health and illness 2: exam 4: Immunity
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
what is immunity
the normal physiologic response to microorganisms and proteins as well as conditions associated with an inadequate or excessive immune response
immune response photo
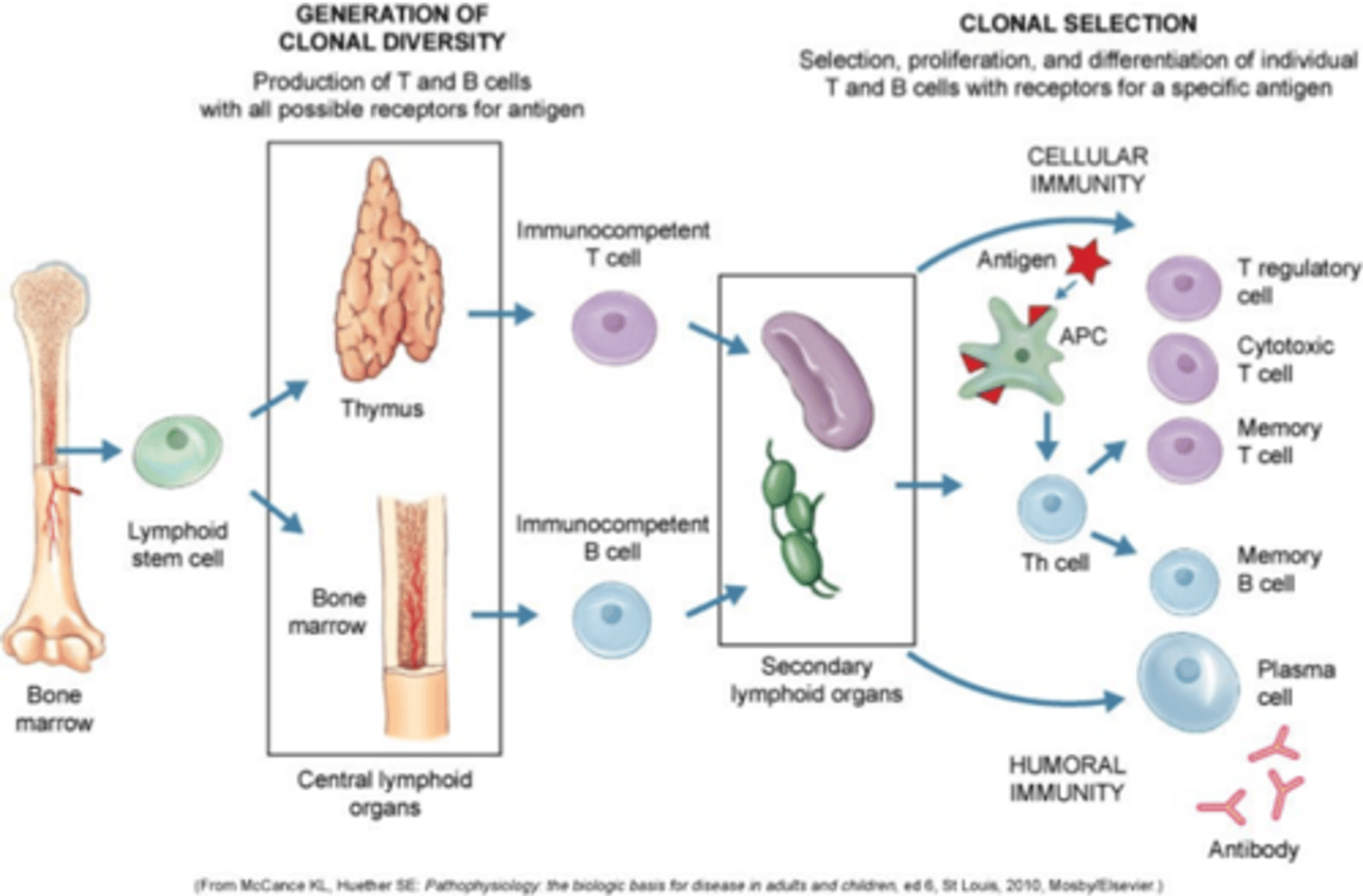
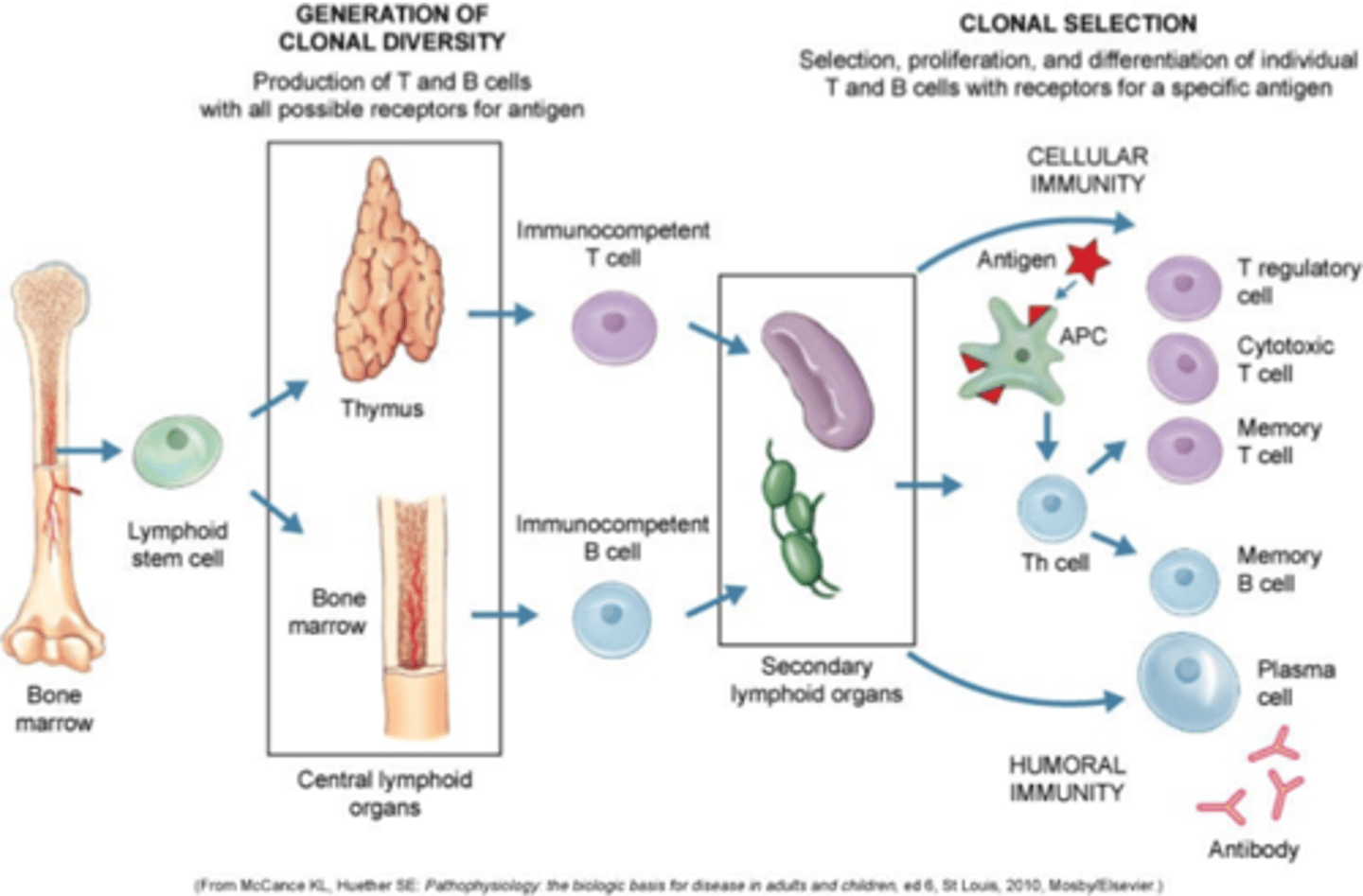
innate vs adaptive immunity
types of altered immunity
-immunocompromised/immunodeficient
-hypersensitive
immunocompromised/immunodeficient s/s
-report of frequent infections
-report of poor wound healing
-fatigue
-malaise
-weight loss
clinical findings of immunocompromised
-may appear poorly nourished or having wasting syndrome
-may have chronic wounds
-may have enlarged lymph nodes
-presence of opportunistic infections
4 classes of hypersensitivity
I: immediate
II: tissue specific
III: immune complex mediated
IV: delayed hypersensitivity/cell-mediated
what is I: immediate hypersensitivity
allergies or allergic rxn
what is II: tissue specific hypersensitivity
autoimmune hemolytic anemia
what is III: immune complex mediated hypersensitivity
lupus/RA
what is IV: delayed hypersensitivity/cell-mediated hypersensitivity
transplant rejection
what is antibody involvement in I: immediate hypersensitivity
IgE
what is antibody involvement in II: tissue specific hypersensitivity
IgG or IgM
