Anatomy Final Exam S1
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
Superior
toward the head
Interior
towards the feet
Anterior
To the front
Posterior
to the back
Medial
toward midline
Lateral
away midline
Proximal
close to the connection of the body part
Distal
far from the orgin of body part
Superficial
external/towards the surface
Deep
internal cut
Dorsal Body Cavities
Cranial Cavity (houses brain) and Spinal Cavity (houses spinal cord)
Ventral Body Cavity
Thoracic Cavity (houses heart, lungs, and others) and Abdominopelvic Cavity (houses digestive system/abdominal cavity and most urinary system/pelvic cavity)
Neurons
nerve cells that send messages through the body
Glia
support cells that nourish, connect, and protect neurons
Two types of Nervous Tissue
Neurons, Glia
Epithelial Cells
They line the entire body sometimes containing cilia or villi (hair-like structures) on the surface
Types of Epithelial Tissue
Simple Squamous, Stratified Squamous, Simple Cuboidal, Stratified Cuboidal, Simple Columnar, Pseudostratified Columnar
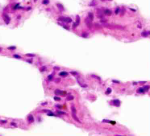
Simple Squamous
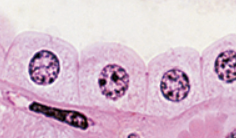
Simple Cuboidal
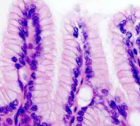
Simple Columnar
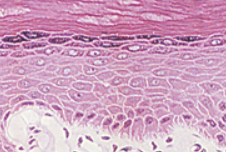
Stratified Squamous
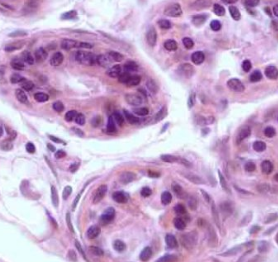
Stratified Cuboidal
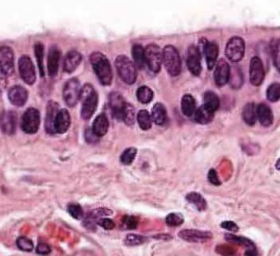
Stratified Columnar
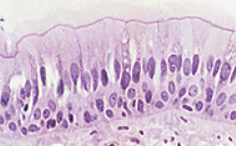
Pseudostratified Columnar
Types of Muscle Tissues
Skeletal Muscle, Smooth Muscle, and Cardiac Muscle
Skeletal Muscle
moves the bones (voluntarily) striated (looks like fish in a river)

Skeletal Muscle
Smooth Muscle
works inside the body to do things involuntarily like making your heart beat and pumping blood; nuclei is within the cells and no striations

Smooth muscle
Cardiac Muscle
pumping the blood in our heart and body; short y shaped cells, striated

Cardiac Muscle
Types of Connective Tissue
Bone, Hyaline Cartilage, Dense Fibrous Connective, Blood, and Adipose Tissue
Bone
provides structure and protection to the body; looks like cut down tree trunk
Hyaline Cartilage
pre-bone; it is in the baby’s skill and their skeleton
Dense Fibrous Connective
makes up tendons and ligaments; resembles skeletal muscles but no striation, densely packed
Blood
carries oxygen to the body, removes carbon dioxide, circulates through blood vessels; small and round
Adipose Tissue
fat cells and energy storage; looks like marshmallows or balloons

