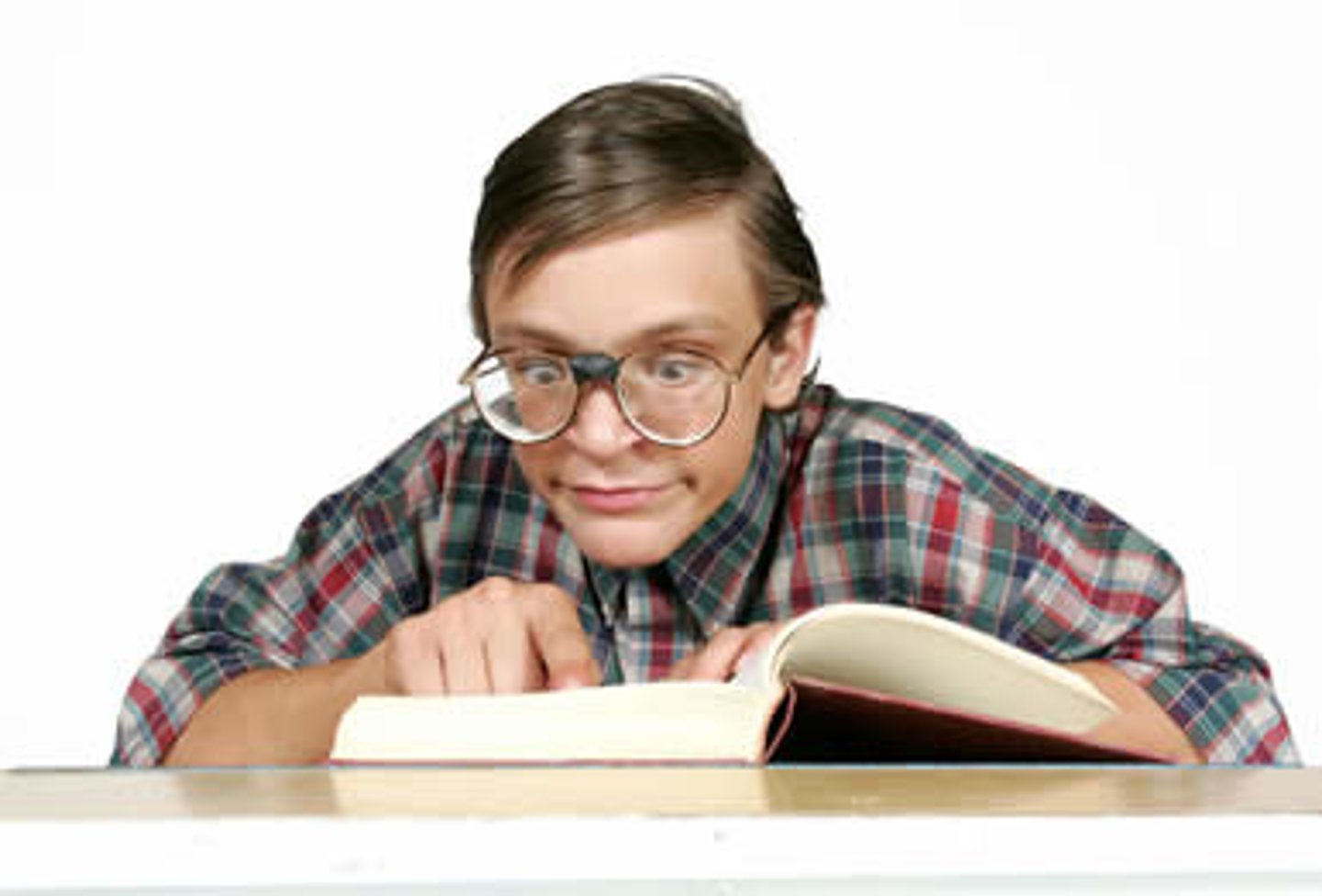

Extinction
The process in which the conditioned response weakens and eventually disappears when the conditioned stimulus is repeatedly presented without the unconditioned stimulus.

