Olfaction, Taste, & Special Senses
1/9
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
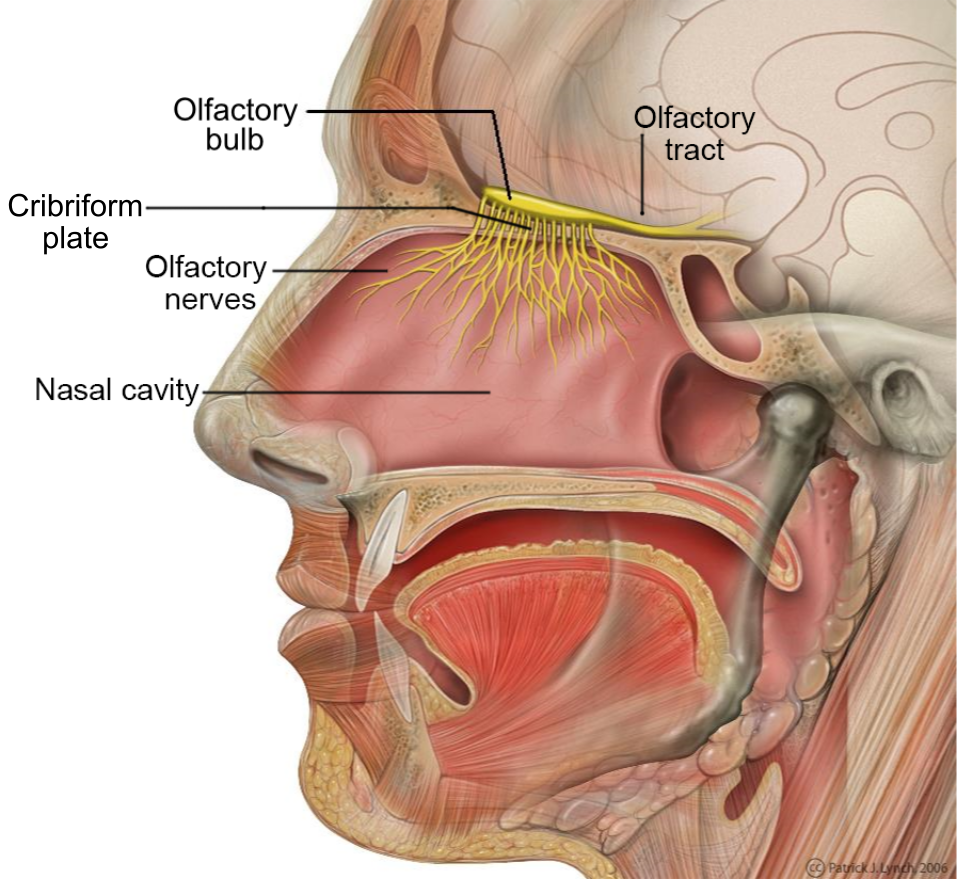
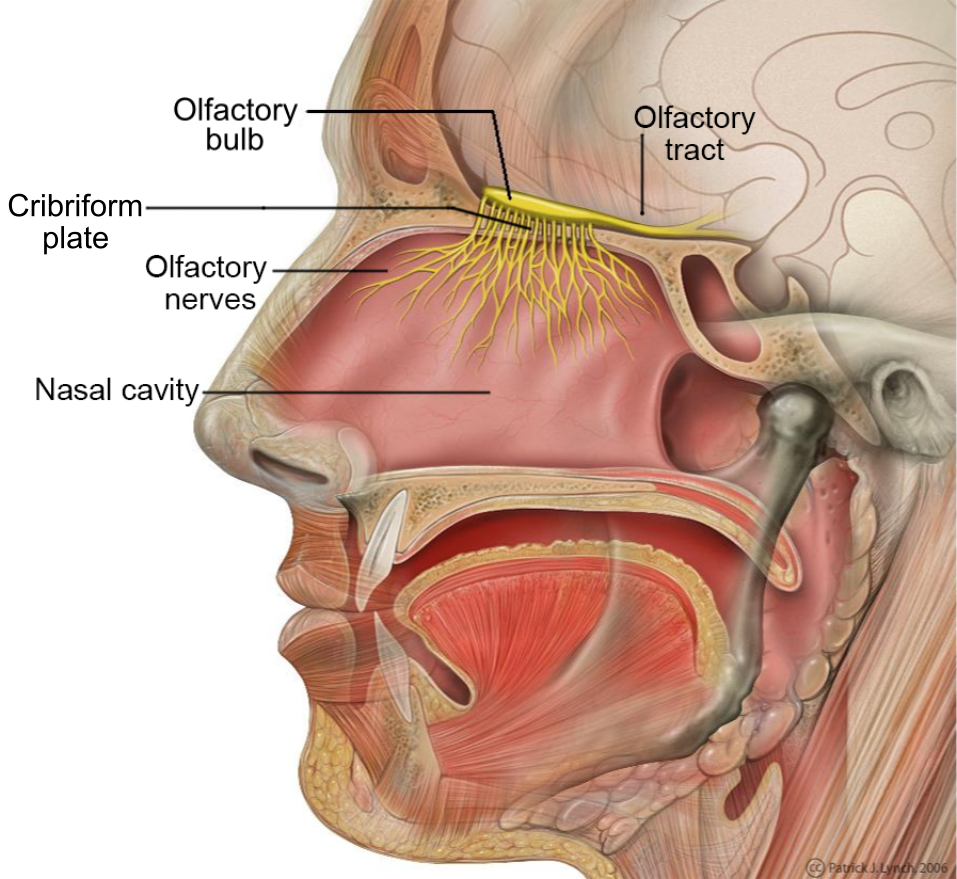
olfactory tract
a bundle of nerve fibers in the brain that transmits smell information from the olfactory bulb to higher brain regions; the neural pathway that carries signals from the olfactory bulb, allowing for the conscious perception and processing of odors and the triggering of memories associated with smells.
