Topic 5
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Describe the structure of DNA and RNA
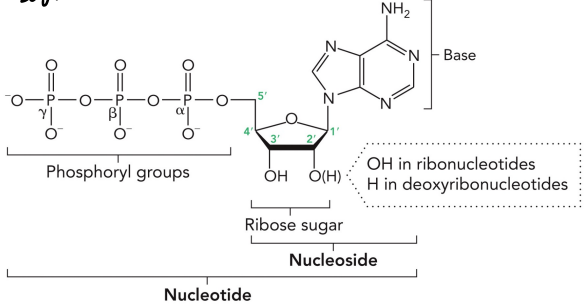
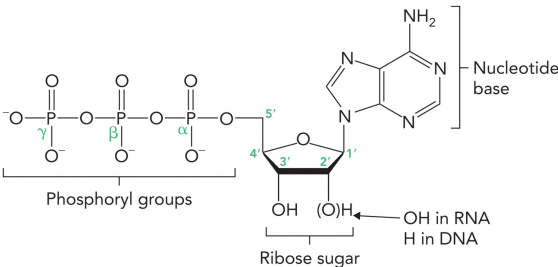
DNA and RNA are formed from nucleotides that are linked together through a phosphodiester backbone in a linear direction
Nucleotide: phosphate + sugar + base
Nucleoside: sugar + base
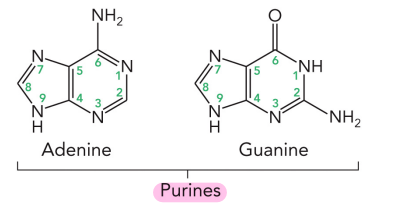
What nitrogenous bases are purines?
Adenine
Guanine
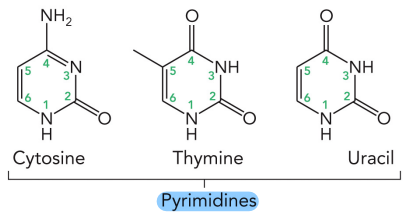
What nitrogenous bases are pyrimidines?
Cytosine
Thymine
Uracil
Describe the primary structure of DNA
Found in all biological molecules
Unique arrangement of deoxyribonucleotides or ribonucleotides arranged in a single chain
Usually depicted as single letters in a row
Describe secondary structure of DNA
Two complementary strands of DNA bind (anneal) together through complementary base pairing in an antiparallel fashion
Resembles a double helix
A nucleotide structure consist of what?
Nucleotide base (pyrimidine or purine)
Ribose ring
Phosphoryl group
What is the most abundant nucleotide?
ATP
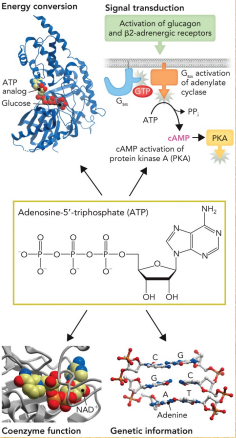
ATP plays an important role in…
Energy currency of metabolic pathways
cAMP from ATP is one of the second messengers in cellular signal
Describe the primary level of DNA
Primary structure: single helix → nucleotides connected by phosphodiester bonds in a 5C → 3C direction
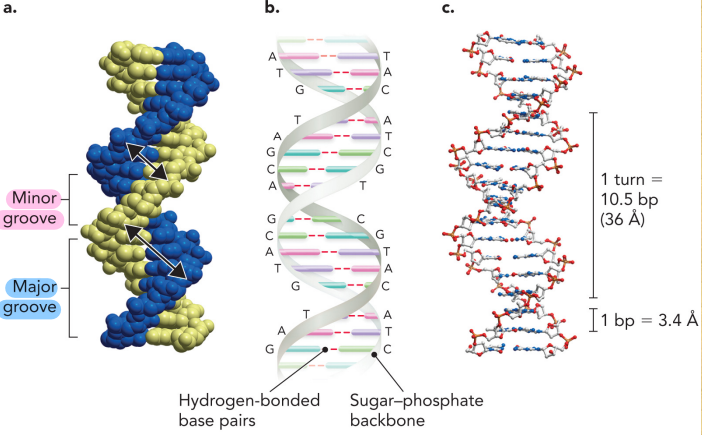
Describe the secondary level of DNA
Secondary: double helix → both strands are antiparallel to each other
5’ → 3’
Hydrophobic interactions, Van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonds
Every turn in the helix have a 10.5 base pair
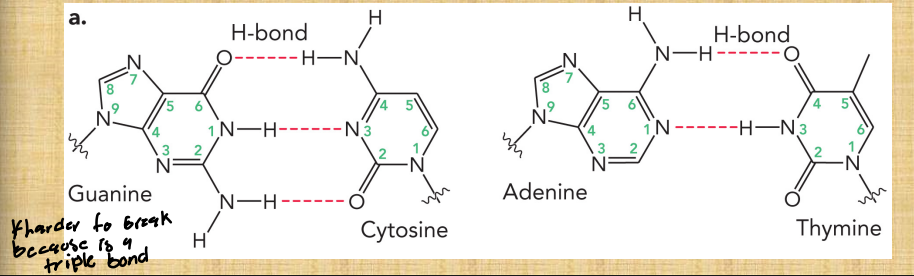
Describe the complementary base pairing
Based on Chargaff’s rule
States that A-T means A binds to T and G-C means that G binds to C
These are called Watson-Crick base pairs
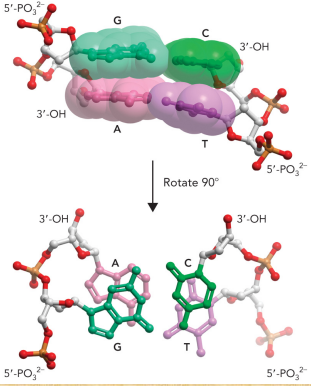
Why does supercoiling form?