Spontaneous Recovery
The reappearance of a previously extinguished conditioned response after a period of rest, suggesting that extinction does not erase the association but suppresses it temporarily.

Stimulus Discrimination
The ability to differentiate between similar stimuli and respond differently to them, learned through the conditioning process.
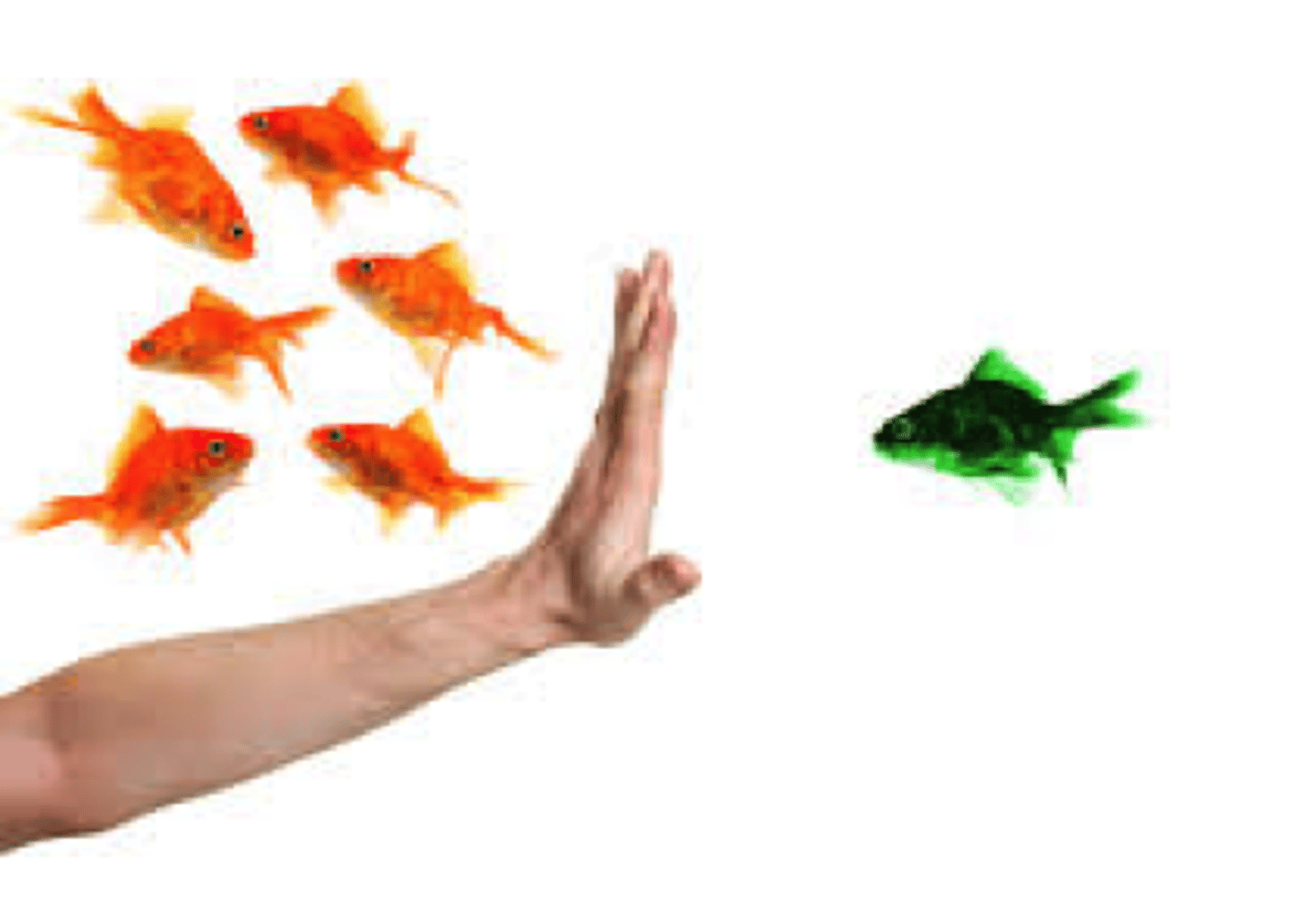
Stimulus Generalization
The tendency to respond to stimuli that are similar to the conditioned stimulus, as a result of the conditioning process.

