4.2 trade protection and exchange ratesFree
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Free trade
International trade with no government intervention imposing restrictions of any kind of imports or exports
Benefits of trade
Greater choice for consumer
Benefits for producer of economies of scale
Increased competition
Greater efficiency in production
Lower prices for consumers
More efficient allocation of resources
Ability to acquire needed resources
Greater flow of ideas and technology
An “engine for growth”
World Trade Organization (WTO)
An international organization with the key objective to promote free trade among countries around the world
Trade protection
Government intervention in international trade involving the imposition of trade barriers intended to limit the quantity of imports and protect the domestic economy from foreign competition
Tariff
A tax on imported goods (indirect)
Quota
A restriction on the quantity of imports
Subsidy
Payment by the government to firms to lower costs of production and price
Tariff diagram

Quota diagram
Subsidy diagram
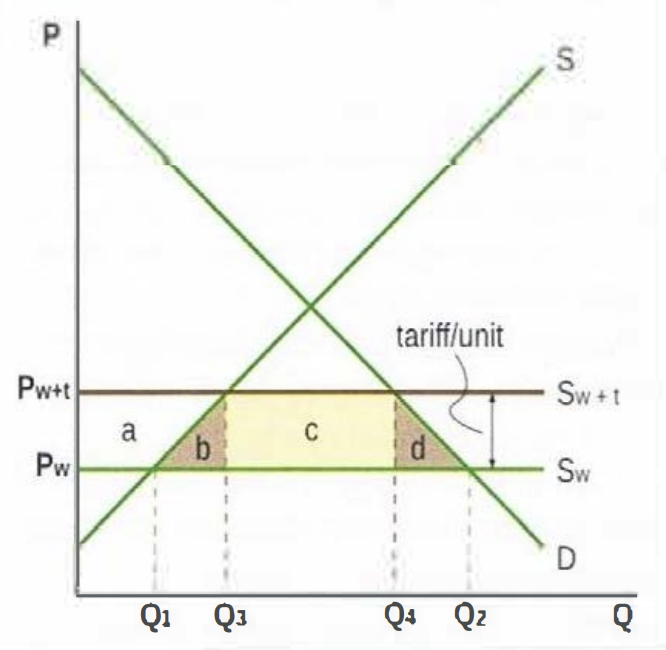
Tariff effect on stakeholders
Domestic producers gain as Q produced goes up from Q1 to Q3, P received goes up from Pw to Pw+t
Workers gain as domestic employment goes up due to increased production
Government gains tariff revenue (yellow area)
Domestic consumers lose, Q bought down from Q2 to Q4 and paid up from Pw to Pw+t
Domestic society lose, there is inefficiency in production since higher cost firms are protected by the higher P
Allocative inefficiency, welfare loss = brown triangles. consumer surplus lost = a + b + c + d, producer surplus gained = a. government revenue gained = c. net loss = b+d
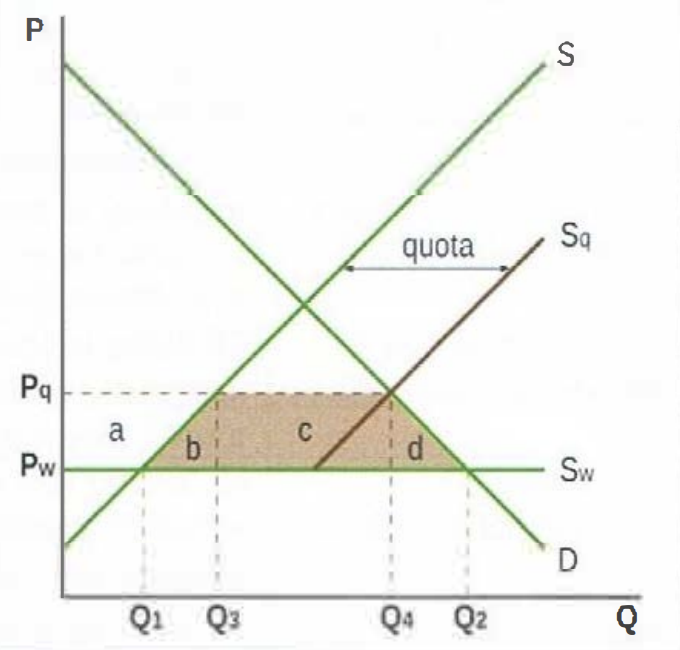
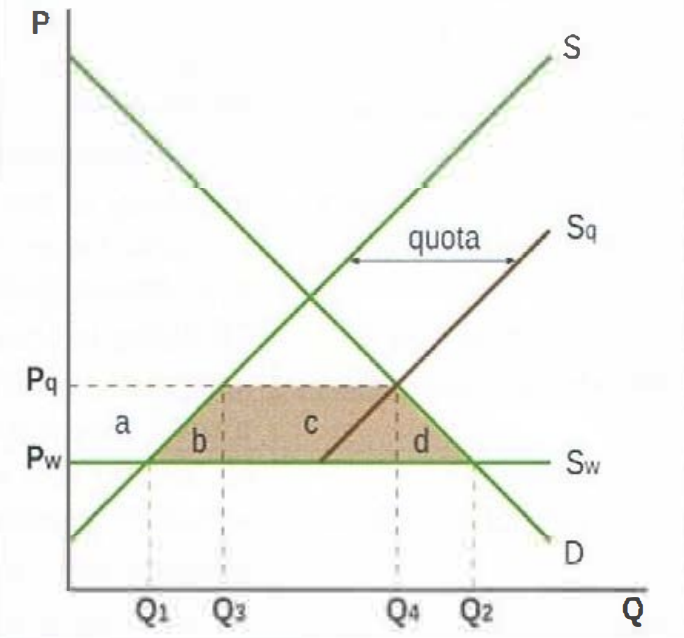
Quota effect on stakeholders
Domestic producers gain as Q produced goes up from Q1 to Q3, P received goes up from Pw to Pq
Workers gain as domestic employment goes up due to increased production
Government unaffected: no revenues or spending
Domestic consumers lose: Q bought down from Q2 to Q1 and paid up from Pw to Pq
Domestic society loses: there is inefficiency in production since higher cost firms are protected by higher P
Allocative inefficiency: shown by welfare loss = brown area (b+c+d) (consumer surplus lost = a+b+c+d; producer surplus gained = a; net loss = b+c+d, since revenues = c, are usually taken by exporting countries
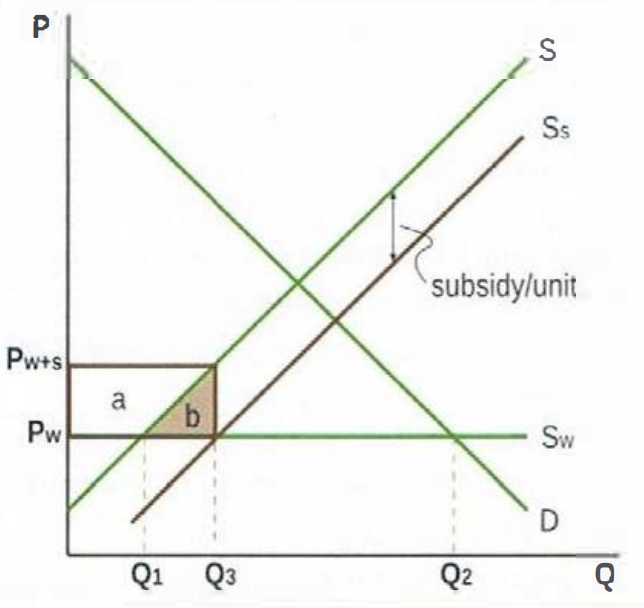
Subsidy effect on stakeholders
Domestic producers gain as Q produced goes up from Q1 to Q3, P received goes up from Pw to Ps
Workers gain as domestic employment goes up due to increased production
