Renal & Urinary System: Pathophysio
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
kidney functions
-filters blood plasma
-regulates osmolarity:
-secretes renin and erythropoietin
-detoxifies free radicals and drugs
-gluconeogenesis
kidney filters: blood plasma
filters blood and returns useful substances to blood, eliminates waste
kidney filters: osmolarity
regulates body fluids, blood volume, BP, and acid/base balance
gluconeogenesis of kidney
synthesis of glucose from amino acid precursors (from non-carb substances)
approximately __________ adults with diabetes of chronic kidney disease
1 out of 3
approximately __________ adults with high BP have chronic kidney disaease
1 out of 5
kidney disease pathology
-worldwide public health problem
-increasing in the US by 8-10% per year
-best treatment: transplant
-most affected are on dialysis
mediare and financial costs of kidney disease
-cost of end stage renal disease (ESRD) was 40 billion in 2009
-cost medicare 28 billion
most common cause of kidney disease
-diabetes
-second most common is hypertension
number of individuals in the US living with ESRD (end stage renal disease) on dialysis
69%
location of kidney
-retroperitoneal
-T12-L3
renal cortex
outer layer of kidney (1cm thick), contains all the glomueruli as well as 85% of the nephron tubules and their loops of Henle
renal medulla
renal columns, pyramids, papilla
renal pelvis
large, central collecting region in the kidney
nephron
functional unit of the kidneys in the renal cortex
components of a nephron
-Bowman's capsule
(with the glomerulus_
-proximal convoluted tubule
-Loop of Henle
-distal convoluted tubule
-collecting duct
glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
the amount of filtrate formed per minute by the two kidneys combined
how much filtrate is absorbed during GFR vs urine excreted
99% of filtrate reabsorbed, leaving 1 to 2 L urine excreted
mechanisms to control GFR activity via adjusting glomerular blood pressure
-autoregulation: juxtaglomerular apparatus--> monitors salinity, changes arteries diameter
-sympathetic control: exercise shunts blood to kidneys and gives to muscles
-hormonal mechanism: renin and angiotensin
renal autoregulation of glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
-increased BP --> constricts afferent arteriole, dilate efferent
-decreased BP --> dilate afferent arteriole, constrict efferent
-stable for BP range of 80 to 170 mmHg (systolic)
-cannot compensate for extreme BP
increased vs decreased GFR (abnormalities)
-increased GFR, urine output rises -> dehydration, electrolyte depletion
-decreased GFR, wastes reabsorbed (azotemia possible)
GFR in males
125 mL/min or 180 L/day
GFR in females
105 ml/min or 150 L/day
hormones that effect the kidney
renin, angiotensin II, aldosterone
renin
an enzyme released by the kidneys when BP drops
angiotensin II
a hormone that constricts blood vessels and increases blood pressure
aldosterone
a hormone that causes the kidneys to retain sodium and excrete potassium
appearance of urine
colorless to deep amber due to urochrome- from breakdown of hemoglobin (RBC's)
odor of urine
due to bacteria degrading urea to ammonia
normal volume of urine per day
1-2 L/day
pH of urine
ranges from 4.5-8.2, usually 6.0
chemical composition of urine
-95% water and 5% solutes
-urea, NaCl, KCl, creatinine, uric acid
tubular secretion of PCT and nephron loop
waste removal and acid-base balance
tubular secretion: waste removal
-urea, uric acid, bile salts, ammonia, catecholamines, many drugs, glucose
-increase BUN (nitrogen byproduct)
-too much can cause kidney failure
tubular secretion: acid-base balance
secretion of hydrogen and bicarbonate ions regulates pH of body fluids
primary function of nephron loop
-water conservation
-generates salinity gradient, allows CD to concentrate urine
-also involved in electrolyte reabsorption
excretion
separation of wastes from body fluids and eliminating them via 4 systems (respiratory, integumentary, digestive, urinary)
respiratory excretion
CO2
integumentary excretion
water, salts, lactic acid, urea
digestive excretion
water, salts, CO2, lipids, bile pigments, cholesterol
urinary excretion
-many metabolic wastes, toxins, drugs, hormones, salts, H+, and water
-primary system for excretion
effects of diuretics
increased urine output and decreased blood volume
using diuretics can lead to...