Bone
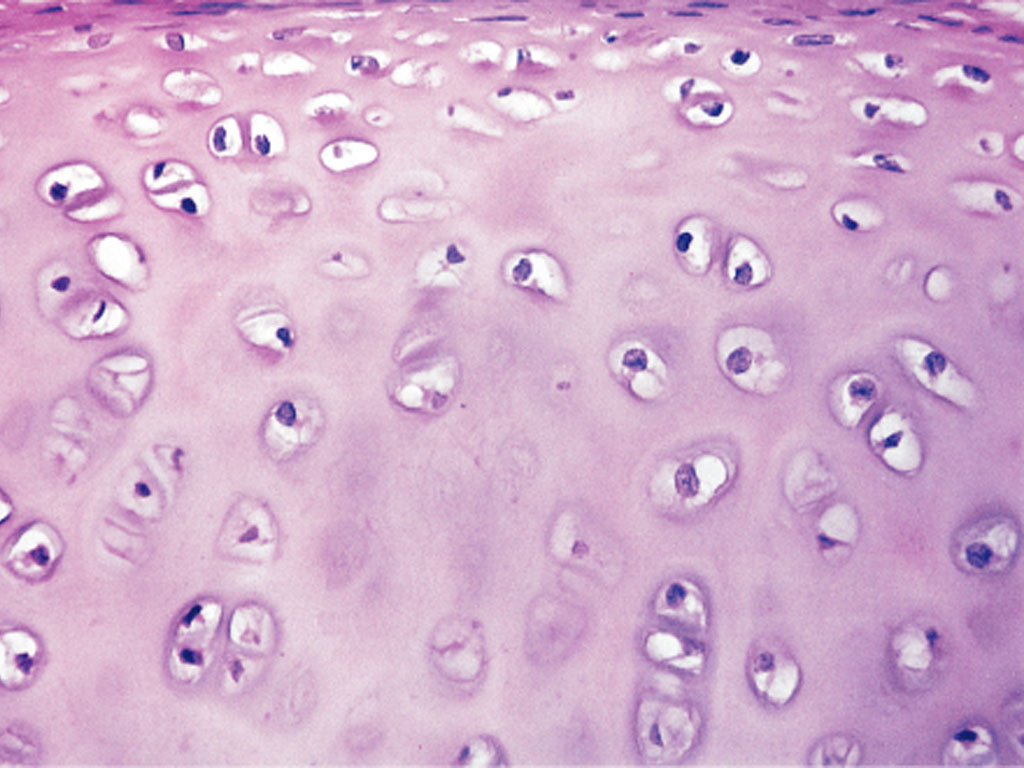
Hyaline Cartilage

Dense Fibrous Connective Tissue
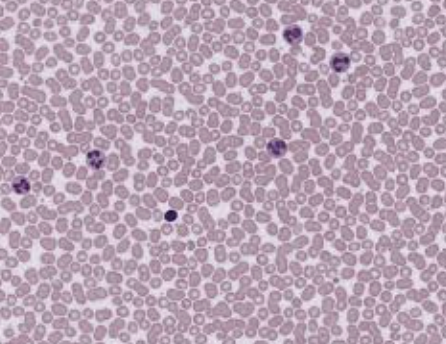
Blood
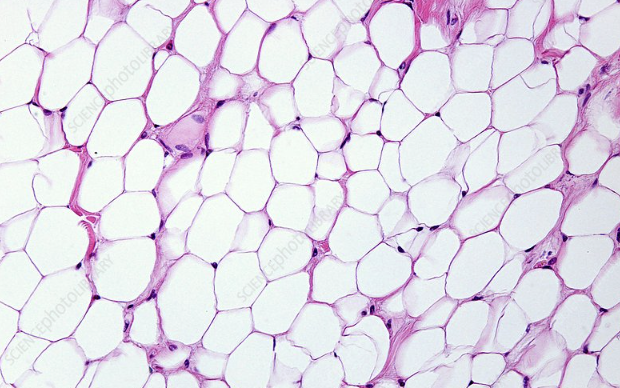
Adipose Tissue
Skeletal System
provides shape and movement, protects organs, produces blood cells, stores minerals
Axial Skeleton
80 bones; includes skull, ribs, spine, sternum, vertebrae, hyoid
Appendicular Skeleton
126 bones; includes upper and lower extremeties, pelvic girdle, phalanges
Parts of Skeleton System
Bones, Cartilage, and Ligaments
Bones
strong living tissue
Cartilage
tissue more flexible than bone
Ligaments
tissue that holds bones into place
Types of Bone
Long Bones, Short Bones, Flat Bones, Irregular Bones, and Sesamoid Bones
Long Bones
provides strength structure, and movement ex: ulna, femur, radius
Short Bones
cube shaped, ex: talus, capitate (carpal) bone
Flat Bones
thin, with a broad surface and often curved; used to protect organs and attach wide muscles; ex: scapula and sternum
Irregular Bones
odd-shaped bones don’t fit into any other category; variety of shapes and sizes; ex: sphenoid bone, vertebra
Sesamoid Bones
short bones that are found within tendons; ex: patella
Anatomy of a Long Bone
Proximal Epiphysis (top), diaphysis (shaft), Distal Epiphysis (bottom)
Compact bone
provides strength and protection, gives bones their smooth, white, and solid appearance, and made up of asteons
Spongy Bone
found at the ends of long bones or center of short or flat bones; contains red marrow
Ossification
the formation of bone from cartilage
Red Bone Marrow
produces blood cells in hemopoiesis; children have every bone filled with this and in adults it is found in flat bones in the skull, vertebrae, sternum, ribs, shoulder blades, and the pelvis
Yellow Bone Marrow
stores fat; replaces red bone marrow; found in hollow spaces of long bones
Bone Cells
Osteoblast, Osteocyte, and Osteoclast
Osteoblast
creates new bone for growth or repair
Osteocyte
maintains existing bone, has long arms to allow to communicate with others
Osteoclast
breakdown old bone; reshapes bone to repair breaks
Cervical Vertebrae
7
Thoracic Vertebrae
12
Lumbar Vertebrae
5
Sacrum
5 fused
Coccyx
4 fused
Atlas
C1 supports head
Axis
C2 pivots head
