chemistry atomic structures, BH & Lewis diagrams, ionic compounds, polyatomic atoms, molecular atoms, acids and bases, pH
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
what is chemistry?
the study of matter
what is matter?
anything that has both mass and volume
what is mass?
amount of matter that makes an object
what is volume?
amount of space occupied
what is an element?
pure substances that cannot be broken down by chemical means
made up of only 1 type of atom
ex: magnesium, iron, sodium
what is a compound?
pure substances that has 2 of more different elements in a fixed ratio chemically bonded together
ex: carbon dioxide, water
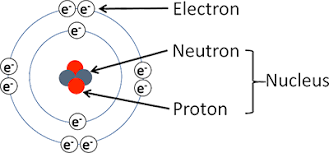
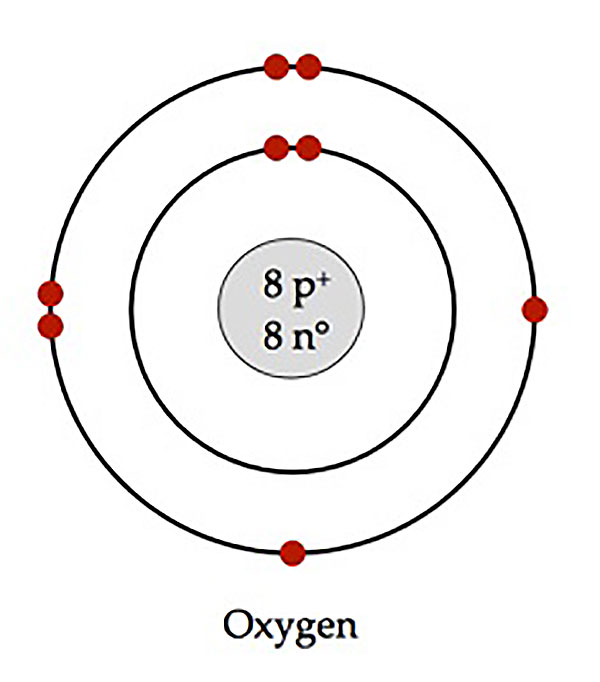
atomic structure
proton, neutron, electron
atoms are electrically neutral
what does the atomic number tell us about the atomic structure?
tells how many protons and electrons an atom has
what does the atomic mass tell us about the atomic structure?
average mass of an element’s atom. mass of protons & neutrons