-hypertension
-congestive heart failure
diuretics mechanism of action
increased GFR and decreased tubular reabsorption
kidney disorders
-infectious: usually from ascending bacteria from UTI
-obstructive
-tumors
-renal failure: acute, chronic or clinical management
renal pain
-slightly below the ribs to the upper part of the thighs. may be bilateral or unilateral
-can mimic low back pain
hallmark symptom of renal pain
costovertebral angle tenderness
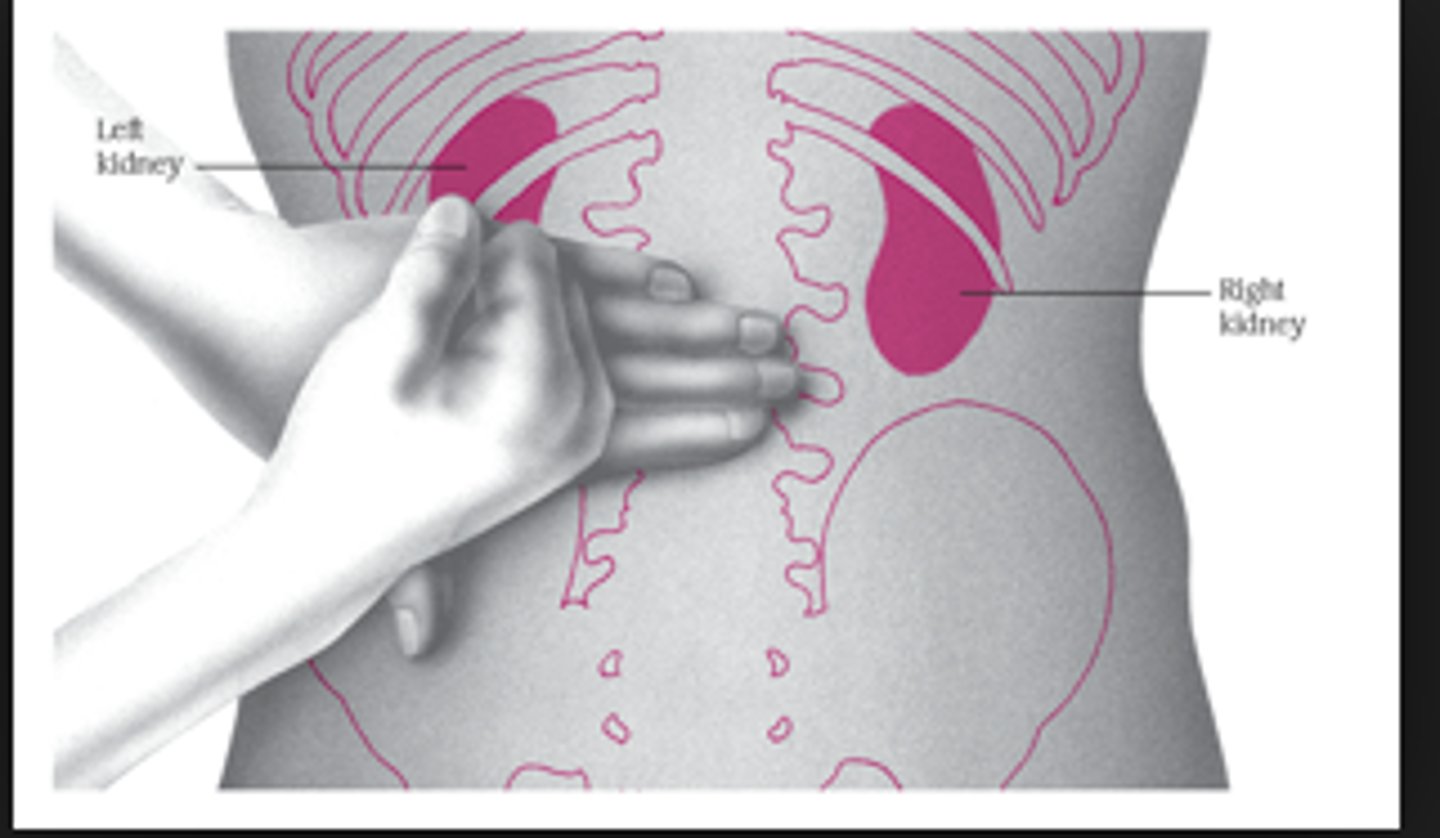
obstructive disorders
-results in urine stasis which predisposes pt's to infection and structural damage
-includes stones, tumors, prostatic hypertrophy, and strictures of the ureters or the urethra
kidney stones in obstructive disorders
-tend to form in the urinary tract under conditions of high solute concentration, low urine volume and low urine pH
-composed of calcium crystals
-usually undetected in radiographs
kidney tumor types
benign or malignant primary tumors
kidney tumor treatment
nephrectomy (kidney removal)
renal cellcarcinoma
-resistant to hormone therapy, immunotherapy, and chemotherapy
-late stage or recurrent diagnosis --> poor prognosis
urinary bladder location
in pelvic cavity, posterior to pubic symphysis
3 layers of urinary bladder
1. parietal peritoneum, superiorly; fibrous adventitia rest
2. muscularis: detrusor muscle, 3 layers smooth muscle
3. mucosa: transitional epithelium
trigone of bladder
openings of ureters and urethra, triangular
rugae of bladder
relaxed bladder wrinkled, highly distensible
capacity of bladder
moderately full: 500ml
max: 800ml
voiding urine - micturition
at 200 ml urine in bladder, stretch receptors send signal to sacral spinal cord
low, normal, high total capacity of urine in bladder
-low: <200 ml
-normal: 300-600 ml
-high: >600 ml
micturition signals ascend to
-inhibitory synapses on sympathetic neurons
-micturition center (integrates info from amygdala, cortex)
micturition signals descending
-further inhibits sympathetic neurons
-stimulates parasympathetic neurons
micturition effect/result
-urinary bladder contraction
-relaxation of internal urethral sphincter
external urethral sphincter
corticospinal tracts to sacral spinal cord inhibit somatic neurons (relaxes)
female urethra vs male urethra
-females: 3 to 4 cm long
-males: 18 cm long
bladder disorders
-incontinence
-cystitis
-tumors
incontinence prevalence
-affects 25% of men and 65% of women (b/w 20 and 60 years old)
-health care expenditure of 26 billion anually
urge incontinence
-the loss of urine in response to a sudden, urgent need to void; the person cannot get to a toilet in time
-from detrusor overactivity
stress incontinence
-when urine leaks during exercise and certain movements that cause pressure on the bladder
-from weakening of pelvic floor muscles or intrinsic urethral sphincter deficiency
interstitial cystitis
inflammation of the bladder lining due to infection, chemical irritants, stones, or trauma
interstitial cytitis causative factors
-being female
-UTI's
-catheterization
-diabetes and any condition resulting in urinary stasis
symptoms of interstitial cystitis in older adults
lethargy, anorexia, confusion, anxiety
tumors of bladder
most originate from transitional epithelial lining
bladder tumor treatment
-benign tumors may be surgically removed
-high risk tumors are managed with intravesical immunotherapy (live tuberculin virus)
-for muscle invasive CA, cystectomy radiation