Because of base stacking
Describe base stacking
Bases are oriented so that hydrogen bonding with another base requires that they are arranged in a planar fashion, parallel to the adjacent bases on the same strand, and located in the interior of the helix
The base pairs are stacked upon each other within van der Waals distance
This provides stability to the molecule through the hydrophobic effect and van der Waals interactions
What are the forms of DNA?
A-form
B-form
Z-form
Describe the A-form of DNA
Short and wide
Right-handed
Dehydrated (cannot bind to water)
Compacted form of DNA
No major and minor grooves
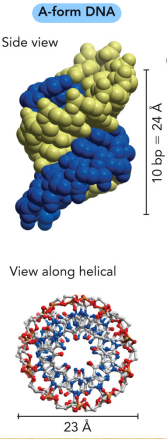
Describe the B-form of DNA
Most stable
Right-handed
Active DNA to make proteins
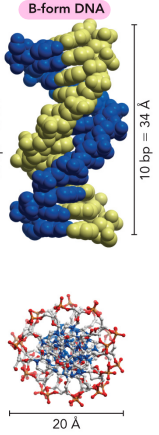
Describe the Z-form of DNA
Most narrow
Left-handed
Compacted form of DNA
It is elongated
No major or minor grooves
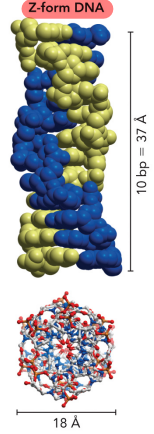
Describe denaturation in DNA
Also called “melting”
Enzymes or chemicals
Occurs under heating or addition of acid or base
Separation into two individual strands
Causes a “hyperchromic shift”
Describe renaturation
Also called “annealing”
Two strands reform a helix
For PCR
Requires lower temperature
Describe the melting temperature (Tm)
It is where 50% is single strand and 50% is double strands
Tm = ~80 to 85 Celcius
The more double bonds are in a molecule, the higher Tm you need
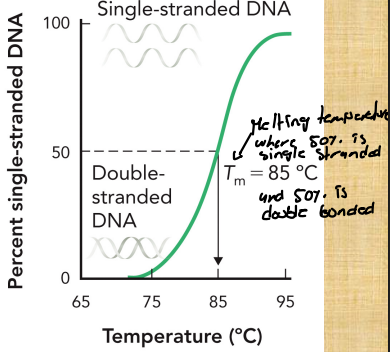
Describe the hyperchromic shift
The difference in absorbance between double-stranded and single-stranded DNA after denaturation
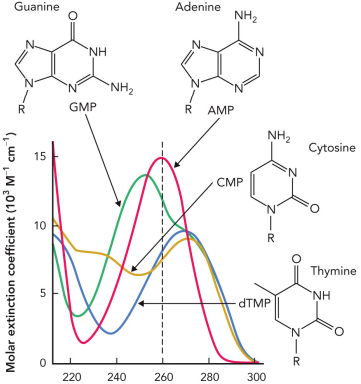
Describe DNA supercoiling
Structure where the majority of the DNA molecules inside a cell fold upon themselves
The area where the double helix crosses itself
Found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes
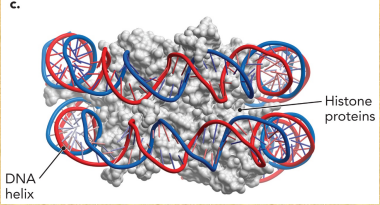
What are the types of supercoils?
Positive supercoil
Negative supercoil

Telomers have a high G-C content. What would be the optimal Tm of a telomere?