what is antibody involvement in III: immune complex mediated hypersensitivity
IgG
what is antibody involvement in IV: delayed hypersensitivity/cell-mediated hypersensitivity
none (lymphocyte and macrophage)
what is leukopenia
low WBC count
causes of leukopenia
-autoimmune diseases
-medications (immunosuppressive, mental health meds, chemo)
-severe illness sepsis
-cancers
-lupus
-HIV/AIDs
-radiation therapy
what is leukocytosis
high WBC count
causes of leukocytosis
-infection
-inflammation
-leukemia
-extreme stress
-med side effects
what are WBC w/ differential labs
look at 5 types of WBCs
what are the WBCs in differential labs
-monocytes
-eosinophils
-neutrophils
-basophils
-lymphocytes
what are monocytes
4-13%
-fights infection and foreign substances
what are eosinophils
1-5%
-plays a role in allergic response and parasite infections
what are neutrophils
40-50%
-fights bacterial infections (left shift)
what are basophils
0.1-25
-plays a role in inflammatory conditions and allergy response
what are lymphocytes
20-40%
-fights viral infections (right shift)
what is the most prevalent inflammatory arthritis
rheumatoid arthritis
characteristics of RA
-course and severity variable
-chronic systemic autoimmune disorder
-abnormal, overactive functioning of immune system
-inflammation of CT
-primarily in joints
-chronic pain, alterations in body image