Domestic consumer unaffected: same Q and same P before and after
Government loses: must pay subsidy equal to the rectangle outlined in brown
Domestic society loses: inefficiency in production since higher cost firms are protected from higher P
Allocative inefficiency, shown by welfare loss = brown triangle (b) (consumer surplus remains same after the subsidy; producer surplus gained due to subsidy = a; government spending lost = a+b; net loss=b
Exchange rates
The value of one currency expressed in terms of another; can be thought of as the “price” of a currency
Freely floating exchange rate
An exchange rate that is determined entirely by demand and supply of the currency, with no government intervention
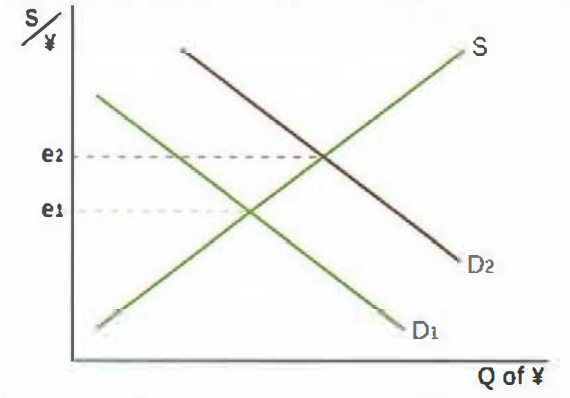
Currency appreciation
An increase in the value of a currency in a freely floating exchange rate system; may occur due to an increase in demand or a decrease in the supply of a currency
Currency depreciation
A decrease in the value of a currency in a freely floating exchange rate system; may occur due to a decrease in demand or an increase in the supply of a currency
Currency appreciation diagram
Administrative barriers
Application of bureacratic standards and regulations imposed on foreign firms in order to protect domestic firms and consumers
Portfolio investment
The purchase of financial investments abroad, such as the purchase of stocks, shares, and bonds of overseas firms and governments
Remittances
The movement of money when nationals working abroad send money back to their home country
Devaluation
A decrease in the value of a currency in a fixed exchange rate system
Revaluation
An increase in the value of a currency in a fixed exchange rate system
Fixed exchange rate
Exists when the central bank buys and sells foreign currencies to ensure the value of its currency stays at a single, predetermined rate
Foreign currency reserves
Stocks of foreign currencies held by a central bank, usually to influence the value of its currency
Managed exchange rate
A system where the government or the central monetary authority intervenes periodically in the foreign exchange market to influence the exchange rate, when deemed necessary to maintain certainty and confidence in the economy
Overvalued currency
A currency whose value or exchange rate is greater than its equilibrium exchange rate, usually achieved through central bank intervention; may occur in a pegged or managed exchange rate system
Undervalued currency
A currency whose value or exchange rate is less than its equilibrium exchange rate, usually achieved through central bank intervention; may occur in a pegged or managed exchange rate system