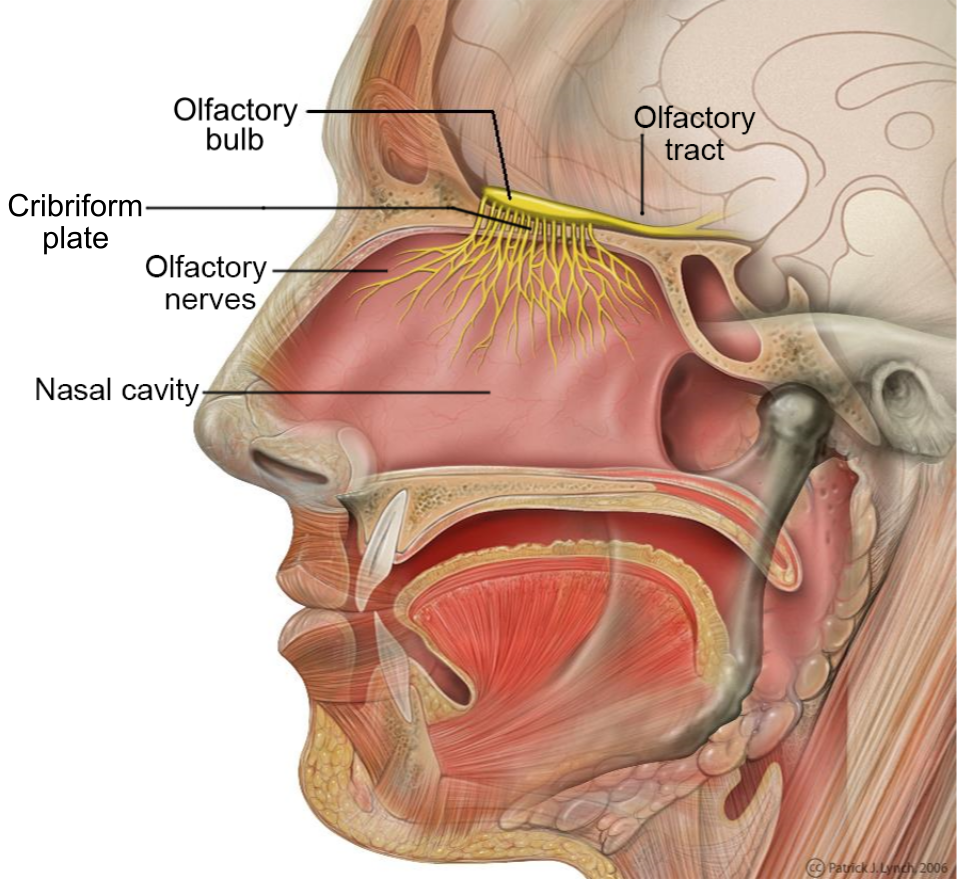
olfactory bulb
part of the brain located in the frontal love that processes smells by receiving signals from the olfactory epithelium int he nose; essential for olfactory transduction, where odor molecules detected in the nasal cavities are transformed into neural signals
olfactory epithelium
a specialized sensory tissue in the upper nasal cavity that detects odors and is responsible for the sense of smell; neuroepithelium
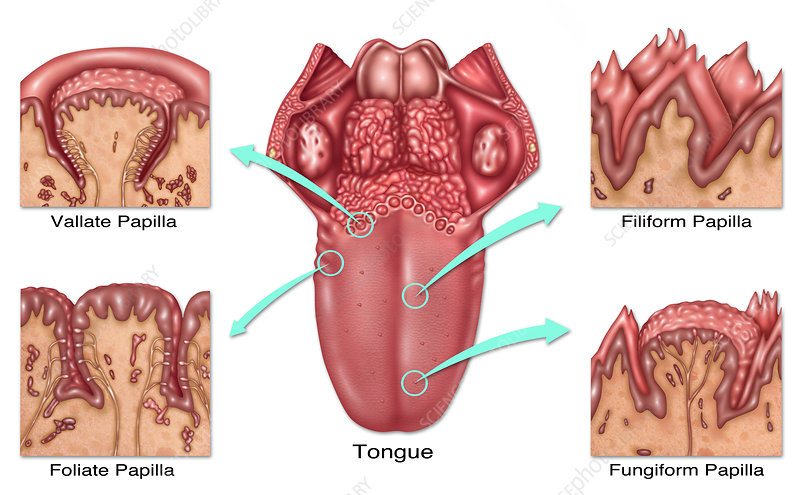