Habituation (Non-Associative Learning)
occurs when organisms grow accustomed to and exhibit a diminished response to a repeated or enduring stimulus.

Higher-Order Conditioning
A process where a previously conditioned stimulus is used to create further associations with new neutral stimuli, resulting in those stimuli also eliciting a conditioned response.

Counterconditioning
Changing a learned response to something more preferred by pairing it with a different experience.
One-Trial Conditioning
Learning that happens quickly after just one pairing of two things.

Biological Preparedness
The innate tendency of organisms to quickly learn associations between certain stimuli and responses that are relevant to their survival, such as food and danger.

Taste Aversion
A learned association between the taste of a particular food and feeling sick, often occurring after only one pairing.

Operant Conditioning
A type of learning in which behavior is strengthened or weakened by consequences, such as reinforcement or punishment.
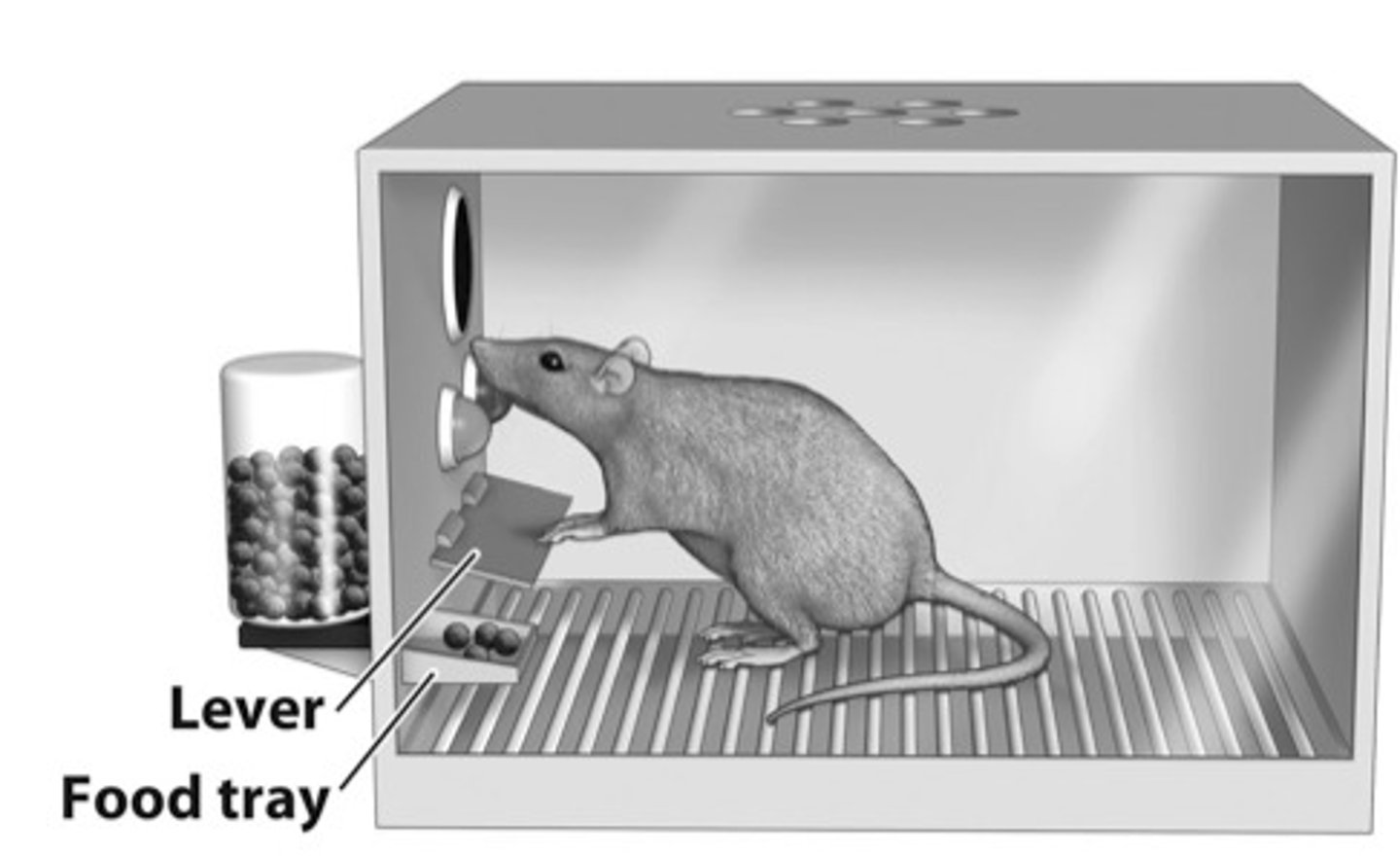
The Law of Effect
Behaviors followed by favorable outcomes are more likely to be repeated, while behaviors followed by unfavorable outcomes are less likely to be repeated.
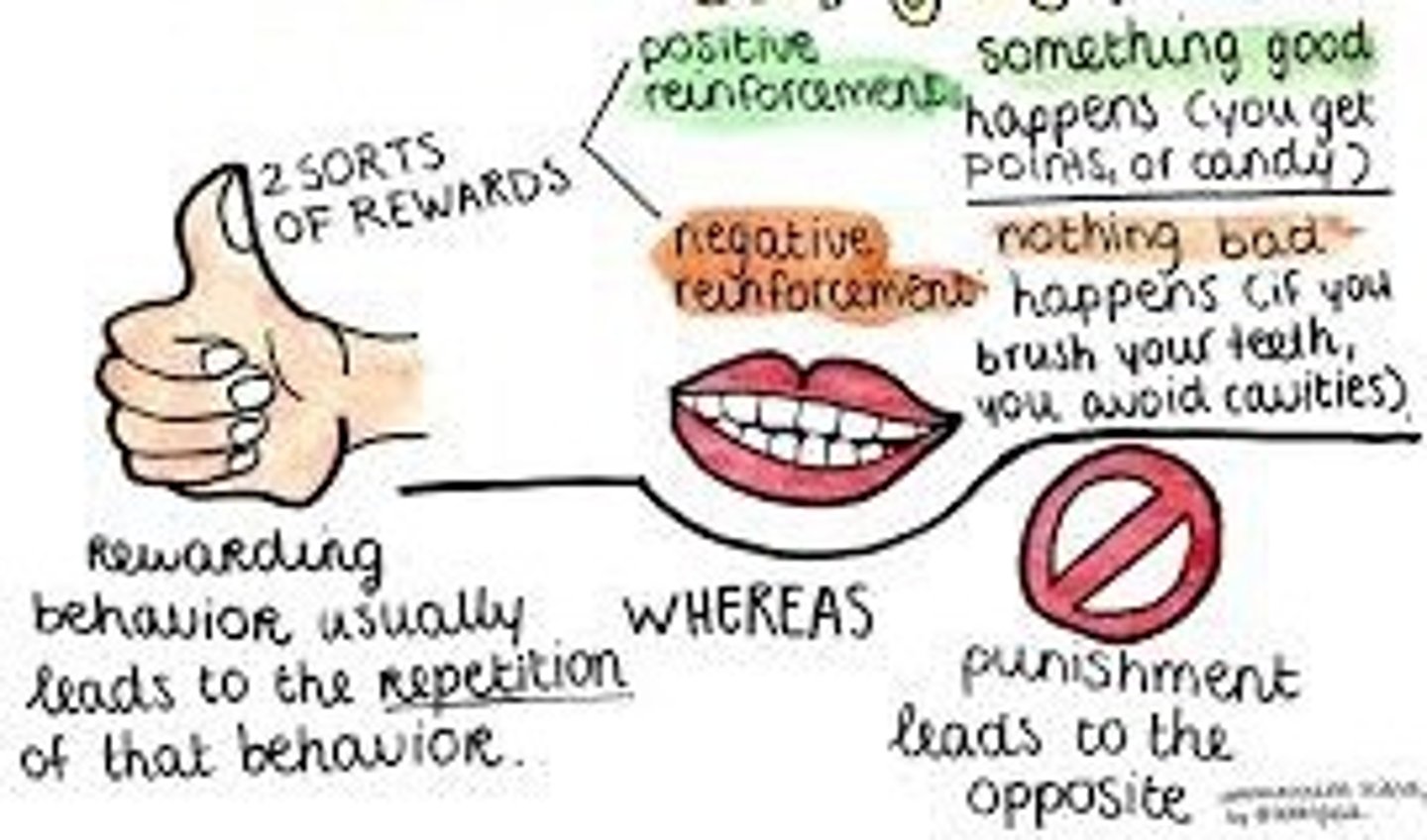
Reinforcement "Repeat"
Any consequence that increases the likelihood of a behavior occurring again in the future.