how do you find an element’s neutrons by looking at the element in a periodic table?
mass # - atomic # = # of neutrons
properties of metals
found on the left side of the periodic table (except hydrogen)
solids at room temp.
lustrous, conductive, malleable
non-metals
found on the right side + hydrogen
all states (solid, liquid, gas)
dull, brittle, non-conductive
transition metals
middle of the table
change from metallic to non-metal properties
metalloids
zigzag (staircase on the right side)
some metallic & some nonmetallic properties
groups/families
vertical columns (up down)
group # = # of valence electrons
periods
horizontal rows (left right)
# of periods = # of orbits (shells)
valence electrons
electrons on the outermost shell of the atom
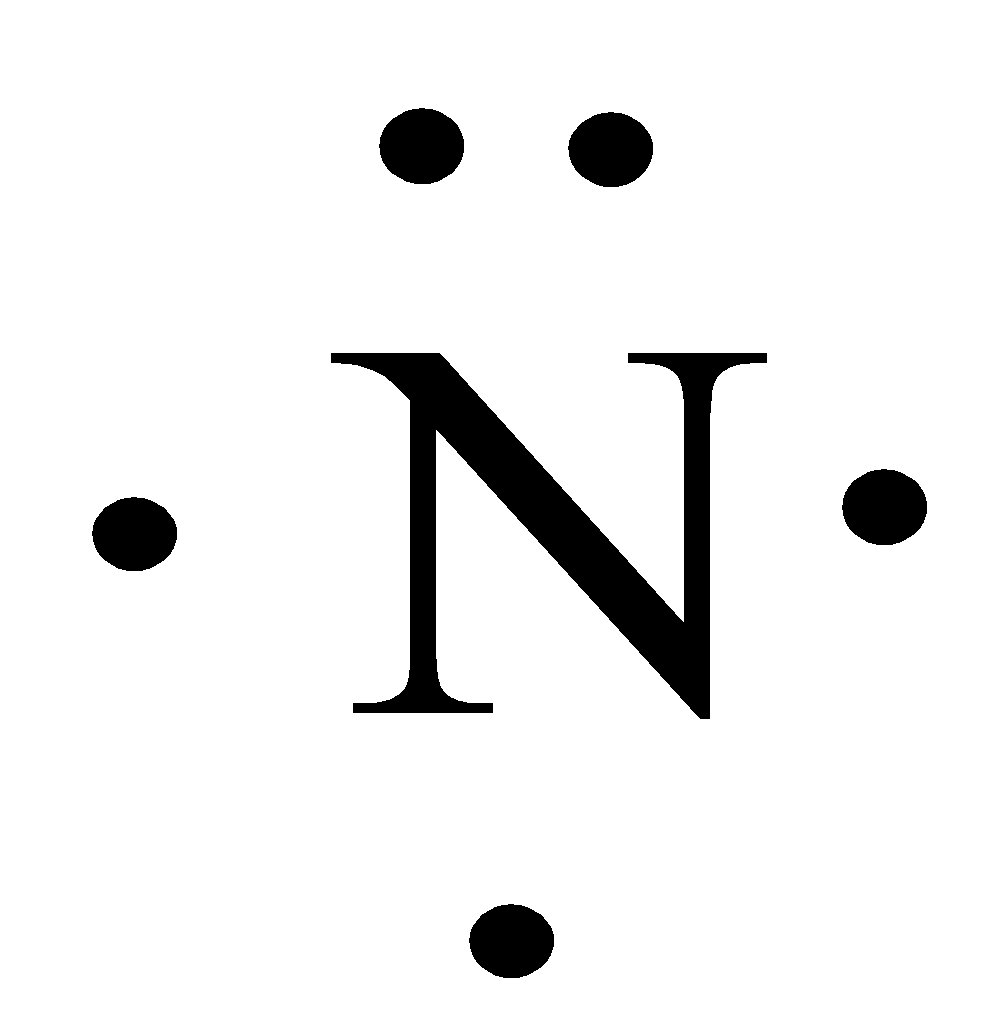
what does the lewis structure tell us about atoms?
only shows valence electrons and the chemical symbol
what does the bohr rutherford diagram tell us about atoms?
# of protons
# of neutrons
# of electrons
subscripts