foliate papillae
leaf like, short vertical folds located on the sides of the back of the tongue
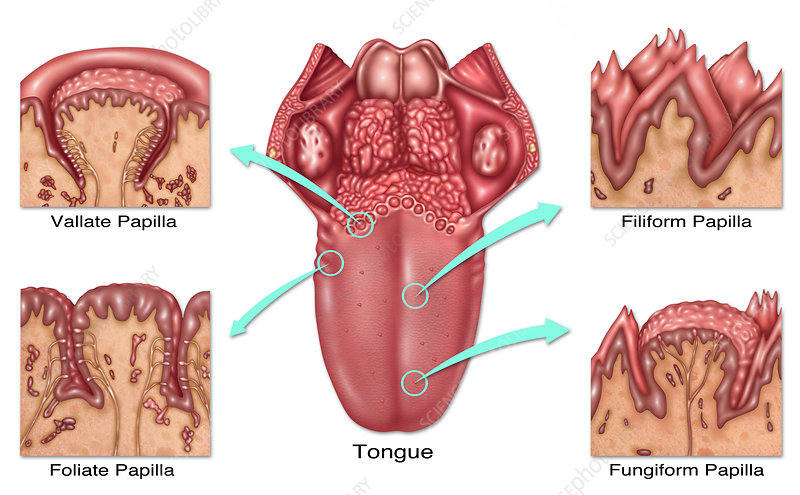
fungiform papillae
mushroom-shaped protrusions on the tongue’s surface that house taste buds, which detect flavors, temperature and touch
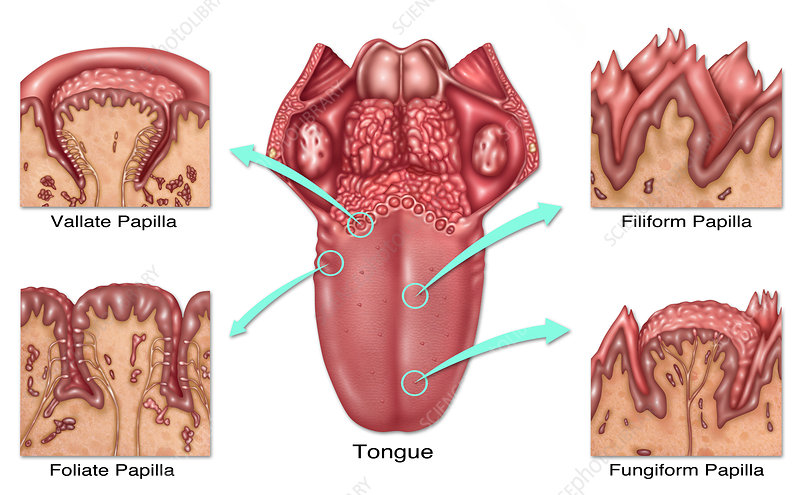
vallate papillae
large, prominent papillae on the back of the tongue that arranged in a v-shaped row
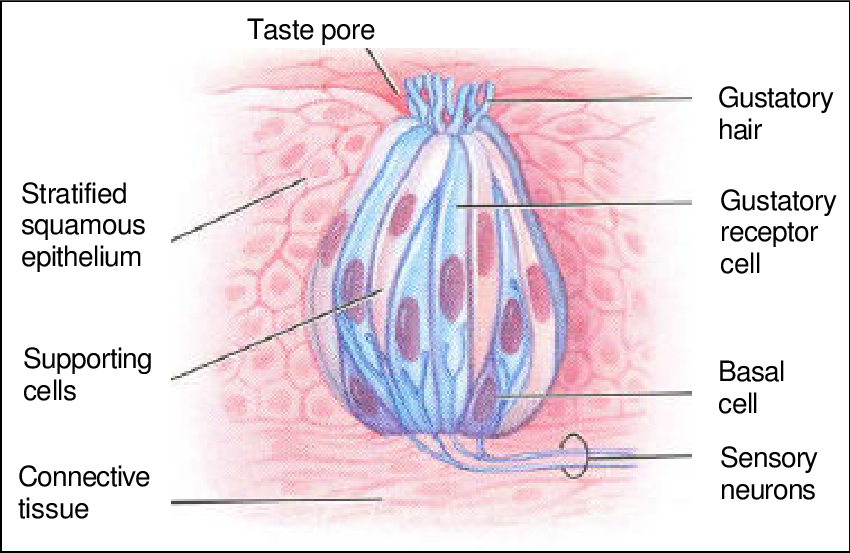
taste buds
sensory organs located on the tongue, soft palate, and throat; responsible for detecting and transmitting taste sensations to the brain
two point discrimination
a non-invasive test of tactile senses that measures the minimum distance at which two points can be perceived as separate; applied stimuli to the skin while the patients vision is blocked

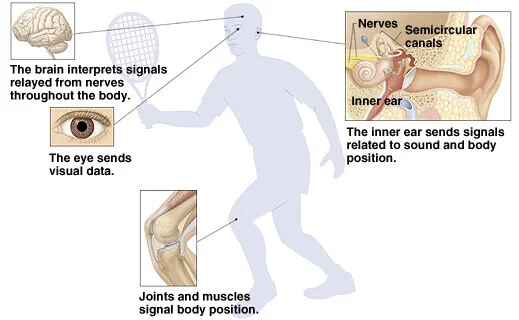
equilibrium
the sense of balance and orientation maintained by the integration of input from the visual system, vestibular system and proprioception.