risk factors for RA
-female 3x more likely
-age 30-60 years
-genetic predisposition
-bacterial/viral infection (epstein barr virus)
-stress and smoking
-environmental factors
-older age
onset of RA
-usually insidious
-acute/precipitated by stressor
-may be preceded by systemic manifestations of inflammation
-polyarticular, symmetrical
-rate of development can fluctuate (symptoms come and go)
what are flare ups in RA
-can last days-months
-more common in winter than summer
stages of RA
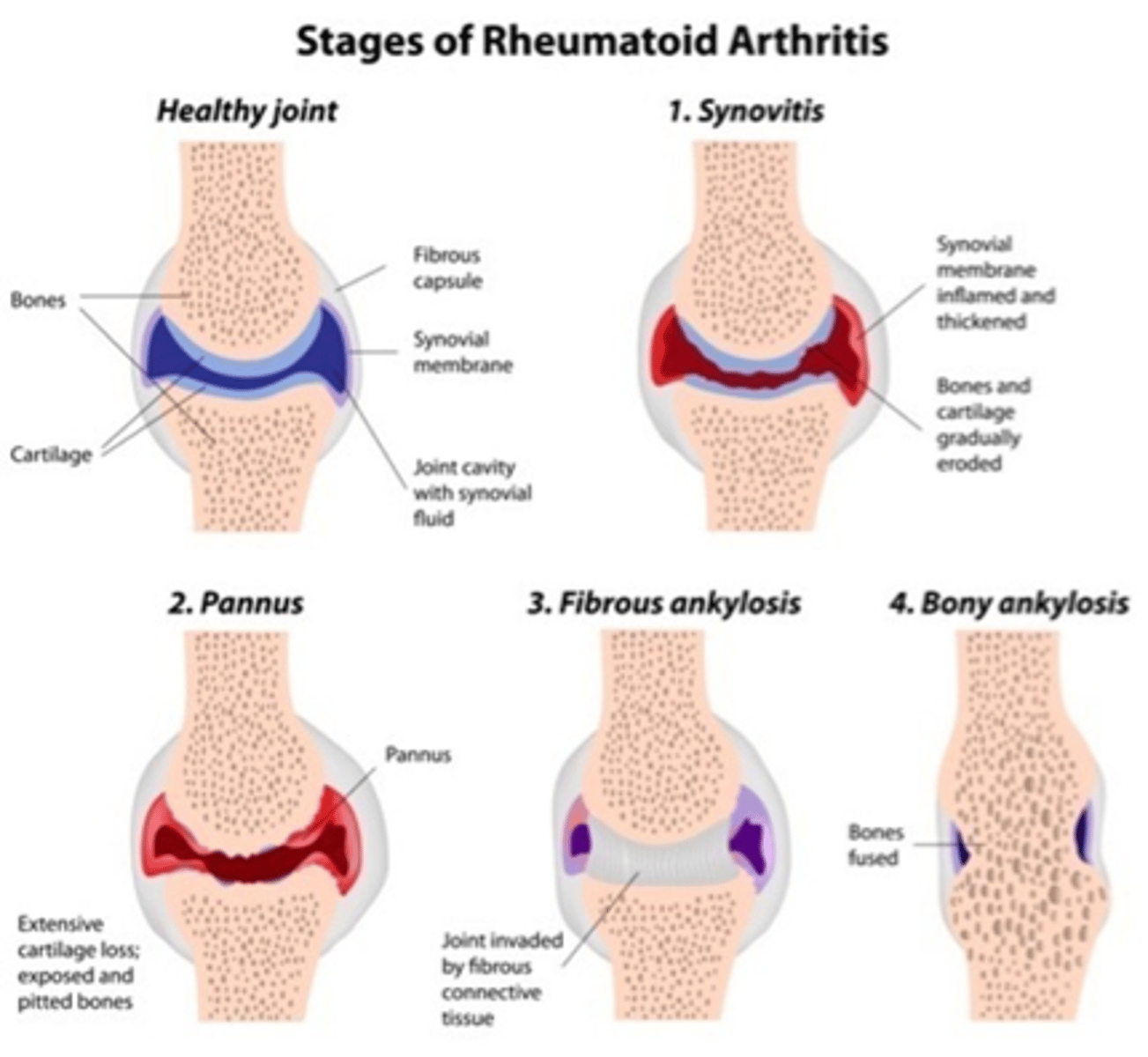
manifestations of RA
-joint pain at rest and movement
-morning stiffness
-anorexia and weight loss
-swelling
-fever
-erythema
-lack of function
-deformities
-rheumatoid nodules (PIP)
dx labs for RA
-anti-CCP positive
-rheumatoid factor
-increased ESR
-increased CRP
-ANA
-elevated WBC
-CBC reveals anemia
dx procedures for RA
-xray
-radionuclide scans
-direct arthroscopy
-synovial fl aspirate
-synovial membrane biopsy
xray for RA
-soft tissue swelling
-erosion of joints
-osteoporosis adjacent progressing to bone-cyst formation
-narrowing of joint space
-subluxation
radionuclide scans for RA
identify inflamed synovium
direct arthroscopy for RA
visualization of area reveals bone irregularities/degeneration of joint
synovial fl aspirate for RA
-greater volume than normal
-cloudy, yellow appearance (inflammatory response, bleeding, degenerative waste products)
-elevated levels of WBCs/leukocytes
-decreased viscosity and complement (C3 and C4)
synovial membrane biopsy for RA
reveals inflammatory changes and development of pannus (inflamed synovial granulation tissue)
nursing dx for RA
-acute and chronic pain
-fatigue
-impaired physical mobility
-self care deficit
-disturbed body image
-ineffective coping
how do we reduce fatigue in RA
-assist with and encourage physical activity
-monitor for fatigue
-provide a safe environment
-monitor for med effectiveness
-encourage foods high in vitamins, protein, and iron
-eat small, frequent meals
nursing interventions for RA
-Place and monitor use of pillows, sandbags, trochanter rolls, splints, braces.
-Encourage frequent changes of position. Assist the patient to move in bed, supporting affected joints above and below, avoiding jerky movements.
-Recommend that patient take a warm bath or shower upon arising or at bedtime. Apply warm, moist compresses to affected joints several times a day. Monitor water temperature of compress, baths, and so on.
üProvide gentle massage.
-Discuss and provide safety needs such as raised chairs and toilet seat, use of handrails in the tub, shower and toilet, proper use of mobility aids and wheelchair safety.
-Encourage verbalization about concerns of disease process, future expectations.