80 Celcius
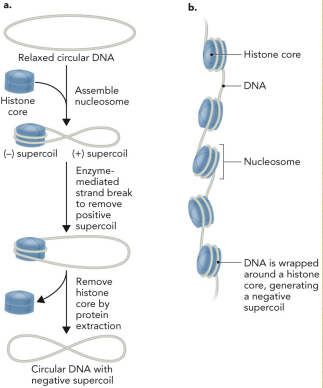
Describe the nucleosome assembly
Circular DNA is wrapped around histone proteins
On turn must be removed in order for this wrapping to occur, which produces a negative supercoil, and which is balanced by adding a positive supercoil
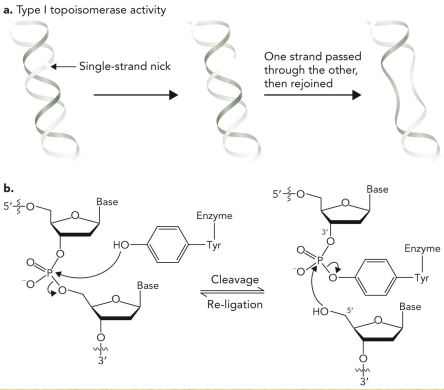
Describe topoisomerases
Enzymes that relive positive supercoils through cleavage and reannealing of DNA
Type 1
Type 2
Describe the type 1 topoisomerases
Cleave one strand of DNA
Reduce supercoiled region by one turn
Describe the type 2 topoisomerases
Cleave two strands of DNA
Reduce supercoiled region by two turns
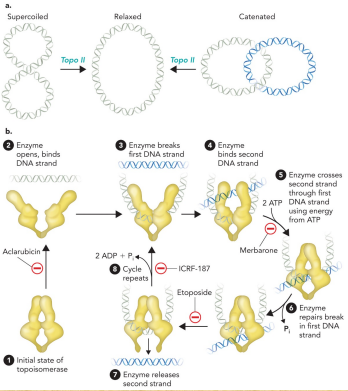
Describe DNA
Deoxyribose sugar
Thymine base
Describe RNA
Ribose sugar
Uracil base
Complex intrastrand structures
Can form ribozymes (catalytic molecules)
Describe ribosomes
RNA molecules with catalytic activity
Ex: ribonuclease P (RNAse P)
Cleaves nucleic acids
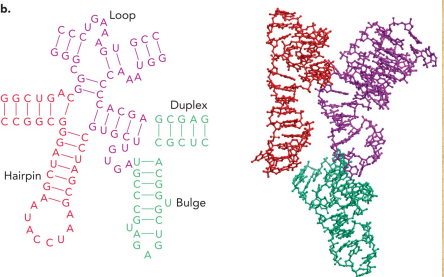
Basic function of tRNA
Help bring amino acids to the site of protein synthesis
Basic function of rRNA
Assembly of ribosomal subunit to make proteins
Basic function of mRNA
Help take genetic message from DNA to form proteins
Describe the unconventional base pairing in RNA and DNA
Triplet interactions can occur between a single-stranded region of DNA, or RNA with an RNA, DNA, or RNA-DNA duplex
This can result in a triple helix (triplex)
Quadruplets can occur among guanine bases found in particular G-rich DNA sequences
Intercalated motif (I-motif) structures consist of hydrogen bonds between hemiprotonated cytosine residues
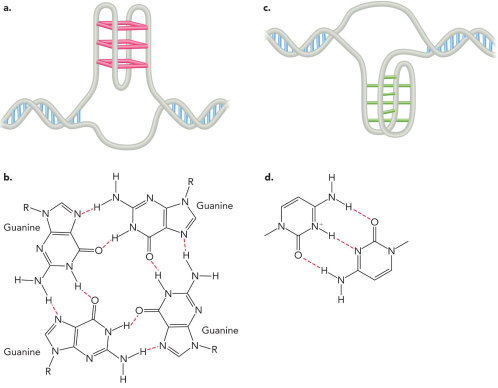
Describe plasmids
Self-replicating of circular DNA
Can carry extra genetic information not contained in chromosomal DNA
Are found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic organism
Contain an original of replication
Can be cloned, conjugated, transformed, or transduced
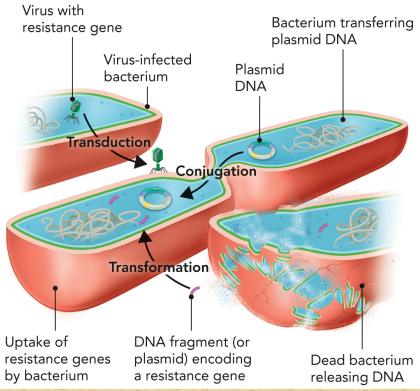
What is the main DNA?