Primary Reinforcers
Things we naturally like, such as food or water.

Secondary Reinforcers
Things we learn to like because they're connected to primary reinforcers or other things we like.
Ex: Money, praise, grades in school, points, applause, trophies or medals.

Reinforcement Discrimination
The ability to distinguish between different stimuli and respond appropriately based on the presence or absence of reinforcement.

Reinforcement Generalization
The tendency to respond similarly to different stimuli that are associated with the same reinforcement.

Positive Reinforcement
Presenting a desirable stimulus after a behavior to increase the likelihood of that behavior happening again in the future.

Negative Reinforcement
Removing an aversive stimulus after a behavior to increase the likelihood of that behavior happening again in the future.
Positive Punishment
Adding an aversive stimulus after a behavior to decrease the likelihood of that behavior happening again in the future.
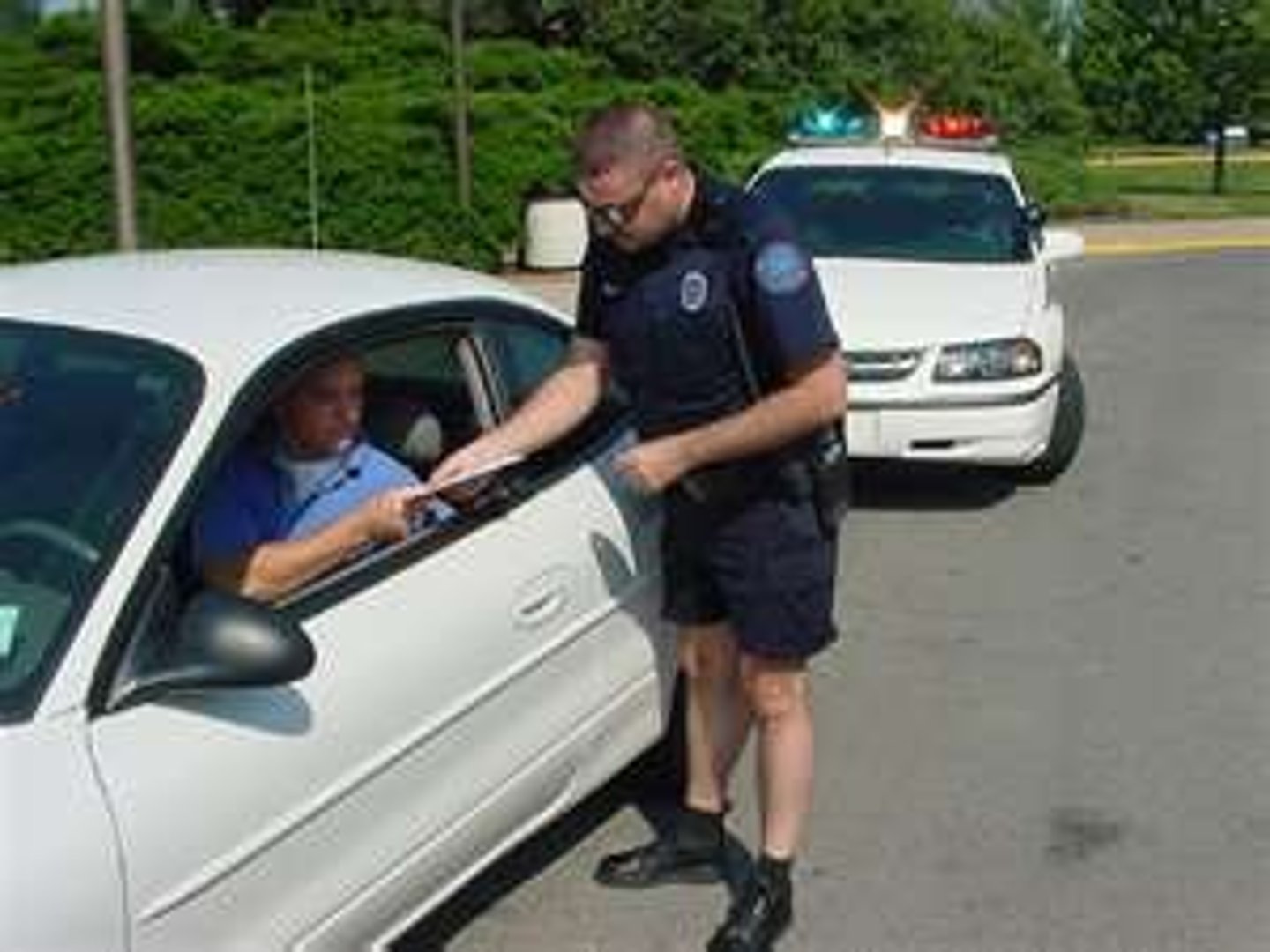