-Encouraged a balanced diet, but make sure the patient understands that special diets won't cure RA. Stress the need for weight control.
pharm therapy for RA
-NSAIDs
-COX-2 enzyme blockers
-DMARDS
-corticosteroids
surgical management for RA
-reconstructive surgery
-synovectomy
-plasmapheresis
-arthroplasty
what is reconstructive surgery for RA
-indicated when pain cannot be relieved by conservative measures and the threat of loss of independence is eminent
what is synovectomy for RA
excision of synovial membrane
what is plasmapheresis for RA
-may be done for severe, life threatening exacerbation
-removes circulating antibodies from plasma, decreasing attacks on the clients tissues
pt hx for osteoarthritis
-C/O palpable bony joint enlargement
-morning stiffness (lasting <30 mins)
-pain
pt hx for RA
-pain duration >6 weeks
-morning stiffness >30 mins
-systemic symptoms (fatigue, anorexia)
physical exam for OA
-reduced ROM
-joint malalignment
-crepitus
physical exam for RA
-synovitis
-joint involvement, symmetrical
-joint destruction
-extra-articular manifestation
radiologic tests for OA
-presence of osteophytes
-joint space narrowing
radiologic tests for RA
-erosions on Xray or MRI
-synovitis noted by US or MRI
lab tests for OA
clear synovial fl
serology for RA
-ESR or CRP
-Anti-CCP
-rheumatoid factor
common types of juvenile arthritis
-oligoarticular JIA
-polyarticular (rheumatoid factor positive or negative) JIA
-psoriatic arthritis
-enthesitis-related arthritis
-systemic JIA
what is oligoarticular JIA
-juvenile idiopathic arthritis
-affects about 50% of children with JIA
-involved four or fewer joints
-large joints (knees, ankles, elbows) typically affected
-often seen in toddler years
-associated with an increased risk of eye inflammation
what is polyarticular (rheumatoid factor positive or negative) JIA
-30-40% of children with JIA affected
-affects 5 or more joints
-peak age of onset is toddler and adolescent years
-polyarticular disease can affect both the large and small joints (hands and feet)
what is psoriatic arthritis
-occurs in children who have a personal or family hx of psoriasis
-can develop swelling of an entire finger or toe= doctylitis
what is enthesitis-related arthritis
-occurs more in boys than girls