Tiny numbers below an element’s symbol
Tells how many of that atom we have in one particle
Coefficient
number placed in-front of a chemical formula/symbol
tells us how many of that particle we have
Parenthesis
Groups elements together
Atom
Basic building block of all matter
Molecule
Formed when 2 or more atoms join together
ions
Positively or negatively charged atom
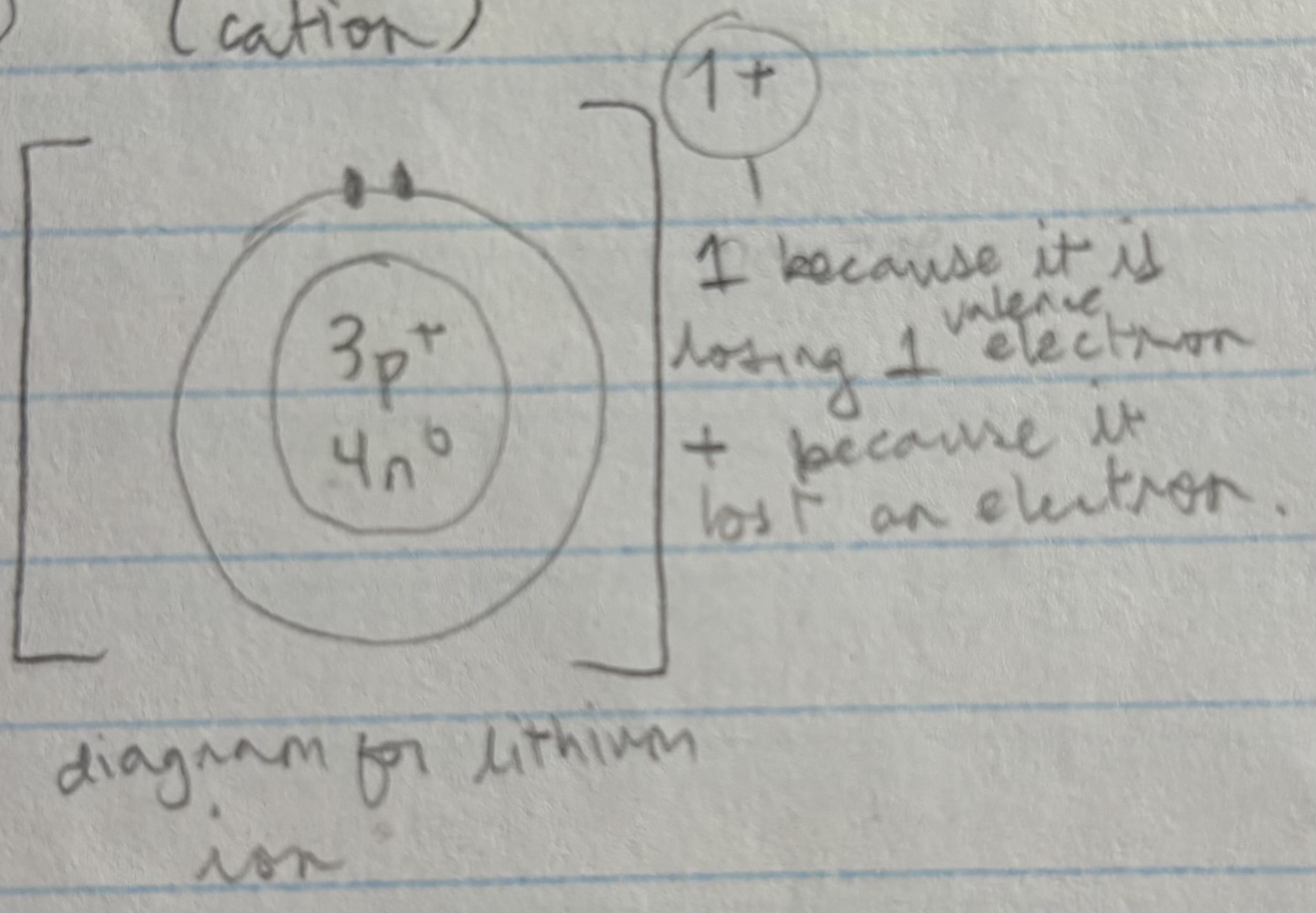
Cation
Positive ions
Usually formed by metals who lose electrons
Anion
Negatively charged ion
Usually formed by non-metals that gain electrons
Bohr rutherford diagram for ion
Lewis structure for ion
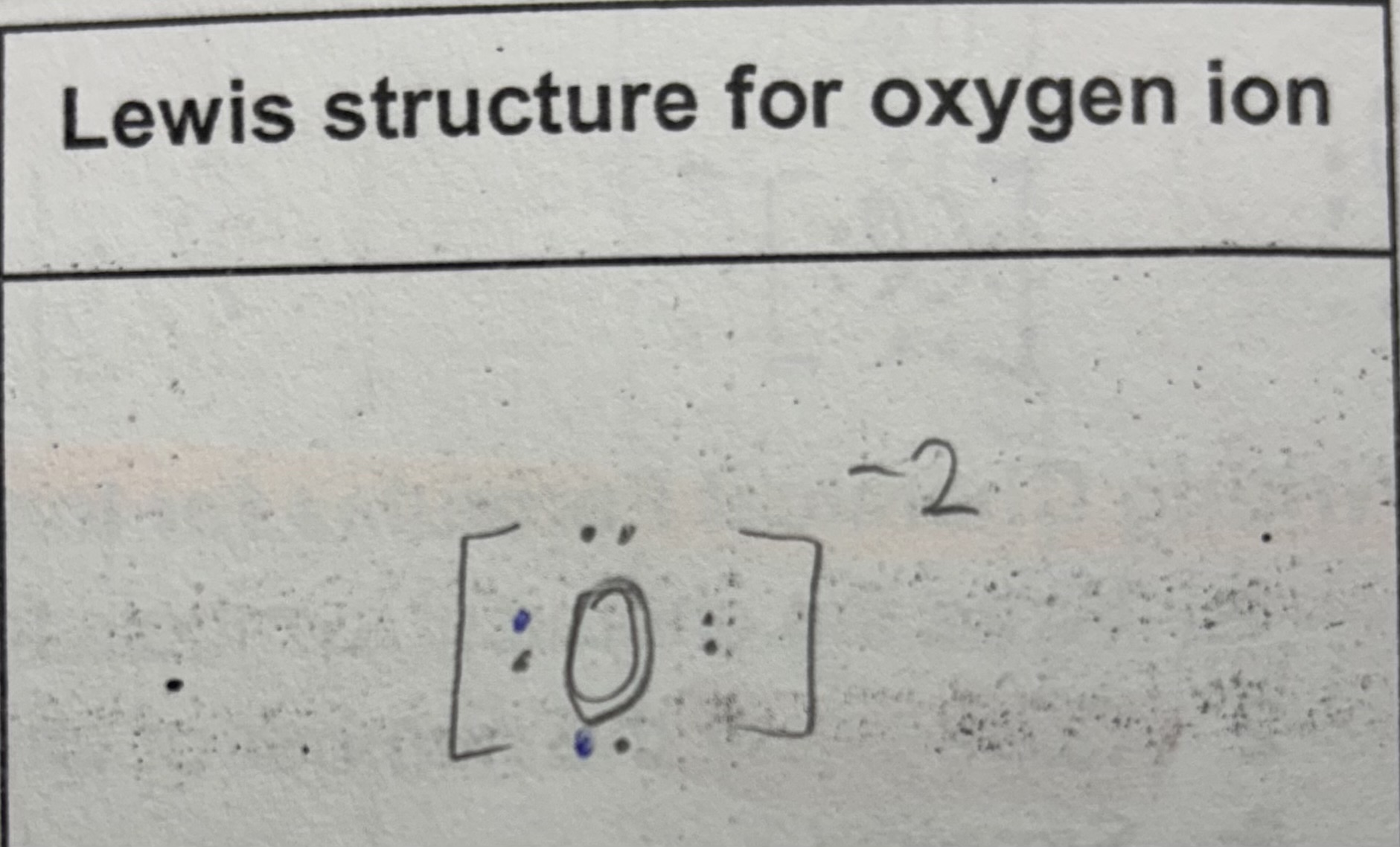
Ionic compounds
Formed between metals & non metals
Neutral
Solids at room temp, brittle, good insulators
Naming ionic compounds
Metal name remains same
Nonmetal ending changes to -ide
Multivalent
Found in the middle of the periodic table
Able to form more than 1 type of ion
The charge will be written after the name of the metal as a roman numeral written in brackets