Negative Punishment
Removing a desirable stimulus after a behavior to decrease the likelihood of that behavior happening again in the future.

Shaping
Gradually reinforcing behaviors that are closer and closer to the desired behavior, leading to the development of a complex behavior or skill.

Instinctive Drift
Animals may go back to their natural instincts instead of learning new behaviors through training (operant conditioning).

Superstitious Behavior
Accidental reinforcement of behaviors, leading to the belief that those behaviors are causing desired outcomes, even when they are not.

Reinforcement Schedules
Patterns determining when and how often reinforcement is given for a behavior, influencing the rate and persistence of that behavior.
Continuous Reinforcement
Reinforcing a behavior every time it occurs.

Partial Reinforcement
Reinforcing a behavior only some of the time it occurs, leading to slower extinction but also less consistent responding.

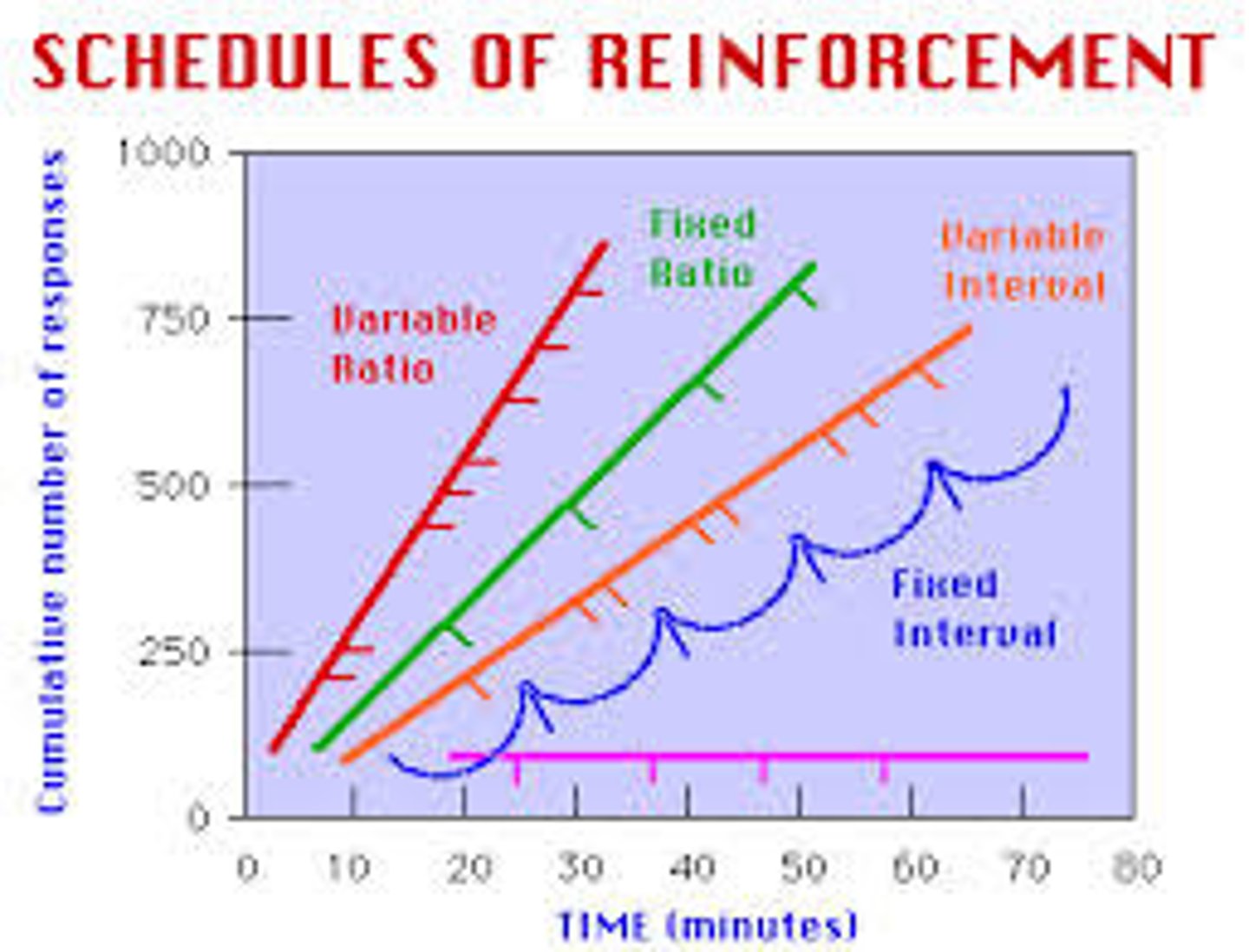
Fixed Interval "FI"
Reinforcement is delivered after a fixed amount of time has passed since the last reinforcement, leading to a predictable pattern of behavior.
This pattern forms a "scalloped" curve on a graph, illustrating how anticipation of reinforcement influences response timing, with subjects optimizing their efforts based on the expected timing of rewards.

Variable Interval "VI"
Reinforcement is delivered after varying amounts of time have passed since the last reinforcement, leading to a steady but moderate rate of responding.