-begins in early adolscence
-often experience tenderness where tendons and ligaments attach to bone
-at risk for developing arthritis in lower back and spine
-at risk for eye disease
what is systemic JIA
-still's disease
-most serious
-least common
-10-15% of children with JIA
-joint inflammation and stiffness
-rash
-periodic fevers
-may cause inflammation of internal organs (heart, liver, spleen, lymph nodes)
risk factors for JIA
-immunogenic susceptibility
-environmental triggers
-genetic predisposition
s/s JIA
-joint swelling, redness, warmth
-pain worse in morning and after inactivity
-mobility limitations
-fever
-rash
-limp in the morning
-delayed growth
inflammatory markers of JIA
-ESR/CRP
-CBC
-ANA
-RF
xray of JIA
slit lamp eye examination- ocular manifestations
nursing dx of JIA
-acute pain
-impaired physical mobility
-disturbed body image
-self care deficit
-deficient knowledge
nursing interventions for JIA
-PT
-activity
-pain relief
-ROM
-emotional support
-health education
meds for JIA
-NSAIDs
-methotrexate
-corticosteroids
-etanercept
impact of JIA
-med appt
-school (handwriting/typing/opening items)
-socialization
-stigma
-self care
-healthy eating
-heat/cold tx
what is infection
the invasion and multiplication of microorganisms in body tissues, which may be unapparent or the result of local cellular injury caused by competitive metabolism, toxins, intracellular replication, or antigen-antibody response
contributing factors of infection
-immune defense
-virulence of microorganisms
-type of microorganism
types of pathogens
-bacteria
-viruses
-fungi
-parasites
what is the pathogen that most commonly causes infection
bacteria
what are viruses
nucleic acid, must enter living cells
what are fungi
yeasts, molds
what are parasties
protozoa, helminths, arthropods
what is the host part of infection
-acute illness
-mechanical barriers
-fever
-stress
-phagocytes
-biochemical barriers
-biochemical mediators
-chronic illness
environment part of infection
-sanitation
-water quality
-crowded living conditions
-weather
-air quality
-seasons
parasite part of infection
-encapsulation
-adhesions
-spore formation
-slime layer
-pili
-flagella
-enzymes
what is endemic infection