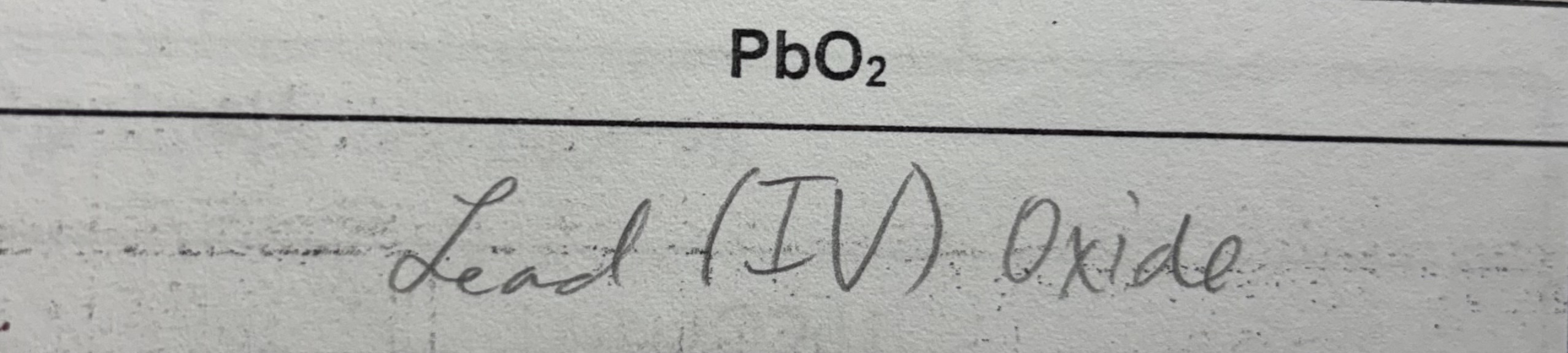
Polyatomic ions
Ion formed by more than one (poly-) atom
One unit, cannot make any changes to their subscripts
Most are anions
Molecular compounds
Non-metal atoms joining together by sharing electrons
Covalent bonding
Sharing of electrons, each atom not strong enough to take each other’s atoms
Diatomic elements
Elements that will always come in pairs
Usually exist as a gas
HOFBrINCl
Hydrogen, oxygen, fluorine, bromine, iodine, nitrogen, chlorine
Nomenclature molecular compounds
Only used in molecular compounds
Chemical reaction
One or more substances change into different substances
Word equation
Names of chemicals written out in full
Irreversible reaction occurs
Reactants written on the left
Products written on the right
Chemical equation
Chemical symbols & formulas are used to represent the chemicals
Dont forget HOFBrINCl
Skeleton equation
Unbalanced chemical equation
Reactant
Chemical used during the reaction
Product
Chemical that is produced during chemical reaction