Hyoid Bone
floating bone under jaw; attachment for floor of mouth, tongue, larynx, epiglottis, and pharynx
True Ribs
pairs 1-7; connected to sternum by cartilage
False Ribs
pairs 8-12; last 2 pairs does not connect to anything at all
Sternum
head: Manubrium; body; tail: Xiphoid Process
Frontalis
raises eyebrow; on the frontal bone
Orbicularis Oculi
blinks and closes eye; below the eye
Orbicualris Oris
closes and protrudes lips; the kissing muscle; around lips/mouth
Zygomaticus Minor
elevates the upper lip; above the zygomaticus bone
Zygomaticus Major
raises corners of the mouth; the smile muscle; under the zygomatic bone
Buccinator
compresses cheek; the whistling muscle/duck-face muscle; transverse underneath the zygomaticus major and minor
Masseter
closes jaw, chewing muscle; runs up and down, around the end of the jawbone
Temporalis
closes jaw, another chewing muscle; on the side of head, the temple
Depressor Anguli Oris
pulls down the corners of mouth, frown muscle; under orbicularis oris
Sternocleidomastoid
flexes neck, rotates head; front of neck going to the back
Platysma
pulls corners of mouth widening it (sadness or fright); in front of sternocleidomastoid
Pectoralis Major
adducts and medially rotates; muscles on your chest
Pectoralis Minor
depresses and downwardly rotates scapula; near the underarm; deeper muscle
Serratus Anterior
pulls scapula anteriorly and down; attaches to the scapula and ribs
Internal Intercostals
depress ribs, decrease size of thoracic cavity (exhaling); between each rib
External Intercostals
lifts ribs, increasing size of thoracic cavity (inhaling); in between each rib on the sides
Internal Oblique
compress abdomen, flex, and rotate vertebral column; closer on the inside (abdomen)
External Obliques
rotate and flex vertebral column; closer to the surface (abdomen)
Rectus Abdominis
flexes vertebral column, walking around, and six pack; upper abdomen (abs)
Transverse Abdominis
compress abdomen; deeper muscle (abs as well)
Latissimus Dorsi
adduction, extension, and medial rotation of arm; connected to humerous
Trapezius
elevation and upward rotation of scapula, extends neck; back of neck and shoulders
Levator Scapulae
elevates the scapula, shrugging shoulders; on each side of spine