refers to the constant presence and/or usual prevalence of a disease or infectious agent in a population within a geographic area
what is epidemic infection
an increase, often sudden, in the number of cases of a disease above what is normally expected in that population in that area
what is pandemic infection
epidemic that has spread over several countries or continents, usually affecting a large number of people
what are healthcare associated infection
-can develop during pts stay in the facility and/or manifest after discharge
-UTI most common
-antibiotic-resistant bacteria
what are antibiotic resistant bacteira
-MRSA
-VRE
-PRSP
-C diff
-ESBL
what are the pathogens that cause biologic threat infections
-anthrax
-small pox
-botulism
-pneumonic plague
-viral hemorrhagic fevers
what are the pediatric infections and communicable disease pathogens
-pertussis
-hep b
-varicella
-measles
-rubella
primary infection prevention
-handwashing
-immunizations
secondary infection prevention
screening
what is herd immunity
works to control the spread of disease within a population when a specific amount of that population (threshold) becomes immune to the disease through vaccination or infection and recovery
managing fever interventions
-eliminate underlying cause of fever (hyperthermia)
-destroy causative microorganisms
-drug therapy
-external cooling
-fl administration
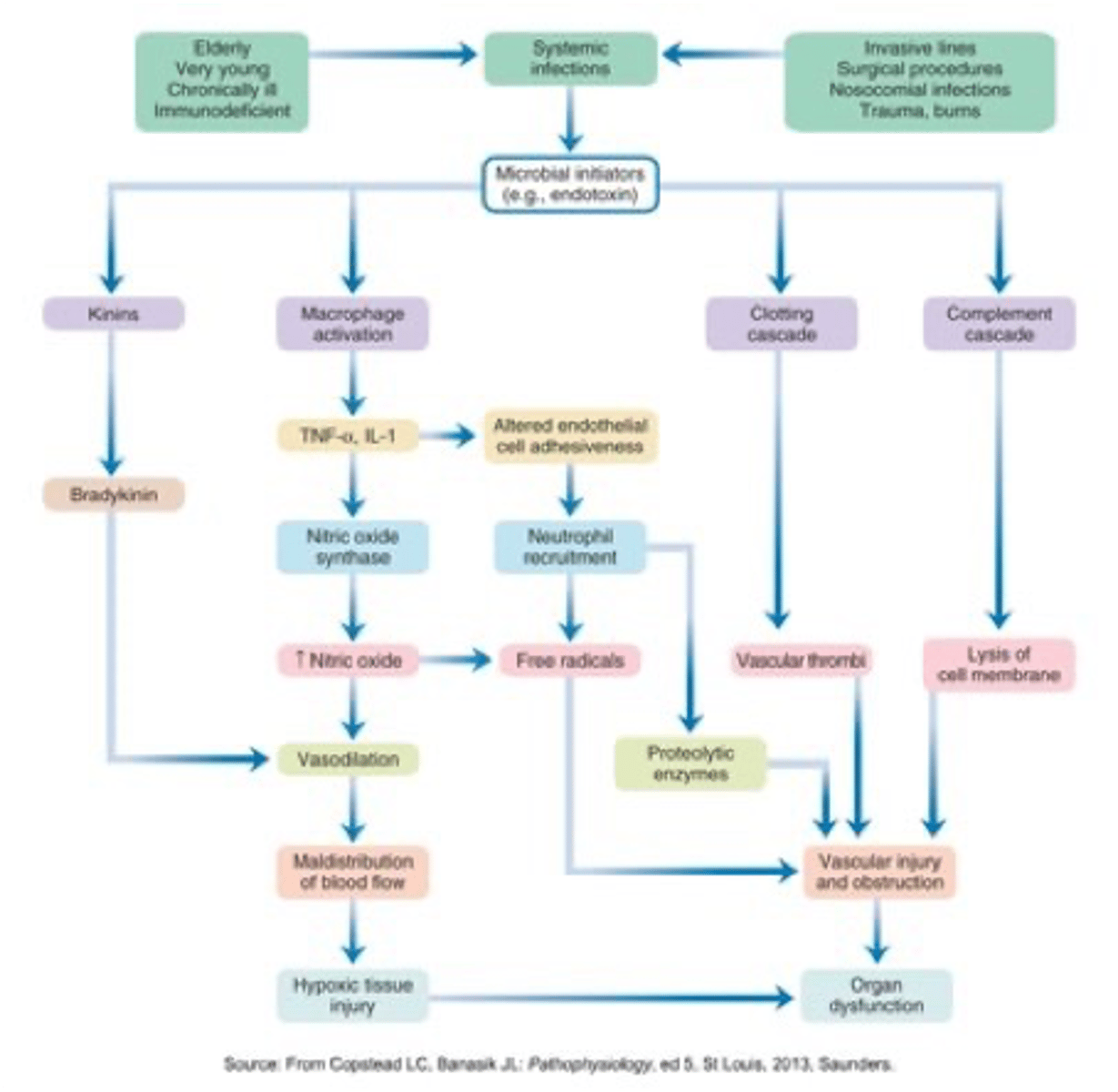
consequence of uncontrolled infection
Once the body's compensatory mechanisms (e.g., vascular, renal, nervous, respiratory) are overcome, the following process occurs:
Septic shock --> Multisystem failure --> Death
consequence of uncontrolled infection chart
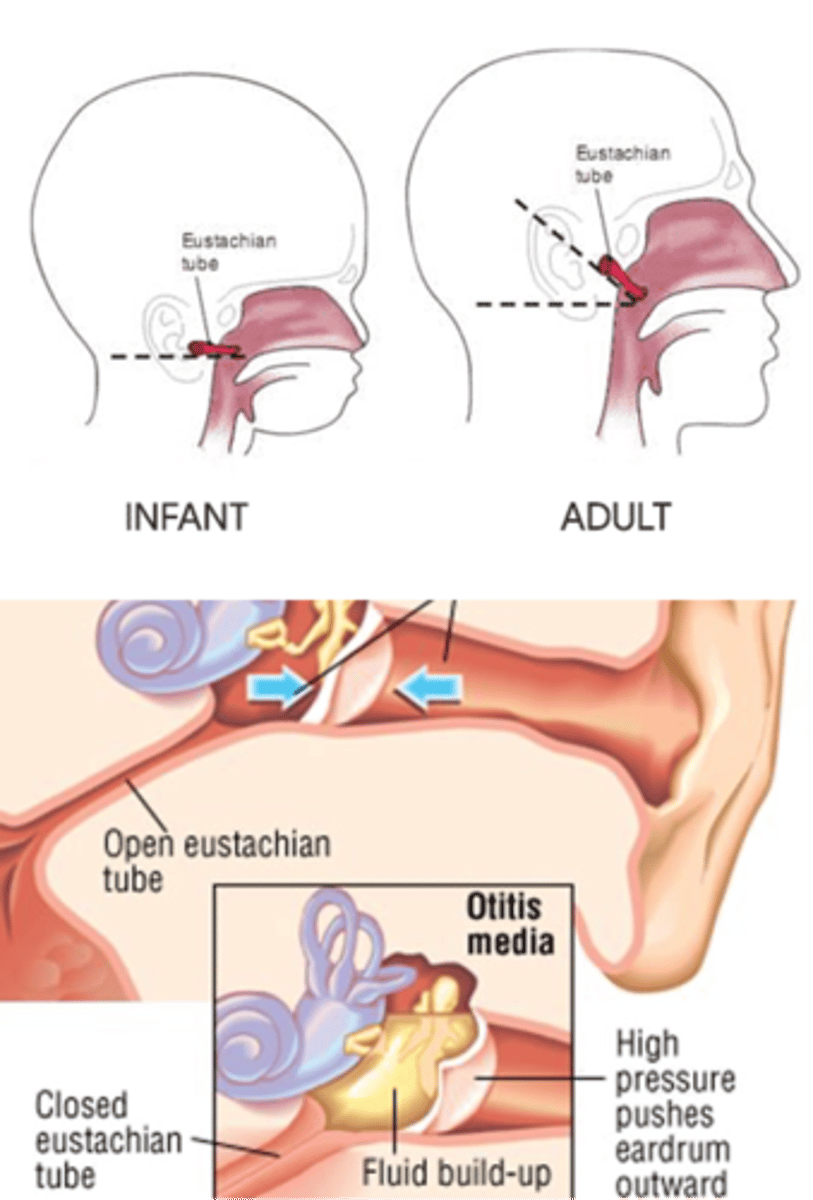
How do the eustachian tubes differ in kids?
eustachian tubes are shorter and more horizontal than adults
when do eustachian tubes peak
-first 2 years of life
-when children enter school (5-7 years)
eustachian tube anatomy: infant vs adult
bacterial causes of otitis media
-strep
-PNA
-H influenza
-M. cat
viral causes of OM
RSV, influenza
pathophysiology of OM
-bacterial infection
-viral
-allergies
-enlarged adnoids
risk factors for OM
-winter months
-daycare/schools
-smoker or livers with smoker
-cleft pallet
-down syndrome
-lack of immunizations
-bottle feeding lying down