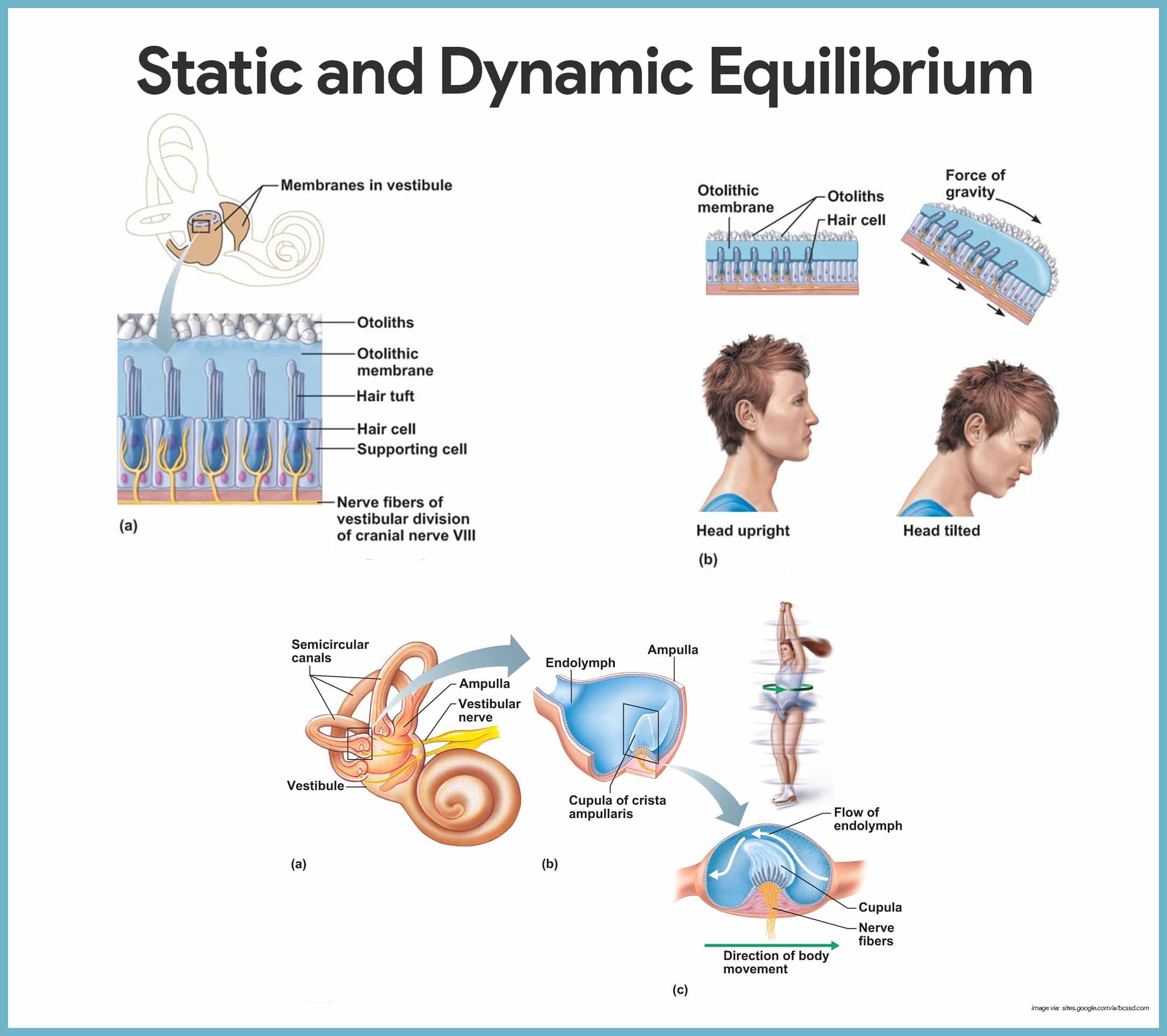
balance
reliance on the brain integrating sensory information from the vestibular system (detection of head motion and position), proprioception (information about posture & muscles & joints) and the visual system (spatial orientation relative to environment); integration used to generate motor outputs that adjust posture and eye movements to maintain stability