Chromosomal DNA
What is the acquired DNA?
Plasmid DNA
Describe conjugation
Two bacteria naturally come together and share DNA
Describe transformation
Environmental dependent
Describe transduction
Virus place bacteria into the bacteria
Describe endonucleases
Enzymes that cleave
Type 1
Type 2
Type 3
Breaking DNA in the inside of the DNA double helix
Specific hydrogen bonds between bases are broken
Describe type 1 and type 3 endonucleases
Require ATP
Describe type 2 endonucleases
Cleave DNA at specific recognition sequences
It is commonly used in labs
Blunt and rough cutters
Describe blunt cutter type 2 endonucleases
This will make a smooth, nice cut
No overhang
Describe rough cutter type 2 endonucleases
Will produce a 5’ overhang
Examples: EcoRI and Hpall
Describe EcoRI
Recognize a specific base sequence
5’ GAATTC ‘3
3’ CTTAAG ‘5
Describe overhangs
Also called “sticky ends”
Easy to combine with ligases
Describe cDNA libraries
Complementary DNA (cDNA)
It is generated from mRNA by reverse transcriptase
RNA fragments serve as primers
DNA polymerases and DNA ligase aid in the generation of cDNA
It is made without introns
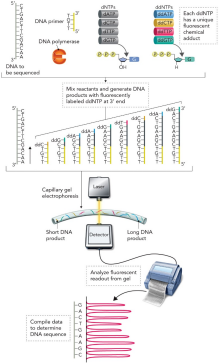
Describe high-throughput DNA sequencing
1977 - Sanger sequencing developed
Uses ddNTPs (dideoxynucleoside triphosphates)
Generates chain termination DNA molecules
Uses fluorescently labeled ddNTPs
Followed by capillary gel electrophoresis
1980 - Nobel Prize awarded for DNA sequencing
Describe polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
A method used to exponentially amplify a specific target DNA segment
Number of DNA molecules increases by 2n in each cycle
Why to use PCR?
Amplifying DNA
Make copies
It can manipulate Tm
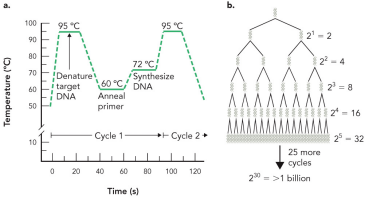
What are the three temperature phases of PCR?
Phase 1 - DNA denaturation
Phase 2 - Annealing
Phase 3 - Primer extension and DNA synthesis
Describe phase 1 - DNA denaturation of PCR
Break DNA/separate
Tm is around ~95C
Describe phase 2 - annealing of PCR
Annealing of primers
Small sequences of DNA that act as a ladder sequence
It has to match 1 strand on helix
Cooling to around ~72C, so DNA primers can anneal to DNA template strand
Describe phase 3 - primer extension and DNA synthesis of PCR
Cooling to ~55C for DNA extension
PCR schematic (picture)
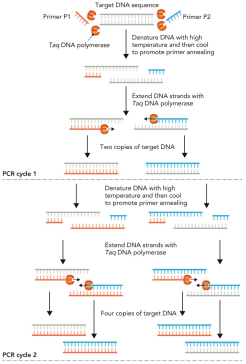
Polymerase chain reaction (picture)
Step 1 is at 95C
Step 2 is at 60C
Describe transcriptome analysis
Gene expression microarrays
Provide a readout of transcript abundance using a predetermined cDNA attached to a solid surface
Next-generation sequencing using RNA sequencing
Provides readout of all transcripts from same gene
Permits identification of alternatively spliced RNA products
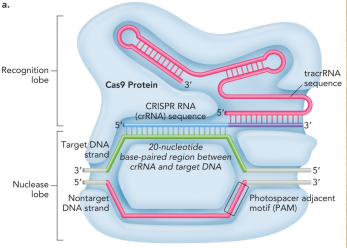
Describe CRISPR-Cas9
An RNA-guided DNA targeting tool
Discovered in the 1990s
CRISPR = clustered regulatory interspersed short palindromic repeats
A form of adaptive immunity based on specific recognition of bacteriophage DNA by complementary RNA that was transcribed
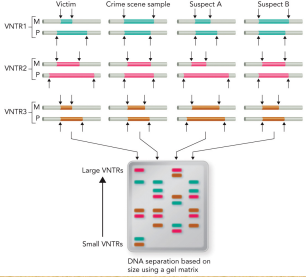
Based on the DNA produced in the gel, who was not at the crime scene?
The victim and suspect A
You perform a PCR experiment but add DNA polymerase instead of Taq polymerase. What will happen?
Replication will not occur