Moderate, Steady Rate: The rate of response fluctuates, slowing down after reinforcement and increasing as the interval lengthens.

Fixed Ratio "FR"
Reinforcement is delivered after a fixed number of responses, leading to a high rate of responding with short pauses after each reinforcement.
Shows a consistent pattern of pauses after each reward, followed by a rapid response increase.

Variable Ratio "VR"
Reinforcement is delivered after an unpredictable number of responses, leading to a high and steady rate of responding with minimal pauses.
Demonstrates a rapid accumulation of responses, with reinforcement given after an unpredictable number of responses.
High Motivation: Results in a high, steady response rate as the next reward is always potentially one response away.

Latent Learning
Sometimes we don't display our learned behavior unless we're motivated to do so

Cognitive Map
a mental representation of the layout of one's environment

Intrinsic motivation
motivation to do a behavior for its own sake (e.g. studying because you're genuinely interested in the topic)

Extrinsic motivation
motivation to do a behavior based on external rewards/punishments (e.g. studying in order to get a good grade, get into college, or avoid being grounded)

Overjustification
The process by which extrinsic rewards can sometimes displace intrinsic motivation

Problem-focused coping
Attempting to alleviate stress directly by changing the stressor or the way we interact with that stressor.

Emotion-focused coping
attempting to alleviate stress by avoiding or ignoring a stressor and attending to emotional needs related to one's stress reaction