Law of conservation of mass
In any given chemical reaction, the total the reactants equals the total mass of the product
Acids
Substances that produce hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water
Acid properties
sour
Conductive
React w metals
React w carbonates & bicarbonates
Neutralize bases
pH lower than 7
Bases
Substance that produces hydroxide ions (OH¯) when dissolved in water
Bases properties
Bitter
Conductive
Dont react w metals
Feels slippery
Neutralize acids
pH level higher than 7
Neutral
pH of 7
Neutral substance is distilled water
Neither acidic nor basic
Neutralization
Type of reaction in which acid and a base react to form an ionic compound
acid + base → water + ionic compound
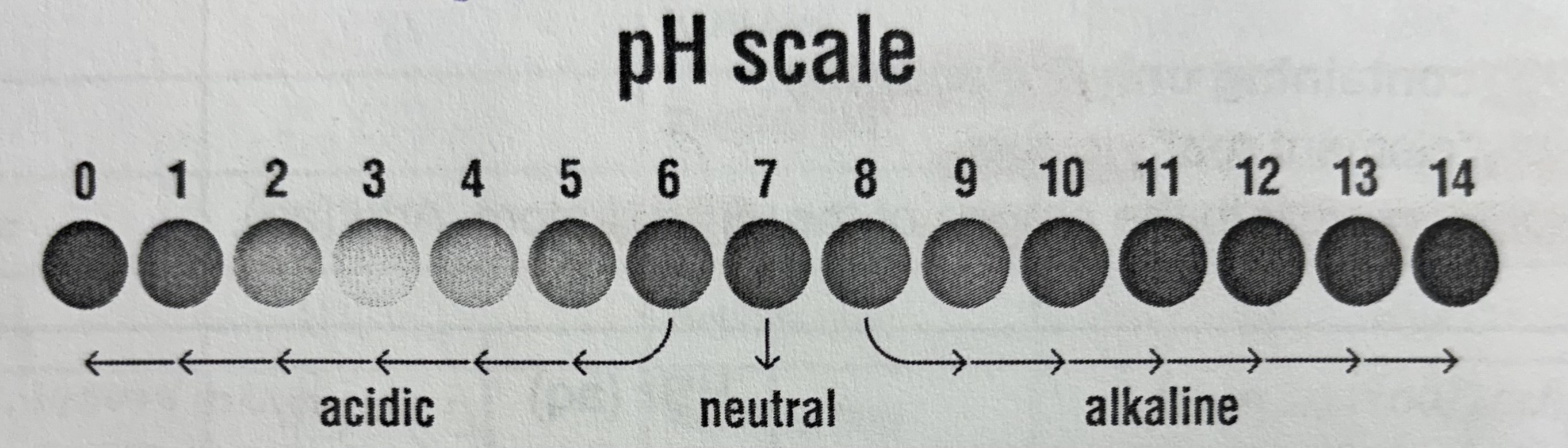
pH
Quantitative measure of how acidic or basic a solution is
Stands for power of hydrogen
pH scale
logarithmic, for every change in 1 pH concentration changes by 10x
ph 2 to 1 substance has 10x higher H+ concentration
ph 7 to 9 substance has 100x lower H+ concentration